2004 CHEVROLET KODIAK ECU
[x] Cancel search: ECUPage 7 of 366

Front Seats......................................................1-2
Manual Seats................................................1-2
Reclining Seatbacks........................................1-4
Split Bench Seat............................................1-6
Air Suspension Seats......................................1-6
Rear Seats.......................................................1-7
Rear Seat Operation.......................................1-7
Safety Belts.....................................................1-8
Safety Belts: They Are for Everyone.................1-8
Questions and Answers About Safety Belts......1-12
How to Wear Safety Belts Properly.................1-13
Driver Position..............................................1-13
Safety Belt Use During Pregnancy..................1-21
Right Front Passenger Position.......................1-22
Center Passenger Position.............................1-22
Rear Seat Passengers..................................1-23
Safety Belt Extender.....................................1-26
Child Restraints.............................................1-27
Older Children..............................................1-27
Infants and Young Children............................1-29
Child Restraint Systems.................................1-33
Where to Put the Restraint
(Regular Cab Models)................................1-35
Where to Put the Restraint
(Crew Cab Models)....................................1-37Top Strap....................................................1-38
Securing a Child Restraint in a Rear Outside
Seat Position (Crew Cab Models)................1-39
Securing a Child Restraint in the Center
Rear Seat Position (Crew Cab) or
Center
Front Position...........................................1-41
Securing a Child Restraint in the Right
Front Seat Position....................................1-43
Air Bag System..............................................1-48
Where Are the Air Bags?...............................1-52
When Should an Air Bag Inflate?....................1-53
What Makes an Air Bag Inflate?.....................1-53
How Does an Air Bag Restrain?.....................1-53
What Will You See After an
Air Bag Inflates?.......................................1-54
Air Bag Off Switch........................................1-55
Servicing Your Air Bag-Equipped Vehicle.........1-60
Adding Equipment to Your Air Bag-Equipped
Vehicle....................................................1-61
Restraint System Check..................................1-61
Checking Your Restraint Systems...................1-61
Replacing Restraint System Parts
After a Crash............................................1-62
Section 1 Seats and Restraint Systems
1-1
Page 20 of 366

3. Pick up the latch plate and pull the belt across you.
Don’t let it get twisted. The shoulder belt may lock if
you pull the belt across you very quickly. If this
happens, let the belt go back slightly to unlock it.
Then pull the belt across you more slowly.
4. Push the latch plate into the buckle until it clicks.
Pull up on the latch plate to make sure it is secure.
If the belt isn’t long enough, seeSafety Belt
Extender on page 1-26.
Make sure the release button on the buckle is
positioned so you would be able to unbuckle the
safety belt quickly if you ever had to.The lap part of the belt should be worn low and snug on
the hips, just touching the thighs. In a crash, this
applies force to the strong pelvic bones. And you’d be
less likely to slide under the lap belt. If you slid under it,
the belt would apply force at your abdomen. This
could cause serious or even fatal injuries. The shoulder
belt should go over the shoulder and across the
chest. These parts of the body are best able to take belt
restraining forces.
The safety belt locks if there’s a sudden stop or crash,
or if you pull the belt very quickly out of the retractor.
1-14
Page 30 of 366

Lap-Shoulder Belt
The positions next to the windows have lap-shoulder
belts. Here is how to wear one properly.
1. Pick up the latch plate and pull the belt across you.
Do not let it get twisted.
The shoulder belt may lock if you pull the belt
across you very quickly. If this happens, let the belt
go back slightly to unlock it. Then pull the belt
across you more slowly.2. Push the latch plate into the buckle until it clicks.
Pull up on the latch plate to make sure it is secure.
When the shoulder belt is pulled out all the way,
it will lock. If it does, let it go back all the way and
start again. If the belt is not long enough, see
Safety Belt Extender on page 1-26. Make sure the
release button on the buckle is positioned so
you would be able to unbuckle the safety belt
quickly if you ever had to.
3. To make the lap part tight, pull down on the buckle
end of the belt as you pull up on the shoulder part.
1-24
Page 36 of 366
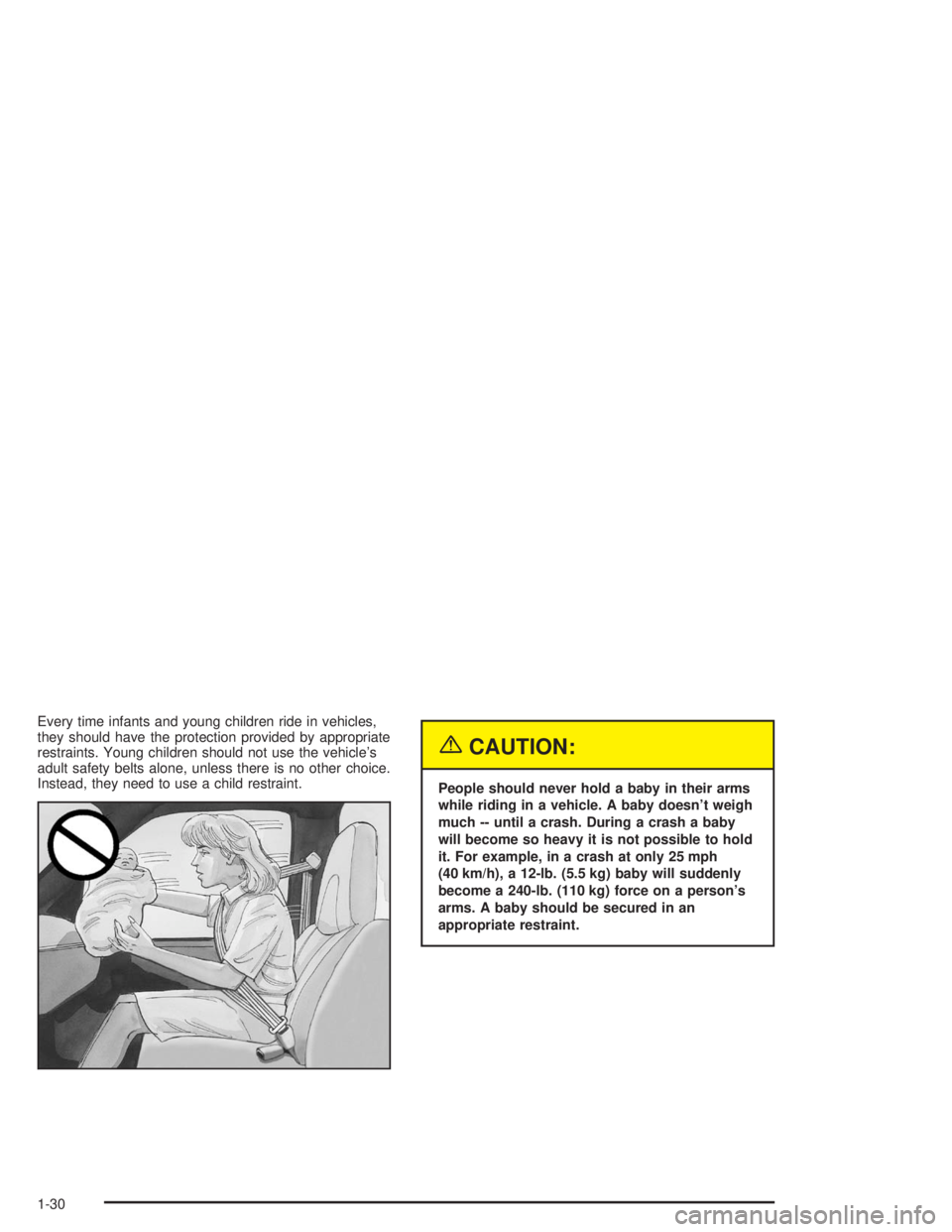
Every time infants and young children ride in vehicles,
they should have the protection provided by appropriate
restraints. Young children should not use the vehicle’s
adult safety belts alone, unless there is no other choice.
Instead, they need to use a child restraint.
{CAUTION:
People should never hold a baby in their arms
while riding in a vehicle. A baby doesn’t weigh
much -- until a crash. During a crash a baby
will become so heavy it is not possible to hold
it. For example, in a crash at only 25 mph
(40 km/h), a 12-lb. (5.5 kg) baby will suddenly
become a 240-lb. (110 kg) force on a person’s
arms. A baby should be secured in an
appropriate restraint.
1-30
Page 38 of 366

For most basic types of child restraints, there are
many different models available. When purchasing a
child restraint, be sure it is designed to be used
in a motor vehicle. If it is, the restraint will have a
label saying that it meets federal motor vehicle
safety standards.
The restraint manufacturer’s instructions that come
with the restraint state the weight and height
limitations for a particular child restraint. In addition,
there are many kinds of restraints available for
children with special needs.
{CAUTION:
Newborn infants need complete support,
including support for the head and neck. This
is necessary because a newborn infant’s neck
is weak and its head weighs so much
compared with the rest of its body. In a crash,
an infant in a rear-facing seat settles into the
restraint, so the crash forces can be
distributed across the strongest part of an
infant’s body, the back and shoulders. Infants
always should be secured in appropriate infant
restraints.
{CAUTION:
The body structure of a young child is quite
unlike that of an adult or older child, for whom
the safety belts are designed. A young child’s
hip bones are still so small that the vehicle’s
regular safety belt may not remain low on the
hip bones, as it should. Instead, it may settle
up around the child’s abdomen. In a crash, the
belt would apply force on a body area that’s
unprotected by any bony structure. This alone
could cause serious or fatal injuries. Young
children always should be secured in
appropriate child restraints.
We know securing a child can present real problems in
a medium-duty vehicle like yours.
If your vehicle is a regular cab model with an
air-suspension seat in the right front passenger’s
position, there is no place in your vehicle to secure a
child restraint. The only answer is to have smaller
children make the trip in another vehicle, where they
can get the protection they need.
1-32
Page 41 of 366

Q:How do child restraints work?
A:A child restraint system is any device designed for
use in a motor vehicle to restrain, seat, or position
children. A built-in child restraint system is a
permanent part of the motor vehicle. An add-on
child restraint system is a portable one, which
is purchased by the vehicle’s owner.
For many years, add-on child restraints have used
the adult belt system in the vehicle. To help
reduce the chance of injury, the child also has to be
secured within the restraint. The vehicle’s belt
system secures the add-on child restraint in the
vehicle, and the add-on child restraint’s harness
system holds the child in place within the restraint.
One system, the three-point harness, has straps that
come down over each of the infant’s shoulders and
buckle together at the crotch. The five-point harness
system has two shoulder straps, two hip straps and a
crotch strap. A shield may take the place of hip
straps. A T-shaped shield has shoulder straps that
are attached to a flat pad which rests low against the
child’s body. A shelf- or armrest-type shield has
straps that are attached to a wide, shelf-like shield
that swings up or to the side.When choosing a child restraint, be sure the child
restraint is designed to be used in a vehicle. If it is, it
will have a label saying that it meets federal motor
vehicle safety standards.
Then follow the instructions for the restraint. You may
find these instructions on the restraint itself or in a
booklet, or both. These restraints use the belt system in
your vehicle, but the child also has to be secured
within the restraint to help reduce the chance of personal
injury. When securing an add-on child restraint, refer
to the instructions that come with the restraint which may
be on the restraint itself or in a booklet, or both, and
to this manual. The child restraint instructions are
important, so if they are not available, obtain a
replacement copy from the manufacturer.
Where to Put the Restraint
(Regular Cab Models)
If your vehicle is a regular cab model with an
air-suspension seat in the right front passenger’s
position, there is no place in your vehicle to secure a
child restraint. The only answer is to have smaller
children make the trip in another vehicle, where they
can get the protection they need.
1-35
Page 42 of 366

{CAUTION:
A child restraint cannot be secured properly in
an air-suspension type seat. This is because
an air-suspension seat is designed to move up
and down for an adult passenger. Don’t use a
child restraint in an air-suspension seat.
If your vehicle is a regular cab model with a static seat
in the right front passenger’s position, or if it has a
bench seat, the child restraint must be secured properly
in the right front passenger’s seat. If your vehicle has
air bags and you need to secure a child restraint in the
right front passenger’s seat, there is a switch on the
instrument panel that you can use to turn off the
passenger’s air bag. SeeAir Bag Off Switch on
page 1-55andSecuring a Child Restraint in the Right
Front Seat Position on page 1-43for more on this,
including important safety information.
Unless the passenger’s air bag has been turned off,
never put a rear-facing child restraint in this vehicle.
Here is why:
{CAUTION:
A child in a rear-facing child restraint can be
seriously injured or killed if the passenger’s air
bag in�ates. This is because the back of the
rear-facing child restraint would be very close
to the in�ating air bag. Do not use a
rear-facing child restraint in this vehicle unless
the passenger’s air bag has been turned off.
Even though the air bag off switch is designed
to turn off the passenger’s frontal air bag, no
system is fail-safe, and no one can guarantee
that an air bag will not deploy under some
unusual circumstance, even though it is turned
off. We recommend that rear-facing child
restraints be transported in vehicles with a
rear seat that will accommodate a rear-facing
child restraint, whenever possible.
If you secure a forward-facing child restraint in
the right front static seat or right front bench
seat, always move the passenger seat as far
back as it will go.
Keep in mind that an unsecured child restraint can
move around in a collision or sudden stop and injure
people in the vehicle – even when no child is in it.
1-36
Page 43 of 366

Where to Put the Restraint
(Crew Cab Models)
Accident statistics show that children are safer if they
are restrained in the rear rather than the front seat. We
recommend that child restraints be secured in a rear
seat position, including an infant riding in a rear-racing
infant seat, a child riding in a forward-facing child
seat and an older child riding in a booster seat.
If your vehicle has air bags and you need to secure a
child restraint in the right front passenger’s seat, there is
a switch on the instrument panel that you can use to
turn off the passenger’s air bag. SeeAir Bag Off Switch
on page 1-55andSecuring a Child Restraint in the
Right Front Seat Position on page 1-43for more on this,
including important safety information.
Unless the passenger’s air bag has been turned off,
never put a rear-facing child restraint in the right front
seat position. Here is why:
{CAUTION:
A child in a rear-facing child restraint can be
seriously injured or killed if the right front
passenger’s air bag in�ates. This is because
the back of the rear-facing child restraint
would be very close to the in�ating air bag. Be
sure to turn off the air bag before using a
rear-facing child restraint in the right front seat
position.
Even though the air bag off switch is designed
to turn off the passenger’s air bag, no system
is fail-safe, and no one can guarantee that an
air bag will not deploy under some unusual
circumstance, even though it is turned off.
General Motors recommends that rear-facing
child restraints be secured in the rear seat,
even if the air bag is off.
If your secure a forward-facing child restraint
in the right front static seat or right front
bench seat, always move the front passenger
seat as far back as it will go. It is better to
secure the child restraint in a rear seat.
1-37