2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER tire pressure
[x] Cancel search: tire pressurePage 20 of 2585

FLUID FILL/CHECK
LOCATIONS
DESCRIPTION
The fluid check/fill point locations are located in
each applicable service manual section.
LUBRICATION POINTS
DESCRIPTION
Lubrication point locations are located in each
applicable Sections.
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
There are two maintenance schedules that show
therequiredservice for your vehicle.
First is ScheduleªBº. It is for vehicles that are
operated under the conditions that are listed below
and at the beginning of the schedule.
²Day or night temperatures are below 32É F (0É
C).
²Stop and go driving.
²Extensive engine idling.
²Driving in dusty conditions.
²Short trips of less than 10 miles (16 km).
²More than 50% of your driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 90É F (32É C).
²Trailer towing.L
²Taxi, police, or delivery service (commercial ser-
vice).L
²Off-road or desert operation.
NOTE: Most vehicles are operated under the condi-
tions listed for Schedule(B(.
Second is ScheduleªAº. It is for vehicles that are
not operated under any of the conditions listed under
Schedule9B9.
Use the schedule that best describes your driving
conditions. Where time and mileage are listed, follow
the interval that occurs first.
CAUTION: Failure to perform the required mainte-
nance items may result in damage to the vehicle.
At Each Stop for Fuel
²Check the engine oil level about 5 minutes after
a fully warmed engine is shut off. Checking the oil
level while the vehicle is on level ground will
improve the accuracy of the oil level reading. Add oil
only when the level is at or below the ADD or MIN
mark.
²Check the windshield washer solvent and add if
required.
Once a Month
²Check tire pressure and look for unusual wear
or damage.
²Inspect the battery and clean and tighten the
terminals as required.
²Check the fluid levels of coolant reservoir, brake
master cylinder and transmission; add as needed.
²Check all lights and all other electrical items for
correct operation.
At Each Oil Change
²Change the engine oil filter.
²Inspect the exhaust system.
²Inspect the brake hoses.
²Inspect the CV joints and front suspension com-
ponents.
²Check the automatic transmission fluid level.
²Check the coolant level, hoses, and clamps.
Tire Rotation
²Rotate the tires at 6,000 miles (10 000 km).
SCHEDULE B
Follow schedule ªBº if you usually operate your
vehicle under one or more of the following conditions.
Change the automatic transmission fluid and filter
every 60,000 miles (96 000 km) if the vehicle is usu-
ally operated under one or more of the conditions
marked with anL.
²Day or night temperatures are below 32É F (0É
C).
²Stop and go driving.
²Extensive engine idling.
²Driving in dusty conditions.
²Short trips of less than 10 miles (16 km).
²More than 50% of your driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 90É F (32É C).
²Trailer towing.L
²Taxi, police, or delivery service (commercial ser-
vice).L
²Off-road or desert operation.
RSLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE0-7
Page 28 of 2585

* This maintenance is recommended by the manu-
facture to the owner but is not required to maintain
the emissions warranty.
³ This maintenance is not required if previously
replaced.
Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
Retain all receipts.
WARNING: You can be badly injured working on or
around a motor vehicle. Do only that service work
for which you have the knowledge and the right
equipment. If you have any doubt about your ability
to perform a service job, take your vehicle to a
competent mechanic.
DESCRIPTION - EXPORT
There are two maintenance schedules that show
therequiredservice for your vehicle.
First is ScheduleªAº. It is for vehicles that are not
operated under any of the conditions listed under
Schedule9B9.
Second is ScheduleªBº. It is for vehicles that are
operated under the conditions that are listed below
and at the beginning of the schedule.
²Day or night temperatures are below 0É C (32É
F).
²Stop and go driving.
²Extensive engine idling.
²Driving in dusty conditions.
²Short trips of less than 16 km (10 miles).
²More than 50% of your driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 32É C (90É F).
²Trailer towing.L
²Taxi, police, or delivery service (commercial ser-
vice).L
²Off-road or desert operation.
NOTE: Most vehicles are operated under the condi-
tions listed for Schedule(B(.Use the schedule that best describes your driving
conditions. Where time and mileage are listed, follow
the interval that occurs first.
CAUTION: Failure to perform the required mainte-
nance items may result in damage to the vehicle.
At Each Stop for Fuel
²Check the engine oil level about 5 minutes after
a fully warmed engine is shut off. Checking the oil
level while the vehicle is on level ground will
improve the accuracy of the oil level reading. Add oil
only when the level is at or below the ADD or MIN
mark.
²Check the windshield washer solvent and add if
required.
Once a Month
²Check tire pressure and look for unusual wear
or damage.
²Inspect the battery and clean and tighten the
terminals as required.
²Check the fluid levels of coolant reservoir, brake
master cylinder and transmission, add as needed.
²Check all lights and all other electrical items for
correct operation.
At Each Oil Change
²Change the engine oil filter.
²Inspect the exhaust system.
²Inspect the brake hoses.
²Inspect the CV joints and front suspension com-
ponents.
²Check the automatic transmission fluid level.
²Check the manual transmission fluid level.
²Check the coolant level, hoses, and clamps.
²Rotate the tires at each oil change interval
shown on Schedule ªAº 12 000 km (7,500 miles) or
every other interval shown on Schedule ªBº 10 000
km (6,000 miles).
RSLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE0-15
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 37 of 2585

DESCRIPTION ± DIESEL ENGINES ± EXPORT
There are two maintenance schedules that show
therequiredservice for your vehicle.
First is ScheduleªAº. It is for vehicles that are not
operated under any of the conditions listed under
Schedule9B9.
Second is ScheduleªBº. It is for vehicles that are
operated under the conditions that are listed below
and at the beginning of the schedule.
²Extensive engine idling.
²Driving in dusty conditions.
²More than 50% of your driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 32É C (90É F).
²Trailer towing.
²Taxi, police, or delivery service (commercial ser-
vice).
NOTE: Most vehicles are operated under the condi-
tions listed for Schedule(B(.
Use the schedule that best describes your driving
conditions. Where time and mileage are listed, follow
the interval that occurs first.
CAUTION: Failure to perform the required mainte-
nance items may result in damage to the vehicle.
At Each Stop for Fuel
²Check the engine oil level about 5 minutes after
a fully warmed engine is shut off. Checking the oil
level while the vehicle is on level ground willimprove the accuracy of the oil level reading. Add oil
only when the level is at or below the ADD or MIN
mark.
²Check the windshield washer solvent and add if
required.
Once a Month
²Check the tire pressure and look for unusual
wear or damage.
²Inspect the battery and clean and tighten the
terminals as required.
²Check the fluid levels of coolant deaeration bot-
tle, brake master cylinder and transmission, add as
needed.
²Check all lights and all other electrical items for
correct operation.
At Each Oil Change
²Change the engine oil filter.
²Inspect the exhaust system.
²Inspect the brake hoses.
²Inspect the CV joints and front suspension com-
ponents.
²Check the manual transmission fluid level.
²Check the coolant level, hoses, and clamps.
²Inspect engine accessory drive belts. Replace as
necessary.
²Inspect for the presence of water in the fuel fil-
ter/water separator unit.
²Rotate the tires at each oil change interval (20
000 km).
SCHEDULE A - DIESEL ENGINES
Kilometers 20 000 km 40 000 km 60 000 km 80 000 km 100 000
km
Change engine oil and engine oil filter.XXXX X
Inspect engine air filter element. Replace as
necessary.XX X
Replace engine air filter element X X
Replace fuel filter/water separator unit.XXXX X
Inspect timing belt tensioner and replace if
necessary. ³X
Replace engine timing belt and idler
pulleys.X
Check front end alignment. X X
Inspect the tie rod ends and boot seals. X X
Inspect the brake linings.XXXX X
0 - 24 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCERS
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 55 of 2585

CAUTION: Do not use an arbor press to install the
sealing boot on the ball joint. Damage to the seal-
ing boot will occur if excessive pressure is applied
to the sealing boot when it is being installed.
(3) Place Installer, Special Tool 6758, over seal
boot and squarely align it with bottom edge of seal
boot (Fig. 20). Apply hand pressure to Special Tool
6758 until seal boot is pressed squarely against top
surface of lower control arm.
(4) Wipe any grease off the ball joint stem.(5) Place the shield over the top of the seal boot
and stretch it into the groove at the top of the seal
boot.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to install a normal grease
zirc in the ball joint and lubricate the joint through
the zirc fitting.
(6) Reinstall steering knuckle on vehicle. (Refer to
2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/KNUCKLE - INSTALLA-
TION)
LOWER CONTROL ARM
DESCRIPTION
The lower control arm is mounted to the front sus-
pension crossmember using a pivot bolt through the
center of the front pivot bushing, and the front sus-
pension cradle crossmember reinforcement traps the
rear bushing in the crossmember (Fig. 1).
The lower control arm is an iron casting with two
rubber bushings and a ball joint. The lower control
arm front bushing is the spool type and is pressed
into the lower control arm. The standard (Low-line,
High-line) lower control arm rear bushing is a
push-on bushing that is pushed over a stem on the
rear of the lower control arm. The lower control arm
rear bushing used on all other models is a hydro-
bushing that is pressed on. It has liquid filled voids
that provide more effective dampening than the stan-
dard bushing. Vehicles with rear hydro-bushings uti-
lize a different lower control arm than vehicles with
standard bushings. They have a straight slightly
tapered round stem where the hydro-bushing is
mounted whereas the standard arm has a straight
stem with a squared knob on the end to retain the
bushing.
The lower control arm ball joint is pressed into the
outer end of the arm. The ball joint has a tapered
stud and retainer nut for fastening it to the steering
knuckle.
OPERATION
The lower control arm supports the lower end of
the steering knuckle and allows for the up and down
movement of the suspension during the jounce and
rebound travel. The lower control arm ball joint con-
nects the arm to the steering knuckle.
REMOVAL - LOWER CONTROL ARM
(1) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(2) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Remove the steering knuckle. (Refer to 2 -
SUSPENSION/FRONT/KNUCKLE - REMOVAL)
Fig. 19 Installer Positioned On Ball Joint Seal Boot
1 - INSTALLER 6758
2 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
3 - SEAL BOOT SHIELD
Fig. 20 Installing Ball Joint Seal Boot (Typical)
1 - SHIELD (NOT ON RG VEHICLE)
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 6758
3 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
4 - BALL JOINT SEAL BOOT
2 - 12 FRONT SUSPENSIONRS
LOWER BALL JOINT SEAL BOOT (Continued)
Page 94 of 2585
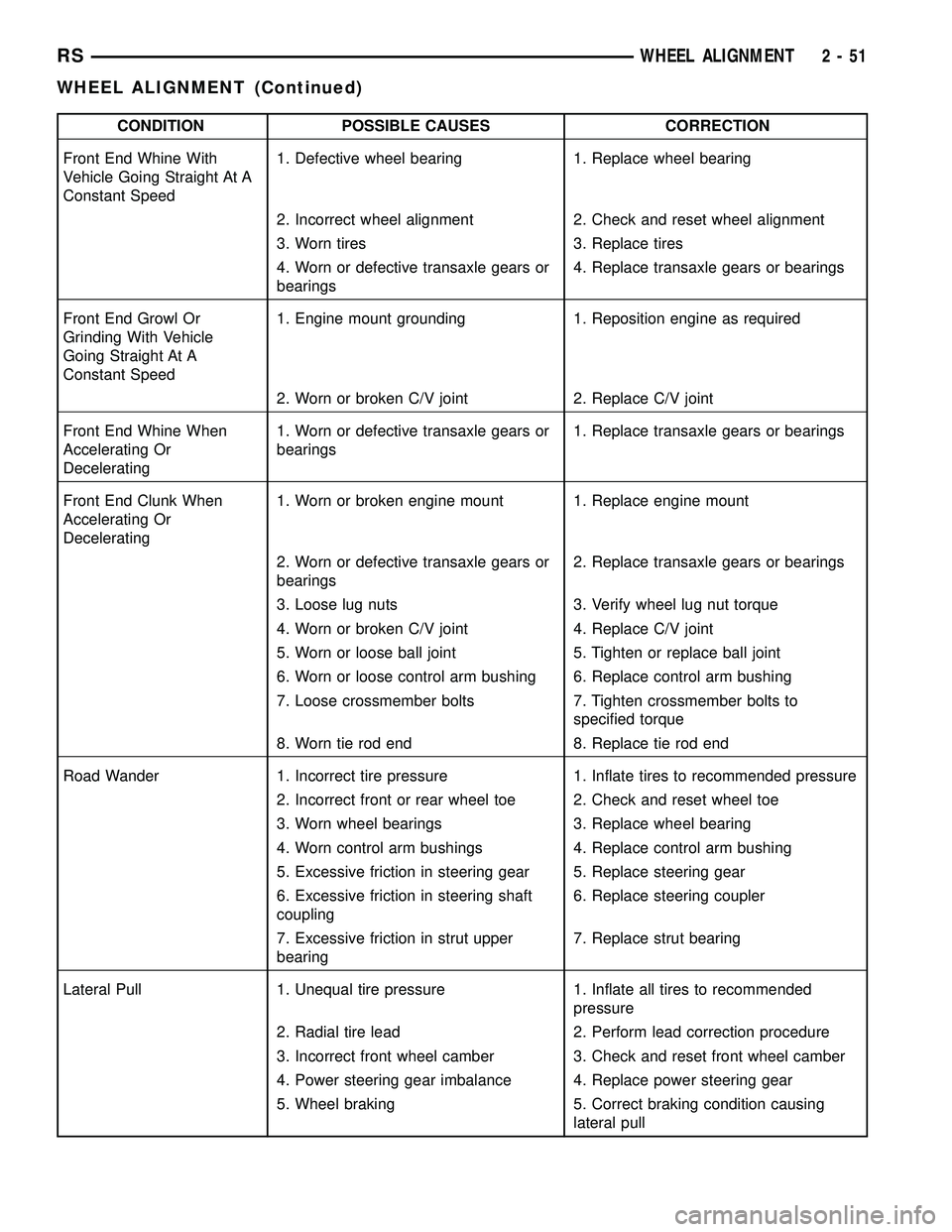
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Front End Whine With
Vehicle Going Straight At A
Constant Speed1. Defective wheel bearing 1. Replace wheel bearing
2. Incorrect wheel alignment 2. Check and reset wheel alignment
3. Worn tires 3. Replace tires
4. Worn or defective transaxle gears or
bearings4. Replace transaxle gears or bearings
Front End Growl Or
Grinding With Vehicle
Going Straight At A
Constant Speed1. Engine mount grounding 1. Reposition engine as required
2. Worn or broken C/V joint 2. Replace C/V joint
Front End Whine When
Accelerating Or
Decelerating1. Worn or defective transaxle gears or
bearings1. Replace transaxle gears or bearings
Front End Clunk When
Accelerating Or
Decelerating1. Worn or broken engine mount 1. Replace engine mount
2. Worn or defective transaxle gears or
bearings2. Replace transaxle gears or bearings
3. Loose lug nuts 3. Verify wheel lug nut torque
4. Worn or broken C/V joint 4. Replace C/V joint
5. Worn or loose ball joint 5. Tighten or replace ball joint
6. Worn or loose control arm bushing 6. Replace control arm bushing
7. Loose crossmember bolts 7. Tighten crossmember bolts to
specified torque
8. Worn tie rod end 8. Replace tie rod end
Road Wander 1. Incorrect tire pressure 1. Inflate tires to recommended pressure
2. Incorrect front or rear wheel toe 2. Check and reset wheel toe
3. Worn wheel bearings 3. Replace wheel bearing
4. Worn control arm bushings 4. Replace control arm bushing
5. Excessive friction in steering gear 5. Replace steering gear
6. Excessive friction in steering shaft
coupling6. Replace steering coupler
7. Excessive friction in strut upper
bearing7. Replace strut bearing
Lateral Pull 1. Unequal tire pressure 1. Inflate all tires to recommended
pressure
2. Radial tire lead 2. Perform lead correction procedure
3. Incorrect front wheel camber 3. Check and reset front wheel camber
4. Power steering gear imbalance 4. Replace power steering gear
5. Wheel braking 5. Correct braking condition causing
lateral pull
RSWHEEL ALIGNMENT2-51
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 95 of 2585

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Excessive Steering Free
Play1. Incorrect Steering Gear Adjustment 1. Adjust Or Replace Steering Gear
2. Worn or loose tie rod ends 2. Replace or tighten tie rod ends
3. Loose steering gear mounting bolts 3. Tighten steering gear bolts to specified
torque
4. Loose or worn steering shaft coupler 4. Replace steering shaft coupler
Excessive Steering Effort 1. Low tire pressure 1. Inflate all tires to recommended
pressure
2. Lack of lubricant in steering gear 2. Replace steering gear
3. Low power steering fluid level 3. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
correct level
4. Loose power steering pump drive
belt4. Correctly adjust power steering pump
drive belt
5. Lack of lubricant in ball joints 5. Lubricate or replace ball joints
6. Steering gear malfunction 6. Replace steering gear
7. Lack of lubricant in steering coupler 7. Replace steering coupler
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WHEEL ALIGNMENT
PRE-WHEEL ALIGNMENT INSPECTION
Before any attempt is made to change or correct
the wheel alignment, the following inspection and
necessary corrections must be made to ensure proper
alignment.
(1) Verify that the fuel tank is full of fuel. If the
tank is not full, the reduction in weight will affect
the curb height of the vehicle and the alignment
angles.
(2) The passenger and luggage compartments of
the vehicle should be free of any load that is not fac-
tory equipment.
(3) Check the tires on the vehicle. All tires must be
the same size and in good condition with approxi-
mately the same amount of tread wear. Inflate all
the tires to the recommended air pressure.
(4) Check the front wheel and tire assemblies for
excessive radial runout.
(5) Inspect lower ball joints and all steering link-
age for looseness, binding, wear or damage. Repair as
necessary.
(6) Check suspension fasteners for proper torque
and retighten as necessary.
(7) Inspect all suspension component rubber bush-
ings for signs of wear or deterioration. Replace any
faulty bushings or components before aligning the
vehicle.
(8) Check the vehicle's curb height to verify it is
within specifications. Refer to Curb Height Measure-
ment.
WHEEL ALIGNMENT SETUP
(1) Position the vehicle on an alignment rack.
(2) Install all required alignment equipment on
the vehicle per the alignment equipment manufactur-
er's instructions. On this vehicle, a four-wheel align-
ment is recommended.
NOTE: Prior to reading the vehicle's alignment
readouts, the front and rear of vehicle should be
jounced. Induce jounce (rear first, then front) by
grasping the center of the bumper and jouncing
each end of vehicle an equal number of times. The
bumper should always be released when vehicle is
at the bottom of the jounce cycle.
(3) Read the vehicle's current front and rear align-
ment settings. Compare the vehicle's current align-
ment settings to the vehicle specifications for camber,
caster and toe-in. (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/
WHEEL ALIGNMENT - SPECIFICATIONS)
(4) If front camber and caster are not within spec-
ifications, proceed to CAMBER AND CASTER below.
If caster and camber are within specifications, pro-
ceed to TOE which can be found following CAMBER
AND CASTER. Rear camber, caster and toe are not
adjustable. If found not to be within specifications,
reinspect for damaged suspension or body compo-
nents and replace as necessary.
CAMBER AND CASTER
Camber and caster settings on this vehicle are
determined at the time the vehicle is designed, by
the location of the vehicle's suspension components.
This is referred to as NET BUILD. The result is no
2 - 52 WHEEL ALIGNMENTRS
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 98 of 2585

rotate inner tie rods of steering gear (Fig. 12) to set
front toe to the preferred toe specification. (Refer to 2
- SUSPENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - SPECIFI-
CATIONS)
(3) Tighten tie rod jam nuts (Fig. 12) to 75 N´m
(55 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Adjust steering gear to tie rod boots at the
inner tie rod.
(5) Remove steering wheel clamp.
(6) Remove the alignment equipment.
(7) Road test the vehicle to verify the steering
wheel is straight and the vehicle does not wander or
pull.STANDARD PROCEDURE - CURB HEIGHT
MEASUREMENT
The wheel alignment is to be checked and all align-
ment adjustments made with the vehicle at its
required curb height specification.
Vehicle height is to be checked with the vehicle on
a flat, level surface, preferably a vehicle alignment
rack. The tires are to be inflated to the recommended
pressure. All tires are to be the same size as stan-
dard equipment. Vehicle height is checked with the
fuel tank full of fuel, and no passenger or luggage
compartment load.
Vehicle height is not adjustable. If the measure-
ment is not within specifications, inspect the vehicle
for bent or weak suspension components. Compare
the parts tag on the suspect coil spring(s) to the
parts book and the vehicle sales code, checking for a
match. Once removed from the vehicle, compare the
coil spring height to a correct new or known good coil
spring. The heights should vary if the suspect spring
is weak.
(1) Measure from the inboard edge of the wheel
opening fender lip directly above the wheel center
(spindle), to the floor or alignment rack surface.
(2) When measuring, the maximum left-to-right
differential is not to exceed 12.5 mm (0.5 in.).
(3) Compare the measurements to the specifica-
tions listed in the following Curb Height Specifica-
tions charts.
CURB HEIGHT SPECIFICATIONS
VEHICLE FRONT REAR
CARGO VAN755mm 11mm
29.72 in. 0.43 in795mm 11mm
31.30 in. 0.43 in.
ALL OTHERS755mm 11mm
29.72 in. 0.43 in770mm 11mm
30.31 in. 0.43 in.
Fig. 12 Front Wheel Toe Adjustment
1 - INNER TIE ROD SERRATION
2 - OUTER TIE ROD JAM NUT
3 - OUTER TIE ROD END
4 - INNER TIE ROD
5 - STEERING KNUCKLE
RSWHEEL ALIGNMENT2-55
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 124 of 2585

²Engine
²Transmission
²Exhaust
²Propeller shaft (vibration)
²Vehicle body (drumming)
Driveline module noises are normally divided into
two categories: gear noise or bearing noise. A thor-
ough and careful inspection should be completed to
determine the actual source of the noise before
replacing the driveline module.
The rubber mounting bushings help to dampen-out
driveline module noise when properly installed.
Inspect to confirm that no metal contact exists
between the driveline module case and the body. The
complete isolation of noise to one area requires
expertise and experience. Identifying certain types of
vehicle noise baffles even the most capable techni-
cians. Often such practices as:
²Increase tire inflation pressure to eliminate tire
noise.
²Listen for noise at varying speeds with different
driveline load conditions
²Swerving the vehicle from left to right to detect
wheel bearing noise.
All driveline module assemblies produce noise to a
certain extent. Slight carrier noise that is noticeable
only at certain speeds or isolated situations should be
considered normal. Carrier noise tends to peak at a
variety of vehicle speeds. Noise isNOT ALWAYSan
indication of a problem within the carrier.
TIRE NOISE
Tire noise is often mistaken for driveline module
noise. Tires that are unbalanced, worn unevenly or
are worn in a saw-tooth manner are usually noisy.
They often produce a noise that appears to originate
in the driveline module.
Tire noise changes with different road surfaces, but
driveline module noise does not. Inflate all four tires
with approximately 20 psi (138 kPa) more than the
recommended inflation pressure (for test purposes
only). This will alter noise caused by tires, but will
not affect noise caused by the differential. Rear axle
noise usually ceases when coasting at speeds less
than 30 mph (48 km/h); however, tire noise contin-
ues, but at a lower frequency, as the speed is
reduced.
After test has been completed lower tire pressure
back to recommended pressure.
GEAR NOISE (DRIVE PINION AND RING GEAR)
Abnormal gear noise is rare and is usually caused
by scoring on the ring gear and drive pinion. Scoring
is the result of insufficient or incorrect lubricant in
the carrier housing.Abnormal gear noise can be easily recognized. It
produces a cycling tone that will be very pronounced
within a given speed range. The noise can occur dur-
ing one or more of the following drive conditions:
²Drive
²Road load
²Float
²Coast
Abnormal gear noise usually tends to peak within
a narrow vehicle speed range or ranges. It is usually
more pronounced between 30 to 40 mph (48 to 64
km/h) and 50 to 60 mph (80 to 96 km/h). When objec-
tionable gear noise occurs, note the driving condi-
tions and the speed range.
BEARING NOISE (DRIVE PINION AND
DIFFERENTIAL)
Defective bearings produce a rough growl that is
constant in pitch and varies with the speed of vehi-
cle. Being aware of this will enable a technician to
separate bearing noise from gear noise.
Drive pinion bearing noise that results from defec-
tive or damaged bearings can usually be identified by
its constant, rough sound. Drive pinion front bearing
is usually more pronounced during a coast condition.
Drive pinion rear bearing noise is more pronounced
during a drive condition. The drive pinion bearings
are rotating at a higher rate of speed than either the
differential side bearings or the axle shaft bearing.
Differential side bearing noise will usually produce
a constant, rough sound. The sound is much lower in
frequency than the noise caused by drive pinion bear-
ings.
Bearing noise can best be detected by road testing
the vehicle on a smooth road (black top). However, it
is easy to mistake tire noise for bearing noise. If a
doubt exists, the tire treads should be examined for
irregularities that often causes a noise that resem-
bles bearing noise.
ENGINE AND TRANSMISSION NOISE
Sometimes noise that appears to be in the driv-
eline module assembly is actually caused by the
engine or the transmission. To identify the true
source of the noise, note the approximate vehicle
speed and/or RPM when the noise is most noticeable.
Stop the vehicle next to a flat brick or cement wall
(this will help reflect the sound). Place the transaxle
inNEUTRAL. Accelerate the engine slowly up
through the engine speed that matches the vehicle
speed noted when the noise occurred. If the same
noise is produced, it usually indicates that the noise
is being caused by the engine or transaxle.
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-25
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)