2003 GMC SIERRA DENALI service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 330 of 428

I Tires
Your new vehicle comes with high-quality tires made by
a leading tire manufacturer. If you ever have questions
about your
tire warranty and where to obtain service,
see your
GMC Warranty booklet for det+
Poorly maintained and improperly used tires
are dangerous.
0 Overloading your tires can cause
overheating as a result of too much
friction. You could have an air-out and a
serious accident. See "Loading Your
Vehicle" in the Index.
CAUTION: (Continued)
0 Underinflated tires pose the same danger
as overloaded tires. The resulting accident
could cause serious injury. Check all tires
frequently to maintain the recommended
pressure. Tire pressure should be checked
when your tires are cold.
0 Overinflated tires are more likely to be cut,
punctured or broken by a sudden impact
- such as when you hit a pothole.
Keep tires at the recommended pressure.
Worn, old tires can cause accidents. If
your tread
is badly worn, or if your tires
have been damaged, replace them.
5-6 1
Page 332 of 428
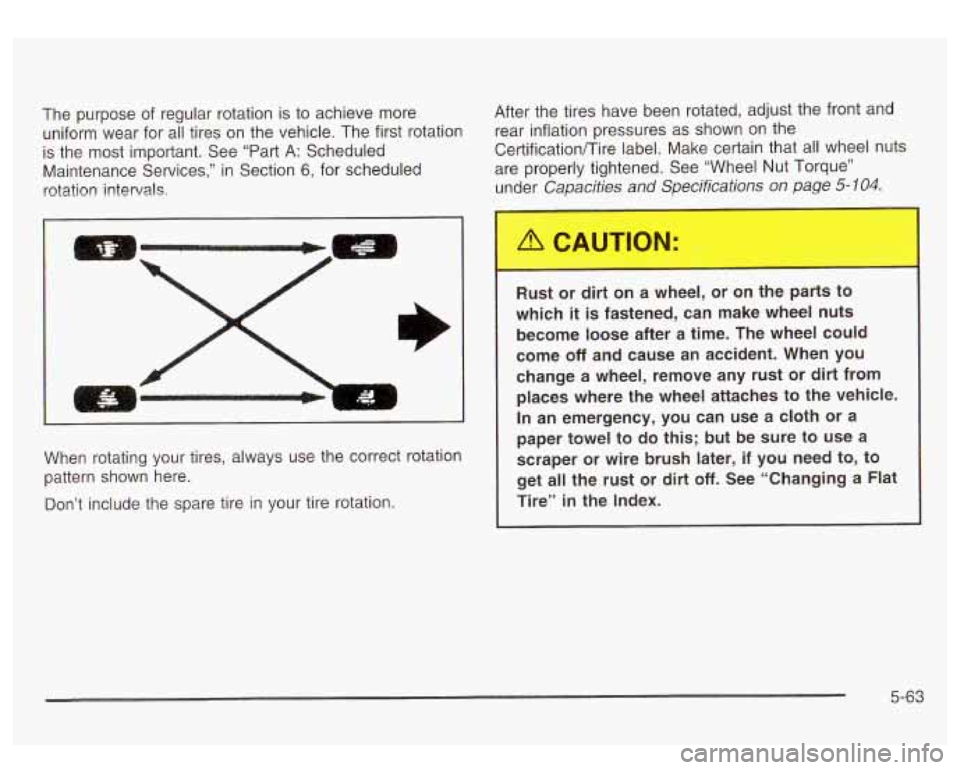
The purpose of regular rotation is to achieve more
uniform wear for all tires on the vehicle. The first rotation
is the most important. See “Part A: Scheduled
Maintenance Services,” in Section
6, for scheduled
rotation
intervals;
After the tires have been rotated, adjust the front and
rear inflation pressures as shown on the
CertificationEire label. Make certain that all wheel nuts
are properly tightened. See “Wheel Nut Torque”
under
Capacities and Specificatiol on ge 5-104.
When rotating your tires, always use the correct rotation
pattern shown here.
Don’t include the spare tire in your tire rotation. Rust or dirt on a
wheel, or on the parts to
which
it is fastened, can make wheel nuts
become loose after a time. The wheel could
come
off and cause an accident. When you
change a wheel, remove any rust or dirt from
places where the wheel attaches to the vehicle,
In an emergency, you can use a cloth or a
paper towel to do
this; but be sure to use a
scraper or wire brush later,
if you need to, to
get all the rust or dirt
off. See “Changing a Flal
Tire”
in the Index.
5-63
Page 333 of 428
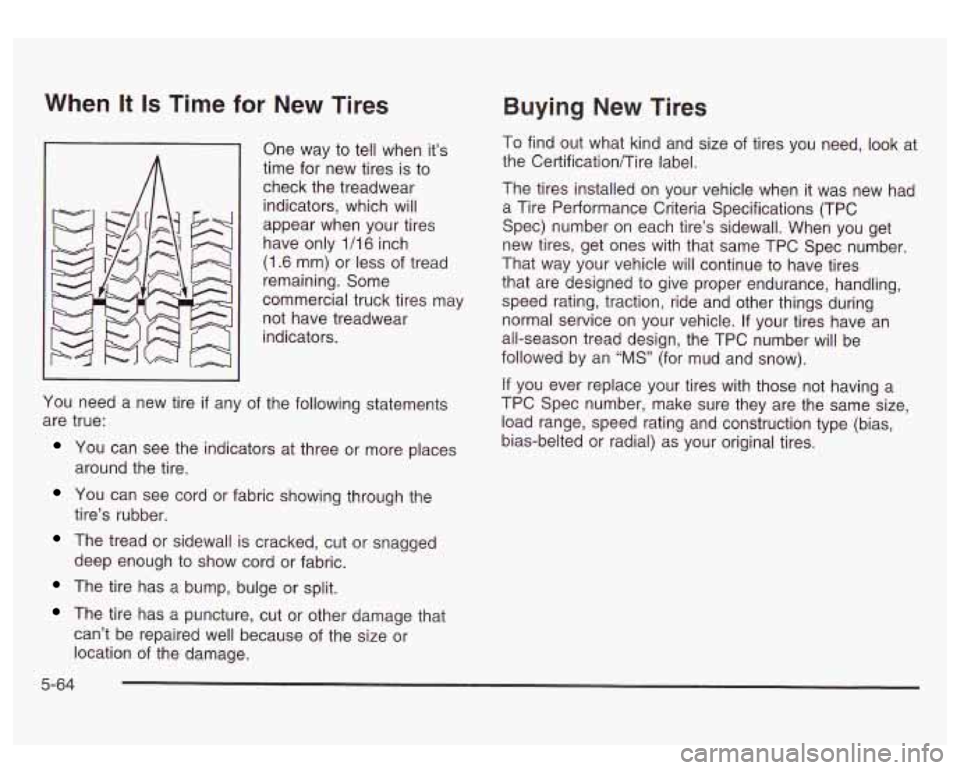
When It Is Time for New Tires
One way to tell when it’s
time for new tires is to
check the treadwear
indicators, which will
appear when your tires
have only 1/16 inch
(1.6 mm) or less of tread
remaining. Some
commercial truck tires may
not have treadwear
indicators.
You need a new tire
if any of the following statements
are true:
You can see the indicators at three or more places
You can see cord or fabric showing through the
The tread or sidewall is cracked, cut or snagged
The tire has a bump, bulge or split.
around
the tire.
tire’s rubber.
deep enough to show cord or fabric.
Buying New Tires
To find out what kind and size of tires you need, look at
the Certificationflire label.
The tires installed on your vehicle when it was new had
a Tire Performance Criteria Specifications (TPC
Spec) number on each tire’s sidewall. When you get
new tires, get ones with that same TPC Spec number.
That way your vehicle will continue to have tires
that are designed to give proper endurance, handling,
speed rating, traction, ride and other things during
normal service on your vehicle.
If your tires have an
all-season tread design, the TPC number will be
followed by an
“MS” (for mud and snow).
If you ever replace your tires with those not having a
TPC Spec number, make sure they are the same size,
load range, speed rating and construction type (bias,
bias-belted or radial) as your original tires.
The tire has a puncture, cut or other damage that
can’t be repaired well because of the size or
location of the damage.
5-64
Page 335 of 428

While the tires available on General Motors passenger
cars and light trucks may vary with respect
to these
grades, they must also conform to federal safety
requirements and additional General Motors Tire
Performance Criteria (TPC) standards.
Treadwear
The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on
the wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled
conditions on a specified government test course.
For example, a tire graded
150 would wear one and
a half
(1.5) times as well on the government course as
a tire graded
100. The relative performance of tires
depends upon the actual conditions of their use,
however, and may depart significantly from the norm
due to variations in driving habits, service practices and
differences in road characteristics and climate.
Traction - AA, A, B, C
The traction grades, from highest to lowest, are AA, A,
B, and C. Those grades represent the tire’s ability
to stop on wet pavement as measured under controlled
conditions on specified government test surfaces of
asphalt and concrete.
A tire marked C may have poor
traction performance. Warning: The traction grade
assigned to this tire is based on straight-ahead braking
traction tests, and does not include acceleration,
cornering, hydroplaning, or peak traction characteristics.
Temperature - A, B, C
The temperature grades are A (the highest), B, and C,
representing the tire’s resistance to the generation
of heat and its ability to dissipate heat when tested
under controlled conditions on a specified indoor
laboratory test wheel. Sustained high temperature can
cause the material of the tire to degenerate and
reduce tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to
sudden tire failure. The grade C corresponds
to a
level of performance which all passenger car tires must
meet under the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard
No. 109. Grades B and A represent higher levels of
performance on the laboratory test wheel than the
minimum required by law.
Warning: The temperature grade for this tire is
established for a tire that is properly inflated and not
overloaded. Excessive speed, underinflation, or
excessive loading, either separately or in combination.
can cause heat buildup and possible tire failure.
5-66
Page 360 of 428

Sheet Metal Damage
If your vehicle is damaged and requires sheet metal
repair or replacement, make sure the body repair shop
applies anti-corrosion material to parts repaired
or
replaced to restore corrosion protection.
Original manufacturer replacement parts will provide the
corrosion protection while maintaining the warranty.
Finish Damage
Any stone chips, fractures or deep scratches in the
finish should be repaired right away. Bare metal
will corrode quickly and may develop into major repair
expense.
Minor chips and scratches can be repaired with touch-up
materials avaliable from your dealer or other service
outlets. Larger areas of finish damage can be corrected
in your dealer’s body and paint shop.
Underbody Maintenance
Chemicals used for ice and snow removal and dust
control can collect on the underbody.
If these are not
removed, accelerated corrosion (rust) can occur on
the underbody parts such as fuel lines, frame, floor pan
and exhaust system even though they have corrosion
protection. At
least every spring, flush these materials from the
underbody with plain water. Clean any areas where mud
and debris can collect. Dirt packed in close areas of
the frame should be loosened before being flushed.
Your dealer or an underbody car washing system can
do this for you.
Chemical Paint Spotting
Some weather and atmospheric conditions can create a
chemical fallout. Airborne pollutants can fall upon and
attack painted surfaces on your vehicle. This damage
can take two forms; blotchy, ringlet-shaped
discolorations, and small irregular dark spots etched into
the paint surface.
Although no defect in the paint job causes this,
GM will
repair, at no charge to the owner, the surfaces of
new vehicles damaged by this fallout condition within
12 months or 12,000 miles (20 000 km) of purchase,
whichever occurs first.
5-91
Page 363 of 428

Vehicle Identification
Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
SAMPLE4UX1 M072675
This is the legal identifier for your vehicle. It appears on
a plate in the front corner of the instrument panel, on
the driver’s side. You can see it
if you look through the
windshield from outside your vehicle. The VIN also
appears on the Vehicle Certification and Service Parts
labels and the certificates of title and registration.
Engine Identification
The 8th character in your VIN is the engine code. This
code will help you identify your engine, specifications
and replacement parts.
Service Parts Identification Label
You’ll find this label located in the glove box. It’s very
helpful
if you ever need to order parts. On this label is:
your VIN,
the model designation,
paint information and
a list of all production options and special
equipment.
Be sure that this label is not removed from the vehicle.
5-94
Page 376 of 428
Section 6 Maintenance Schedule
Maintenance Schedule ...................................... 6.2
introduction
................................................... 6.2
Your Vehicle and the Environment
.................... 6-2
Maintenance Requirements
.............................. 6-2
How This Section is Organized
......................... 6-3
Part A: Scheduled Maintenance Services
........... 6-4
Using Your Maintenance Schedule
.................... 6-4
Scheduled Maintenance
................................... 6-5
Part
B: Owner Checks and Services ................ 6-10
At Each Fuel Fill
.......................................... 6-10
At Least Once a Month
................ ......... 6-10
At Least Twice a Year
............................... 6-11 At Least
Once a Year
................................... 6-11
Part
C: Periodic Maintenance Inspections ......... 6.14
Steering and Suspension Inspection
................ 6.14
Exhaust System inspection
............................ 6-14
Fuel System Inspection
.................................. 6.14
Engine Cooling System inspection
................... 6.14
(All-Wheel Drive) Inspection
........................ 6.15
Brake System Inspection
................................ 6.15
Part
D: Recommended Fluids and Lubricants .... 6-16
Part E: Maintenance Record
........................... 6.18
Transfer Case and
Front Axle
6- 1
Page 378 of 428

How This Section is Organized
This maintenance schedule is divided into five parts:
“Part
A: Scheduled Maintenance Services” explains
what to have done and how often. Some
of these
services can be complex,
so unless you are technically
qualified and have the necessary equipment, you
should
let your dealer’s service department or another
qualified service center do these jobs.
Perfc. ..ring rr.,.nte..,nce worl.
3n a vehicle can
be dangerous.
In trying to do some jobs, you
can be seriously injured.
Do your own
maintenance work only if you have the
required know-how and the proper tools and
equipment for the job. If you have any doubt,
have a qualified technician do the work.
I
If you want to get the service information, see Service
Publications Ordering Information on page
7- 10.
“Part B: Owner Checks and Services” tells you what
should be checked and when. It also explains what
you can easily do
to help keep your vehicle in good
condition.
“Part C: Periodic Maintenance Inspections” explains
important inspections that your dealer’s service
department or another qualified service center should
perform.
“Part
D: Recommended Fluids and Lubricants” lists
some recommended products necessary to help
keep your vehicle properly maintained. These products,
or their equivalents, should be used whether you do
the work yourself or have it done.
“Part
E: Maintenance Record” is a place for you to
record and keep track of the maintenance performed on
your vehicle. Keep your maintenance receipts. They
may be needed to qualify your vehicle for warranty
repairs.
6-3