2004 DAEWOO LACETTI sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 317 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 71
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MAIN RELAY CIRCUIT CHECK (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
When the ignition is turned On or to the START position,
the main relay is energized. The main relay then supply
voltage to the engine fuse block fuse Ef11. The Electronic
Ignition (EI) system ignition coil, Evaporative Emission
(EVAP) Canister Purge Solenoid and Heated Oxygen
Sensor (HO2S) are supplied voltage through the engine
fuse block fuse Ef11. The fuel injectors are supplied volt-
age through the engine fuse block fuse Ef11.Diagnostic Aids
S An intermittent problem may be caused by a poor
connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a
broken wire inside the insulation.
S A fault main relay will cause a no start condition.
There will be no voltage supplied to the EI system
ignition coil, or the fuel injectors. Without voltage
supplied to these components, they will not oper-
ate.
Main Relay Circuit Check (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the engine fuse block fuse Ef11.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. With a test light connected to the ground,
probe the fuse terminals nearest the main relay
for fuse Ef11.
Is the light on at both terminal?–System OKGo to Step 2
2Is the light on at only one terminal?–Go to Step 3Go to Step 4
3Repair the open in the wiring between the main relay
connector terminal 87 and the fuse Ef11.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 319 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 73
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MAIN RELAY CIRCUIT CHECK (1.8L DOHC)
Circuit Description
When the ignition is turned On or to the START position,
the main relay is energized. The main relay then supply
voltage to the engine fuse block fuse F2. The Electronic
Ignition (EI) system ignition coil, Evaporative Emission
(EVAP) Canister Purge Solenoid and Heated Oxygen
Sensor (HO2S) are supplied voltage through the engine
fuse block fuse F2. The fuel injectors are supplied voltage
through the engine fuse block fuse F2.Diagnostic Aids
S An intermittent problem may be caused by a poor
connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a
broken wire inside the insulation.
S A fault main relay will cause a no start condition.
There will be no voltage supplied to the EI system
ignition coil, or the fuel injectors. Without voltage
supplied to these components, they will not oper-
ate.
Main Relay Circuit Check (1.8L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the I/P fuse block fuse F2.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. With a test light connected to the ground,
probe the fuse terminals nearest the ignition
relay for fuse F2.
Is the light on at both terminal?–System OKGo to Step 2
2Is the light on at only one terminal?–Go to Step 3Go to Step 4
3Repair the open in the wiring between the ignition
relay connector terminal 87 and the fuse F2.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 321 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 75
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE CHECK
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor measures
the changes in the intake manifold pressure which result
from engine load (intake manifold vacuum) and rpm
changes. The MAP sensor converts these changes into a
voltage output. The engine control module (ECM) sends
a 5–volt reference voltage to the MAP sensor. As the in-
take manifold pressure changes, the output voltage of the
MAP sensor also changes. A low voltage (high vacuum)
output of 1 to 2 volts is present at idle. A high voltage (low
vacuum) output of 4.0 to 4.8 volts is present at wide open
throttle. The MAP sensor is also used under certain condi-
tions to measure baro–metric pressure. This allows the
ECM to make adjustments for altitude changes. The ECMuses the MAP sensor for fuel delivery and ignition timing
changes.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
2. Applying 34 kPa (10 inches Hg) of vacuum to the
MAP sensor should cause the voltage to change.
Subtract the second voltage reading from the first.
That voltage value should be more than 1.5 volts.
When applying vacuum to the MAP sensor, the
change in the voltage should happen instantly. A
slow voltage change indicates a faulty MAP sensor.
3. Disconnect the MAP sensor from the bracket and
twist the MAP sensor. Output changes more than
0.1 volt indicate a faulty connector or connection.
Page 322 of 2643
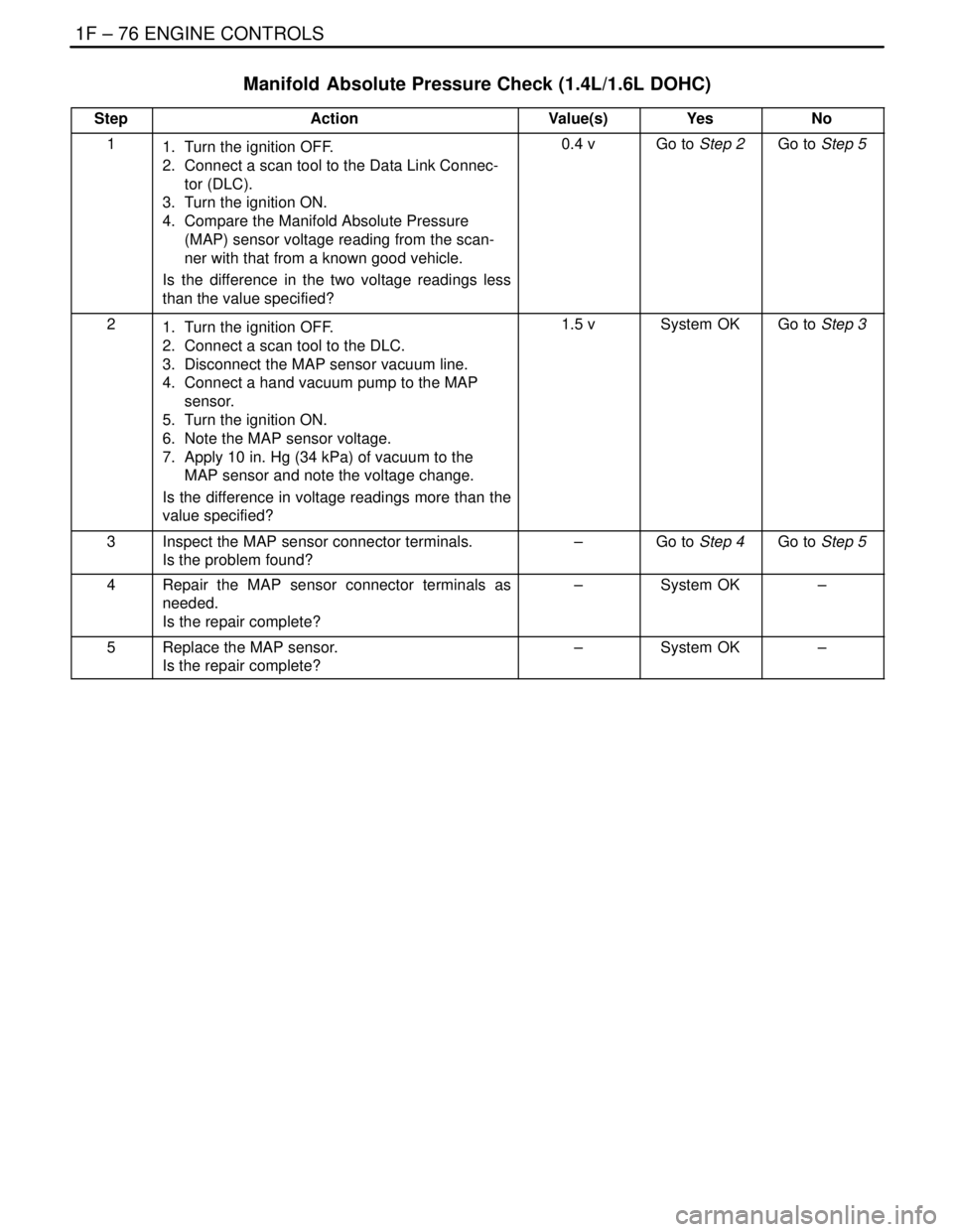
1F – 76IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Manifold Absolute Pressure Check (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Connect a scan tool to the Data Link Connec-
tor (DLC).
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. Compare the Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) sensor voltage reading from the scan-
ner with that from a known good vehicle.
Is the difference in the two voltage readings less
than the value specified?0.4 vGo to Step 2Go to Step 5
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Connect a scan tool to the DLC.
3. Disconnect the MAP sensor vacuum line.
4. Connect a hand vacuum pump to the MAP
sensor.
5. Turn the ignition ON.
6. Note the MAP sensor voltage.
7. Apply 10 in. Hg (34 kPa) of vacuum to the
MAP sensor and note the voltage change.
Is the difference in voltage readings more than the
value specified?1.5 vSystem OKGo to Step 3
3Inspect the MAP sensor connector terminals.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
4Repair the MAP sensor connector terminals as
needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
5Replace the MAP sensor.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 323 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 77
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE CHECK (1.8L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor measures
the changes in the intake manifold pressure which result
from engine load (intake manifold vacuum) and rpm
changes. The MAP sensor converts these changes into a
voltage output. The engine control module (ECM) sends
a 5–volt reference voltage to the MAP sensor. As the in-
take manifold pressure changes, the output voltage of the
MAP sensor also changes. A low voltage (high vacuum)
output of 1 to 2 volts is present at idle. A high voltage (low
vacuum) output of 4.0 to 4.8 volts is present at wide open
throttle. The MAP sensor is also used under certain condi-
tions to measure baro–metric pressure. This allows the
ECM to make adjustments for altitude changes. The ECMuses the MAP sensor for fuel delivery and ignition timing
changes.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
2. Applying 34 kPa (10 inches Hg) of vacuum to the
MAP sensor should cause the voltage to change.
Subtract the second voltage reading from the first.
That voltage value should be more than 1.5 volts.
When applying vacuum to the MAP sensor, the
change in the voltage should happen instantly. A
slow voltage change indicates a faulty MAP sensor.
3. Disconnect the MAP sensor from the bracket and
twist the MAP sensor. Output changes more than
0.1 volt indicate a faulty connector or connection.
Page 324 of 2643
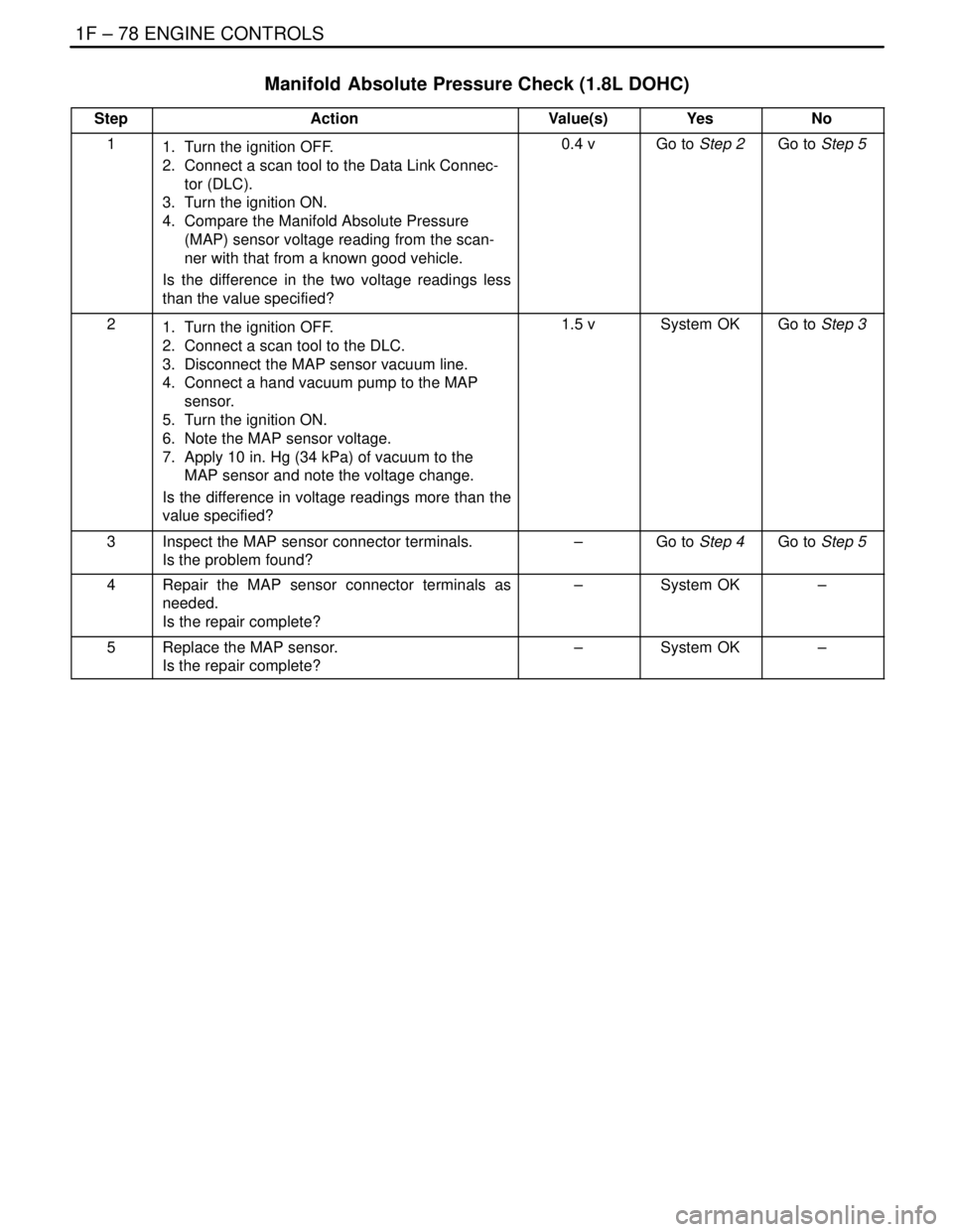
1F – 78IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Manifold Absolute Pressure Check (1.8L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Connect a scan tool to the Data Link Connec-
tor (DLC).
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. Compare the Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) sensor voltage reading from the scan-
ner with that from a known good vehicle.
Is the difference in the two voltage readings less
than the value specified?0.4 vGo to Step 2Go to Step 5
21. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Connect a scan tool to the DLC.
3. Disconnect the MAP sensor vacuum line.
4. Connect a hand vacuum pump to the MAP
sensor.
5. Turn the ignition ON.
6. Note the MAP sensor voltage.
7. Apply 10 in. Hg (34 kPa) of vacuum to the
MAP sensor and note the voltage change.
Is the difference in voltage readings more than the
value specified?1.5 vSystem OKGo to Step 3
3Inspect the MAP sensor connector terminals.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
4Repair the MAP sensor connector terminals as
needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
5Replace the MAP sensor.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 331 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 85
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
IGNITION SYSTEM CHECK (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The Electronic Ignition (EI) system uses a waste spark
method of spark distribution. In this type of EI system, the
Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is mounted to the oil
pump near a slotted wheel that is a part of the crankshaft
pulley. The CKP sensor sends reference pulses to the en-
gine control module (ECM). The ECM then triggers the EI
system ignition coil. Once the ECM triggers the EI system
ignition coil, both of the connected spark plugs fire at the
same time. One cylinder is on its compression stroke at
the same time that the other is on the exhaust stroke, re-
sulting in lower energy needed to fire the spark plug in the
cylinder on its exhaust stroke.
This leaves the remainder of the high voltage to be used
to fire the spark plug in the cylinder on its compression
stroke. Since the CKP sensor is in a fixed position, timing
adjustments are not possible or needed.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostictable.
2. It is important to check for the presence of spark to
all of the cylinders to isolate the problem to either
EI system ignition coil inputs or outputs.
5. In checking the ECM outputs for the electronic
spark timing signal, it recommended to use an os-
cilloscope to view the varying voltage signals. In
measuring these outputs with a voltmeter, intermit-
tent errors may occur that cannot be seen by a volt-
meter.
6. After confirming ECM inputs for the electronic spark
timing to the EI system ignition coil are OK, it can
be determined that a faulty EI system ignition coil is
at fault.
11. After confirming proper CKP sensor inputs to the
ECM and no wiring problems present, it can be de-
termined that the ECM is at fault.
24. This step, along with step 25, checks for battery
voltage and a ground to the EI system ignition coil.
Ignition System Check (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
CAUTION : Use only electrically insulated pliers when handling ignition wires with the engine running to prevent
an electrical shock.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Remove the spark plugs.
2. Inspect for wet spark plugs, cracks, wear, im-
proper gap, burned electrodes, or heavy de-
posits.
3. Replace the spark plugs as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OKGo to Step 2
2Check for the presence of spark from all of the igni-
tion wires while cranking the engine.
Is spark present from all of the ignition wires?–System OKGo to Step 3
31. Measure the resistance of the ignition wires.
2. Replace any ignition wire(s) with a resistance
above the value specified.
3. Check for the presence of spark from all of the
ignition wires.
Is spark present from all of the ignition wires?30,000 WSystem OKGo to Step 4
4Is spark present from at least one of the ignition
wires, but not all of the ignition wires?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 12
51. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Electronic Ignition (EI) system
ignition coil connector.
3. While cranking the engine, measure the volt-
age at the EI system ignition coil connector
terminal 1.
Does the voltage fluctuate within the values speci-
fied?0.2–2.0 vGo to Step 6Go to Step 7
Page 332 of 2643

1F – 86IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
6While cranking the engine, measure the voltage at
the EI system ignition coil connector terminal 1.
Does the voltage fluctuate within the values speci-
fied?0.2–2.0 vGo to Step 10Go to Step 8
7Check for an open in the wire from the EI system
ignition coil connector terminal 1 to the engine con-
trol module (ECM) connector terminal 31.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 9Go to Step 11
8Check for an open in the wire from the EI system
ignition coil connector terminal 1 to the ECM connec-
tor terminal 32.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 9Go to Step 11
91. Repair the wiring as needed.
2. Connect the EI system ignition coil connector.
3. Check for the presence of spark from all of the
ignition wires.
Is spark present from all of the ignition wires?–System OK–
101. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the electronic ignition system ignition
coil.
3. Connect the EI system ignition coil connector.
4. Check for the presence of spark from all of the
ignition wires.
Is spark present from all of the ignition wires?–System OK–
111. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the ECM.
3. Connect the EI system ignition coil connector.
4. Check for the presence of spark from all of the
ignition wires.
Is spark present from all of the ignition wires?–System OK–
121. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Crankshaft Position (CKP) sen-
sor connector.
3. Measure the resistance between the CKP sen-
sor terminals 1 and 2.
Is the resistance within the value specified?400–600 WGo to Step 13Go to Step 28
131. Measure the resistance between the CKP sen-
sor terminals 1 and 3.
2. Measure the resistance between the CKP sen-
sor terminals 2 and 3.
3. Is the resistance infinite (open circuit)?
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14Go to Step 28
141. Turn the ignition ON.
2. Measure the voltage between the CKP sensor
connector terminals 1 and 3.
Is the voltage within the value specified?1.3–1.5 v
(2.4–2.7 v)*Go to Step 20Go to Step 15
15Measure the voltage between the CKP sensor con-
nector terminal 1 and ground.
Is the voltage within the value specified?1.3–1.5 v
(2.4–2.7 v)*Go to Step 17Go to Step 16