2003 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE lights
[x] Cancel search: lightsPage 500 of 2199

The RKE system includes two transmitters when
the vehicle is shipped from the factory, but the sys-
tem can retain the vehicle access codes of up to four
transmitters. The transmitter codes are retained in
the RKE receiver memory, even if the battery is dis-
connected. If an RKE transmitter is faulty or lost,
new transmitter vehicle access codes can be pro-
grammed into the system using a DRBIIItscan tool
and the appropriate diagnostic information.
This vehicle also offers several customer program-
mable features, which allows the selection of several
optional electronic features to suit individual prefer-
ences. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CON-
SOLE/ELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFO CENTER -
DESCRIPTION). Customer programmable feature
options affecting the RKE system include:
²Remote Unlock- Allows the option of having
only the driver side front door unlock when the RKE
transmitter Unlock button is depressed the first time
and the remaining doors and the liftgate unlock
when the button is depressed a second time, or hav-
ing all doors and the liftgate unlock upon the first
depression of the RKE transmitter Unlock button.
²Remote Linked to Memory- If the vehicle is
equipped with the Memory System, this feature
allows the option of having the RKE transmitter
Unlock button activate the recall of the stored set-
tings, or having the recall function assigned solely to
the memory switch on the driver side front door trim
panel.
²Sound Horn on Lock- Allows the option of
having the horn sound a short chirp as an audible
verification that the doors have locked, or having no
audible verification.
²Flash Lights with Lock- Allows the option of
having the lights flash as an optical verification that
the doors have locked, or having no optical verifica-
tion.
This group covers the following components of the
RKE system:
²RKE Receiver
²RKE Transmitter
Certain functions and features of the RKE system
rely upon resources shared with other electronic
modules in the vehicle over the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus network. The
PCI data bus network allows the sharing of sensor
information. This helps to reduce wire harness com-
plexity, internal controller hardware, and component
sensor current loads. At the same time, this system
provides increased reliability, enhanced diagnostics,
and allows the addition of many new feature capabil-
ities. For diagnosis of these electronic modules or of
the PCI data bus network, the use of a DRBIIItscan
tool and the appropriate diagnostic information are
required.The other electronic modules that may affect RKE
system operation are as follows:
²Body Control Module (BCM)- (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/BODY CONTROL/CENTRAL TIMER MOD-
ULE - DESCRIPTION).
²Driver Door Module (DDM)- (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/DOOR MODULE - DESCRIPTION).
²Electronic Vehicle Information Center
(EVIC)- (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD
CONSOLE/ELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFO CENTER
- DESCRIPTION).
²Passenger Door Module (PDM)- (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/DOOR MODULE - DESCRIPTION).
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)- (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL
MODULES/POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE -
DESCRIPTION).
Hard wired circuitry connects the RKE system
components via the PDM to the electrical system of
the vehicle. These hard wired circuits are integral to
several wire harnesses, which are routed throughout
the vehicle and retained by many different methods.
These circuits may be connected to each other, to the
vehicle electrical system and to the RKE system com-
ponents through the use of a combination of soldered
splices, splice block connectors, and many different
types of wire harness terminal connectors and insu-
lators. Refer to the appropriate wiring information.
The wiring information includes wiring diagrams,
proper wire and connector repair procedures, further
details on wire harness routing and retention, as well
as pin-out and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
COMBINATION FLASHER
The combination flasher is a smart relay that func-
tions as both the turn signal system and the hazard
warning system flasher. The combination flasher con-
tains active electronic Integrated Circuitry (IC) ele-
ments. This flasher can be energized by the BCM to
flash all of the park/turn signal/front side marker
lamps as an optical alert for the RKE panic function
and, if the Flash Lights with Lock programmable fea-
ture is enabled, as an optical verification for the RKE
lock event. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/
LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/COMBINATION FLASHER
- DESCRIPTION).
HORN RELAY
The horn relay is a electromechanical device that
switches battery current to the horn when the horn
switch grounds the relay coil. The horn relay is
located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC) in
WJPOWER LOCKS 8N - 3
POWER LOCKS (Continued)
Page 502 of 2199

See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
more information on the features, use and operation
of the power lock system.
OPERATION - REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY
SYSTEM
The Passenger Door Module (PDM) contains the
RKE system control logic and the RKE receiver.
When the RKE receiver recognizes a Lock, Unlock or
Panic message from a valid RKE transmitter, the
RKE receiver provides that input to the PDM. The
PDM circuitry and programming responds by sending
the proper messages to the other electronic modules
over the Programmable Communications Interface
(PCI) data bus.
When an RKE lock message is received, the doors
and the liftgate lock, the interior lighting fades to off,
the horn chirps (if this feature is enabled), the exte-
rior lamps flash (if this feature is enabled) and, if the
vehicle is so equipped, the Vehicle Theft Security
System (VTSS) is armed. When an RKE unlock mes-
sage is received, the driver side front door (or all
doors and the liftgate if this feature is enabled)
unlock, the interior lighting is turned on and, if the
vehicle is so equipped, the VTSS is disarmed. If the
vehicle is equipped with the Memory System and the
RKE Linked to Memory feature is enabled, the RKE
unlock message also recalls the driver seat, outside
mirror and radio settings assigned to the RKE trans-
mitter that sent the unlock signal.
When an RKE panic message is received, it causes
the exterior lamps (including the headlights) to flash,
and the horn to pulse for about three minutes, or
until a second panic message is received. A vehicle
speed of about 24 kilometers-per-hour (15 miles-per-
hour) will also cancel the panic event.
See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
more information on the features, use and operation
of the RKE system.
OPERATION - LIFTGATE FLIP-UP GLASS
POWER RELEASE SYSTEM
When the liftgate mounted flip-up glass release
switch is depressed, battery current is directed to the
electric release motor that is integral to the flip-up
glass latch located inside the liftgate. When the
release motor is energized the latch releases and the
flip-up glass can be opened. A liftgate flip-up glass
limit switch is integral to the liftgate latch actuator
mechanism. The limit switch automatically enables
or disables the liftgate flip-up glass power release cir-
cuitry, depending upon the position of the liftgate
latch lock mechanism. When the liftgate latch is
unlocked, the limit switch closes and battery current
is available at the release switch. When the liftgatelatch is locked , the limit switch opens, and the
release switch is disabled.
See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
more information on the features, use and operation
of the liftgate flip-up glass power release system.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER LOCK
SYSTEM
Following are tests that will help to diagnose the
hard wired components and circuits of the power lock
system. However, these tests may not prove conclu-
sive in the diagnosis of this system. In order to
obtain conclusive testing of the power lock system,
the Programmable Communications Interface (PCI)
data bus network and all of the electronic modules
that provide inputs to, or receive outputs from the
power lock system components must be checked.
The most reliable, efficient, and accurate means to
diagnose the power lock system requires the use of a
DRBIIItscan tool and the proper Diagnostic Proce-
dures manual. The DRBIIItscan tool can provide
confirmation that the PCI data bus is functional, that
all of the electronic modules are sending and receiv-
ing the proper messages on the PCI data bus, and
that the power lock motors are being sent the proper
hard wired outputs by the door modules for them to
perform their power lock system functions.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, details of wire
harness routing and retention, connector pin-out
information and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
PRELIMINARY DIAGNOSIS
As a preliminary diagnosis for the power lock sys-
tem, note the system operation while you actuate
both the Lock and Unlock functions with the power
lock switches and with the Remote Keyless Entry
(RKE) transmitter. Then, proceed as follows:
²If the entire power lock system fails to function
with either the power lock switches or the RKE
transmitter, check the fused B(+) fuse in the Power
Distribution Center. If the fuse is OK, proceed to
diagnosis of the door modules. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/
DOOR MODULE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
²If the power lock system functions with both
power lock switches, but not with the RKE transmit-
ter, proceed to diagnosis of the Remote Keyless Entry
(RKE) system. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER
LOCKS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REMOTE
KEYLESS ENTRY SYSTEM).
WJPOWER LOCKS 8N - 5
POWER LOCKS (Continued)
Page 503 of 2199

²If the power lock system functions with the RKE
transmitter, but not with one or both power lock
switches, proceed to diagnosis of the door modules.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CON-
TROL MODULES/DOOR MODULE - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING).
²If the driver side power lock switch operates
only the driver side front door power lock motor, but
all other power lock motors operate with the passen-
ger side power lock switch or the RKE transmitter,
use a DRBIIItscan tool and the appropriate diagnos-
tic information to diagnose the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus.
²If only one power lock motor fails to operate
with both power lock switches and the RKE trans-
mitter, proceed to diagnosis of the power lock motor.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER LOCKS/POWER
LOCK MOTOR - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REMOTE KEYLESS
ENTRY SYSTEM
Following are tests that will help to diagnose the
Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) system. However, these
tests may not prove conclusive in the diagnosis of
this system. In order to obtain conclusive testing of
the RKE system, the Programmable Communications
Interface (PCI) data bus network and all of the elec-
tronic modules that provide inputs to, or receive out-
puts from the RKE system components must be
checked.
The most reliable, efficient, and accurate means to
diagnose the RKE system requires the use of a
DRBIIItscan tool and the appropriate diagnostic
information. The DRBIIItscan tool can provide con-
firmation that the PCI data bus is functional, that all
of the electronic modules are sending and receiving
the proper messages on the PCI data bus, and that
the RKE receiver is being sent the proper radio fre-
quency signals by the RKE transmitters to perform
its RKE system functions.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, details of wire
harness routing and retention, connector pin-out
information and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
PRELIMINARY DIAGNOSIS
As a preliminary diagnosis for the RKE system,
note the system operation while you perform both the
Lock and Unlock functions with the power lock
switches and with the Remote Keyless Entry (RKE)
transmitter. Then, proceed as follows:
²If the entire power lock system fails to function
with either the power lock switches or the RKE
transmitter, check the fused B(+) fuse in the PowerDistribution Center. If the fuse is OK, proceed to the
diagnosis for the door modules. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/
DOOR MODULE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
²If the power lock system functions with both
power lock switches, but not with the RKE transmit-
ter, proceed to the diagnosis for the RKE transmitter.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER LOCKS/RE-
MOTE KEYLESS ENTRY TRANSMITTER - DIAG-
NOSIS AND TESTING).
²If the driver side power lock switch operates
only the driver side front door power lock motor, but
all other power lock motors operate with the passen-
ger side power lock switch or the RKE transmitter,
use a DRBIIItscan tool and the appropriate diagnos-
tic information to diagnose the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus.
If the problem being diagnosed involves only the
Sound Horn on Lock or the Flash Lights with Locks
features, be certain that these programmable fea-
tures are enabled. If the features are enabled and the
service horn and turn signals still operate, the Body
Control Module (BCM) and the PCI data bus must be
tested. For diagnosis of the BCM or the PCI data
bus, the use of a DRBIII scan tool and the appropri-
ate diagnostic information are required.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - LIFTGATE FLIP-UP
GLASS POWER RELEASE SYSTEM
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, details of wire
harness routing and retention, connector pin-out
information and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
(1) Check the fused B(+) fuse in the Junction
Block (JB). If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the
shorted circuit or component as required and replace
the faulty fuse.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) fuse
in the JB. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, repair the
open fused B(+) circuit to the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) as required.
(3) Disconnect the liftgate wire harness connector
for the liftgate lock motor and flip-up glass limit
switch from the motor and switch connector recepta-
cle. Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) cir-
cuit cavity of the liftgate wire harness connector for
the liftgate lock motor and flip-up glass limit switch.
If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open fused
B(+) circuit between the liftgate lock motor and
flip-up glass limit switch and the JB as required.
(4) Check for continuity between the two liftgate
flip-up glass limit switch terminals. There should be
continuity with the liftgate latch unlocked, and no
continuity with the latch locked. If OK, go to Step 5.
8N - 6 POWER LOCKSWJ
POWER LOCKS (Continued)
Page 508 of 2199

POWER MIRRORS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
POWER MIRRORS
DESCRIPTION.........................11
OPERATION...........................12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
MIRRORS...........................12
AUTOMATIC DAY/NIGHT MIRROR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - REAR VIEW MIRROR.....12
DESCRIPTION - OUTSIDE REAR VIEW
MIRROR............................13
OPERATION
OPERATION - REAR VIEW MIRROR.......13
OPERATION - OUTSIDE REAR VIEW
MIRROR............................13
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC DAY
/ NIGHT MIRROR......................13POWER FOLD-AWAY MIRROR - EXPORT
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
FOLD-AWAY MIRROR - EXPORT..........14
REMOVAL.............................14
POWER MIRROR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................15
SIDEVIEW MIRROR
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SIDEVIEW
MIRROR............................16
POWER MIRRORS
DESCRIPTION
Driver and passenger side power operated outside
rear view mirrors are standard factory-installed
equipment on this model. The power mirror system
allows the driver to adjust both outside mirrors elec-
trically from the driver seat position by operating a
switch on the driver side front door trim panel. The
power mirror system receives non-switched battery
current through a fuse in the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) so that the power mirrors remain oper-
ational, regardless of the ignition switch position.
The standard equipment power operated outside
rear view mirrors are also equipped with the heated
mirror system, which will only operate when the
ignition switch is in the On position and the rear
window defogger switch is turned on. When the rear
window defogger switch is in the On position, electric
heater grids on the rear window glass and behind
both outside rear view mirror glasses are energized.
These electric heater grids produce heat to help clear
the rear window glass and outside rear view mirrors
of ice, snow, or fog. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
HEATED MIRRORS - DESCRIPTION) for more
information on this feature.
A driver side automatic dimming outside mirror
that dims the mirror to reduce the glare of bright
lights approaching the vehicle from behind, and a
memory system that automatically positions the
power mirrors for two different drivers are optionalfactory-installed equipment on this model. (Refer to 8
- ELECTRICAL/POWER MIRRORS/AUTOMATIC
DAY / NIGHT MIRROR - DESCRIPTION) for more
information. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER
SEATS - DESCRIPTION) for more information.
This group covers the following components of the
power mirror system:
²Power mirrors
²Power mirror switch.
Certain functions and features of the power mirror
system rely upon resources shared with other elec-
tronic modules in the vehicle over the Programmable
Communications Interface (PCI) data bus network.
The PCI data bus network allows the sharing of sen-
sor information. This helps to reduce wire harness
complexity, internal controller hardware, and compo-
nent sensor current loads. At the same time, this sys-
tem provides increased reliability, enhanced
diagnostics, and allows the addition of many new fea-
ture capabilities. For diagnosis of these electronic
modules or of the PCI data bus network, the use of a
DRB scan tool and the proper Diagnostic Procedures
manual are recommended.
The other electronic modules that may affect power
mirror system operation are as follows:
²Body Control Module (BCM)(Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/BODY CONTROL/CENTRAL TIMER MODUL
- DESCRIPTION) for more information.
²Driver Door Module (DDM)(Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
WJPOWER MIRRORS 8N - 11
Page 546 of 2199

(4) Check to be certain that nobody is in the vehi-
cle, then reconnect the battery negative cable.
(5) Using the DRBIIIt, read and record the active
(current) Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) data.
(6) Next, use the DRBIIItto read and record any
stored (historical) DTC data.
(7) If any DTC is found in Step 5 or Step 6, refer
to the appropriate diagnostic information.
(8) Use the DRBIIItto erase the stored DTC data.
If any problems remain, the stored DTC data will not
erase. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic informa-
tion to diagnose any stored DTC that will not erase.
If the stored DTC information is successfully erased,
go to Step 9.
(9) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position for
about fifteen seconds, and then back to the On posi-
tion. Observe the airbag indicator in the instrument
cluster. It should light for six to eight seconds, and
then go out. This indicates that the supplemental
restraint system is functioning normally and that the
repairs are complete. If the airbag indicator fails to
light, or lights and stays on, there is still an active
supplemental restraint system fault or malfunction.
Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information to
diagnose the problem.
AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Airbag Control Module (ACM) is also some-
times referred to as the Occupant Restraint Control-
ler (ORC) (Fig. 6). The ACM is concealed underneath
the center floor console, where it is secured by four
screws to a stamped steel mounting bracket welded
onto the top of the floor panel transmission tunnel
just forward of the park brake mechanism in the pas-
senger compartment of the vehicle.
Concealed within a hollow in the center of the die
cast aluminum ACM housing is the electronic cir-
cuitry of the ACM which includes a microprocessor,
an electronic impact sensor, an electronic safing sen-
sor, and an energy storage capacitor. A stamped
metal cover plate is secured to the bottom of the
ACM housing with four screws to enclose and protect
the internal electronic circuitry and components. A
printed label on the top of the ACM housing provides
a visual verification of the proper orientation of the
unit, and should always be pointed toward the front
of the vehicle.
Two molded plastic electrical connector receptacles
exit the forward side of the ACM housing. These two
receptacles connect the ACM to the vehicle electrical
system through a dedicated take out and connector of
the instrument panel wire harness, and a dedicated
take out and connector of the airbag overlay wire
harness. For vehicles equipped with the optional side
curtain airbags, both ACM connector receptacles are
black in color and the ACM contains a second bi-di-
rectional safing sensor for the side airbags. For vehi-
cles not equipped with the optional side curtain
airbags, the ACM connector receptacles are both
gray.
The impact sensor and safing sensor internal to
the ACM are calibrated for the specific vehicle, and
are only serviced as a unit with the ACM. The ACM
cannot be repaired or adjusted and, if damaged or
faulty, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The microprocessor in the Airbag Control Module
(ACM) contains the supplemental restraint system
logic circuits and controls all of the supplemental
restraint system components. The ACM uses
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) and can communicate
with other electronic modules in the vehicle as well
as with the DRBIIItscan tool using the Programma-
ble Communications Interface (PCI) data bus net-
work. This method of communication is used for
control of the airbag indicator in the ElectroMechani-
cal Instrument Cluster (EMIC) and for supplemental
restraint system diagnosis and testing through the
16-way data link connector located on the driver side
lower edge of the instrument panel. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/COMMUNICATION - OPERATION).
Fig. 6 Airbag Control Module
1 - AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE
2 - ORIENTATION ARROW
3 - LABEL
4 - MOUNTING HOLES (4)
5 - CONNECTOR RECEPTACLE (2)
WJRESTRAINTS 8O - 9
RESTRAINTS (Continued)
Page 596 of 2199
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SENTRY KEY
IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
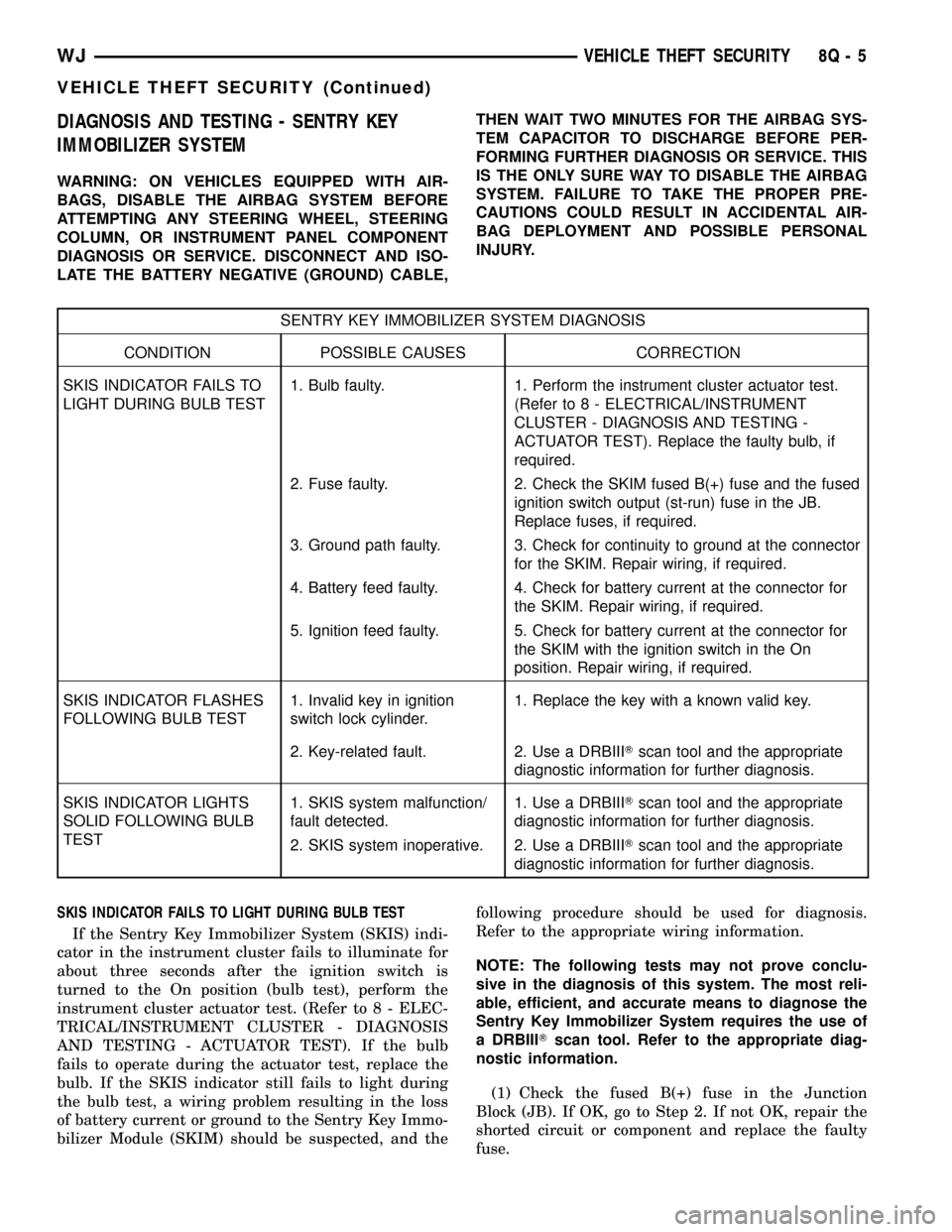
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
SKIS INDICATOR FAILS TO
LIGHT DURING BULB TEST1. Bulb faulty. 1. Perform the instrument cluster actuator test.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING -
ACTUATOR TEST). Replace the faulty bulb, if
required.
2. Fuse faulty. 2. Check the SKIM fused B(+) fuse and the fused
ignition switch output (st-run) fuse in the JB.
Replace fuses, if required.
3. Ground path faulty. 3. Check for continuity to ground at the connector
for the SKIM. Repair wiring, if required.
4. Battery feed faulty. 4. Check for battery current at the connector for
the SKIM. Repair wiring, if required.
5. Ignition feed faulty. 5. Check for battery current at the connector for
the SKIM with the ignition switch in the On
position. Repair wiring, if required.
SKIS INDICATOR FLASHES
FOLLOWING BULB TEST1. Invalid key in ignition
switch lock cylinder.1. Replace the key with a known valid key.
2. Key-related fault. 2. Use a DRBIIITscan tool and the appropriate
diagnostic information for further diagnosis.
SKIS INDICATOR LIGHTS
SOLID FOLLOWING BULB
TEST1. SKIS system malfunction/
fault detected.1. Use a DRBIIITscan tool and the appropriate
diagnostic information for further diagnosis.
2. SKIS system inoperative. 2. Use a DRBIIITscan tool and the appropriate
diagnostic information for further diagnosis.
SKIS INDICATOR FAILS TO LIGHT DURING BULB TEST
If the Sentry Key Immobilizer System (SKIS) indi-
cator in the instrument cluster fails to illuminate for
about three seconds after the ignition switch is
turned to the On position (bulb test), perform the
instrument cluster actuator test. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/INSTRUMENT CLUSTER - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING - ACTUATOR TEST). If the bulb
fails to operate during the actuator test, replace the
bulb. If the SKIS indicator still fails to light during
the bulb test, a wiring problem resulting in the loss
of battery current or ground to the Sentry Key Immo-
bilizer Module (SKIM) should be suspected, and thefollowing procedure should be used for diagnosis.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information.
NOTE: The following tests may not prove conclu-
sive in the diagnosis of this system. The most reli-
able, efficient, and accurate means to diagnose the
Sentry Key Immobilizer System requires the use of
a DRBIIITscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diag-
nostic information.
(1) Check the fused B(+) fuse in the Junction
Block (JB). If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the
shorted circuit or component and replace the faulty
fuse.
WJVEHICLE THEFT SECURITY 8Q - 5
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY (Continued)
Page 597 of 2199

(2) Check for battery voltage at the fused B(+) fuse
in the JB. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, repair the
open B(+) circuit between the JB fuse and the Power
Distribution Center (PDC).
(3) Check the fused ignition switch output (st-run)
fuse in the JB. If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, repair
the shorted circuit or component and replace the
faulty fuse.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Check for battery voltage at the fused ignition switch
output (st-run) fuse in the JB. If OK, go to Step 5. If
not OK, repair the open fused ignition switch output
(st-run) circuit between the JB fuse and the ignition
switch as required.
(5) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Disconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector for the Sentry Key Immobilizer Module
(SKIM) from the SKIM connector. Check for continu-
ity between the ground circuit of the instrument
panel wire harness connector for the SKIM and a
good ground. There should be continuity. If OK, go to
Step 6. If not OK, repair the open ground circuit.
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable. Check for
battery voltage at the fused B(+) circuit cavity of the
instrument panel wire harness connector for the
SKIM. If OK, go to Step 7. If not OK, repair the open
fused B(+) circuit between the SKIM and the JB
fuse.
(7) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Check for battery voltage at the fused ignition switch
output (st-run) circuit of the instrument panel wire
harness connector for the SKIM. If OK, refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information and use a
DRBIIItscan tool to complete the diagnosis of the
SKIS. If not OK, repair the open fused ignition
switch output (st-run) circuit between the SKIM and
the JB fuse.
SKIS INDICATOR FLASHES OR LIGHTS SOLID FOLLOWING
BULB TEST
A SKIS indicator that flashes following a successful
bulb test indicates that an invalid key has been
detected, or that a key-related fault has been set. A
SKIS indicator that lights solid following a successful
bulb test indicates that the SKIM has detected a sys-
tem malfunction or that the SKIS is inoperative. In
either case, fault information will be stored in the
SKIM memory. For retrieval of this fault information
and further diagnosis of the SKIS, the PCI data bus,
the SKIM message outputs to the instrument cluster,
the SKIM message outputs to the Body Control Mod-
ule (BCM), or the message inputs and outputs
between the SKIM and the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM), a DRBIIItscan tool and the appropriate
diagnostic information are required. Following are
preliminary troubleshooting guidelines to be followed
during diagnosis using a DRBIIItscan tool:(1) Using the DRBIIItscan tool, read and record
the faults as they exist in the SKIM when you first
begin your diagnosis of the vehicle. It is important to
document these faults because the SKIM does not
differentiate between historical and active faults. If
this problem turns out to be an intermittent condi-
tion, this information may become invaluable to your
diagnosis.
(2) Using the DRBIIItscan tool, erase all of the
faults from the SKIM.
(3) Cycle the ignition switch to the Off position,
then back to the On position.
(4) Using the DRBIIItscan tool, read any faults
that are now present in the SKIM. These are the
active faults.
(5) Using this active fault information, refer to the
proper procedure in the appropriate diagnostic infor-
mation for the additional specific diagnostic steps.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SKIS
INITIALIZATION
The Sentry Key Immobilizer System (SKIS) must
be initialized following a Sentry Key Immobilizer
Module (SKIM) replacement. SKIS initialization
requires the use of a DRBIIItscan tool. Initialization
will also require that you have access to the unique
four-digit PIN code that was assigned to the original
SKIM. The PIN codemustbe used to enter the
Secured Access Mode in the SKIM. This PIN number
may be obtained from the vehicle owner, from the
original vehicle invoice, or from the DaimlerChrysler
Customer Center. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELEC-
TRONIC CONTROL MODULES - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE - PCM/SKIM PROGRAMMING).
NOTE: If a Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is
replaced on a vehicle equipped with the Sentry Key
Immobilizer System (SKIS), the unique Secret Key
data must be transferred from the Sentry Key
Immobilizer Module (SKIM) to the new PCM using
the PCM replacement procedure. This procedure
also requires the use of a DRBIIITscan tool and the
unique four-digit PIN code to enter the Secured
Access Mode in the SKIM. Refer to the appropriate
diagnostic information for the proper PCM replace-
ment procedures.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SENTRY KEY
TRANSPONDER PROGRAMMING
All Sentry Keys included with the vehicle are pre-
programmed to work with the Sentry Key Immobi-
lizer System (SKIS) when it is shipped from the
8Q - 6 VEHICLE THEFT SECURITYWJ
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY (Continued)
Page 1874 of 2199

BODY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BODY
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WATER LEAKS........................1
WIND NOISE..........................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BODY
LUBRICATION.........................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRILLING AND
WELDING............................3
SPECIFICATIONS
BODY LUBRICANTS....................3
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE.............4
SPECIAL TOOLS
BODY...............................4DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE........5
DOOR - FRONT.........................11
DOORS - REAR.........................19
EXTERIOR.............................25
HOOD.................................33
INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEM.............36
INTERIOR..............................69
PAINT.................................81
SEATS................................83
STATIONARY GLASS.....................93
SUNROOF.............................96
WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS..................105
BODY STRUCTURE.....................112
BODY
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WATER LEAKS
Water leaks can be caused by poor sealing,
improper body component alignment, body seam
porosity, missing plugs, or blocked drain holes. Cen-
trifugal and gravitational force can cause water to
drip from a location away from the actual leak point,
making leak detection difficult. All body sealing
points should be water tight in normal wet-driving
conditions. Water flowing downward from the front of
the vehicle should not enter the passenger or luggage
compartment. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal water tight under all conditions. At
times, side glass or door seals will allow water to
enter the passenger compartment during high pres-
sure washing or hard driving rain (severe) condi-
tions. Overcompensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop a water leak that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After completing
a repair, water test vehicle to verify leak has stopped
before returning vehicle to use.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE WATER LEAK TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place, body
drains are clear, and body components are properly
aligned and sealed. If component alignment or seal-
ing is necessary, refer to the appropriate section of
this group for proper procedures.
WATER LEAK TESTS
WARNING: DO NOT USE ELECTRIC SHOP LIGHTS
OR TOOLS IN WATER TEST AREA. PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT.
When the conditions causing a water leak have
been determined, simulate the conditions as closely
as possible.
²If a leak occurs with the vehicle parked in a
steady light rain, flood the leak area with an open-
ended garden hose.
²If a leak occurs while driving at highway speeds
in a steady rain, test the leak area with a reasonable
velocity stream or fan spray of water. Direct the
spray in a direction comparable to actual conditions.
²If a leak occurs when the vehicle is parked on an
incline, hoist the end or side of the vehicle to simu-
late this condition. This method can be used when
the leak occurs when the vehicle accelerates, stops or
turns. If the leak occurs on acceleration, hoist the
front of the vehicle. If the leak occurs when braking,
hoist the back of the vehicle. If the leak occurs on left
turns, hoist the left side of the vehicle. If the leak
occurs on right turns, hoist the right side of the vehi-
cle. For hoisting recommendations refer to Group 0,
Lubrication and Maintenance, General Information
section.
WATER LEAK DETECTION
To detect a water leak point-of-entry, do a water
test and watch for water tracks or droplets forming
on the inside of the vehicle. If necessary, remove inte-
rior trim covers or panels to gain visual access to the
WJBODY 23 - 1