Page 2167 of 3189
Coil Spring and Shock Absorber
COMPONENTS=NJSU0008
NAX017
1. Strut mount upper plate
2. Strut spacer
3. Strut mount insulator
4. Thrust bearing
5. Upper spring seat
6. Upper rubber seat
7. Bound bumper rubber
8. Coil spring
9. Shock absorber10. Wheel hub and steering knuckle
11. Cotter pin
12. Washer
13. Bushing
14. Transverse link
15. Bushing
16. Washer
17. Connecting rod
18. Member pin stay19. Suspension member
20. Washer
21. Bushing
22. Washer
23. Bushing
24. Clamp
25. Stabilizer
26. Washer
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
FRONT SUSPENSION
Coil Spring and Shock Absorber
SU-9
Page 2172 of 3189
Service Data and Specifications (SDS)
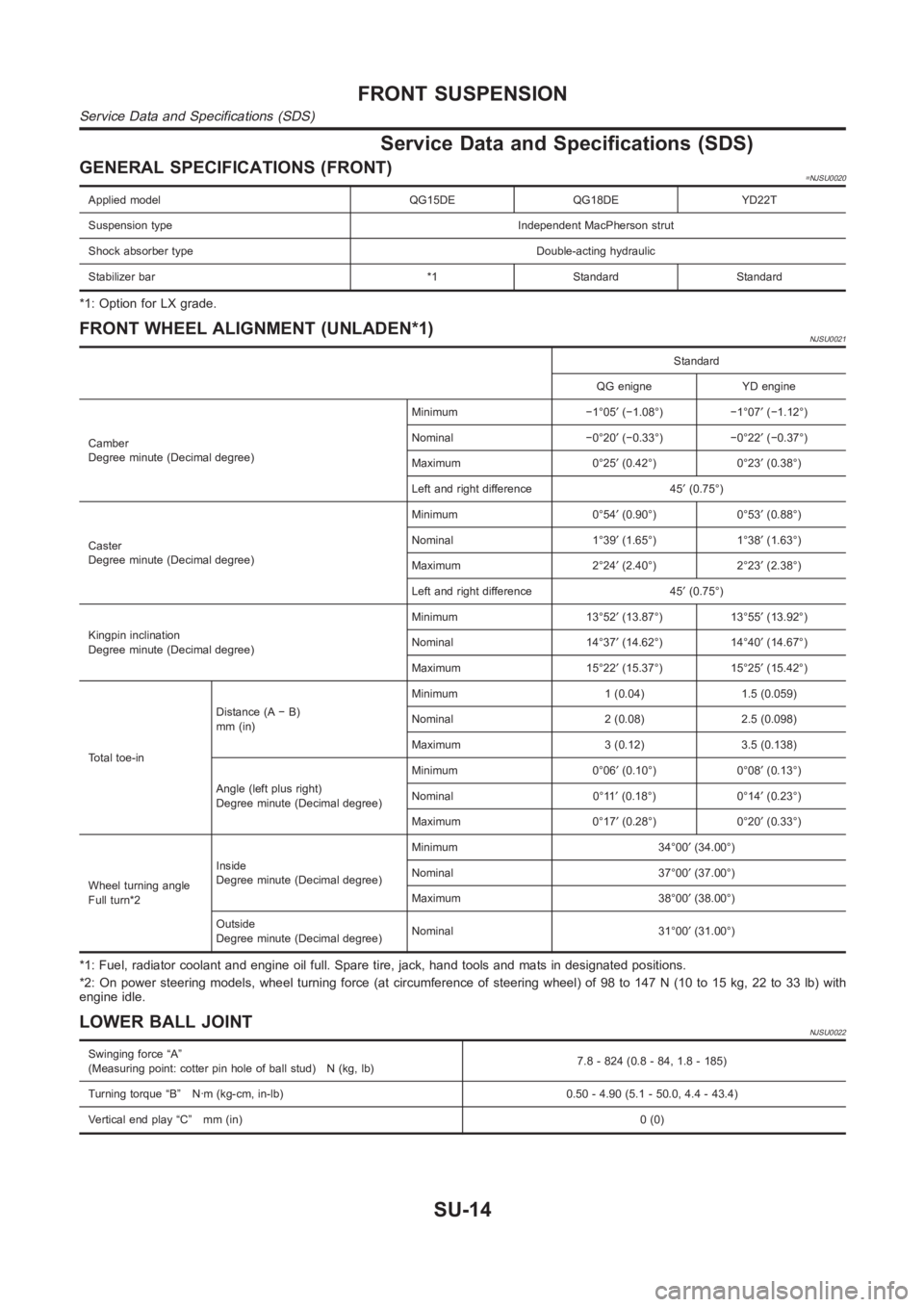
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS (FRONT)=NJSU0020
Applied model QG15DE QG18DE YD22T
Suspension type Independent MacPherson strut
Shock absorber type Double-acting hydraulic
Stabilizer bar *1 Standard Standard
*1: Option for LX grade.
FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT (UNLADEN*1)NJSU0021
Standard
QG enigne YD engine
Camber
Degree minute (Decimal degree)Minimum −1°05′(−1.08°) −1°07′(−1.12°)
Nominal −0°20′(−0.33°) −0°22′(−0.37°)
Maximum 0°25′(0.42°) 0°23′(0.38°)
Left and right difference 45′(0.75°)
Caster
Degree minute (Decimal degree)Minimum 0°54′(0.90°) 0°53′(0.88°)
Nominal 1°39′(1.65°) 1°38′(1.63°)
Maximum 2°24′(2.40°) 2°23′(2.38°)
Left and right difference 45′(0.75°)
Kingpin inclination
Degree minute (Decimal degree)Minimum 13°52′(13.87°) 13°55′(13.92°)
Nominal 14°37′(14.62°) 14°40′(14.67°)
Maximum 15°22′(15.37°) 15°25′(15.42°)
Total toe-inDistance (A − B)
mm (in)Minimum 1 (0.04) 1.5 (0.059)
Nominal 2 (0.08) 2.5 (0.098)
Maximum 3 (0.12) 3.5 (0.138)
Angle (left plus right)
Degree minute (Decimal degree)Minimum 0°06′(0.10°) 0°08′(0.13°)
Nominal 0°11′(0.18°) 0°14′(0.23°)
Maximum 0°17′(0.28°) 0°20′(0.33°)
Wheel turning angle
Full turn*2Inside
Degree minute (Decimal degree)Minimum 34°00′(34.00°)
Nominal 37°00′(37.00°)
Maximum 38°00′(38.00°)
Outside
Degree minute (Decimal degree)Nominal 31°00′(31.00°)
*1: Fuel, radiator coolant and engine oil full. Spare tire, jack, hand tools and mats in designated positions.
*2: On power steering models, wheel turning force (at circumference of steering wheel) of 98 to 147 N (10 to 15 kg, 22 to 33 lb) with
engine idle.
LOWER BALL JOINTNJSU0022
Swinging force “A”
(Measuring point: cotter pin hole of ball stud) N (kg, lb)7.8 - 824 (0.8 - 84, 1.8 - 185)
Turning torque “B” N·m (kg-cm, in-lb) 0.50 - 4.90 (5.1 - 50.0, 4.4 - 43.4)
Vertical end play “C” mm (in)0(0)
FRONT SUSPENSION
Service Data and Specifications (SDS)
SU-14
Page 2177 of 3189
4. Check front suspension for looseness.
5. Check steering linkage for looseness.
6. Check that front shock absorbers work properly.
7. Check vehicle posture (Unladen).
SFA948A
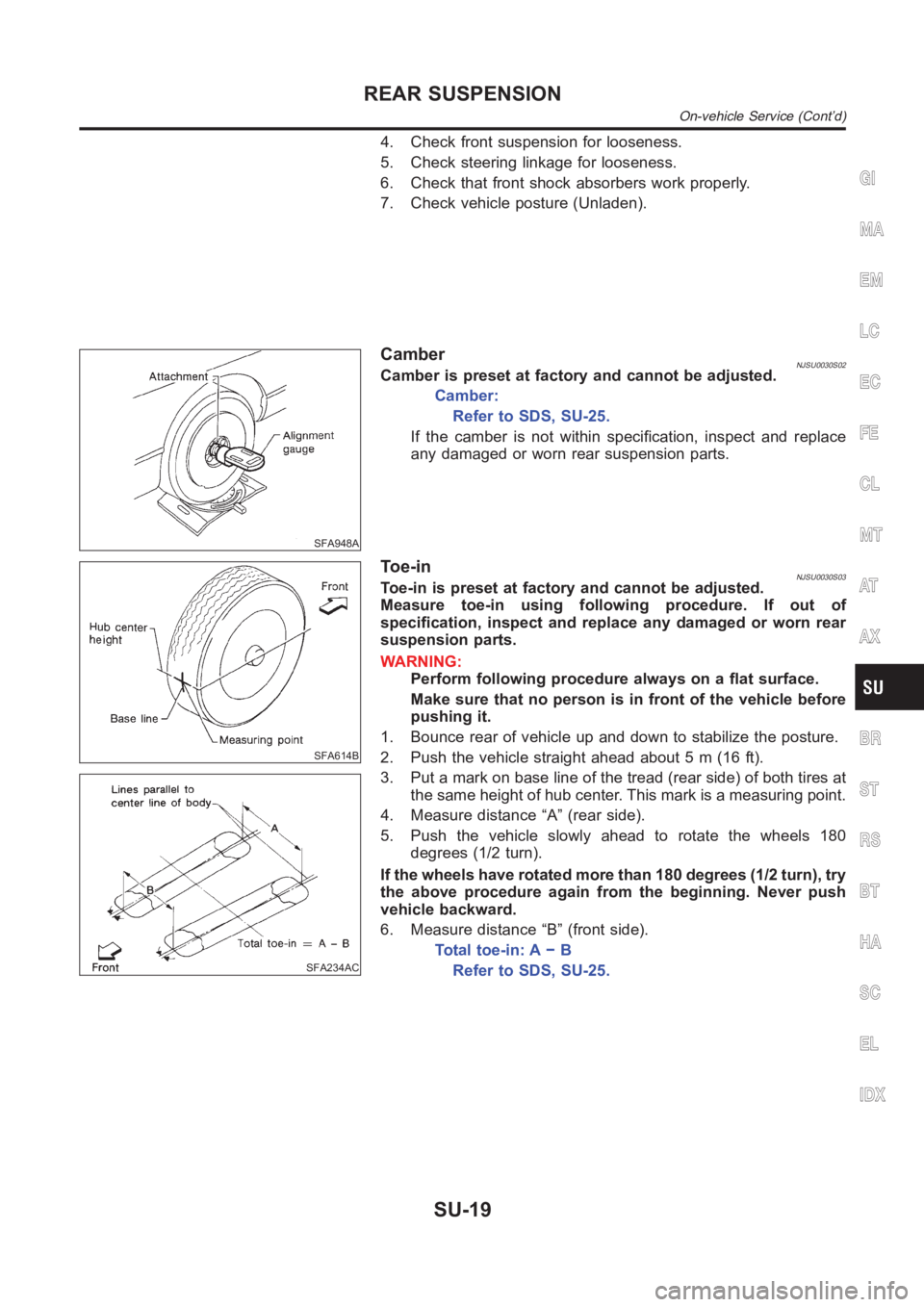
CamberNJSU0030S02Camber is preset at factory and cannot be adjusted.
Camber:
Refer to SDS, SU-25.
If the camber is not within specification, inspect and replace
any damaged or worn rear suspension parts.
SFA614B
SFA234AC
To e - i nNJSU0030S03Toe-in is preset at factory and cannot be adjusted.
Measure toe-in using following procedure. If out of
specification, inspect and replace any damaged or worn rear
suspension parts.
WARNING:
Perform following procedure always on a flat surface.
Make sure that no person is in front of the vehicle before
pushing it.
1. Bounce rear of vehicle up and down to stabilize the posture.
2. Push the vehicle straight ahead about 5 m (16 ft).
3. Put a mark on base line of the tread (rear side) of both tires at
the same height of hub center. This mark is a measuring point.
4. Measure distance “A” (rear side).
5. Push the vehicle slowly ahead to rotate the wheels 180
degrees (1/2 turn).
If the wheels have rotated more than 180 degrees (1/2 turn), try
the above procedure again from the beginning. Never push
vehicle backward.
6. Measure distance “B” (front side).
Total toe-in: A − B
Refer to SDS, SU-25.
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
REAR SUSPENSION
On-vehicle Service (Cont’d)
SU-19
Page 2190 of 3189
NJBR0005
NVH Troubleshooting ChartNJBR0005S01Use the table below to help you find the cause of the symptom. If necessary, repair or replace these parts.
Reference page
BR-27, 31
BR-27, 31
BR-27, 31
—
—
BR-29, 35
—
—
—
BR-29, 35
AX-3
SU-4, AX-3
SU-4
SU-4
ST-5
SUSPECTED PARTS
(Possible cause)
Pads - damaged
Pads - uneven wear
Shims damaged
Rotor imbalance
Rotor damage
Rotor runout
Rotor deformation
Rotor deflection
Rotor rust
Rotor thickness variation
DRIVE SHAFT
AXLE AND SUSPENSION
TIRES
ROAD WHEEL
STEERING
Symptom BRAKENoise X X X———————XXXXX
Shake ——— X ——————XXXXX
Shimmy, Jud-
der———XXXXXXX—XXXX
X: Applicable
—: Not Applicable
NOISE, VIBRATION AND HARSHNESS (NVH) TROUBLESHOOTING
NVH Troubleshooting Chart
BR-6
Page 2229 of 3189
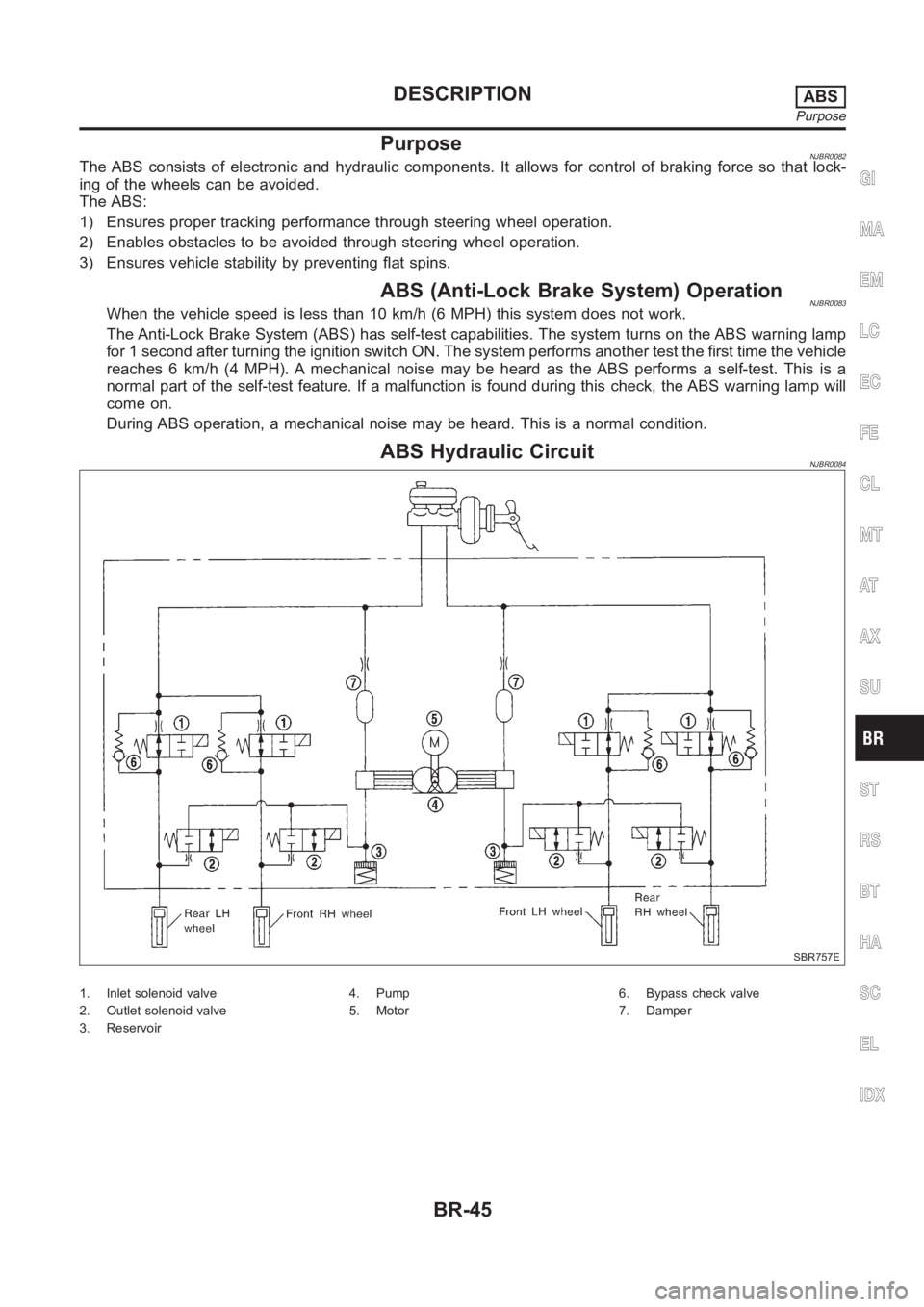
PurposeNJBR0082The ABS consists of electronic and hydraulic components. It allows for control of braking force so that lock-
ing of the wheels can be avoided.
The ABS:
1) Ensures proper tracking performance through steering wheel operation.
2) Enables obstacles to be avoided through steering wheel operation.
3) Ensures vehicle stability by preventing flat spins.
ABS (Anti-Lock Brake System) OperationNJBR0083When the vehicle speed is less than 10 km/h (6 MPH) this system does not work.
The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) has self-test capabilities. The system turns on the ABS warning lamp
for 1 second after turning the ignition switch ON. The system performs another test the first time the vehicle
reaches 6 km/h (4 MPH). A mechanical noise may be heard as the ABS performs a self-test. This is a
normal part of the self-test feature. If a malfunction is found during thischeck, the ABS warning lamp will
come on.
During ABS operation, a mechanical noise may be heard. This is a normal condition.
ABS Hydraulic CircuitNJBR0084
SBR757E
1. Inlet solenoid valve
2. Outlet solenoid valve
3. Reservoir4. Pump
5. Motor6. Bypass check valve
7. Damper
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
SU
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
DESCRIPTIONABS
Purpose
BR-45
Page 2376 of 3189
MKIA0054E
ReplacementNJEL0010For removal and installation of spiral cable, refer to RS-29,
“Installation — Air Bag Module and Spiral Cable”.
Each switch can be replaced without removing combination
switch base.
CEL406
To remove combination switch base, remove base attaching
screw.
SEL151V
Before installing the steering wheel, align the steering wheel
guide pins with the screws which secure the combination
switch as shown in the left figure.
COMBINATION SWITCH
Replacement
EL-40
Page 2767 of 3189

NOTE:
The road map data is based on data stored in the map DVD-ROM.
SEL686V
In map-matching, alternative routes to reach the destination
will be shown and prioritized, after the road on which the
vehicle is currently driven has been judged and the current-lo-
cation mark has been repositioned.
If there is an error in distance and/or direction, the alternative
routes will be shown in different order of priority, and the wrong
road can be avoided.
If two roads are running in parallel, they are of the same pri-
ority. Therefore, the current-location mark may appear on
either of them alternately, depending on maneuvering of the
steering wheel and configuration of the road.
SKIA0613E
Map-matching does not function correctly when the road on
which the vehicle is driving is new and not recorded in the map
DVD-ROM, or when the road pattern stored in the map data
and the actual road pattern are different due to repair.
When driving on a road not present in the map, the map-
matching function may find another road and position the cur-
rent-location mark on it. Then, when the correct road is
detected, the current-location mark may leap to it.
Effective range for comparing the vehicle position and travel
direction calculated by the distance and direction with the road
data read from the map DVD-ROM is limited. Therefore, when
there is an excessive gap between the current vehicle position
and the position on the map, correction by map-matching is not
possible.
SEL526V
GPS (GLOBAL POSITIONING SYSTEM)NJEL0592S04GPS (Global Positioning System) has been developed and con-
trolled by the US Department of Defense. The system utilizes GPS
satellite (NAVSTAR), sending out radio waves while flying on an
orbit around the earth at the height of approx. 21,000 km (13,000
miles).
The GPS receiver calculates the vehicle’s position in three dimen-
sions (latitude/longitude/altitude) according to the time lag of the
radio waves received from four or more GPS satellites (three-di-
mensional positioning). If radio waves were received only from
three GPS satellites, the GPS receiver calculates the vehicle’s
position in two dimensions (latitude/longitude), utilizing the altitude
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
IDX
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
System Description (Cont’d)
EL-431
Page 2841 of 3189
Cause (condition) -:While driving ooo:Display Driving condition Remarks (correction, etc.)
PlaceIn a parking lot
SEL709V
When driving in a parking lot, or other
location where there are no roads on
the map, matching may place the
vehicle mark on a nearby road. When
the vehicle returns to the road, the
vehicle mark may have deviated from
the correct location.
When driving in circle or turning the
steering wheel repeatedly, direction
errors accumulate, and the vehicle
mark may deviate from the correct
location.
If after travelling about 10 km (6
miles) the correct location has not
been restored, perform location
correction and, if necessary,
direction correction. Turn table
SEL710V
When the ignition switch is OFF, the
navigation system cannot get the sig-
nal from the gyroscope (angular speed
sensor). Therefore, the displayed
direction may be wrong and the cor-
rect road may not be easily returned to
after rotating the vehicle on a turn
table with the ignition switch OFF.
Slippery roadsOn snow, wet roads, gravel, or other
roads where tires may slip easily,
accumulated mileage errors may
cause the vehicle mark to deviate from
the correct road.
SlopesWhen parking in sloped garages,
when travelling on banked roads, or in
other cases where the vehicle turns
when tilted, an error in the turning
angle will occur, and the vehicle mark
may deviate from the road.
Map dataRoad not displayed on the map screen
SEL699V
When driving on new roads or other
roads not displayed on the map
screen, map matching does not func-
tion correctly and matches the location
to a nearby road. When the vehicle
returns to a road which is on the map,
the vehicle mark may deviate from the
correct road.
Different road pattern
(Changed due to repair)
ELK0201D
If the road pattern stored in the map
data and the actual road pattern are
different, map matching does not func-
tion correctly and matches the location
to a nearby road. The vehicle mark
may deviate from the correct road.
Vehicle Use of tire chainsWhen tire chains are used, the mile-
age is not correctly detected, and the
vehicle mark may deviate from the
correct road.Drive the vehicle for a while. If
the distance is still deviated,
adjust it by using the distance
adjustment function. (If the tire
chain is removed, recover the
original value.)
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
CL
MT
AT
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
IDX
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
Example of Symptoms Judged Not Abnormal (Cont’d)
EL-505