2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Fill location
[x] Cancel search: Fill locationPage 1253 of 2199

FORM-IN-PLACE GASKET AND SEALER
APPLICATION
Assembling parts using a form-in-place gasket
requires care but it's easier then using precut gaskets.
MopartGasket Maker material should be applied
sparingly 1 mm (0.040 in.) diameter or less of sealant
to one gasket surface. Be certain the material sur-
rounds each mounting hole. Excess material can eas-
ily be wiped off. Components should be torqued in
place within 15 minutes. The use of a locating dowel
is recommended during assembly to prevent smear-
ing material off the location.
MopartEngine RTV GEN II or ATF RTV gasket
material should be applied in a continuous bead
approximately 3 mm (0.120 in.) in diameter. All
mounting holes must be circled. For corner sealing, a
3.17 or 6.35 mm (1/8 or 1/4 in.) drop is placed in the
center of the gasket contact area. Uncured sealant
may be removed with a shop towel. Components
should be torqued in place while the sealant is still
wet to the touch (within 10 minutes). The usage of a
locating dowel is recommended during assembly to
prevent smearing material off the location.
MopartGasket Sealant in an aerosol can should be
applied using a thin, even coat sprayed completely
over both surfaces to be joined, and both sides of a
gasket. Then proceed with assembly. Material in a
can w/applicator can be brushed on evenly over the
sealing surfaces. Material in an aerosol can should be
used on engines with multi-layer steel gaskets.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR DAMAGED
OR WORN THREADS
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Damaged or worn threads can be repaired. Essen-
tially, this repair consists of:
²Drilling out worn or damaged threads.
²Tapping the hole with a special Heli-Coil Tap, or
equivalent.
²Installing an insert into the tapped hole to bring
the hole back to its original thread size.
STANDARD PROCEDUREÐHYDROSTATIC LOCK
CAUTION: DO NOT use the starter motor to rotate
the crankshaft. Severe damage could occur.
When an engine is suspected of hydrostatic lock
(regardless of what caused the problem), follow the
steps below.
(1) Perform the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).(2) Disconnect the negative cable(s) from the bat-
tery.
(3) Inspect air cleaner, induction system, and
intake manifold to ensure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(4) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs to
catch any fluid that may possibly be under pressure
in the cylinder head. Remove the spark plugs.
(5) With all spark plugs removed, rotate the crank-
shaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(6) Identify the fluid in the cylinders (coolant, fuel,
oil, etc.).
(7) Be sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders.
(8) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from occurring again.
(9) Squirt a small amount of engine oil into the
cylinders to lubricate the walls. This will prevent
damage on restart.
(10) Install new spark plugs. Tighten the spark
plugs to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Drain engine oil. Remove and discard the oil
filter.
(12) Install the drain plug. Tighten the plug to 34
N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(13) Install a new oil filter.
(14) Fill engine crankcase with the specified
amount and grade of oil. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE - SPECIFICATIONS).
(15) Connect the negative cable(s) to the battery.
(16) Start the engine and check for any leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE
HONING
Before honing, stuff plenty of clean shop towels
under the bores and over the crankshaft to keep
abrasive materials from entering the crankshaft
area.
(1)
Used carefully, the Cylinder Bore Sizing Hone
C-823, equipped with 220 grit stones, is the best tool
for this job. In addition to deglazing, it will reduce
taper and out-of-round, as well as removing light scuff-
ing, scoring and scratches. Usually, a few strokes will
clean up a bore and maintain the required limits.
CAUTION: DO NOT use rigid type hones to remove
cylinder wall glaze.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done if
the cylinder bore is straight and round. Use a cylin-
der surfacing hone, Honing Tool C-3501, equipped
with 280 grit stones (C-3501-3810). about 20-60
strokes, depending on the bore condition, will be suf-
ficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Using honing
oil C-3501-3880, or a light honing oil, available from
major oil distributors.
9 - 10 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1254 of 2199

CAUTION: DO NOT use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits, or kerosene.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a crosshatch pattern.
The hone marks should INTERSECT at 40É to 60É
for proper seating of rings (Fig. 3).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between 200 and
300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 40É to 60É
angle. Faster up and down strokes increase the cross-
hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned to remove all traces of abrasive. Use a brush
to wash parts with a solution of hot water and deter-
gent. Dry parts thoroughly. Use a clean, white, lint-
free cloth to check that the bore is clean. Oil the
bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE AND
OIL GALLERY PLUGS
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 4).CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount. Make certain the new plug
is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper drive
plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of
the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside the
lead-in chamfer.
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Mark the hinge locations on the hood panel for
alignment reference during installation. Remove the
engine compartment lamp. Remove the hood.
(3) Remove the radiator drain cock and radiator
cap to drain the coolant. DO NOT waste usable cool-
ant. If the solution is clean, drain the coolant into a
clean container for reuse.
(4) Remove the upper radiator hose and coolant
recovery hose.
(5) Remove the lower radiator hose.
(6) Remove upper radiator support retaining bolts
and remove radiator support.
Fig. 3 Cylinder Bore Crosshatch Pattern
1 - CROSSHATCH PATTERN
2 - INTERSECT ANGLE
Fig. 4 Core Hole Plug Removal
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - REMOVE PLUG WITH PLIERS
3 - STRIKE HERE WITH HAMMER
4 - DRIFT PUNCH
5 - CUP PLUG
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 11
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1347 of 2199

CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) -
RIGHT
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder head covers are made of die cast mag-
nesium, and are not interchangeable from side-to-
side. It is imperative that nothing rest on the
cylinder head covers. Prolonged contact with other
items may wear a hole in the cylinder head cover.
REMOVAL - RIGHT SIDE
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove air cleaner assembly, resonator assem-
bly and air inlet hose.
(3) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(4) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(5) Remove air conditioning compressor retaining
bolts and move compressor to the left.
(6) Remove heater hoses.
(7) Disconnect injector and ignition coil connectors.
(8) Disconnect and remove positive crankcase ven-
tilation (PCV) hose.
(9) Remove oil fill tube.
(10) Un-clip injector and ignition coil harness and
move away from cylinder head cover.
(11) Remove right rear breather tube and filter
assembly.
(12) Remove cylinder head cover retaining bolts.
(13) Remove cylinder head cover.
NOTE: The gasket may be used again, provided no
cuts, tears, or deformation has occurred.
CLEANING
Clean cylinder head cover gasket surface.
Clean head rail, if necessary.
INSTALLATION - RIGHT SIDE
CAUTION: Do not use harsh cleaners to clean the
cylinder head covers. Severe damage to covers
may occur.
CAUTION: DO NOT allow other components includ-
ing the wire harness to rest on or against the
engine cylinder head cover. Prolonged contact with
other objects may wear a hole in the cylinder head
cover.
(1) Clean cylinder head cover and both sealing sur-
faces. Inspect and replace gasket as necessary.(2) Install cylinder head cover and hand start all
fasteners. Verify that all double ended studs are in
the correct location shown in (Fig. 38).
(3) Tighten cylinder head cover bolts and double
ended studs to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs).
(4) Install right rear breather tube and filter
assembly.
(5) Connect injector, ignition coil electrical connec-
tors and harness retaining clips.
(6) Install the oil fill tube.
(7) Install PCV hose.
(8) Install heater hoses.
(9) Install air conditioning compressor retaining
bolts.
(10) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(11) Fill Cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(12) Install air cleaner assembly, resonator assem-
bly and air inlet hose.
(13) Connect battery negative cable.
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS
DESCRIPTION
The valves are made of heat resistant steel and
have chrome plated stems to prevent scuffing. Each
valve is actuated by a roller rocker arm which pivots
on a stationary lash adjuster. All valves use three
bead lock keepers to retain the springs and promote
valve rotation.
Fig. 38 Cylinder Head CoverÐRight
ITEM DESCRIPTION TORQUE
1 Cover Fasteners 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.)
9 - 104 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
Page 1423 of 2199
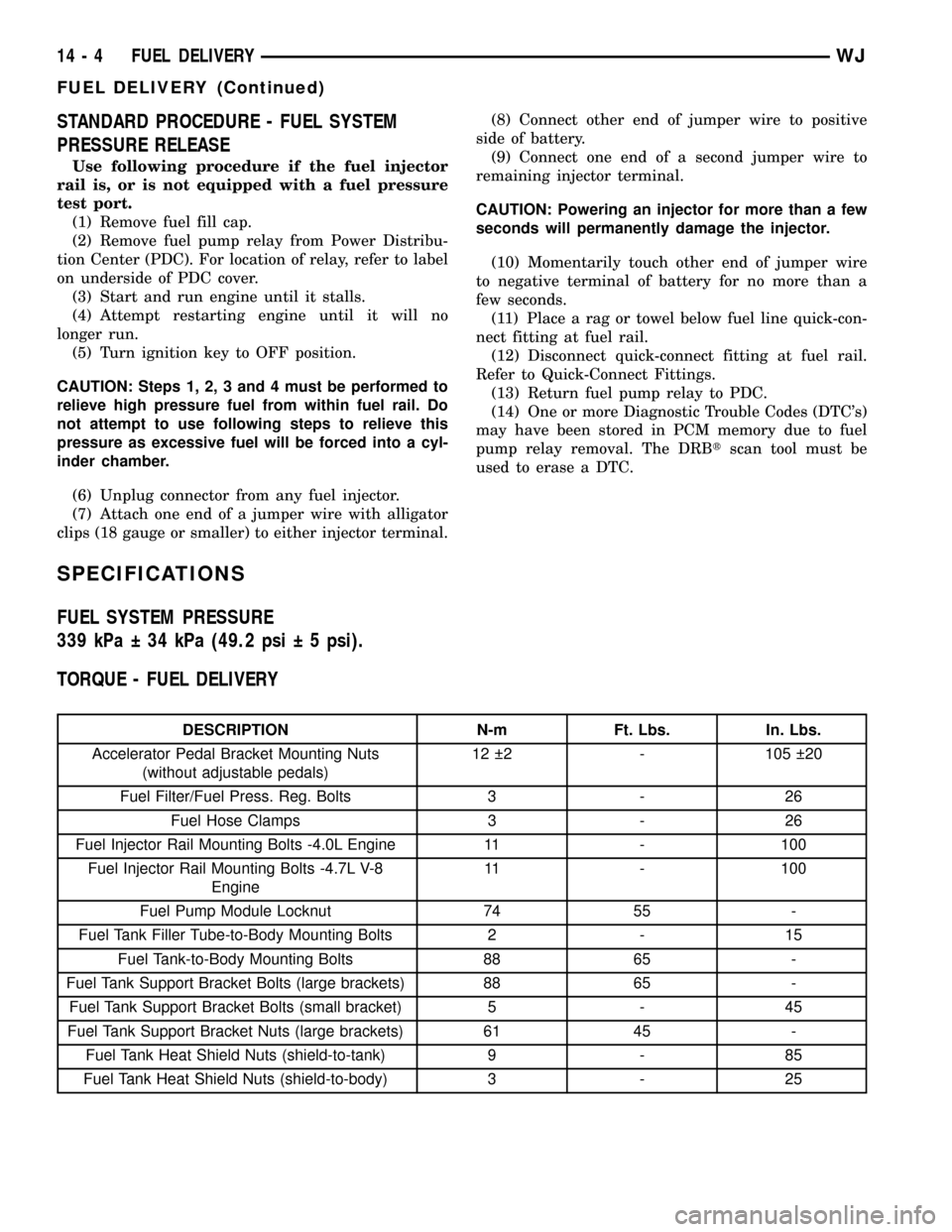
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE
Use following procedure if the fuel injector
rail is, or is not equipped with a fuel pressure
test port.
(1) Remove fuel fill cap.
(2) Remove fuel pump relay from Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC). For location of relay, refer to label
on underside of PDC cover.
(3) Start and run engine until it stalls.
(4) Attempt restarting engine until it will no
longer run.
(5) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
CAUTION: Steps 1, 2, 3 and 4 must be performed to
relieve high pressure fuel from within fuel rail. Do
not attempt to use following steps to relieve this
pressure as excessive fuel will be forced into a cyl-
inder chamber.
(6) Unplug connector from any fuel injector.
(7) Attach one end of a jumper wire with alligator
clips (18 gauge or smaller) to either injector terminal.(8) Connect other end of jumper wire to positive
side of battery.
(9) Connect one end of a second jumper wire to
remaining injector terminal.
CAUTION: Powering an injector for more than a few
seconds will permanently damage the injector.
(10) Momentarily touch other end of jumper wire
to negative terminal of battery for no more than a
few seconds.
(11) Place a rag or towel below fuel line quick-con-
nect fitting at fuel rail.
(12) Disconnect quick-connect fitting at fuel rail.
Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(13) Return fuel pump relay to PDC.
(14) One or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
may have been stored in PCM memory due to fuel
pump relay removal. The DRBtscan tool must be
used to erase a DTC.
SPECIFICATIONS
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
339 kPa 34 kPa (49.2 psi 5 psi).
TORQUE - FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Accelerator Pedal Bracket Mounting Nuts
(without adjustable pedals)12 2 - 105 20
Fuel Filter/Fuel Press. Reg. Bolts 3 - 26
Fuel Hose Clamps 3 - 26
Fuel Injector Rail Mounting Bolts -4.0L Engine 11 - 100
Fuel Injector Rail Mounting Bolts -4.7L V-8
Engine11 - 100
Fuel Pump Module Locknut 74 55 -
Fuel Tank Filler Tube-to-Body Mounting Bolts 2 - 15
Fuel Tank-to-Body Mounting Bolts 88 65 -
Fuel Tank Support Bracket Bolts (large brackets) 88 65 -
Fuel Tank Support Bracket Bolts (small bracket) 5 - 45
Fuel Tank Support Bracket Nuts (large brackets) 61 45 -
Fuel Tank Heat Shield Nuts (shield-to-tank) 9 - 85
Fuel Tank Heat Shield Nuts (shield-to-body) 3 - 25
14 - 4 FUEL DELIVERYWJ
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
Page 1435 of 2199

CAUTION: The left and right fuel rails are replaced
as an assembly. Do not attempt to separate rail
halves at connector tube (Fig. 22). Due to design of
tube, it does not use any clamps. Never attempt to
install a clamping device of any kind to tube. When
removing fuel rail assembly for any reason, be care-
ful not to bend or kink tube.
(1) Remove fuel tank filler tube cap.
(2) Perform Fuel System Pressure Release Proce-
dure.
(3) Remove negative battery cable at battery.
(4) Remove air duct at throttle body air box.
(5) Remove air box at throttle body.
(6) Remove wiring at rear of generator.
(7) Disconnect fuel line latch clip and fuel line at
fuel rail. A special tool will be necessary for fuel line
disconnection. Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(8) Remove vacuum lines at throttle body.(9) Disconnect electrical connectors at all 8 fuel
injectors. To remove connector refer to (Fig. 23). Push
red colored slider away from injector (1). While push-
ing slider, depress tab (2) and remove connector (3)
from injector. The factory fuel injection wiring har-
ness is numerically tagged (INJ 1, INJ 2, etc.) for
injector position identification. If harness is not
tagged, note wiring location before removal.
(10) Disconnect electrical connectors at throttle
body.
(11) Disconnect electrical connectors at MAP and
IAT sensors.
Fig. 21 Fuel Injector Rail/Fuel DamperÐ4.0L Engine
1 - INJ. #1
2 - INJ. #2
3 - INJ. #3
4 - INJ. #4
5 - INJ. #5
6 - INJ. #6
7 - FUEL INJECTOR RAIL
8 - FUEL DAMPER
9 - PRESSURE TEST PORT CAP
10 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
11 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
Fig. 22 FUEL INJECTOR RAIL - 4.7L V-8 EN
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
2 - INJ.#7
3 - INJ.#5
4 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
5 - INJ.#3
6 - FUEL INJECTOR RAIL
7 - INJ.#1
8 - CONNECTOR TUBE
9 - INJ.#2
10 - INJ.#4
11 - INJ.#6
12 - INJ.#8
13 - PRESSURE TEST PORT CAP
14 - 16 FUEL DELIVERYWJ
FUEL RAIL (Continued)
Page 1436 of 2199

(12) Remove first three ignition coils on each bank
(cylinders #1, 3, 5, 2, 4 and 6). Refer to Ignition Coil
Removal/Installation.
(13) Remove 4 fuel rail mounting bolts (Fig. 22).
(14) Gently rock and pullleftside of fuel rail until
fuel injectors just start to clear machined holes in
cylinder head. Gently rock and pullrightside of rail
until injectors just start to clear cylinder head holes.
Repeat this procedure (left/right) until all injectors
have cleared cylinder head holes.
(15) Remove fuel rail (with injectors attached)
from engine.
(16) If fuel injectors are to be removed, refer to
Fuel Injector Removal/Installation.
REMOVAL - 4.0L
The fuel damper is not serviced separately.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH ENGINE OFF.
THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED BEFORE
SERVICING FUEL RAIL.
(1) Remove fuel tank filler tube cap.
(2) Perform Fuel System Pressure Release Proce-
dure.
(3) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.(4) Remove air tube at top of throttle body. Note:
Some engine/vehicles may require removal of air
cleaner ducts at throttle body.
(5) Disconnect electrical connectors at all 6 fuel
injectors. To remove connector refer to (Fig. 25). Push
red colored slider away from injector (1). While push-
ing slider, depress tab (2) and remove connector (3)
from injector. The factory fuel injection wiring har-
ness is numerically tagged (INJ 1, INJ 2, etc.) for
injector position identification. If harness is not
tagged, note wiring location before removal.
(6) Remove oxygen sensor wiring clip nuts at fuel
rail mounting studs (certain emissions packages
only).
(7) Disconnect fuel supply line latch clip and fuel
line at fuel rail. Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(8) Disconnect throttle cable at throttle body. Refer
to Throttle Cable Removal/Installation.
Fig. 23 Remove/Install Injector ConnectorÐ4.7L V-8
Engine
Fig. 24 Fuel Rail MountingÐ4.0L Engine
1 - INJ. #1
2 - INJ. #2
3 - INJ. #3
4 - INJ. #4
5 - INJ. #5
6 - INJ. #6
7 - FUEL INJECTOR RAIL
8 - FUEL DAMPER
9 - PRESSURE TEST PORT CAP
10 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
11 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
WJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 17
FUEL RAIL (Continued)
Page 1531 of 2199
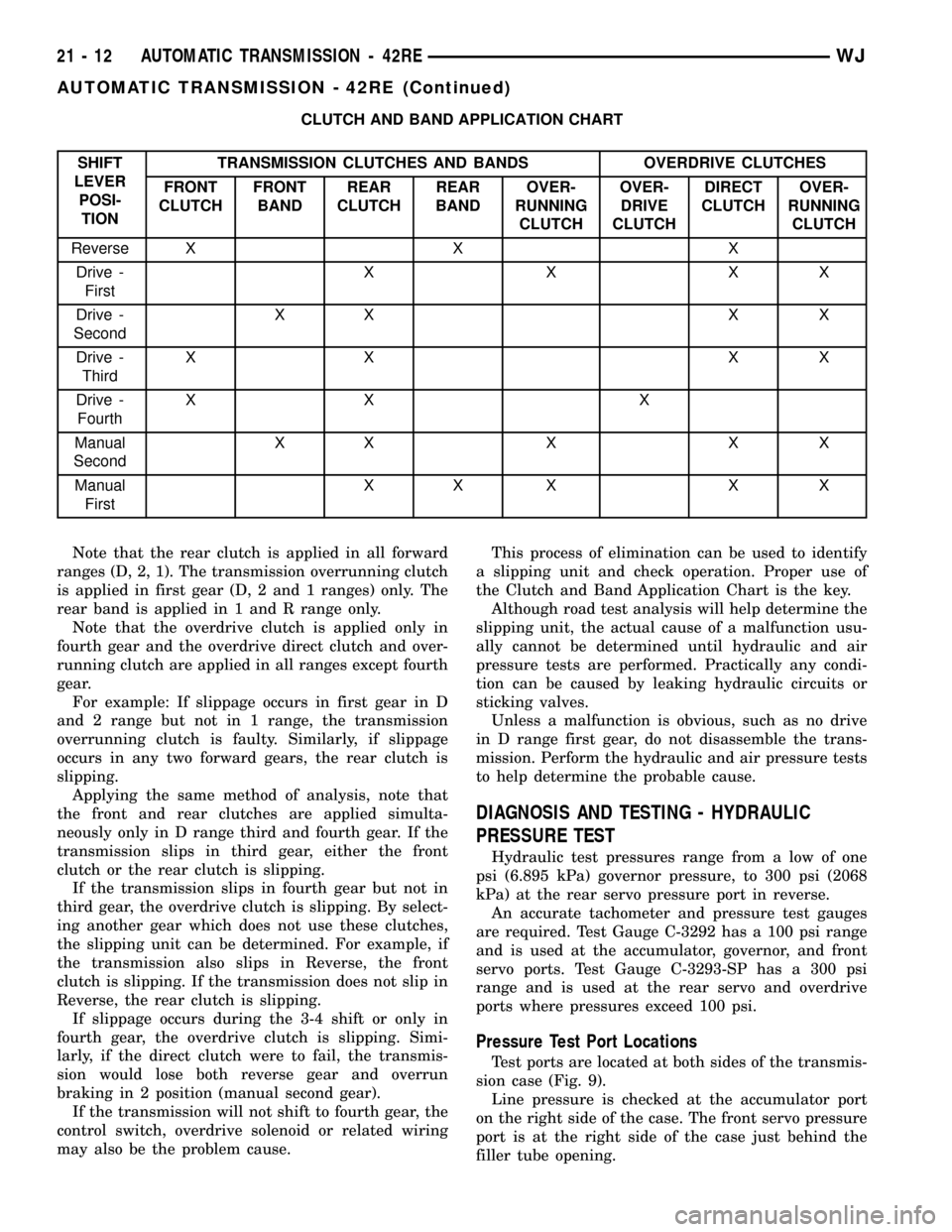
CLUTCH AND BAND APPLICATION CHART
SHIFT
LEVER
POSI-
TIONTRANSMISSION CLUTCHES AND BANDS OVERDRIVE CLUTCHES
FRONT
CLUTCHFRONT
BANDREAR
CLUTCHREAR
BANDOVER-
RUNNING
CLUTCHOVER-
DRIVE
CLUTCHDIRECT
CLUTCHOVER-
RUNNING
CLUTCH
Reverse X X X
Drive -
FirstXXXX
Drive -
SecondXX X X
Drive -
ThirdXX XX
Drive -
FourthXX X
Manual
SecondXXXXX
Manual
FirstXX X X X
Note that the rear clutch is applied in all forward
ranges (D, 2, 1). The transmission overrunning clutch
is applied in first gear (D, 2 and 1 ranges) only. The
rear band is applied in 1 and R range only.
Note that the overdrive clutch is applied only in
fourth gear and the overdrive direct clutch and over-
running clutch are applied in all ranges except fourth
gear.
For example: If slippage occurs in first gear in D
and 2 range but not in 1 range, the transmission
overrunning clutch is faulty. Similarly, if slippage
occurs in any two forward gears, the rear clutch is
slipping.
Applying the same method of analysis, note that
the front and rear clutches are applied simulta-
neously only in D range third and fourth gear. If the
transmission slips in third gear, either the front
clutch or the rear clutch is slipping.
If the transmission slips in fourth gear but not in
third gear, the overdrive clutch is slipping. By select-
ing another gear which does not use these clutches,
the slipping unit can be determined. For example, if
the transmission also slips in Reverse, the front
clutch is slipping. If the transmission does not slip in
Reverse, the rear clutch is slipping.
If slippage occurs during the 3-4 shift or only in
fourth gear, the overdrive clutch is slipping. Simi-
larly, if the direct clutch were to fail, the transmis-
sion would lose both reverse gear and overrun
braking in 2 position (manual second gear).
If the transmission will not shift to fourth gear, the
control switch, overdrive solenoid or related wiring
may also be the problem cause.This process of elimination can be used to identify
a slipping unit and check operation. Proper use of
the Clutch and Band Application Chart is the key.
Although road test analysis will help determine the
slipping unit, the actual cause of a malfunction usu-
ally cannot be determined until hydraulic and air
pressure tests are performed. Practically any condi-
tion can be caused by leaking hydraulic circuits or
sticking valves.
Unless a malfunction is obvious, such as no drive
in D range first gear, do not disassemble the trans-
mission. Perform the hydraulic and air pressure tests
to help determine the probable cause.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TEST
Hydraulic test pressures range from a low of one
psi (6.895 kPa) governor pressure, to 300 psi (2068
kPa) at the rear servo pressure port in reverse.
An accurate tachometer and pressure test gauges
are required. Test Gauge C-3292 has a 100 psi range
and is used at the accumulator, governor, and front
servo ports. Test Gauge C-3293-SP has a 300 psi
range and is used at the rear servo and overdrive
ports where pressures exceed 100 psi.
Pressure Test Port Locations
Test ports are located at both sides of the transmis-
sion case (Fig. 9).
Line pressure is checked at the accumulator port
on the right side of the case. The front servo pressure
port is at the right side of the case just behind the
filler tube opening.
21 - 12 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1581 of 2199

ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - BANDS
FRONT BAND
The front (kickdown) band adjusting screw is
located on the left side of the transmission case
above the manual valve and throttle valve levers.
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Loosen band adjusting screw locknut (Fig. 69).
Then back locknut off 3-5 turns. Be sure adjusting
screw turns freely in case. Apply lubricant to screw
threads if necessary.
(3) Tighten band adjusting screw to 8 N´m (72 in.
lbs.) torque with Inch Pound Torque Wrench
C-3380-A, a 3-in. extension and appropriate TorxŸ
socket.
CAUTION: If Adapter C-3705 is needed to reach the
adjusting screw, tighten the screw to only 5 N´m
(47-50 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Back off front band adjusting screw 3 turns.
(5) Hold adjuster screw in position and tighten
locknut to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Lower vehicle.
REAR BAND
The transmission oil pan must be removed for
access to the rear band adjusting screw.
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Remove transmission oil pan and drain fluid.(3) Loosen band adjusting screw locknut 5-6 turns
(Fig. 70). Be sure adjusting screw turns freely in
lever.
(4) Tighten adjusting screw to 8 N´m (72 in. lbs.)
torque.
(5) Back off adjusting screw 4 turns.
(6) Hold adjusting screw in place and tighten lock-
nut to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Position new gasket on oil pan and install pan
on transmission. Tighten pan bolts to 17 N´m (13 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(8) Lower vehicle and refill transmission with
MopartATF +4, type 9602, fluid.
Fig. 68 Rear Band
1 - ADJUSTING SCREW
2 - LOCKNUT
3 - LEVER
4 - REAR BAND
5 - REACTION PIN
6 - O-RINGS
7 - PIVOT PINFig. 69 Front Band Adjustment Screw Location
1 - LOCK-NUT
2 - FRONT BAND ADJUSTER
Fig. 70 Rear Band Adjusting Screw Location
1 - ADJUSTING SCREW
2 - REAR BAND LEVER
3 - LOCKNUT
21 - 62 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
BANDS (Continued)