2003 CHRYSLER CARAVAN seats
[x] Cancel search: seatsPage 1180 of 2177

ENGINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ENGINE 2.4L.............................. 1ENGINE 3.3/3.8L......................... 74
ENGINE 2.4L
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ENGINE 2.4L
DESCRIPTION..........................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION............3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE............4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL..............6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
LEAK INSPECTION.....................8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST.........9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST................................9
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE
AND OIL GALLERY PLUGS..............10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR OF
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS.........10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HYDROSTATIC
LOCKED ENGINE.....................10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-
PLACE GASKETS AND SEALERS.........11
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE
GASKET SURFACE PREPARATION........11
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
BEARING CLEARANCE USING
PLASTIGAGE........................12
REMOVAL - ENGINE ASSEMBLY...........13
INSTALLATION - ENGINE ASSEMBLY........16
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - 2.4L ENGINE.........17
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE............20
SPECIAL TOOLS
2.4L ENGINE.........................21AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL.............................24
INSTALLATION.........................24
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
REMOVAL.............................24
INSTALLATION.........................24
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION.........................24
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET............................24
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD.............25
CLEANING............................26
INSPECTION..........................26
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD..........26
CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL(S)
REMOVAL.............................27
INSTALLATION.........................28
CAMSHAFT(S)
DESCRIPTION.........................28
OPERATION...........................28
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
CAMSHAFT END PLAY.................29
REMOVAL.............................29
CLEANING............................29
INSPECTION..........................30
INSTALLATION.........................30
CYLINDER HEAD COVER
REMOVAL.............................31
CLEANING............................31
INSPECTION..........................31
INSTALLATION.........................31
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS
DESCRIPTION.........................32
CLEANING............................32
VALVE SPRINGS & SEALS
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD ON.........32
RSENGINE9-1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1185 of 2177
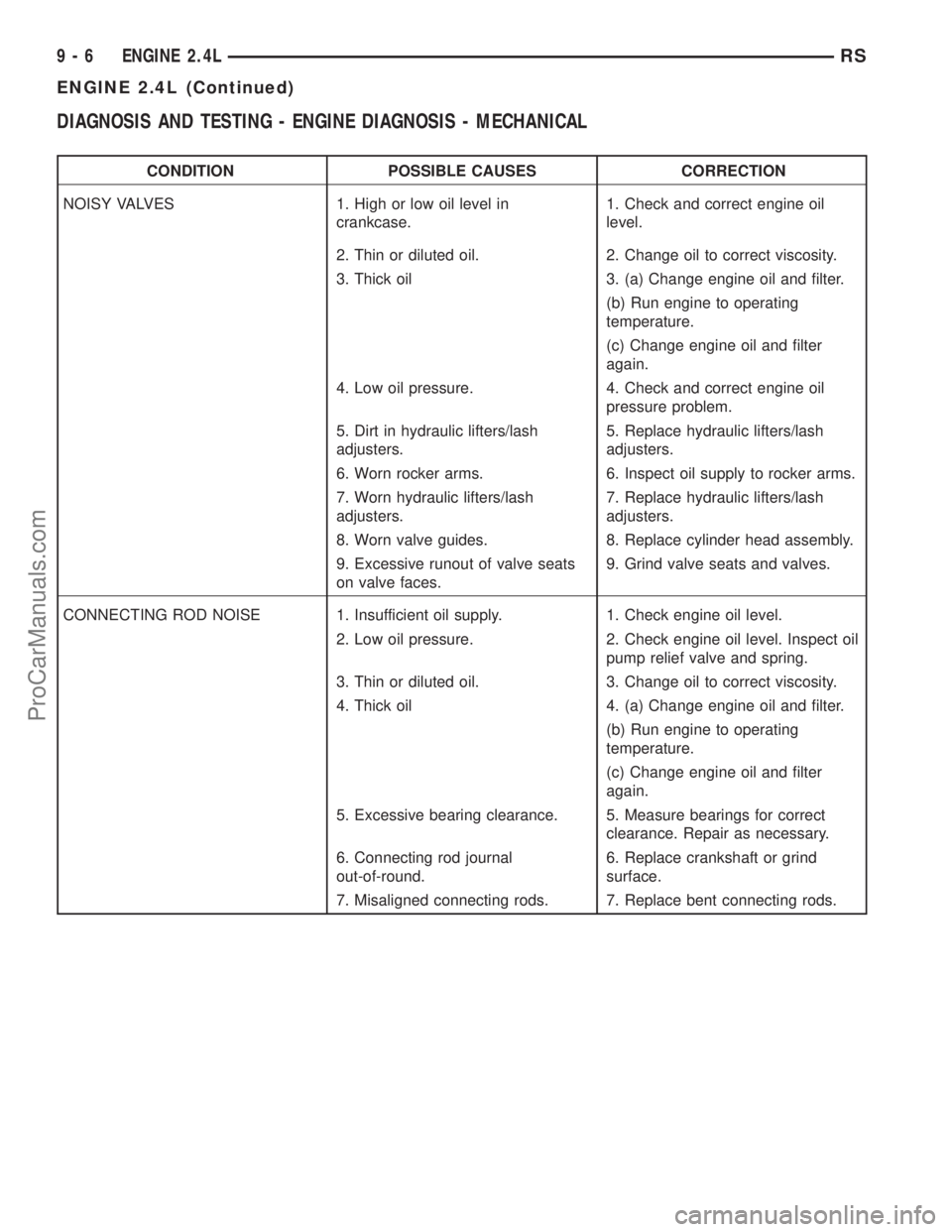
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. Check and correct engine oil
level.
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil to correct viscosity.
3. Thick oil 3. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
4. Low oil pressure. 4. Check and correct engine oil
pressure problem.
5. Dirt in hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.5. Replace hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.
6. Worn rocker arms. 6. Inspect oil supply to rocker arms.
7. Worn hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.7. Replace hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.
8. Worn valve guides. 8. Replace cylinder head assembly.
9. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.9. Grind valve seats and valves.
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil
pump relief valve and spring.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Thick oil 4. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
5. Excessive bearing clearance. 5. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary.
6. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.6. Replace crankshaft or grind
surface.
7. Misaligned connecting rods. 7. Replace bent connecting rods.
9 - 6 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1203 of 2177

AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Unsnap 2 clips.
(2) Lift cover and pull toward the engine and
remove cover tabs from air box.
(3) Lift cover and remove the element (Fig. 11).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the air filter element into air box (Fig.
11).
(2) Move cover so that the tabs insert into the air
box.
(3) Push cover down and snap the 2 clips.
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Disconnect the inlet air temperature sensor
(Fig. 12).
(3) Remove the inlet hose to throttle body (Fig. 11).
(4) Remove the bolt for air box at upper radiator
cross member.
(5) Pull air box up and off over the single locating
pin.
(6) Remove air box from vehicle
INSTALLATION
(1) Install air box into vehicle and onto the locat-
ing pin.(2) Install bolt to hold air box to the upper radia-
tor cross member.
(3) Install the inlet hose to the throttle body.
(4) Connect the inlet air temperature sensor (Fig.
12).
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The cross flow designed, aluminum cylinder head
contains dual over-head camshafts with four valves
per cylinder (Fig. 13). The valves are arranged in two
in-line banks. The intake valves face toward the
front of the vehicle. The exhaust valves face the dash
panel. The cylinder head incorporates powdered
metal valve guides and seats. The cylinder head is
sealed to the block using a multi-layer steel head
gasket and retaining bolts.
Integral oil galleries provide lubrication passages
to the hydraulic lash adjusters, camshafts, and valve
mechanisms.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
Fig. 11 AIR BOX COVER
Fig. 12 IAT SENSOR 2.4L
9 - 24 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1211 of 2177

(6) If the PCV valve was removed, apply Mopart
Thread Sealant with Teflon to threads and install
valve to cylinder head cover. Tighten PCV valve to 8
N´m (70 in. lbs.).
(7) Connect PCV and make-up air hoses to cylin-
der head cover.
(8) Install upper intake manifold. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION)
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS
DESCRIPTION
The valves are made of heat resistant steel. They
have chrome plated stems to prevent scuffing. Viton
rubber valve stem seals are integral with the spring
seats. The valves have three-bead lock keepers to
retain springs and to promote valve rotation.
CLEANING
(1) Clean all valves thoroughly and discard
burned, warped and cracked valves.
VALVE SPRINGS & SEALS
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD ON
(1) Remove cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove camshafts (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYL-
INDER HEAD/CAMSHAFT(S) - REMOVAL).
(3) Rotate crankshaft until piston is at TDC on
compression.
(4) With air hose attached to adapter tool installed
in spark plug hole, apply 90-120 psi air pressure.(5) Using Special Tool MD-998772-A with adapter
6779 (Fig. 33), compress valve springs and remove
valve locks.
(6) Remove valve spring(s).
(7) Remove valve stem seal(s) by a using valve
stem seal tool (Fig. 35).
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD OFF
(1) With cylinder head removed from cylinder
block, compress valve springs using a universal valve
spring compressor.
(2) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring
retainers, valve stem seals and valve springs.
(3) Before removing valves,remove any burrs
from valve stem lock grooves to prevent dam-
age to the valve guides.Identify valves, locks and
retainers to insure installation in original location.
(4) Inspect the valves. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYL-
INDER HEAD/VALVE SPRINGS - INSPECTION)
INSPECTION
(1) Whenever valves have been removed for inspec-
tion, reconditioning or replacement, valve springs
should be tested for correct tension. Discard the
springs that do not meet specifications. The following
specifications apply to both intake and exhaust
valves springs:
²Valve Closed Nominal TensionÐ76 lbs. @ 38.0
mm (1.50 in.)
²Valve Open Nominal TensionÐ136 lbs. @ 29.75
mm (1.17 in.)
(2) Inspect each valve spring for squareness with a
steel square and surface plate, test springs from both
ends. If the spring is more than 1.5 mm (1/16 inch)
out of square, install a new spring.
Fig. 32 Cylinder Head Cover Tightening Sequence
(Typical Cover Shown)
Fig. 33 Valve Spring - Removal/Installation
1 - VALVE SPRING COMPRESSOR MD 998772A
2 - AIR HOSE
9 - 32 ENGINE 2.4LRS
CYLINDER HEAD COVER (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1253 of 2177

ENGINE 3.3/3.8L
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L
DESCRIPTION.........................76
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION...........76
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE...........78
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL.............80
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
LEAK INSPECTION....................82
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST........83
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST...............................83
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
BEARING CLEARANCE USING
PLASTIGAGE........................84
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-
PLACE GASKETS AND SEALERS.........84
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE
GASKET SURFACE PREPARATION........85
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HYDROSTATIC
LOCKED ENGINE.....................85
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR OF
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS.........86
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE
AND OIL GALLERY PLUGS..............86
REMOVAL - ENGINE ASSEMBLY...........86
INSTALLATION - ENGINE ASSEMBLY........89
SPECIFICATIONS
3.3/3.8L ENGINE......................91
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE............95
SPECIAL TOOLS
3.3/3.8L ENGINE......................95
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL.............................98
INSTALLATION.........................98
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
REMOVAL.............................99
INSTALLATION.........................99
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION.........................99
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET............................99
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD............100
CLEANING...........................100INSPECTION.........................101
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD.........101
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
DESCRIPTION........................102
CYLINDER HEAD COVER - RIGHT
REMOVAL............................102
INSTALLATION........................103
CYLINDER HEAD COVER - LEFT
REMOVAL............................103
INSTALLATION........................103
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS
DESCRIPTION........................104
OPERATION..........................104
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFACING
VALVESANDVALVESEATS ............104
REMOVAL............................105
CLEANING...........................105
INSPECTION.........................105
INSTALLATION........................106
VALVE SPRINGS
DESCRIPTION........................106
OPERATION..........................106
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD OFF.......106
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD ON........106
INSPECTION.........................108
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD OFF . . . 108
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD ON....108
ROCKER ARMS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ROCKER ARMS.........109
DESCRIPTION - PUSHRODS...........109
OPERATION
OPERATION - ROCKER ARMS..........109
OPERATION - PUSHRODS.............109
REMOVAL - ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT....109
DISASSEMBLY - ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT. . 109
ASSEMBLY - ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT . . . 109
INSTALLATION - ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT..110
VALVE STEM SEALS
DESCRIPTION........................111
REMOVAL............................112
INSTALLATION........................112
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION........................112
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE
HONING............................112
CLEANING...........................112
9 - 74 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1259 of 2177
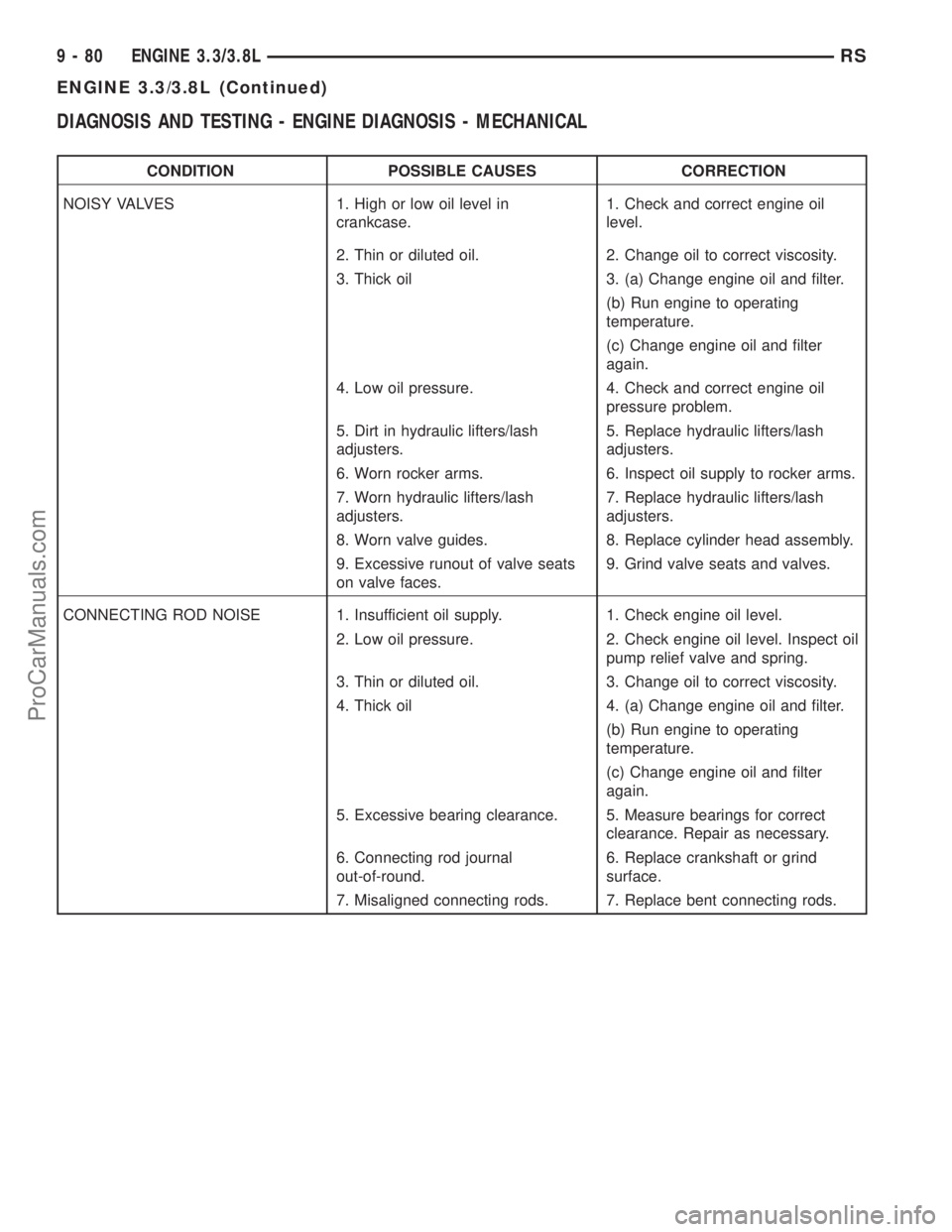
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. Check and correct engine oil
level.
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil to correct viscosity.
3. Thick oil 3. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
4. Low oil pressure. 4. Check and correct engine oil
pressure problem.
5. Dirt in hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.5. Replace hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.
6. Worn rocker arms. 6. Inspect oil supply to rocker arms.
7. Worn hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.7. Replace hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.
8. Worn valve guides. 8. Replace cylinder head assembly.
9. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.9. Grind valve seats and valves.
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil
pump relief valve and spring.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Thick oil 4. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
5. Excessive bearing clearance. 5. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary.
6. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.6. Replace crankshaft or grind
surface.
7. Misaligned connecting rods. 7. Replace bent connecting rods.
9 - 80 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1278 of 2177

AIR CLEANER HOUSING
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Disconnect the inlet air temperature sensor
(Fig. 16).
(3) Remove the inlet hose to throttle body.
(4) Remove the bolt for air box at upper radiator
cross member.
(5) Pull air box up and off over the single locating
pin.
(6) Remove air box from vehicle
INSTALLATION
(1) Install air box into vehicle and onto the locat-
ing pin.
(2) Install bolt to hold air box to the upper radia-
tor cross member.
(3) Install the inlet hose to the throttle body.
(4) Connect the inlet air temperature sensor (Fig.
16).
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The aluminum cylinder heads (Fig. 17) are
designed to create high flow combustion chambers to
improve performance, while minimizing the change
to the burn rate in the chamber. The cylinder head
incorporates the combustion chamber. Two valves
per-cylinder are used with inserted valve seats and
guides. A multi-layer steel (MLS) type gasket is used
between the cylinder head and engine block.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An
engine cylinder head gasket leaking between adja-
cent cylinders will result in approximately a 50±70%
reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
Fig. 16 Inlet Air Temperature Sensor
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-99
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1279 of 2177

CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD
(1) Drain the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Remove upper and lower intake manifolds.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANI-
FOLD - REMOVAL)
WARNING: INTAKE MANIFOLD GASKET IS MADE
OF VERY THIN METAL AND MAY CAUSE PER-
SONAL INJURY, HANDLE WITH CARE.
(4) Remove the cylinder head covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(5) Remove the spark plugs from cylinder head.(6) Remove the dipstick and tube (Fig. 18).
(7) Remove exhaust manifold(s). (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL)
(8) Remove rocker arm and shaft assemblies.(Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS -
REMOVAL) Remove push rods andmark positions
to ensure installation in original locations.
(9) Remove the eight head bolts from each cylinder
head and remove cylinder heads (Fig. 22).
CLEANING
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components and multi-layer
steel cylinder head gaskets.
NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets require
a scratch free sealing surface.
Remove all gasket material from cylinder head and
block (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCE-
Fig. 17 Cylinder Head and Components
1 - VALVE LOCKS 5 - SPRING SEATS
2 - RETAINERS 6 - CYLINDER HEAD
3 - VALVE SPRINGS 7 - VALVE - EXHAUST
4 - VALVE STEM SEALS 8 - VALVE - INTAKE
9 - 100 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com