2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER width
[x] Cancel search: widthPage 1469 of 2585
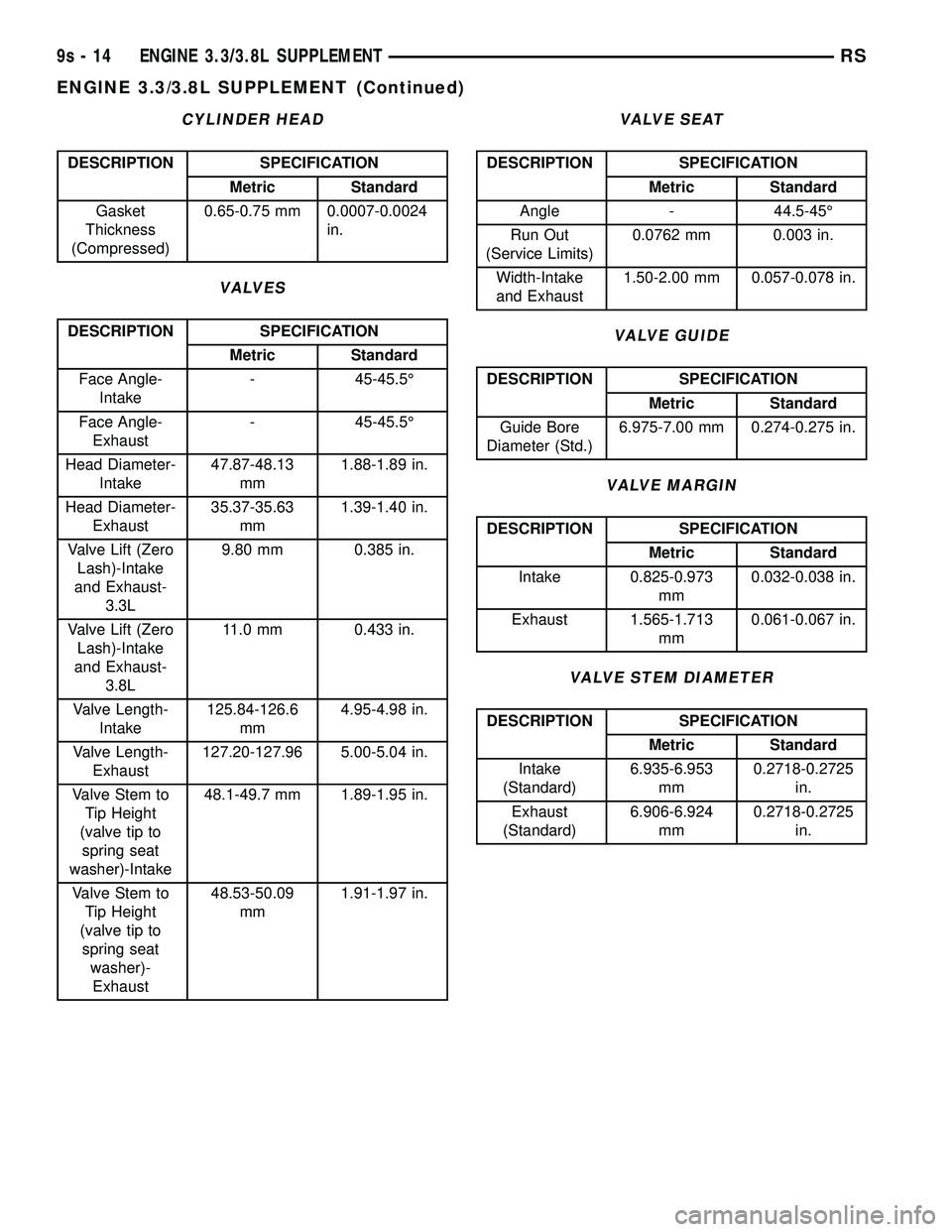
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Gasket
Thickness
(Compressed)0.65-0.75 mm 0.0007-0.0024
in.
VALVES
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Face Angle-
Intake- 45-45.5É
Face Angle-
Exhaust- 45-45.5É
Head Diameter-
Intake47.87-48.13
mm1.88-1.89 in.
Head Diameter-
Exhaust35.37-35.63
mm1.39-1.40 in.
Valve Lift (Zero
Lash)-Intake
and Exhaust-
3.3L9.80 mm 0.385 in.
Valve Lift (Zero
Lash)-Intake
and Exhaust-
3.8L11.0 mm 0.433 in.
Valve Length-
Intake125.84-126.6
mm4.95-4.98 in.
Valve Length-
Exhaust127.20-127.96 5.00-5.04 in.
Valve Stem to
Tip Height
(valve tip to
spring seat
washer)-Intake48.1-49.7 mm 1.89-1.95 in.
Valve Stem to
Tip Height
(valve tip to
spring seat
washer)-
Exhaust48.53-50.09
mm1.91-1.97 in.
VALVE SEAT
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Angle - 44.5-45É
Run Out
(Service Limits)0.0762 mm 0.003 in.
Width-Intake
and Exhaust1.50-2.00 mm 0.057-0.078 in.
VALVE GUIDE
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Guide Bore
Diameter (Std.)6.975-7.00 mm 0.274-0.275 in.
VALVE MARGIN
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Intake 0.825-0.973
mm0.032-0.038 in.
Exhaust 1.565-1.713
mm0.061-0.067 in.
VALVE STEM DIAMETER
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Metric Standard
Intake
(Standard)6.935-6.953
mm0.2718-0.2725
in.
Exhaust
(Standard)6.906-6.924
mm0.2718-0.2725
in.
9s - 14 ENGINE 3.3/3.8L SUPPLEMENTRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L SUPPLEMENT (Continued)
Page 1476 of 2585
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS
DESCRIPTION
The valves have chrome plated valve stems with
four-bead lock grooves. The valve stem seals are
made of Viton rubber.
OPERATION
The two valves per cylinder are opened using
hydraulic lifters, push rods, and rocker arms.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFACING VALVES
AND VALVE SEATS
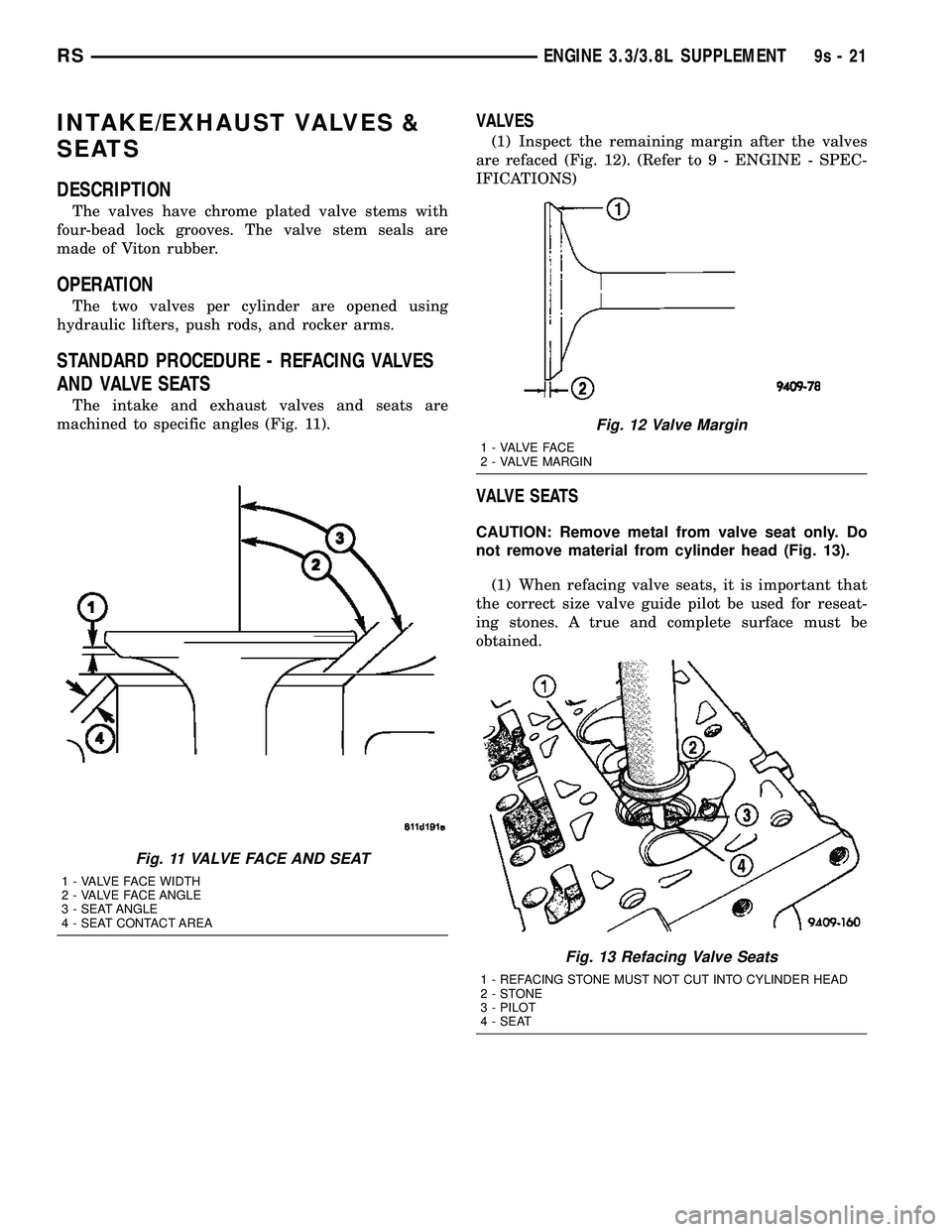
The intake and exhaust valves and seats are
machined to specific angles (Fig. 11).
VALVES
(1) Inspect the remaining margin after the valves
are refaced (Fig. 12). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPEC-
IFICATIONS)
VALVE SEATS
CAUTION: Remove metal from valve seat only. Do
not remove material from cylinder head (Fig. 13).
(1) When refacing valve seats, it is important that
the correct size valve guide pilot be used for reseat-
ing stones. A true and complete surface must be
obtained.
Fig. 11 VALVE FACE AND SEAT
1 - VALVE FACE WIDTH
2 - VALVE FACE ANGLE
3 - SEAT ANGLE
4 - SEAT CONTACT AREA
Fig. 12 Valve Margin
1 - VALVE FACE
2 - VALVE MARGIN
Fig. 13 Refacing Valve Seats
1 - REFACING STONE MUST NOT CUT INTO CYLINDER HEAD
2-STONE
3 - PILOT
4 - SEAT
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L SUPPLEMENT9s-21
Page 1477 of 2585
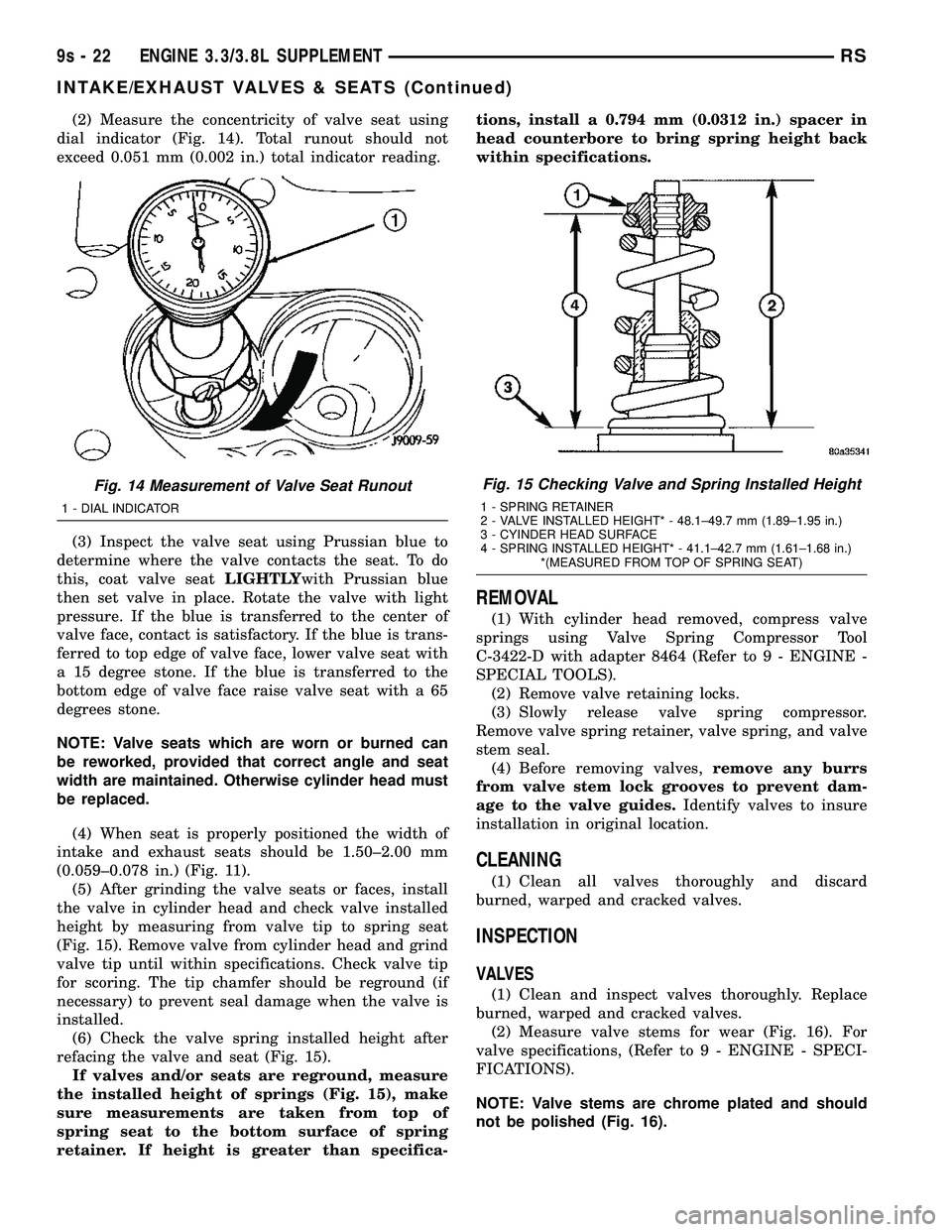
(2) Measure the concentricity of valve seat using
dial indicator (Fig. 14). Total runout should not
exceed 0.051 mm (0.002 in.) total indicator reading.
(3) Inspect the valve seat using Prussian blue to
determine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this, coat valve seatLIGHTLYwith Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to top edge of valve face, lower valve seat with
a 15 degree stone. If the blue is transferred to the
bottom edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 65
degrees stone.
NOTE: Valve seats which are worn or burned can
be reworked, provided that correct angle and seat
width are maintained. Otherwise cylinder head must
be replaced.
(4) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake and exhaust seats should be 1.50±2.00 mm
(0.059±0.078 in.) (Fig. 11).
(5) After grinding the valve seats or faces, install
the valve in cylinder head and check valve installed
height by measuring from valve tip to spring seat
(Fig. 15). Remove valve from cylinder head and grind
valve tip until within specifications. Check valve tip
for scoring. The tip chamfer should be reground (if
necessary) to prevent seal damage when the valve is
installed.
(6) Check the valve spring installed height after
refacing the valve and seat (Fig. 15).
If valves and/or seats are reground, measure
the installed height of springs (Fig. 15), make
sure measurements are taken from top of
spring seat to the bottom surface of spring
retainer. If height is greater than specifica-tions, install a 0.794 mm (0.0312 in.) spacer in
head counterbore to bring spring height back
within specifications.
REMOVAL
(1) With cylinder head removed, compress valve
springs using Valve Spring Compressor Tool
C-3422-D with adapter 8464 (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
SPECIAL TOOLS).
(2) Remove valve retaining locks.
(3) Slowly release valve spring compressor.
Remove valve spring retainer, valve spring, and valve
stem seal.
(4) Before removing valves,remove any burrs
from valve stem lock grooves to prevent dam-
age to the valve guides.Identify valves to insure
installation in original location.
CLEANING
(1) Clean all valves thoroughly and discard
burned, warped and cracked valves.
INSPECTION
VALVES
(1) Clean and inspect valves thoroughly. Replace
burned, warped and cracked valves.
(2) Measure valve stems for wear (Fig. 16). For
valve specifications, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECI-
FICATIONS).
NOTE: Valve stems are chrome plated and should
not be polished (Fig. 16).
Fig. 14 Measurement of Valve Seat Runout
1 - DIAL INDICATOR
Fig. 15 Checking Valve and Spring Installed Height
1 - SPRING RETAINER
2 - VALVE INSTALLED HEIGHT* - 48.1±49.7 mm (1.89±1.95 in.)
3 - CYINDER HEAD SURFACE
4 - SPRING INSTALLED HEIGHT* - 41.1±42.7 mm (1.61±1.68 in.)
*(MEASURED FROM TOP OF SPRING SEAT)
9s - 22 ENGINE 3.3/3.8L SUPPLEMENTRS
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)
Page 1525 of 2585

FUEL INJECTION
OPERATION
OPERATION - INJECTION SYSTEM
All engines used in this section have a sequential
Multi-Port Electronic Fuel Injection system. The MPI
system is computer regulated and provides precise
air/fuel ratios for all driving conditions. The Power-
train Control Module (PCM) operates the fuel injec-
tion system.
The PCM regulates:
²Ignition timing
²Air/fuel ratio
²Emission control devices
²Cooling fan
²Charging system
²Idle speed
²Vehicle speed control
Various sensors provide the inputs necessary for
the PCM to correctly operate these systems. In addi-
tion to the sensors, various switches also provide
inputs to the PCM.
The PCM can adapt its programming to meet
changing operating conditions.
Fuel is injected into the intake port above the
intake valve in precise metered amounts through
electrically operated injectors. The PCM fires the
injectors in a specific sequence. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the PCM maintains an air fuel ratio
of 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel by constantly adjust-
ing injector pulse width. Injector pulse width is the
length of time the injector is open.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width by opening
and closing the ground path to the injector. Engine
RPM (speed) and manifold absolute pressure (air
density) are theprimaryinputs that determine
injector pulse width.
OPERATION - MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for
Wide Open Throttle (WOT). There are several differ-
ent modes of operation that determine how the PCM
responds to the various input signals.
There are two different areas of operation, OPEN
LOOP and CLOSED LOOP.
During OPEN LOOP modes the PCM receives
input signals and responds according to preset PCM
programming. Inputs from the upstream and down-
stream heated oxygen sensors are not monitored dur-
ing OPEN LOOP modes, except for heated oxygensensor diagnostics (they are checked for shorted con-
ditions at all times).
During CLOSED LOOP modes the PCM monitors
the inputs from the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensors. The upstream heated oxygen
sensor input tells the PCM if the calculated injector
pulse width resulted in the ideal air-fuel ratio of 14.7
to one. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen content
through the upstream heated oxygen sensor, the
PCM can fine tune injector pulse width. Fine tuning
injector pulse width allows the PCM to achieve opti-
mum fuel economy combined with low emissions.
For the PCM to enter CLOSED LOOP operation,
the following must occur:
(1) Engine coolant temperature must be over 35ÉF.
²If the coolant is over 35ÉF the PCM will wait 38
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 50ÉF the PCM will wait 15
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 167ÉF the PCM will wait 3
seconds.
(2) For other temperatures the PCM will interpo-
late the correct waiting time.
(3) O2 sensor must read either greater than 0.745
volts or less than 0.29 volt.
(4) The multi-port fuel injection systems has the
following modes of operation:
²Ignition switch ON (Zero RPM)
²Engine start-up
²Engine warm-up
²Cruise
²Idle
²Acceleration
²Deceleration
²Wide Open Throttle
²Ignition switch OFF
(5) The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up,
deceleration with fuel shutoff and wide open throttle
modes are OPEN LOOP modes. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the acceleration, deceleration (with
A/C on), idle and cruise modes,with the engine at
operating temperatureare CLOSED LOOP modes.
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the ignition switch activates the fuel injec-
tion system, the following actions occur:
²The PCM monitors the engine coolant tempera-
ture sensor and throttle position sensor input. The
PCM determines basic fuel injector pulse width from
this input.
²The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure
from the MAP sensor input to modify injector pulse
width.
When the key is in the ON position and the engine
is not running (zero rpm), the Auto Shutdown (ASD)
and fuel pump relays de-energize after approximately
14 - 18 FUEL INJECTIONRS
Page 1526 of 2585

1 second. Therefore, battery voltage is not supplied to
the fuel pump, ignition coil, fuel injectors and heated
oxygen sensors.
ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. If the vehicle is in
park or neutral (automatic transaxles) or the clutch
pedal is depressed (manual transaxles) the ignition
switch energizes the starter relay when the engine is
not running. The following actions occur when the
starter motor is engaged.
²If the PCM receives the camshaft position sensor
and crankshaft position sensor signals, it energizes
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay and fuel pump relay.
If the PCM does not receive both signals within
approximately one second, it will not energize the
ASD relay and fuel pump relay. The ASD and fuel
pump relays supply battery voltage to the fuel pump,
fuel injectors, ignition coil, (EGR solenoid and PCV
heater if equipped) and heated oxygen sensors.
²The PCM energizes the injectors (on the 69É
degree falling edge) for a calculated pulse width until
it determines crankshaft position from the camshaft
position sensor and crankshaft position sensor sig-
nals. The PCM determines crankshaft position within
1 engine revolution.
²After determining crankshaft position, the PCM
begins energizing the injectors in sequence. It adjusts
injector pulse width and controls injector synchroni-
zation by turning the individual ground paths to the
injectors On and Off.
²When the engine idles within 64 RPM of its
target RPM, the PCM compares current MAP sensor
value with the atmospheric pressure value received
during the Ignition Switch On (zero RPM) mode.
Once the ASD and fuel pump relays have been
energized, the PCM determines injector pulse width
based on the following:
²MAP
²Engine RPM
²Battery voltage
²Engine coolant temperature
²Inlet/Intake air temperature (IAT)
²Throttle position
²The number of engine revolutions since cranking
was initiated
During Start-up the PCM maintains ignition tim-
ing at 9É BTDC.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Engine coolant temperature
²Inlet/Intake air temperature (IAT)²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²A/C switch status
²Battery voltage
²Vehicle speed
²Speed control
²O2 sensors
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts ignition timing and engine idle
speed. Engine idle speed is adjusted through the idle
air control motor.
CRUISE OR IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature this
is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During cruising or idle
the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Inlet/Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Camshaft position
²Knock sensor
²Throttle position
²Exhaust gas oxygen content (O2 sensors)
²A/C switch status
²Battery voltage
²Vehicle speed
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off.
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed and ignition
timing. The PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio according
to the oxygen content in the exhaust gas (measured
by the upstream and downstream heated oxygen sen-
sor).
The PCM monitors for engine misfire. During
active misfire and depending on the severity, the
PCM either continuously illuminates or flashes the
malfunction indicator lamp (Check Engine light on
instrument panel). Also, the PCM stores an engine
misfire DTC in memory, if 2nd trip with fault.
The PCM performs several diagnostic routines.
They include:
²Oxygen sensor monitor
²Downstream heated oxygen sensor diagnostics
during open loop operation (except for shorted)
²Fuel system monitor
²EGR monitor (if equipped)
²Purge system monitor
²Catalyst efficiency monitor
²All inputs monitored for proper voltage range,
rationality.
RSFUEL INJECTION14-19
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)
Page 1527 of 2585

²All monitored components (refer to the Emission
section for On-Board Diagnostics).
The PCM compares the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensor inputs to measure catalytic
convertor efficiency. If the catalyst efficiency drops
below the minimum acceptable percentage, the PCM
stores a diagnostic trouble code in memory, after 2
trips.
During certain idle conditions, the PCM may enter
a variable idle speed strategy. During variable idle
speed strategy the PCM adjusts engine speed based
on the following inputs.
²A/C status
²Battery voltage
²Battery temperature or Calculated Battery Tem-
perature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine run time
²Inlet/Intake air temperature
²Vehicle mileage
ACCELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. The PCM recog-
nizes an abrupt increase in Throttle Position sensor
output voltage or MAP sensor output voltage as a
demand for increased engine output and vehicle
acceleration. The PCM increases injector pulse width
in response to increased fuel demand.
²Wide Open Throttle-open loop
DECELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During decelera-
tion the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²A/C status
²Battery voltage
²Inlet/Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Exhaust gas oxygen content (upstream heated
oxygen sensor)
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Throttle position sensor
²IAC motor (solenoid) control changes in response
to MAP sensor feedback
The PCM may receive a closed throttle input from
the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) when it senses an
abrupt decrease in manifold pressure. This indicates
a hard deceleration (Open Loop). In response, the
PCM may momentarily turn off the injectors. This
helps improve fuel economy, emissions and engine
braking.
WIDE-OPEN-THROTTLE MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. During wide-open-
throttle operation, the following inputs are used by
the PCM:
²Inlet/Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine speed
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Throttle position
When the PCM senses a wide-open-throttle condi-
tion through the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) it de-
energizes the A/C compressor clutch relay. This
disables the air conditioning system and disables
EGR (if equipped).
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width to supply a
predetermined amount of additional fuel, based on
MAP and RPM.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
When the operator turns the ignition switch to the
OFF position, the following occurs:
²All outputs are turned off, unless 02 Heater
Monitor test is being run. Refer to the Emission sec-
tion for On-Board Diagnostics.
²No inputs are monitored except for the heated
oxygen sensors. The PCM monitors the heating ele-
ments in the oxygen sensors and then shuts down.
FUEL CORRECTION or ADAPTIVE MEMORIES
DESCRIPTION
In Open Loop, the PCM changes pulse width with-
out feedback from the O2 Sensors. Once the engine
warms up to approximately 30 to 35É F, the PCM
goes into closed loopShort Term Correctionand
utilizes feedback from the O2 Sensors. Closed loop
Long Term Adaptive Memoryis maintained above
170É to 190É F unless the PCM senses wide open
throttle. At that time the PCM returns to Open Loop
operation.
OPERATION
Short Term
The first fuel correction program that begins func-
tioning is the short term fuel correction. This system
corrects fuel delivery in direct proportion to the read-
ings from the Upstream O2 Sensor.
The PCM monitors the air/fuel ratio by using the
input voltage from the O2 Sensor. When the voltage
reaches its preset high or low limit, the PCM begins
to add or remove fuel until the sensor reaches its
switch point. The short term corrections then begin.
The PCM makes a series of quick changes in the
injector pulse-width until the O2 Sensor reaches its
14 - 20 FUEL INJECTIONRS
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)
Page 1528 of 2585
opposite preset limit or switch point. The process
then repeats itself in the opposite direction.
Short term fuel correction will keep increasing or
decreasing injector pulse-width based upon the
upstream O2 Sensor input. The maximum range of
authority for short term memory is 25% (+/-) of base
pulse-width. Short term is violated and is lost when
ignition is turned OFF.
Long Term
The second fuel correction program is the long
term adaptive memory. In order to maintain correct
emission throughout all operating ranges of the
engine, a cell structure based on engine rpm and load
(MAP) is used.
Ther number of cells varies upon the driving con-
ditions. Two cells are used only during idle, based
upon TPS and Park/Neutral switch inputs. There
may be two other cells used for deceleration, based
on TPS, engine rpm, and vehicle speed. The other
twelve cells represent a manifold pressure and an
rpm range. Six of the cells are high rpm and the
other six are low rpm. Each of these cells has a spe-
cific MAP voltage range Typical Adaptive Memory
Fuel Cells.As the engine enters one of these cells the PCM
looks at the amount of short term correction being
used. Because the goal is to keep short term at 0 (O2
Sensor switching at 0.5 volt), long term will update
in the same direction as short term correction was
moving to bring the short term back to 0. Once short
term is back at 0, this long term correction factor is
stored in memory.
The values stored in long term adaptive memory
are used for all operating conditions, including open
loop and cold starting. However, the updating of the
long term memory occurs after the engine has
exceeded approximately 170É-190É F, with fuel control
in closed loop and two minutes of engine run time.
This is done to prevent any transitional temperature
or start-up compensations from corrupting long term
fuel correction.
Long term adaptive memory can change the pulse-
width by as much as 25%, which means it can correct
for all of short term. It is possible to have a problem
that would drive long term to 25% and short term to
another 25% for a total change of 50% away from
base pulse-width calculation.
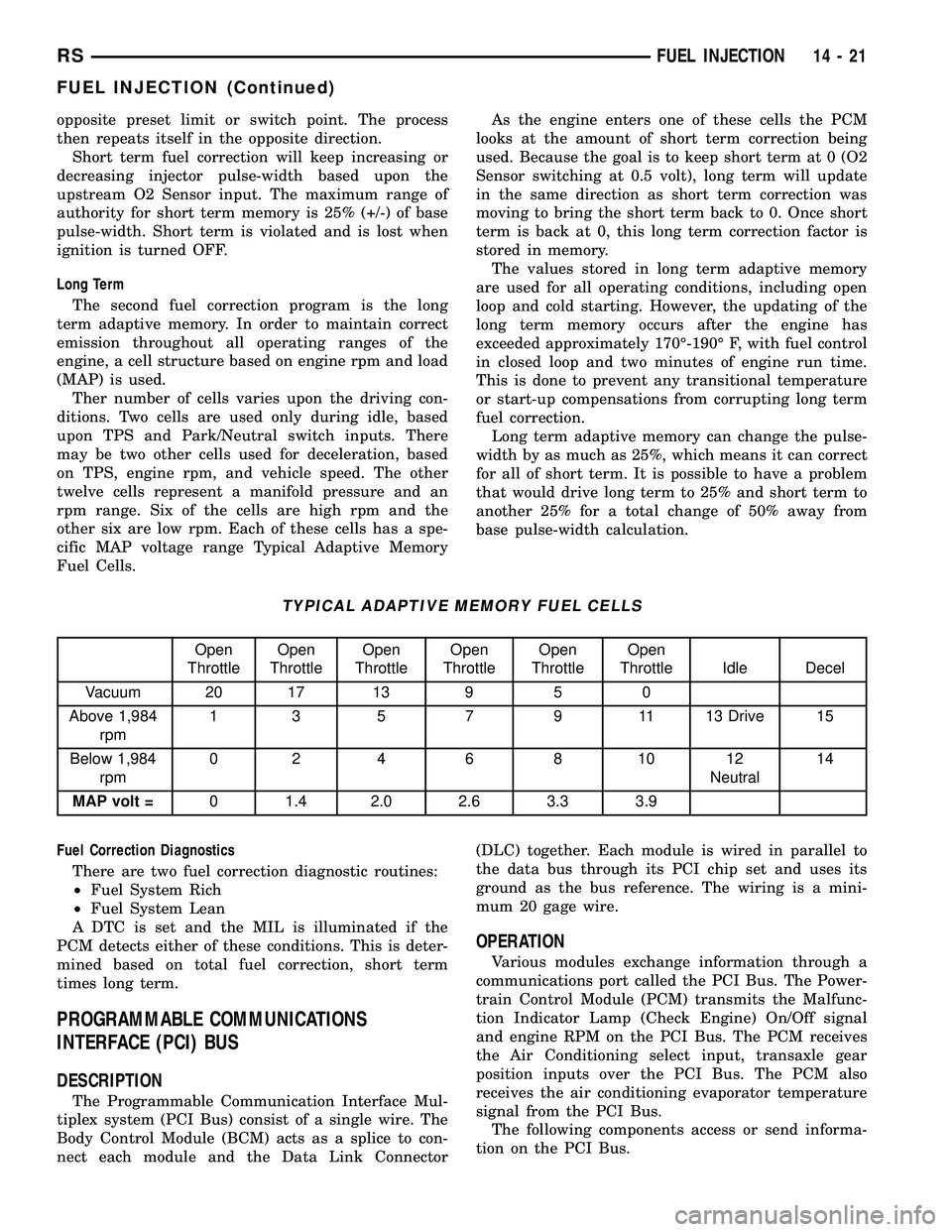
TYPICAL ADAPTIVE MEMORY FUEL CELLS
Open
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
ThrottleOpen
Throttle Idle Decel
Vacuum 20 17 13 9 5 0
Above 1,984
rpm1 3 5 7 9 11 13 Drive 15
Below 1,984
rpm02 4 6 8 1012
Neutral14
MAP volt =0 1.4 2.0 2.6 3.3 3.9
Fuel Correction Diagnostics
There are two fuel correction diagnostic routines:
²Fuel System Rich
²Fuel System Lean
A DTC is set and the MIL is illuminated if the
PCM detects either of these conditions. This is deter-
mined based on total fuel correction, short term
times long term.
PROGRAMMABLE COMMUNICATIONS
INTERFACE (PCI) BUS
DESCRIPTION
The Programmable Communication Interface Mul-
tiplex system (PCI Bus) consist of a single wire. The
Body Control Module (BCM) acts as a splice to con-
nect each module and the Data Link Connector(DLC) together. Each module is wired in parallel to
the data bus through its PCI chip set and uses its
ground as the bus reference. The wiring is a mini-
mum 20 gage wire.
OPERATION
Various modules exchange information through a
communications port called the PCI Bus. The Power-
train Control Module (PCM) transmits the Malfunc-
tion Indicator Lamp (Check Engine) On/Off signal
and engine RPM on the PCI Bus. The PCM receives
the Air Conditioning select input, transaxle gear
position inputs over the PCI Bus. The PCM also
receives the air conditioning evaporator temperature
signal from the PCI Bus.
The following components access or send informa-
tion on the PCI Bus.
RSFUEL INJECTION14-21
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)
Page 1533 of 2585

INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Install the crankshaft sensor.
(2) Install crankshaft sensor bolt and tighten.
(3) Connect the electrical connector (Fig. 8).
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
ENGINE SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The PCM receives a signal from the TCM to indi-
cate vehicle speed on automatic transmission cars.
On 4 cylinder Manual transmission cars (if equipped)
vehicle, a dedicated vehicle speed sensor is connectedto the PCM.On V-6 Manual transmission cars (if
equipped) vehicle, the ABS module provides the sig-
nal to the PCM for vehicle speed.
OPERATION
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) supplies
the road speed and distance traveled inputs to the
PCM. From these inputs and the throttle position
sensor input, the PCM determines when a decelera-
tion condition occurs.
FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION
The injectors are positioned in the intake manifold
or cylinder head with the nozzle ends directly above
the intake valve port (Fig. 10).
OPERATION
The fuel injectors are 12 volt electrical solenoids
(Fig. 11). The injector contains a pintle that closes off
an orifice at the nozzle end. When electric current is
supplied to the injector, the armature and needle
move a short distance against a spring, allowing fuel
to flow out the orifice. Because the fuel is under high
pressure, a fine spray is developed in the shape of a
hollow cone or two streams. The spraying action
atomizes the fuel, adding it to the air entering the
combustion chamber. Fuel injectors are not inter-
changeable between engines.
The PCM provides battery voltage to each injector
through the ASD relay. Injector operation is con-
trolled by a ground path provided for each injector by
the PCM. Injector on-time (pulse-width) is variable,
Fig. 7 Timing Slots
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER DRIVE PLATE
2 - SLOTS
Fig. 8 CRANKSHAFT SENSOR 2.4L
Fig. 9 CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR LOCATION
2.4L
14 - 26 FUEL INJECTIONRS
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)