2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE transfer case oil
[x] Cancel search: transfer case oilPage 1739 of 2199
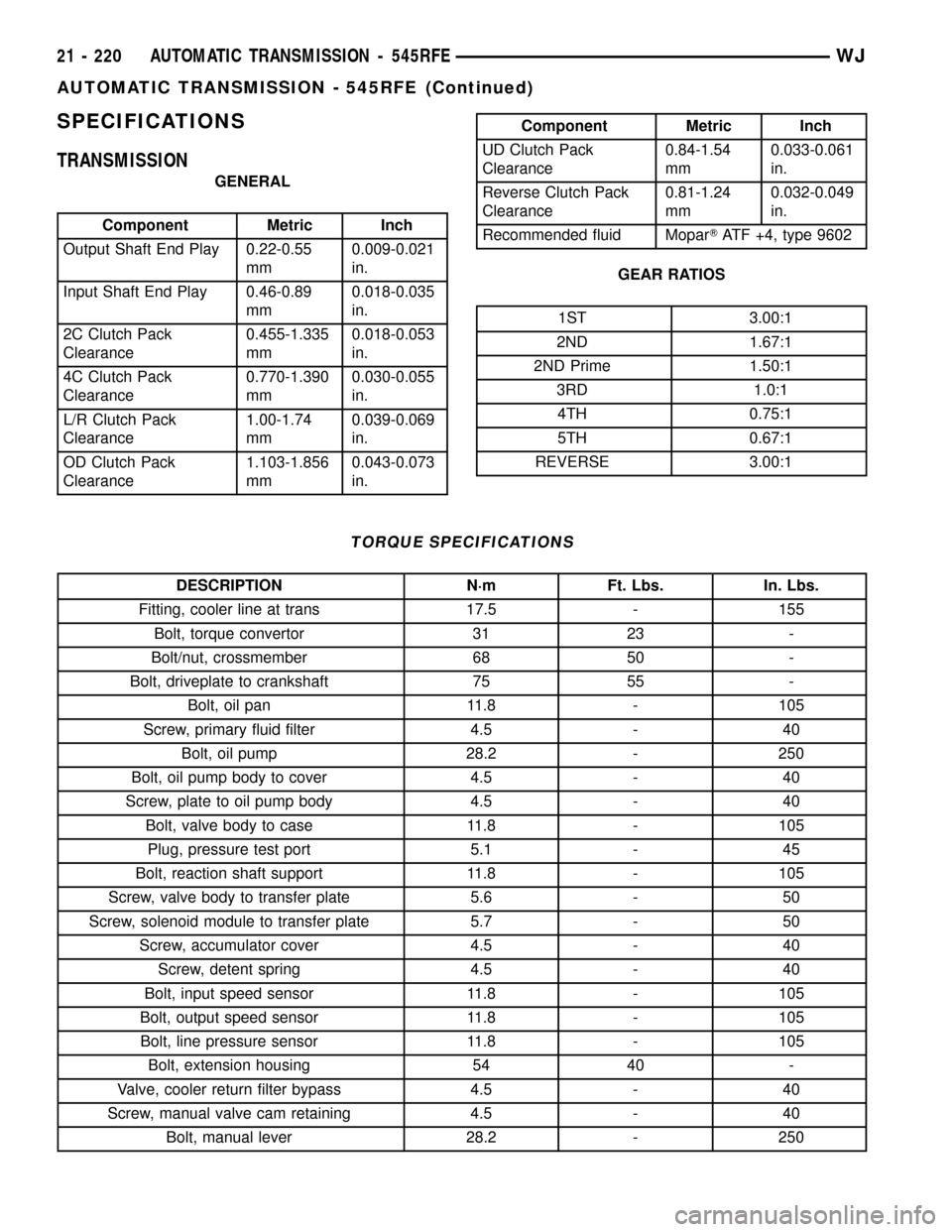
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSMISSION
GENERAL
Component Metric Inch
Output Shaft End Play 0.22-0.55
mm0.009-0.021
in.
Input Shaft End Play 0.46-0.89
mm0.018-0.035
in.
2C Clutch Pack
Clearance0.455-1.335
mm0.018-0.053
in.
4C Clutch Pack
Clearance0.770-1.390
mm0.030-0.055
in.
L/R Clutch Pack
Clearance1.00-1.74
mm0.039-0.069
in.
OD Clutch Pack
Clearance1.103-1.856
mm0.043-0.073
in.
Component Metric Inch
UD Clutch Pack
Clearance0.84-1.54
mm0.033-0.061
in.
Reverse Clutch Pack
Clearance0.81-1.24
mm0.032-0.049
in.
Recommended fluid MoparTATF +4, type 9602
GEAR RATIOS
1ST 3.00:1
2ND 1.67:1
2ND Prime 1.50:1
3RD 1.0:1
4TH 0.75:1
5TH 0.67:1
REVERSE 3.00:1
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Fitting, cooler line at trans 17.5 - 155
Bolt, torque convertor 31 23 -
Bolt/nut, crossmember 68 50 -
Bolt, driveplate to crankshaft 75 55 -
Bolt, oil pan 11.8 - 105
Screw, primary fluid filter 4.5 - 40
Bolt, oil pump 28.2 - 250
Bolt, oil pump body to cover 4.5 - 40
Screw, plate to oil pump body 4.5 - 40
Bolt, valve body to case 11.8 - 105
Plug, pressure test port 5.1 - 45
Bolt, reaction shaft support 11.8 - 105
Screw, valve body to transfer plate 5.6 - 50
Screw, solenoid module to transfer plate 5.7 - 50
Screw, accumulator cover 4.5 - 40
Screw, detent spring 4.5 - 40
Bolt, input speed sensor 11.8 - 105
Bolt, output speed sensor 11.8 - 105
Bolt, line pressure sensor 11.8 - 105
Bolt, extension housing 54 40 -
Valve, cooler return filter bypass 4.5 - 40
Screw, manual valve cam retaining 4.5 - 40
Bolt, manual lever 28.2 - 250
21 - 220 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1744 of 2199

(6) Using Spring Compressor 8250 and a suitable
shop press, compress the 4C piston return spring and
install the snap-ring (Fig. 54).
(7) Assemble and install the 4C clutch pack into
the retainer/bulkhead (Fig. 53) with the steel separa-
tor plate against the piston.
(8) Install the 4C reaction plate and snap-ring into
the retainer/bulkhead (Fig. 53). The 4C reaction plate
is non-directional.
(9) Measure the 4C clutch clearance. The correct
clutch clearance is 0.77-1.39 mm (0.030-0.055 in.).
The snap-ring is selectable. Install the chosen snap-
ring and re-measure to verify the selection.
(10) Install the 2C piston into the retainer/bulk-
head (Fig. 53).
(11) Position the 2C Belleville spring onto the 2C
piston.
(12) Position the 2C Belleville spring snap-ring
onto the 2C Belleville spring (Fig. 53).
(13) Using Spring Compressor 8249 and a suitable
shop press (Fig. 55), compress the belleville spring
until the snap-ring is engaged with the snap-ring
groove in the retainer/bulkhead.
ADAPTER HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the transfer case from the transmis-
sion.
(2) Using a screw mounted on a slide hammer,
remove the adapter housing seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean the adapter seal bore in the adapter
housing of any residue or particles remaining from
the original seal.
(2) Install new oil seal in the adapter housing
using Seal Installer C-3860-A (Fig. 56). A properly
installed seal is flush to the face of the seal bore.
(3) Install the transfer case onto the transmission.
Fig. 54 Compress 4C Piston Return Spring Using
Tool 8250
1 - PRESS
2 - TOOL 8250
Fig. 55 Compress 2C Belleville Spring Using Tool
8249
1 - PRESS
2 - TOOL 8249
Fig. 56 Adapter Housing Seal Installation
1 - TOOL C-3860-A
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 225
4C RETAINER/BULKHEAD (Continued)
Page 1782 of 2199

INSTALLATION
(1) Place the floor shifter lever in PARK position.
(2) Loosen the adjustment screw on the shift cable.
(3) Verify that the park lock cable adjustment tab
is pulled upward to the unlocked position.
(4) Install wiring harness to the shifter assembly
bracket. Engage any wire connectors removed from
the shifter assembly.
(5) Install the transfer case shift cable to the
shifter assembly bracket. Install clip to hold cable to
the bracket.
(6) Snap the transfer case shift cable, if equipped,
onto the transfer case shift lever pin.
(7) Install the park lock cable into the shifter
assembly bracket and into the shifter BTSI lever.(Re-
fer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC/SHIFT INTERLOCK MECHANISM -
ADJUSTMENTS)
(8) Install the shift cable to the shifter assembly
bracket. Push cable into the bracket until secure.
(9) Install shifter assembly onto the shifter assem-
bly studs on the floor pan.
(10) Install the nuts to hold the shifter assembly
onto the floor pan. Tighten nuts to 28 N´m (250
in.lbs.).
(11) Snap the shift cable onto the shift lever pin.
(12) Verify that the shift lever is in the PARK posi-
tion.
(13) Tighten the adjustment screw to 7 N´m (65
in.lbs.).
(14) Place the key in the accessory position.
(15) Push downward on the park lock cable adjust-
ment tab to lock the adjustment.
(16) Verify correct shifter, park lock, and BTSI
operation.
(17) Install any console parts removed for access to
shift lever assembly and shift cables. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - INSTALLA-
TION)
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The Solenoid Switch Valve (SSV) is located in the
valve body and controls the direction of the transmis-
sion fluid when the L/R-TCC solenoid is energized.
OPERATION
The Solenoid Switch Valve controls line pressure
from the LR-TCC solenoid. In 1st gear, the SSV will
be in the downshifted position, thus directing fluid to
the L/R clutch circuit. In 2nd, 3rd, 4th,and 5th gears,
the solenoid switch valve will be in the upshifted
position and directs the fluid into the torque con-
verter clutch (TCC) circuit.When shifting into 1st gear, a special hydraulic
sequence is performed to ensure SSV movement into
the downshifted position. The L/R pressure switch is
monitored to confirm SSV movement. If the move-
ment is not confirmed (the L/R pressure switch does
not close), 2nd gear is substituted for 1st. A DTC will
be set after three unsuccessful attempts are made to
get into 1st gear in one given key start.
SOLENOIDS
DESCRIPTION
The typical electrical solenoid used in automotive
applications is a linear actuator. It is a device that
produces motion in a straight line. This straight line
motion can be either forward or backward in direc-
tion, and short or long distance.
A solenoid is an electromechanical device that uses
a magnetic force to perform work. It consists of a coil
of wire, wrapped around a magnetic core made from
steel or iron, and a spring loaded, movable plunger,
which performs the work, or straight line motion.
The solenoids used in transmission applications
are attached to valves which can be classified asnor-
mally openornormally closed. Thenormally
opensolenoid valve is defined as a valve which
allows hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is
applied to the solenoid. Thenormally closedsole-
noid valve is defined as a valve which does not allow
hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is applied
to the solenoid. These valves perform hydraulic con-
trol functions for the transmission and must there-
fore be durable and tolerant of dirt particles. For
these reasons, the valves have hardened steel pop-
pets and ball valves. The solenoids operate the valves
directly, which means that the solenoids must have
very high outputs to close the valves against the siz-
able flow areas and line pressures found in current
transmissions. Fast response time is also necessary
to ensure accurate control of the transmission.
The strength of the magnetic field is the primary
force that determines the speed of operation in a par-
ticular solenoid design. A stronger magnetic field will
cause the plunger to move at a greater speed than a
weaker one. There are basically two ways to increase
the force of the magnetic field:
1. Increase the amount of current applied to the
coil or
2. Increase the number of turns of wire in the coil.
The most common practice is to increase the num-
ber of turns by using thin wire that can completely
fill the available space within the solenoid housing.
The strength of the spring and the length of the
plunger also contribute to the response speed possi-
ble by a particular solenoid design.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 263
SHIFT MECHANISM (Continued)
Page 1786 of 2199

STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 112) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 113).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 114) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock-free power transfer, it is
natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impeller
and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston with friction material was added to the tur-
bine assembly to provide this mechanical lock-up.
In order to reduce heat build-up in the transmission
and buffer the powertrain against torsional vibrations,
the TCM can duty cycle the L/R-CC Solenoid to achieve
a smooth application of the torque converter clutch.
This function, referred to as Electronically Modulated
Converter Clutch (EMCC) can occur at various times
depending on the following variables:
²Shift lever position
²Current gear range
²Transmission fluid temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Input speed
²Throttle angle
²Engine speed
Fig. 112 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 113 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 114 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 267
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1798 of 2199

(8) Position the accumulator cover onto the valve
body.
(9) Install the screws to hold the accumulator
cover onto the valve body. Tighten the screws to 4.5
N´m (40 in. lbs.).
(10) Install the TRS selector plate onto the valve
body and the manual valve.
(11) Install the solenoid and pressure switch
assembly onto the valve body.
(12) Install the screws to hold the solenoid and
pressure switch assembly onto the valve body.
Tighten the screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in. lbs.). Tighten
the screws adjacent to the arrows cast into the bot-
tom of the transfer plate first.
(13) Position the detent spring onto the valve body.
(14) Install the screw to hold the detent spring
onto the valve body. Tighten the screw to 4.5 N´m (40
in. lbs.).
(15) Install new clutch passage seals onto the
valve body, if necessary
INSTALLATION
(1) Check condition of seals on valve body and the
solenoid and pressure switch assembly. Replace seals
if cut or worn.
(2) Place TRS selector plate in the PARK position.
(3) Place the transmission in the PARK position.
(4) Lubricate seal on the solenoid and pressure
switch assembly connector with petroleum jelly.(5) Position valve body in transmission and align
the manual lever on the valve body to the pin on the
transmission manual shift lever.
(6) Seat valve body in case and install one or two
bolts to hold valve body in place.
(7) Tighten valve body bolts alternately and evenly
to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Install a new primary oil filter seal in the oil
pump inlet bore. Seat the seal in the bore with the
butt end of a hammer, or other suitable tool.
CAUTION: The primary oil filter seal MUST be fully
installed flush against the oil pump body. DO NOT
install the seal onto the filter neck and attempt to
install the filter and seal as an assembly. Damage to
the transmission will result.
(9) Place replacement filter in position on valve
body and into the oil pump.
(10) Install screw to hold filter to valve body.
Tighten screw to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
(11) Connect the solenoid and pressure switch
assembly connector.
(12) Install oil pan. Tighten pan bolts to 12 N´m
(105 in. lbs.) torque.
(13) Lower vehicle and fill transmission with
MopartATF +4, type 9602, fluid.
(14) Check and adjust gearshift cable, if necessary.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 279
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1803 of 2199

REAR RETAINER - NV242HD
(1) Remove extension housing bolts.
(2) Tap extension housing with plastic or rawhide
mallet to loosen sealer (Fig. 10).
(3) Separate extension housing from rear retainer.
(4) Remove rear bearing snap-ring (Fig. 11).
(5) Remove bolts holding rear retainer to rear case
half.
(6) Loosen rear retainer with pry tool to break
sealer bead. Pry only against retainer boss as shown
(Fig. 12).
(7) Slide retainer off case and output shaft (Fig.
13).
OIL PUMP AND REAR CASE HALF
(1) Remove rear bearing O.D. retaining ring with
snap ring pliers. Then tilt pump and slide it off out-
put shaft (Fig. 14)
(2) Remove pickup tube O-ring from pump (Fig.
15) but do not disassemble pump; it is not a repair-
able part.
(3) Remove seal from oil pump with pry tool.
(4) Remove bolts attaching rear case to front case
(Fig. 16). Note position of the two black finish bolts
at each end of the case. These bolts go through the
case dowels and require a washer under the bolt
head.
Fig. 10 Remove Extension Housing
1 - EXTENSION HOUSING
2 - PLASTIC HAMMER
3 - REAR RETAINER
Fig. 11 Remove the Output Bearing Snap-ring
1 - REAR RETAINER
2 - SNAP-RING
3 - REAR BEARING
Fig. 12 Loosening Rear Retainer
1 - REAR RETAINER
2-TAB(2)
3 - SCREWDRIVER
4-TAB
Fig. 13 Rear Retainer Removal
1 - MAINSHAFT
2 - REAR RETAINER
21 - 284 TRANSFER CASE - NV242WJ
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 1804 of 2199

(5) Remove rear case from front case (Fig. 17).
Insert screwdrivers into slots cast into each end of
case. Then pry upward to break sealer bead and
remove rear case.
CAUTION: Do not pry on the sealing surface of
either case half as the surfaces will become dam-
aged.
(6) Remove oil pickup tube and screen from rear
case (Fig. 18).
Fig. 14 Oil Pump Removal
1 - OIL PUMP
Fig. 15 Pickup Tube O-Ring Location
1 - OIL PUMP
2 - O-RING
Fig. 16 Spline And Dowel Bolt Locations
1 - DOWEL BOLT AND WASHER (2)
2 - CASE BOLTS
3 - SPLINE HEAD BOLT (1)
Fig. 17 Loosening/Removing Rear Case
1 - MAINSHAFT
2 - SCREWDRIVER
3 - FRONT CASE
4 - SCREWDRIVER
5 - REAR CASE
Fig. 18 Oil Pickup Screen, Hose And Tube Removal
1 - CONNECTING HOSE
2 - PICKUP SCREEN
3 - PICKUP TUBE
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 285
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 1811 of 2199

(7) Inspect low range annulus gear (Fig. 42).Gear
is not a serviceable component. If damaged,
replace gear and front case as assembly.
(8) Remove oil seals from following components:
²front bearing retainer.
²rear retainer.
²oil pump.
²case halves.
DIFFERENTIAL
(1) Mark differential case halves for reference.
(2) Remove differential case bolts.
(3) Invert differential on workbench.
(4) Separate top case from bottom case. Use slots
in case halves to pry them apart (Fig. 43).
(5) Remove thrust washers and planet gears from
case pins (Fig. 44).
(6) Remove mainshaft and sprocket gears from
bottom case (Fig. 45). Note gear position for reference
before separating them.
CLEANING
Clean the transfer case parts with a standard
parts cleaning solvent. Remove all traces of sealer
from the cases and retainers with a scraper and all
purpose cleaner. Use compressed air to remove sol-
vent residue from oil feed passages in the case
halves, retainers, gears, and shafts.
The oil pickup screen can be cleaned with solvent.
Shake excess solvent from the screen after cleaning
and allow it to air dry. Do not use compressed air.
Fig. 42 Inspecting Low Range Annulus Gear
1 - LOW RANGE ANNULUS GEAR
Fig. 43 Separating Differential Case Halves
1 - TOP CASE
2 - CASE BOLTS
3 - CASE BOLTS
4 - CASE SLOTS
5 - CASE BOLTS
Fig. 44 Planet Gears And Thrust Washer Removal
1 - MAINSHAFT GEAR
2 - THRUST WASHERS (12)
3 - PLANET GEARS (6)
21 - 292 TRANSFER CASE - NV242WJ
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)