2003 FORD WINDSTAR seats
[x] Cancel search: seatsPage 94 of 240
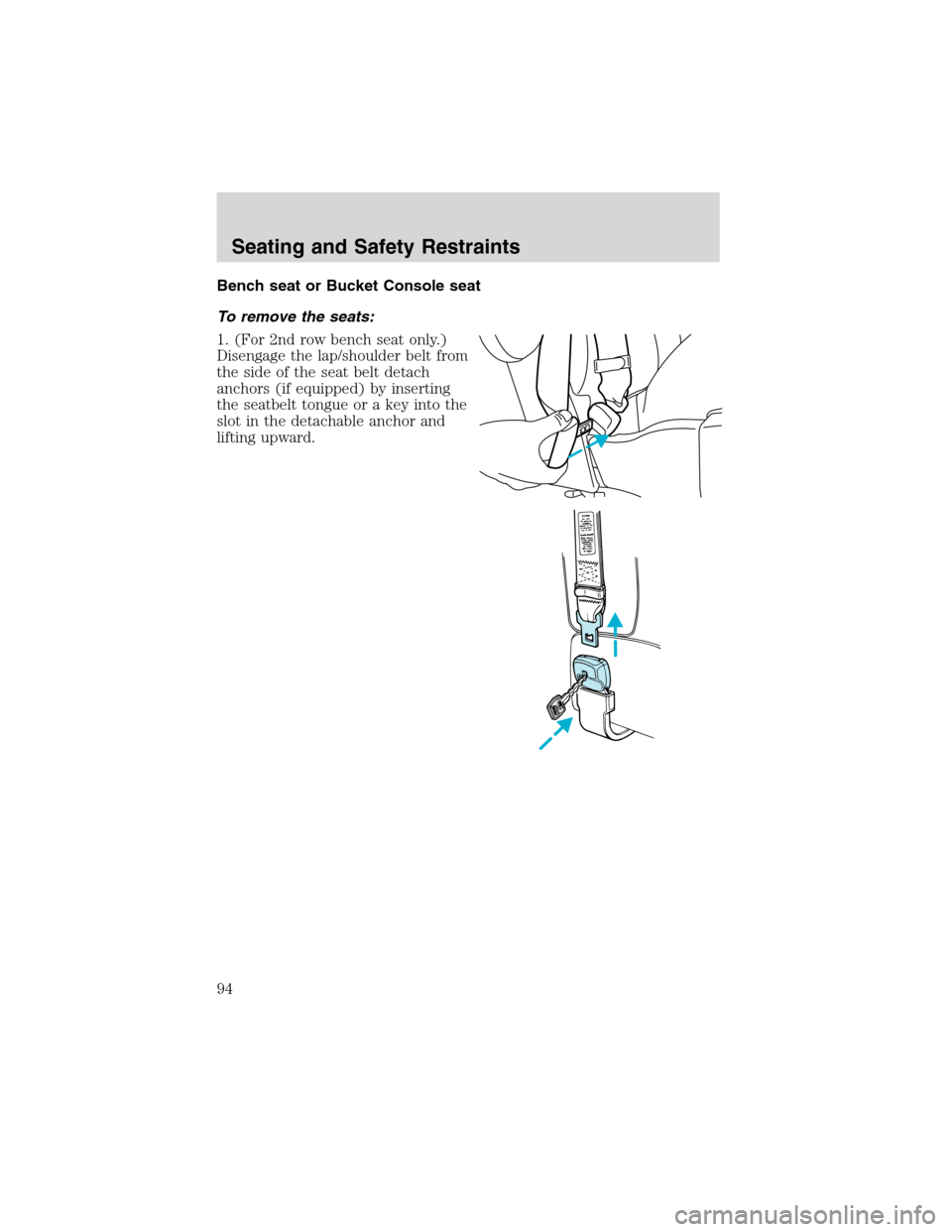
Bench seat or Bucket Console seat
To remove the seats:
1. (For 2nd row bench seat only.)
Disengage the lap/shoulder belt from
the side of the seat belt detach
anchors (if equipped) by inserting
the seatbelt tongue or a key into the
slot in the detachable anchor and
lifting upward.
Seating and Safety Restraints
94
Page 97 of 240
Always latch the vehicle seat to the floor, whether the seat is
occupied or empty. If not latched, the seat may cause injury
during a sudden stop.
Bucket seats
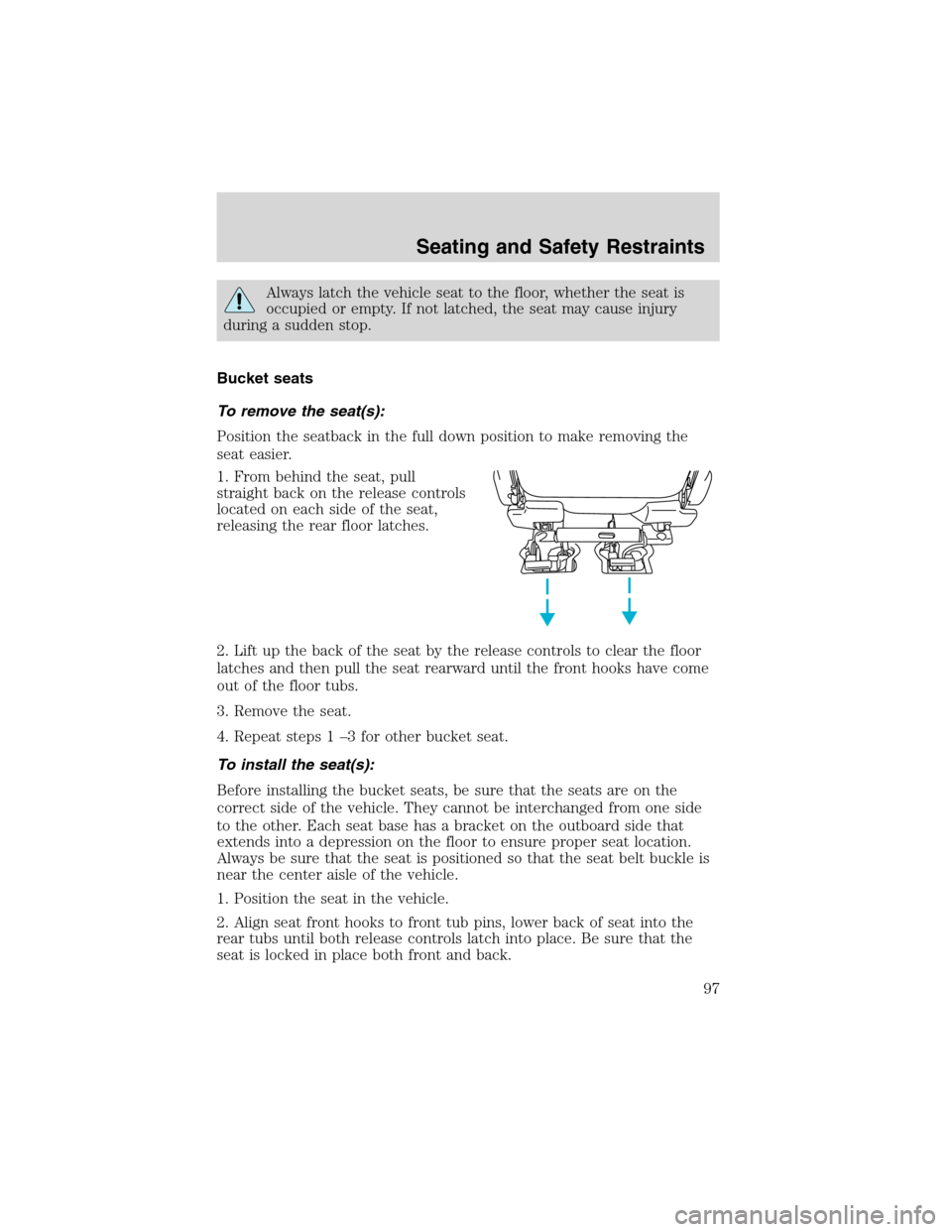
To remove the seat(s):
Position the seatback in the full down position to make removing the
seat easier.
1. From behind the seat, pull
straight back on the release controls
located on each side of the seat,
releasing the rear floor latches.
2. Lift up the back of the seat by the release controls to clear the floor
latches and then pull the seat rearward until the front hooks have come
out of the floor tubs.
3. Remove the seat.
4. Repeat steps 1–3 for other bucket seat.
To install the seat(s):
Before installing the bucket seats, be sure that the seats are on the
correct side of the vehicle. They cannot be interchanged from one side
to the other. Each seat base has a bracket on the outboard side that
extends into a depression on the floor to ensure proper seat location.
Always be sure that the seat is positioned so that the seat belt buckle is
near the center aisle of the vehicle.
1. Position the seat in the vehicle.
2. Align seat front hooks to front tub pins, lower back of seat into the
rear tubs until both release controls latch into place. Be sure that the
seat is locked in place both front and back.
Seating and Safety Restraints
97
Page 99 of 240

accident conditions (crash severity, belt usage, etc.) were not
appropriate to activate these safety devices. Front air bags and
pretensioners are designed to activate only in frontal and near-frontal
collisions, not rollovers, side-impacts, or rear-impacts unless the collision
causes sufficient longitudinal deceleration.
Driver and passenger dual-stage air bag supplemental restraints
The dual-stage air bags offer the capability to tailor the level of air bag
inflation energy. A lower, less forceful energy level is provided for more
common, moderate-severity impacts. A higher energy level is used for
the most severe impacts. Refer toAir bag supplemental restraints
section in this chapter.
Front crash severity sensor
The front crash severity sensor enhances the ability to detect the
severity of an impact. Positioned up front, it provides valuable
information early in the crash event on the severity of the impact. This
allows your Personal safety system to distinguish between different levels
of crash severity and modify the deployment strategy of the dual-stage
air bags and safety belt pretensioners.
Driver’s seat position sensor
The driver’s seat position sensor allows your Personal safety system to
tailor the deployment level of the driver dual-stage air bag based on seat
position. The system is designed to help protect smaller drivers sitting
close to the driver air bag by providing a lower air bag output level.
Passenger occupant classification sensor (OCS)
For air bags to do their job they must inflate with great force, and this
force can pose a potentially deadly risk to occupants that are very close
to the air bag when it begins to inflate. For some occupants, this occurs
because they are initially sitting very close to the air bag. For other
occupants, this occurs when the occupant is not properly restrained by
seat belts or child safety seats and they move forward during pre-crash
braking. The most effective way to reduce the risk of unnecessary
injuries is to make sure all occupants are properly restrained. Accident
statistics suggest that children are much safer when properly restrained
in the rear seating positions than in the front.
Air bags can kill or injure a child in a child seat.NEVERplace a
rear-facing child seat in front of an active air bag. If you must
use a forward-facing child seat in the front seat, move the seat all the
way back.
Seating and Safety Restraints
99
Page 101 of 240

The Restraints control module (RCM) monitors its own internal circuits
and the circuits for the air bag supplemental restraints, crash sensor(s),
safety belt pretensioners, front safety belt buckle sensors, driver seat
position sensor, and passenger occupant classification sensor. In addition,
the RCM also monitors the restraints warning light in the instrument
cluster. A difficulty with the system is indicated by one or more of the
following.
•The warning light will either flash or stay lit.
•The warning light will not illuminate immediately after ignition is
turned on.
•A series of five beeps will be heard. The tone pattern will repeat
periodically until the problem and warning light are repaired.
If any of these things happen, even intermittently, have the Personal
safety system serviced at your dealership or by a qualified technician
immediately. Unless serviced, the system may not function properly in
the event of a collision.
Safety belt precautions
Always drive and ride with your seatback upright and the lap
belt snug and low across the hips.
To reduce the risk of injury, make sure children sit where they
can be properly restrained.
Never let a passenger hold a child on his or her lap while the
vehicle is moving. The passenger cannot protect the child from
injury in a collision.
All occupants of the vehicle, including the driver, should always
properly wear their safety belts, even when an air bag (SRS) is
provided.
It is extremely dangerous to ride in a cargo area, inside or
outside of a vehicle. In a collision, people riding in these areas
are more likely to be seriously injured or killed. Do not allow people to
ride in any area of your vehicle that is not equipped with seats and
safety belts. Be sure everyone in your vehicle is in a seat and using a
safety belt properly.
Seating and Safety Restraints
101
Page 115 of 240

force, there is the risk of death or serious injuries such as fractures,
facial and eye injuries or internal injuries, particularly to occupants who
are not properly restrained or are otherwise out of position at the time
of air bag deployment. Thus, it is extremely important that occupants be
properly restrained as far away from the air bag module as possible while
maintaining vehicle control.
Several air bag system components get hot after inflation. Do not
touch them after inflation.
If the air bag has deployed,the air bag will not function
again and must be replaced immediately.If the air bag is not
replaced, the unrepaired area will increase the risk of injury in a
collision.
The SRS consists of:
•driver and passenger air bag modules (which include the inflators and
air bags).
•side air bags (if equipped). Refer toSide air bag systemlater in this
chapter.
•one or more impact and safing sensors.
•a readiness light and tone.
•diagnostic module.
•and the electrical wiring which connects the components.
The diagnostic module monitors its own internal circuits and the
supplemental air bag electrical system warning (including the impact
sensors), the system wiring, the air bag system readiness light, the air
bag back up power and the air bag ignitors.
Side air bag system (if equipped)
Do not place objects or mount equipment on or near the air bag
cover on the side of the seatbacks of the front seats or in front
seat areas that may come into contact with a deploying air bag. Failure
to follow these instructions may increase the risk of personal injury in
the event of a collision.
Seating and Safety Restraints
115
Page 116 of 240
Do not use accessory seat covers. The use of accessory seat
covers may prevent the deployment of the side air bags and
increase the risk of injury in an accident.
Do not lean your head on the door. The side air bag could injure
you as it deploys from the side of the seatback.
Do not attempt to service, repair, or modify the air bag SRS, its
fuses or the seat cover on a seat containing an air bag. See your
Ford or Lincoln Mercury dealer.
All occupants of the vehicle should always wear their safety belts
even when an air bag SRS is provided.
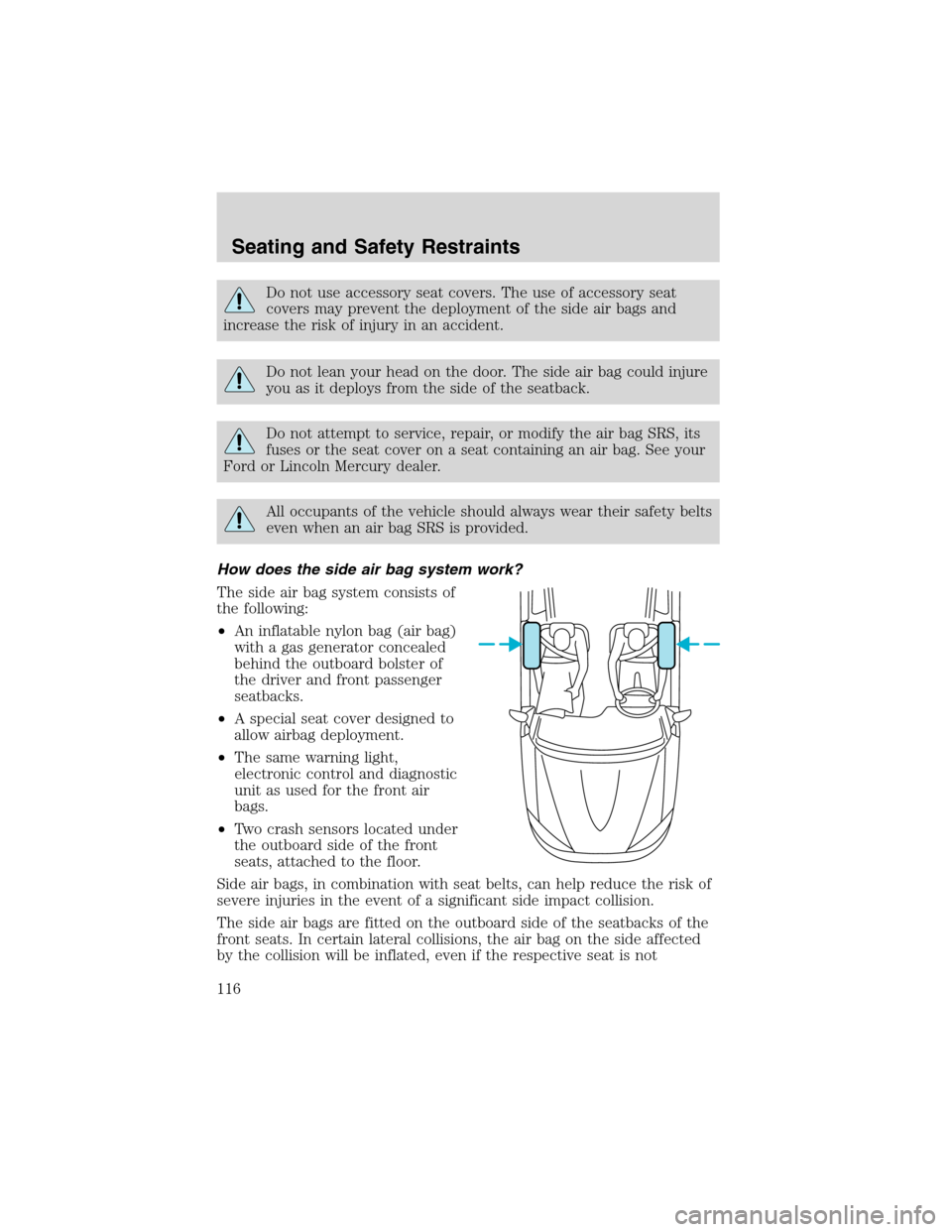
How does the side air bag system work?
The side air bag system consists of
the following:
•An inflatable nylon bag (air bag)
with a gas generator concealed
behind the outboard bolster of
the driver and front passenger
seatbacks.
•A special seat cover designed to
allow airbag deployment.
•The same warning light,
electronic control and diagnostic
unit as used for the front air
bags.
•Two crash sensors located under
the outboard side of the front
seats, attached to the floor.
Side air bags, in combination with seat belts, can help reduce the risk of
severe injuries in the event of a significant side impact collision.
The side air bags are fitted on the outboard side of the seatbacks of the
front seats. In certain lateral collisions, the air bag on the side affected
by the collision will be inflated, even if the respective seat is not
Seating and Safety Restraints
116
Page 118 of 240
![FORD WINDSTAR 2003 2.G Owners Manual or younger and who weigh 18 kg [40 lbs] or less) ride in your vehicle,
you must put them in safety seats made especially for children. Check
your local and state or provincial laws for specific requir FORD WINDSTAR 2003 2.G Owners Manual or younger and who weigh 18 kg [40 lbs] or less) ride in your vehicle,
you must put them in safety seats made especially for children. Check
your local and state or provincial laws for specific requir](/manual-img/11/5421/w960_5421-117.png)
or younger and who weigh 18 kg [40 lbs] or less) ride in your vehicle,
you must put them in safety seats made especially for children. Check
your local and state or provincial laws for specific requirements
regarding the safety of children in your vehicle. When possible, always
place children under age 12 in the rear seat of your vehicle. Accident
statistics suggest that children are safer when properly restrained in the
rear seating positions than in the front seating position.
Never let a passenger hold a child on his or her lap while the
vehicle is moving. The passenger cannot protect the child from
injury in a collision.
Always follow the instructions and warnings that come with any infant or
child restraint you might use.
Children and safety belts
If the child is the proper size, restrain the child in a safety seat. Children
who are too large for child safety seats (as specified by your child safety
seat manufacturer) should always wear safety belts.
Follow all the important safety restraint and air bag precautions that
apply to adult passengers in your vehicle.
If the shoulder belt portion of a combination lap and shoulder belt can
be positioned so it does not cross or rest in front of the child’s face or
neck, the child should wear the lap and shoulder belt. Moving the child
closer to the center of the vehicle may help provide a good shoulder belt
fit.
Do not leave children, unreliable adults, or pets unattended in
your vehicle.
Child booster seats
Children outgrow a typical convertible or toddler seat when they weigh
40 pounds and are around 4 years of age. Although the lap/shoulder belt
will provide some protection, these children are still too small for
lap/shoulder belts to fit properly, which could increase the risk of serious
injury.
To improve the fit of both the lap and shoulder belt on children who
have outgrown child safety seats, Ford Motor Company recommends use
of a belt-positioning booster.
Booster seats position a child so that safety belts fit better. They lift the
child up so that the lap belt rests low across the hips and the knees
Seating and Safety Restraints
118
Page 119 of 240

bend comfortably. Booster seats also make the shoulder belt fit better
and more comfortably for growing children.
When children should use booster seats
Children need to use booster seats from the time they outgrow the
toddler seat until they are big enough for the vehicle seat and
lap/shoulder belt to fit properly. Generally this is when they weigh about
80 lbs (about 8 to 12 years old).
Booster seats should be used until you can answer YES to ALL of these
questions:
•Can the child sit all the way back
against the vehicle seat back with
knees bent comfortably at the
edge of the seat without
slouching?
•Does the lap belt rest low across the hips?
•Is the shoulder belt centered on the shoulder and chest?
•Can the child stay seated like this for the whole trip?
Types of booster seats
There are two types of belt-positioning booster seats:
•Those that are backless.
If your backless booster seat has a
removable shield, remove the
shield and use the lap/shoulder
belt. If a seating position has a
low seat back and no head
restraint, a backless booster seat
may place your child’s head (top
of ear level) above the top of the
seat. In this case, move the
backless booster to another
seating position with a higher seat back and lap/shoulder belts.
Seating and Safety Restraints
119