2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER warning light
[x] Cancel search: warning lightPage 663 of 2585

WARNING: DO NOT CONNECT THE BATTERY NEG-
ATIVE CABLE (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RE-
STRAINTS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH MAY RESULT IF
THE SYSTEM TEST IS NOT PERFORMED PROP-
ERLY.
OCCUPANT RESTRAINT
CONTROLLER
DESCRIPTION
The front driver and passenger airbag system is
designed to reduce the risk of fatality or serious
injury, caused by a frontal impact of the vehicle.
The Occupant Restraint Controller (ORC) is also
sometimes referred to as the Airbag Control Module
(ACM). The ORC contains the impact sensor and
energy reserve capacitor. It is mounted on a bracket,
under the instrument panel, just forward of the stor-
age bin. The ORC monitors the system to determine
the system readiness. The ORC contains on-board
diagnostics and will light the AIRBAG warning lamp
in the message center when a problem occurs.
OPERATION
The impact sensor provides verification of the
direction and severity of the impact. One impact sen-
sor is used. It is located inside the Occupant
Restraint Controller (ORC). The impact sensor is an
accelerometer that senses deceleration. The decelera-
tion pulses are sent to a microprocessor which con-
tains a decision algorithm. When an impact is severe
enough to require airbag protection, the ORC micro-
processor sends a signal that completes the electrical
circuit to the driver and passenger airbags. The
impact sensor is calibrated for the specific vehicle
and reacts to the severity and direction of an impact.
REMOVAL
NOTE: Diagnose the ORC using the service/diag-
nostic manual.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove storage bin from instrument panel.
Refer to Body, Instrument Panel, Storage Bin,
Removal.
(3) Remove three bolts holding ORC to floor
bracket.
(4) Disconnect the wire connector from ORC.
(5) Remove the ORC assembly from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: DO NOT INSTALL ORC IF MOUNTING
LOCATION IS DEFORMED OR DAMAGED. THIS
WILL CAUSE THE ORC TO BE IMPROPERLY
LOCATED AND COULD RESULT IN OCCUPANT
PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH.
CAUTION: Use correct screws when installing the
ORC.
(1) Install the ORC assembly into vehicle.
(2) Connect the wire connector to the ORC.
(3) Install three bolts holding ORC to floor
bracket. Torque bolts to 7.3 - 9.6 N´m (65 to 85 in.
lbs.)
(4) Install the storage bin onto the instrument
panel. Refer to Body, Instrument Panel, Storage Bin,
Installation.
WARNING: DO NOT CONNECT THE BATTERY NEG-
ATIVE CABLE (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RE-
STRAINTS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH MAY RESULT IF
THE SYSTEM TEST IS NOT PERFORMED PROP-
ERLY.
PASSENGER AIRBAG
DESCRIPTION
WARNING: NEVER DISASSEMBLE THE PASSEN-
GER AIRBAG, THE PASSENGER AIRBAG HAS NO
SERVICEABLE PARTS. IF TAMPERED WITH INTER-
NALLY, THE AIRBAG COULD DEPLOY AND RESULT
IN PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH.
The Passenger Airbag is located beneath the
instrument panel and pad assembly. The airbag is
mounted to the back side of the instrument panel
reinforcement.
The instrument panel top pad is the most visible
part of the passenger airbag system. Located under
the instrument panel top pad are the airbag door, the
passenger airbag cushion and the airbag cushion
supporting components.
The passenger airbag includes a magnesium hous-
ing within which the cushion and inflator are
mounted and sealed.
Following a passenger airbag deployment, the pas-
senger airbag and the instrument panel must be
replaced. The passenger airbag cannot be repaired,
and must be replaced if deployed or damaged in any
way.
8O - 8 RESTRAINTSRS
DRIVER AIRBAG TRIM COVER (Continued)
Page 665 of 2585

(26) Using a trim stick or equivalent, gently pry
off the filler bezel just above the cup holder to expose
the lower screws to center bezel.
(27) Remove two screws and then using a trim
stick or equivalent, gently pry off instrument panel
center bezel.
(28) Remove center bezel wiring connectors to
HVAC control and switch assembly (hazard, rear
wiper/washer, heated seats) and remove bezel.
(29) Slide cup holder assembly from instrument
panel.
(30) Remove nineteen screws to right lower instru-
ment panel trim (glove box surround), unplug glove
box lamp wire connector, and remove panel.
(31) Remove four screws and wiring connectors to
radio and remove radio.
(32) Remove one far left instrument panel speaker
retaining screw.
(33) Remove four screws along top front edge of
instrument panel cover/pad.
(34) Remove seven lower instrument panel cover/
pad retaining screws starting from right of vehicle
and only removing these seven, not all of them.
(35) Remove six upper fence line instrument panel
retaining bolts.
(36) Roll back instrument panel just enough to
increase access to the passenger airbag retaining
bolts at the reinforcement. Lift the instrument panel
up slightly so as not to damage the air distribution to
HVAC unit seal.
(37) Disconnect the passenger airbag electrical
connector. Using a trim stick or equivalent, gently
pry electrical connector off of instrument panel rein-
forcement.
(38) Remove the two passenger airbag to instru-
ment panel cover/pad retaining screws.
(39) Remove the three passenger airbag to instru-
ment panel reinforcement retaining bolts.
(40) Pull rearward slightly on the instrument
panel cover/pad to maneuver passenger airbag out
from reinforcement and instrument panel.
INSTALLATION
DEPLOYED AIRBAG
Transfer all reusable components to the new
instrument panel.
(1) Install new Passenger Airbag into instrument
panel.
(2) Install airbag attaching bolts to the instrument
panel.
(a) Torque the two bolts at instrument panel
retainer bosses to 2.7 .5 N´m (24 5 in. lbs.).
(b) Torque the three bolts that attach the pas-
senger airbag to cross-car beam to 10 2 N´m (90
15 in. lbs.).(3) Connect yellow wire connector to passenger air-
bag and affix connector to instrument panel rein-
forcement with push pins.
(4) Install Instrument panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INSTRUMENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT PANEL
ASSEMBLY - INSTALLATION).
WARNING: DO NOT CONNECT THE BATTERY NEG-
ATIVE CABLE (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RE-
STRAINTS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH MAY RESULT IF
THE SYSTEM TEST IS NOT PERFORMED PROP-
ERLY.
UNDEPLOYED AIRBAG
(1) Pull rearward slightly on the instrument panel
cover/pad to maneuver passenger airbag up onto
reinforcement and instrument panel.
(2) Install the three passenger airbag to instru-
ment panel reinforcement retaining bolts but leave
loose. This will help align the passenger airbag for
the cover/pad fit.
(3) Install the two passenger airbag to instrument
panel cover/pad retaining screws. Torque screws to
2.7 .5 N´m (24 5 in. lbs.).
NOTE: Insure that the instrument panel cover/pad
locator pins are indexed properly at center stack
area prior to reassembly.
(4) Tighten the three passenger airbag to instru-
ment panel reinforcement retaining bolts. Torque
bolts to 10 2 N´m (90 15 in. lbs.).
(5) Connect the passenger airbag electrical connec-
tor. Install the connector onto the instrument panel
reinforcement with the push-pin fasteners.
(6) Roll the instrument panel forward lifting
slightly so as to seat the instrument panel air distri-
bution duct on top of the HVAC unit properly to
avoid any leaks or damage to the seal.
(7) Install six upper fence line instrument panel
retaining bolts.
(8) Install three right side instrument panel A-pil-
lar retaining bolts and tighten the right instrument
panel roll down bolt. Install the smaller 10 mm bolt
first to align the instrument panel properly.
(9) Install three left side instrument panel A-pillar
retaining bolts and tighten the left instrument panel
roll down bolt. Install the smaller 10 mm bolt first to
align the instrument panel properly.
(10) Install seven lower instrument panel cover/
pad retaining screws.
(11) Install four screws along top front edge of
instrument panel cover/pad.
(12) Install one far left instrument panel speaker
retaining screw.
8O - 10 RESTRAINTSRS
PASSENGER AIRBAG (Continued)
Page 1295 of 2585

POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION
Accessory power outlets are standard equipment on
this model. Two power outlets are installed in the
instrument panel center lower bezel, which is located
near the bottom of the instrument panel center stack
area. Two additional power outlets are also incorpo-
rated into the vehicle, one on the left rear C-pillar
trim and the other in the center console, if equipped.
The power outlets bases are secured by a snap fit in
the appropriate bezels. A hinged plug flips closed to
conceal and protect the power outlet base when the
power outlet is not being used.
The power outlet receptacle unit and the power
outlet plugs are each available for service replace-
ment.
OPERATION
The power outlet base or receptacle shell is con-
nected to ground, and an insulated contact in the
bottom of the shell is connected to battery current.
The power outlet on the instrument panel marked
with a battery receives battery voltage from a fuse in
the Integrated Power Module (IPM) at all times. The
other power outlet on the instrument panel marked
with a key receives battery voltage only when the
key is in the on position.
The power outlet located in the center console
receives battery voltage all the time when positioned
between thefront seatsand key-on voltage when
positioned between therear seats. The power outlet
located on the C-pillar receives battery voltage only
when the key is in the on position.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING - POWER OUTLET
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toCigar
Lighter/Power Outletin Wiring Diagrams.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO RESTRAINTS BEFORE ATTEMPT-
ING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN,
SEAT OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAG-
NOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE
PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCI-
DENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE
PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Check the fused B(+) fuse in the Integrated
Power Module (IPM). If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK,
repair the shorted circuit or component as required
and replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) fuse
in the IPM. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, repair the
open fused B(+) circuit to the IPM fuse as required.
(3) Open the power outlet door. Check for continu-
ity between the inside circumference of the power
outlet receptacle and a good ground. There should be
continuity. If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, go to Step
5.
(4) Check for battery voltage at the insulated con-
tact located at the back of the power outlet recepta-
cle. If not OK, go to Step 5.
(5) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the appropriate bezel. Check for conti-
nuity between the ground circuit cavity of the power
outlet wire harness connector and a good ground.
There should be continuity. If OK, go to Step 6. If not
OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground as
required.
(6) Connect the battery negative cable. Check for
battery voltage at the fused B(+) circuit cavity of the
power outlet wire harness connector. If OK, replace
the faulty power outlet receptacle. If not OK, repair
the open fused B(+) circuit to the IPM fuse as
required.
8W - 97 - 4 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMRS
Page 1306 of 2585

(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak. If a leak is
present in this area, remove transmission for further
inspection.
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, oil gallery cup
plug, bedplate to cylinder block mating surfaces
and seal bore. See proper repair procedures for
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as previously described.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, replace compo-
nent(s) as necessary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
(2) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Select a route free from traf-
fic and other forms of congestion, observe all traffic
laws, and accelerate through the gears several times
briskly.
(3) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As spark
plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnor-
mal firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc. Record cyl-
inder number of spark plug for future reference.(4) Remove the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay from
the PDC.
(5) Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the
compression check.
(6) Insert compression gauge adaptor Special Tool
8116 or the equivalent, into the #1 spark plug hole in
cylinder head. Connect the 0±500 psi (Blue) pressure
transducer (Special Tool CH7059) with cable adap-
tors to the DRBIIIt. For Special Tool identification,
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIAL TOOLS).
(7) Crank engine until maximum pressure is
reached on gauge. Record this pressure as #1 cylin-
der pressure.
(8) Repeat the previous step for all remaining cyl-
inders.
(9) Compression should not be less than 689 kPa
(100 psi) and not vary more than 25 percent from cyl-
inder to cylinder.
(10) If one or more cylinders have abnormally low
compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
(11) If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an
abnormally low reading on the second compression
test, it could indicate the existence of a problem in
the cylinder in question.The recommended com-
pression pressures are to be used only as a
guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
should not be disassembled to determine the
cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE PRESSURE CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the pressure cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
RSENGINE 2.4L9-9
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1380 of 2585

(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak. If a leak is
present in this area, remove transmission for further
inspection.
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, oil gallery cup
plug, bedplate to cylinder block mating surfaces
and seal bore. See proper repair procedures for
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as previously described.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, replace compo-
nent(s) as necessary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
(2) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Select a route free from traf-
fic and other forms of congestion, observe all traffic
laws, and accelerate through the gears several times
briskly.
(3) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As spark
plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnor-
mal firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc. Record cyl-
inder number of spark plug for future reference.(4) Remove the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay from
the PDC.
(5) Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the
compression check.
(6) Insert compression gauge adaptor Special Tool
8116 or the equivalent, into the #1 spark plug hole in
cylinder head. Connect the 0±500 psi (Blue) pressure
transducer (Special Tool CH7059) with cable adap-
tors to the DRBIIIt. For Special Tool identification,
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIAL TOOLS).
(7) Crank engine until maximum pressure is
reached on gauge. Record this pressure as #1 cylin-
der pressure.
(8) Repeat the previous step for all remaining cyl-
inders.
(9) Compression should not be less than 689 kPa
(100 psi) and not vary more than 25 percent from cyl-
inder to cylinder.
(10) If one or more cylinders have abnormally low
compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
(11) If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an
abnormally low reading on the second compression
test, it could indicate the existence of a problem in
the cylinder in question.The recommended com-
pression pressures are to be used only as a
guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
should not be disassembled to determine the
cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE PRESSURE CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the pressure cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-83
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1509 of 2585

FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION
The front wheel drive car uses a plastic fuel tank
located rear center of the vehicle.
The Fuel Delivery System consists of: the following
items:
²Electric fuel pump module
²Fuel filter
²Tubes/lines/hoses
²Fuel injectors
The in-tank fuel pump module contains the fuel
pump. The pump is serviced as part of the fuel pump
module. Refer to Fuel Pump Module.
The fuel filter is replaceable only as part of the
fuel pump module.
OPERATION
The fuel system provides fuel pressure by an
in-tank pump module. The Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) controls the operation of the fuel system
by providing battery voltage to the fuel pump
through the fuel pump relay. The PCM requires only
three inputs and a good ground to operate the fuel
pump relay. The three inputs are:
²Ignition voltage
²Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL DELIVERY
SYSTEM
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic Information)
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE
(1) Remove Fuel Pump relay from Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC). For location of relay, refer to label
on underside of PDC cover.
(2) Start and run engine until it stalls.
(3) Attempt restarting engine until it will no
longer run.
(4) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
(5) Return fuel pump relay to PDC.
(6) One or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
may have been stored in PCM memory due to fuel
pump relay removal. The DRB IIItscan tool must be
used to erase a DTC.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING FUEL
TANK
Two different procedures may be used to drain fuel
tank (lowering tank or using DRBIIItscan tool).The quickest draining procedure involves lowering
the fuel tank.
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
SERVICE VEHICLES IN WELL VENTILATED AREAS
AND AVOID IGNITION SOURCES. NEVER SMOKE
WHILE SERVICING THE VEHICLE. THIS MAY
RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH.
As an alternative procedure, the electric fuel pump
may be activated allowing tank to be drained at fuel
rail connection. Refer to DRBIIItscan tool for fuel
pump activation procedures. Before disconnecting
fuel line at fuel rail, release fuel pressure. Refer to
the Fuel System Pressure Release Procedure in this
group for procedures. Disconnect the fuel line at the
fuel rail and remove the plastic retainer from the
fuel rail. Take plastic retainer and install it back into
the fuel line from body. Check the O-ring and make
sure that it is in place and not damaged. Attach end
of special test hose tool number 6539 at fuel line con-
nection from the body line. Position opposite end of
this hose tool to an approved gasoline draining sta-
tion. Activate fuel pump and drain tank until empty.
When done remove the special test hose tool number
6539 from the body line. Remove the plastic retainer
from the special test hose tool number 6539 and rein-
stall it into the fuel line from the body. Check the
O-ring and make sure that it is in place and not
damaged. Install the fuel line to the fuel rail.
If electric fuel pump is not operating, tank must be
lowered for fuel draining. Refer to following proce-
dures.
(1) Remove fuel filler cap.
(2) Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release pro-
cedure.
(3) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(4) Raise vehicle and support.
(5) Certain models are equipped with a separate
grounding wire (strap) connecting the fuel fill tube
assembly to the body. Disconnect wire by removing
screw.
(6) Open fuel fill door and remove screws mount-
ing fuel filler tube assembly to body. Do not discon-
nect rubber fuel fill or vent hoses from tank at this
time.
(7) Place a transmission jack under center of fuel
tank. Apply a slight amount of pressure to fuel tank
with transmission jack.
(8) Remove fuel tank mounting straps.
(9)Lower the tank just enough so that the
filler tube fitting is the highest point of the fuel
tank.
(10) Remove filler tube from fuel tank. Tank will
be drained through this fitting.
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERYRS
Page 1582 of 2585
OPERATION
The power steering pump is a constant displace-
ment vane type pump. The 2.4L pump has an inte-
gral fluid reservoir and there is a secondary remote
non-flow reservoir which acts only as a fluid fill and
check point. The 3.3L/3.8L pump houses very little
fluid and is therefore supplied by a remote flow
through reservoir.
WARNING
WARNING: POWER STEERING FLUID, ENGINE
PARTS AND EXHAUST SYSTEM MAY BE
EXTREMELY HOT IF ENGINE HAS BEEN RUNNING.DO NOT START ENGINE WITH ANY LOOSE OR DIS-
CONNECTED HOSES. DO NOT ALLOW HOSES TO
TOUCH HOT EXHAUST MANIFOLD OR CATALYST.
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
WITH THE ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT PERSONAL
INJURY FROM MOVING PARTS.
CAUTION
CAUTION: When the system is open, cap all open
ends of the hoses, power steering pump fittings or
power steering gear ports to prevent entry of for-
eign material into the components.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - POWER STEERING
PUMP INITIAL OPERATION
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
AND ADJUSTED WITH ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT
INJURY FROM MOVING ENGINE COMPONENTS.
CAUTION: Use only MoparTAutomatic Transmis-
sion Fluid (MS-9602) in power steering system. Use
of other MoparTpower steering fluids (MS5931 and
MS9933) should be avoided to ensure peak perfor-
mance of the power steering system under all oper-
ating conditions. Do not overfill.
Read the fluid level through the side of the power
steering fluid reservoir. The fluid level should indi-
cateªFILL RANGEºwhen the fluid is at a temper-
ature of approximately 21ÉC to 27ÉC (70ÉF to 80ÉF).
(1) Wipe the filler cap and area clean, then remove
the cap.
(2) Fill the fluid reservoir to the proper level and
let the fluid settle for at least two (2) minutes.
(3) Start the engine and let run for a few seconds,
then turn the engine off.
(4) Add fluid if necessary. Repeat the above steps
until the fluid level remains constant after running
the engine.
(5) Raise the front wheels off the ground.
(6) Start the engine.
(7) Slowly turn the steering wheel right and left,
lightly contacting the wheel stops.
(8) Add fluid if necessary.
(9) Lower the vehicle, then turn the steering wheel
slowly from lock-to-lock.
(10) Stop the engine. Check the fluid level and
refill as required.
(11) If the fluid is extremely foamy, allow the vehi-
cle to stabilize a few minutes, then repeat the above
procedure.
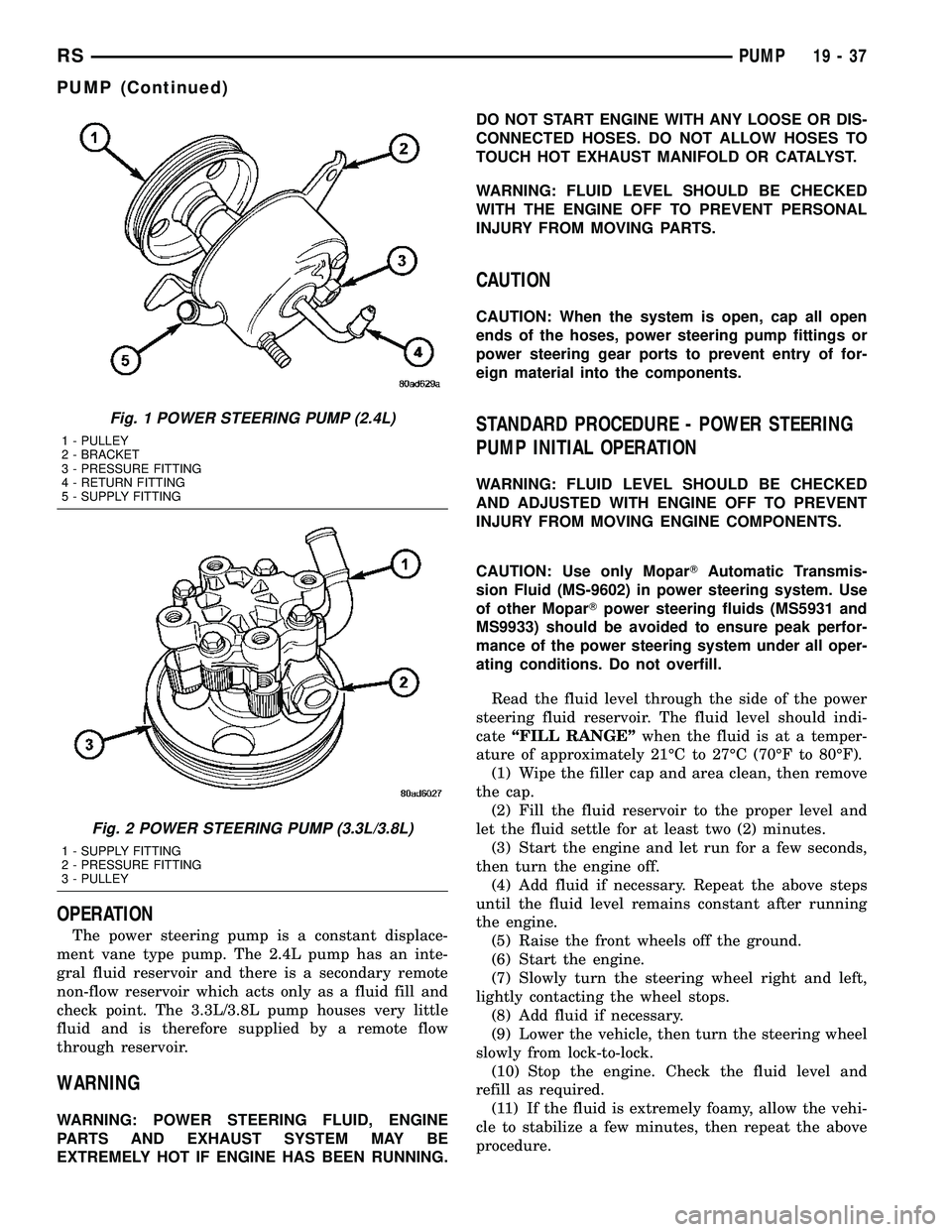
Fig. 1 POWER STEERING PUMP (2.4L)
1 - PULLEY
2 - BRACKET
3 - PRESSURE FITTING
4 - RETURN FITTING
5 - SUPPLY FITTING
Fig. 2 POWER STEERING PUMP (3.3L/3.8L)
1 - SUPPLY FITTING
2 - PRESSURE FITTING
3 - PULLEY
RSPUMP19-37
PUMP (Continued)
Page 2113 of 2585

the vehicle should not enter the passenger or luggage
compartment. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal water tight under all conditions. At
times, side glass or door seals will allow water to
enter the passenger compartment during high pres-
sure washing or hard driving rain (severe) condi-
tions. Overcompensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop a water leak that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After completing
a repair, water test vehicle to verify leak has stopped
before returning vehicle to use.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE WATER LEAK TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place, body
drains are clear, and body components are properly
aligned and sealed. If component alignment or seal-
ing is necessary, refer to the appropriate section of
this group for proper procedures.
WATER LEAK TESTS
WARNING: DO NOT USE ELECTRIC SHOP LIGHTS
OR TOOLS IN WATER TEST AREA. PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT.
When the conditions causing a water leak have
been determined, simulate the conditions as closely
as possible.
²If a leak occurs with the vehicle parked in a
steady light rain, flood the leak area with an open-
ended garden hose.
²If a leak occurs while driving at highway speeds
in a steady rain, test the leak area with a reasonable
velocity stream or fan spray of water. Direct the
spray in a direction comparable to actual conditions.
²If a leak occurs when the vehicle is parked on an
incline, hoist the end or side of the vehicle to simu-
late this condition. This method can be used when
the leak occurs when the vehicle accelerates, stops or
turns. If the leak occurs on acceleration, hoist the
front of the vehicle. If the leak occurs when braking,
hoist the back of the vehicle. If the leak occurs on left
turns, hoist the left side of the vehicle. If the leak
occurs on right turns, hoist the right side of the vehi-
cle. For hoisting recommendations (Refer to LUBRI-
CATION & MAINTENANCE/HOISTING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
WATER LEAK DETECTION
To detect a water leak point-of-entry, do a water
test and watch for water tracks or droplets forming
on the inside of the vehicle. If necessary, remove inte-
rior trim covers or panels to gain visual access to the
leak area. If the hose cannot be positioned without
being held, have someone help do the water test.Some water leaks must be tested for a considerable
length of time to become apparent. When a leak
appears, find the highest point of the water track or
drop. The highest point usually will show the point of
entry. After leak point has been found, repair the
leak and water test to verify that the leak has
stopped.
Locating the entry point of water that is leaking
into a cavity between panels can be difficult. The
trapped water may splash or run from the cavity,
often at a distance from the entry point. Most water
leaks of this type become apparent after accelerating,
stopping, turning, or when on an incline.
MIRROR INSPECTION METHOD
When a leak point area is visually obstructed, use
a suitable mirror to gain visual access. A mirror can
also be used to deflect light to a limited-access area
to assist in locating a leak point.
BRIGHT LIGHT LEAK TEST METHOD
Some water leaks in the luggage compartment can
be detected without water testing. Position the vehi-
cle in a brightly lit area. From inside the darkened
luggage compartment inspect around seals and body
seams. If necessary, have a helper direct a drop light
over the suspected leak areas around the luggage
compartment. If light is visible through a normally
sealed location, water could enter through the open-
ing.
PRESSURIZED LEAK TEST METHOD
When a water leak into the passenger compart-
ment cannot be detected by water testing, pressurize
the passenger compartment and soap test exterior of
the vehicle. To pressurize the passenger compart-
ment, close all doors and windows, start engine, and
set heater control to high blower in HEAT position. If
engine can not be started, connect a charger to the
battery to ensure adequate voltage to the blower.
With interior pressurized, apply dish detergent solu-
tion to suspected leak area on the exterior of the
vehicle. Apply detergent solution with spray device or
soft bristle brush. If soap bubbles occur at a body
seam, joint, seal or gasket, the leak entry point could
be at that location.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WIND NOISE
Wind noise is the result of most air leaks. Air leaks
can be caused by poor sealing, improper body compo-
nent alignment, body seam porosity, or missing plugs
in the engine compartment or door hinge pillar areas.
All body sealing points should be airtight in normal
driving conditions. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal airtight under all conditions. At times,
side glass or door seals will allow wind noise to be
23 - 2 BODYRS
BODY (Continued)