2003 CHEVROLET CORVETTE weight
[x] Cancel search: weightPage 9 of 368
Different parts of the power seat control move different
parts of the seat. To move the seat forward or
rearward, move the control in that direction. Move the
control up to raise the seat and down to lower it.
By tilting the back of the control, it will raise or lower the
back of the seat. Tilting the front of the control will
raise or lower the front of the seat.
Your preferred seat position can be stored and recalled
if you have the memory option. See
Memory on
page 2-55.
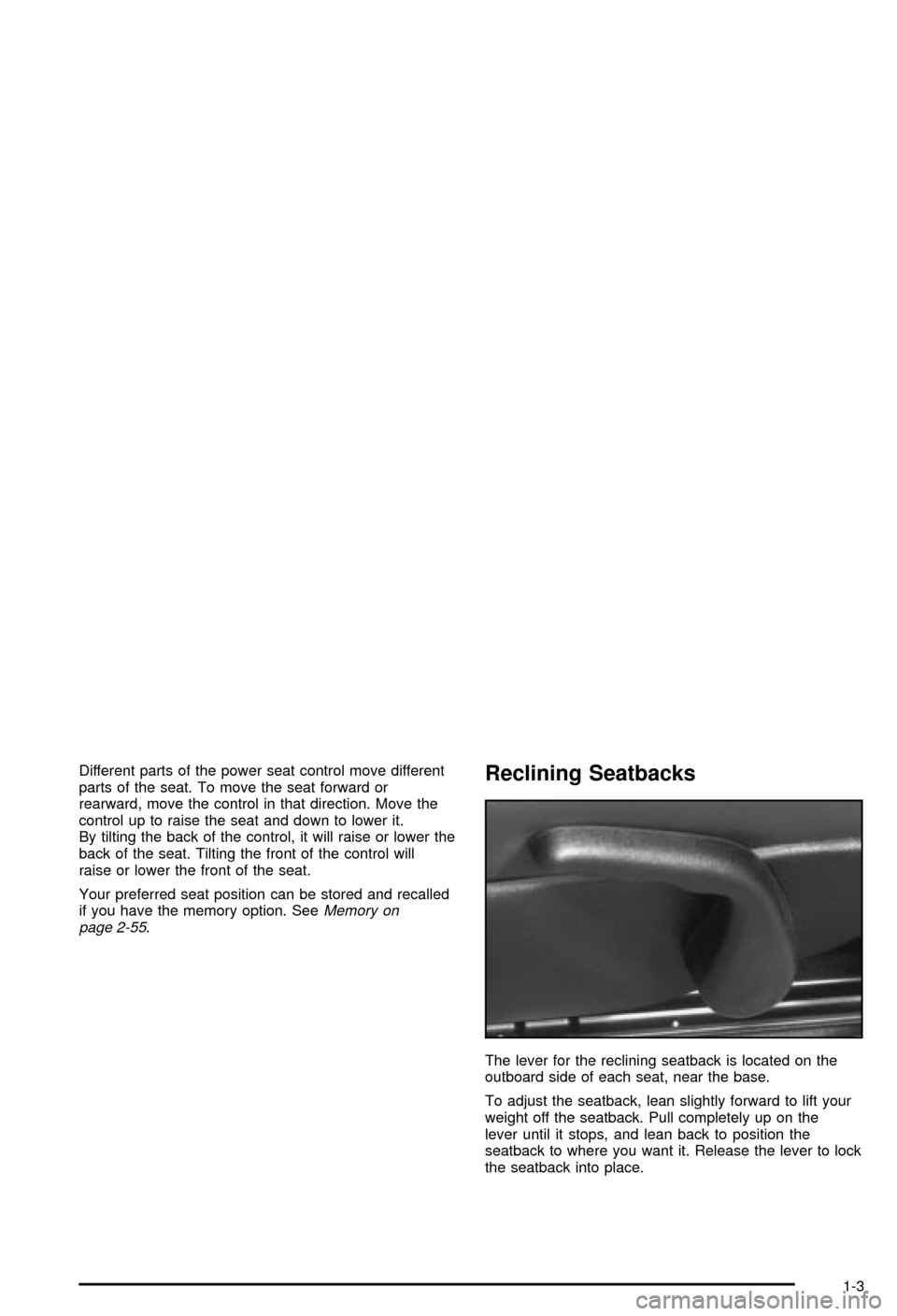
Reclining Seatbacks
The lever for the reclining seatback is located on the
outboard side of each seat, near the base.
To adjust the seatback, lean slightly forward to lift your
weight off the seatback. Pull completely up on the
lever until it stops, and lean back to position the
seatback to where you want it. Release the lever to lock
the seatback into place.
1-3
Page 31 of 368

Q:What are the different types of add-on child
restraints?
A:Add-on child restraints, which are purchased by
the vehicle's owner, are available in four basic
types. Selection of a particular restraint should take
into consideration not only the child's weight,
height and age but also whether or not the restraint
will be compatible with the motor vehicle in
which it will be used.
For most basic types of child restraints, there are
many different models available. When purchasing a
child restraint, be sure it is designed to be used
in a motor vehicle. If it is, the restraint will have a
label saying that it meets federal motor vehicle
safety standards.
The restraint manufacturer's instructions that come
with the restraint state the weight and height
limitations for a particular child restraint. In addition,
there are many kinds of restraints available for
children with special needs.
{CAUTION:
Newborn infants need complete support,
including support for the head and neck. This
is necessary because a newborn infant's neck
is weak and its head weighs so much
compared with the rest of its body. In a crash,
an infant in a rear-facing seat settles into the
restraint, so the crash forces can be
distributed across the strongest part of an
infant's body, the back and shoulders. Infants
always should be secured in appropriate infant
restraints.
1-25
Page 89 of 368

Torque Lock (Automatic Transmission)
If you are parking on a hill and you don't shift your
transmission into PARK (P) properly, the weight of the
vehicle may put too much force on the parking pawl
in the transmission. You may ®nd it difficult to pull the
shift lever out of PARK (P). This is called ªtorque
lock.º To prevent torque lock, set the parking brake and
then shift into PARK (P) properly before you leave
the driver's seat. To ®nd out how, see ªShifting
Into PARK (P)º listed previously in this section.
When you are ready to drive, move the shift lever out of
PARK (P)
beforeyou release the parking brake.
If torque lock does occur, you may need to have another
vehicle push yours a little uphill to take some of the
pressure from the parking pawl in the transmission, so
you can pull the shift lever out of PARK (P).
Shifting Out of Park (P)
(Automatic Transmission)
Your vehicle has an automatic transmission shift lock
control system. You have to fully apply your regular
brake before you can shift from PARK (P) when
the ignition is in ON. See
Automatic Transmission
Operation on page 2-24.
As a reminder, you will see a message in the Driver
Information Center (DIC) that will say PRESS BRAKE
BEFORE SHIFT within 15 seconds unless the brake
is pressed.
If you cannot shift out of PARK (P), ease pressure on
the shift lever ± push the shift lever all the way into
PARK (P) and release the shift lever button as
you maintain brake application. Then press the shift
lever button and move the shift lever into the gear
you wish.
2-33
Page 106 of 368
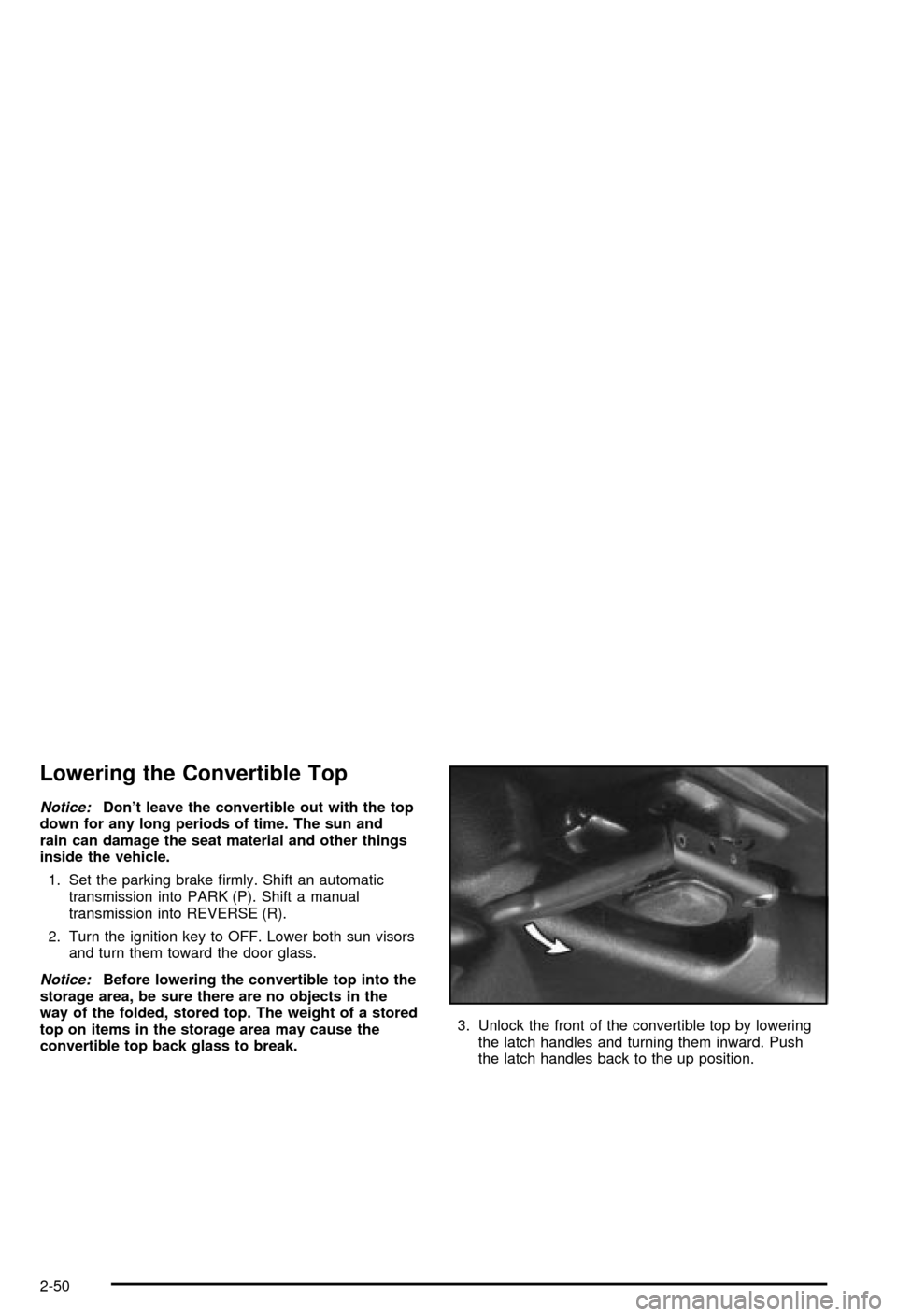

Lowering the Convertible Top
Notice:Don't leave the convertible out with the top
down for any long periods of time. The sun and
rain can damage the seat material and other things
inside the vehicle.
1. Set the parking brake ®rmly. Shift an automatic
transmission into PARK (P). Shift a manual
transmission into REVERSE (R).
2. Turn the ignition key to OFF. Lower both sun visors
and turn them toward the door glass.
Notice:Before lowering the convertible top into the
storage area, be sure there are no objects in the
way of the folded, stored top. The weight of a stored
top on items in the storage area may cause the
convertible top back glass to break.3. Unlock the front of the convertible top by lowering
the latch handles and turning them inward. Push
the latch handles back to the up position.
2-50
Page 195 of 368

Many adults Ð by some estimates, nearly half the adult
population Ð choose never to drink alcohol, so they
never drive after drinking. For persons under 21,
it's against the law in every U.S. state to drink alcohol.
There are good medical, psychological and
developmental reasons for these laws.
The obvious way to eliminate the leading highway
safety problem is for people never to drink alcohol and
then drive. But what if people do? How much is ªtoo
muchº if someone plans to drive? It's a lot less
than many might think. Although it depends on each
person and situation, here is some general information
on the problem.
The Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) of someone
who is drinking depends upon four things:
·The amount of alcohol consumed
·The drinker's body weight
·The amount of food that is consumed before and
during drinking
·The length of time it has taken the drinker to
consume the alcohol.
According to the American Medical Association, a 180 lb
(82 kg) person who drinks three 12 ounce (355 ml)
bottles of beer in an hour will end up with a BAC
of about 0.06 percent. The person would reach thesame BAC by drinking three 4 ounce (120 ml) glasses
of wine or three mixed drinks if each had 1-1/2 ounces
(45 ml) of liquors like whiskey, gin or vodka.
It's the amount of alcohol that counts. For example, if
the same person drank three double martinis (3 ounces
or 90 ml of liquor each) within an hour, the person's
BAC would be close to 0.12 percent. A person
who consumes food just before or during drinking will
have a somewhat lower BAC level.
4-3
Page 196 of 368

There is a gender difference, too. Women generally
have a lower relative percentage of body water
than men. Since alcohol is carried in body water, this
means that a woman generally will reach a higher BAC
level than a man of her same body weight will when
each has the same number of drinks.
The law in an increasing number of U.S. states, and
throughout Canada, sets the legal limit at 0.08 percent.
In some other countries, the limit is even lower. For
example, it is 0.05 percent in both France and Germany.
The BAC limit for all commercial drivers in the United
States is 0.04 percent.
The BAC will be over 0.10 percent after three to six
drinks (in one hour). Of course, as we've seen, it
depends on how much alcohol is in the drinks, and how
quickly the person drinks them.
But the ability to drive is affected well below a BAC of
0.10 percent. Research shows that the driving skills
of many people are impaired at a BAC approaching
0.05 percent, and that the effects are worse at night. All
drivers are impaired at BAC levels above 0.05 percent.Statistics show that the chance of being in a collision
increases sharply for drivers who have a BAC of
0.05 percent or above. A driver with a BAC level of
0.06 percent has doubled his or her chance of having a
collision. At a BAC level of 0.10 percent, the chance
of this driver having a collision is 12 times greater; at a
level of 0.15 percent, the chance is 25 times greater!
The body takes about an hour to rid itself of the alcohol
in one drink. No amount of coffee or number of cold
showers will speed that up. ªI'll be carefulº isn't the right
answer. What if there's an emergency, a need to
take sudden action, as when a child darts into the
street? A person with even a moderate BAC might not
be able to react quickly enough to avoid the collision.
There's something else about drinking and driving that
many people don't know. Medical research shows
that alcohol in a person's system can make crash
injuries worse, especially injuries to the brain, spinal
cord or heart. This means that when anyone who
has been drinking Ð driver or passenger Ð is in a
crash, that person's chance of being killed or
permanently disabled is higher than if the person had
not been drinking.
4-4
Page 198 of 368

Braking
Braking action involvesperception timeandreaction time.
First, you have to decide to push on the brake pedal.
That'sperception time.Then you have to bring up your
foot and do it. That'sreaction time.
Averagereaction timeis about 3/4 of a second. But
that's only an average. It might be less with one driver
and as long as two or three seconds or more with
another. Age, physical condition, alertness, coordination
and eyesight all play a part. So do alcohol, drugs and
frustration. But even in 3/4 of a second, a vehicle moving
at 60 mph (100 km/h) travels 66 feet (20 m). That
could be a lot of distance in an emergency, so keeping
enough space between your vehicle and others is
important.
And, of course, actual stopping distances vary greatly
with the surface of the road (whether it's pavement
or gravel); the condition of the road (wet, dry, icy); tire
tread; the condition of your brakes; the weight of
the vehicle and the amount of brake force applied.Avoid needless heavy braking. Some people drive
in spurts Ð heavy acceleration followed by heavy
braking Ð rather than keeping pace with traffic. This is
a mistake. Your brakes may not have time to cool
between hard stops. Your brakes will wear out much
faster if you do a lot of heavy braking. If you keep pace
with the traffic and allow realistic following distances,
you will eliminate a lot of unnecessary braking.
That means better braking and longer brake life.
If your engine ever stops while you're driving, brake
normally but don't pump your brakes. If you do,
the pedal may get harder to push down. If your engine
stops, you will still have some power brake assist.
But you will use it when you brake. Once the power
assist is used up, it may take longer to stop and
the brake pedal will be harder to push.
4-6
Page 225 of 368

Towing
Towing Your Vehicle
Consult your dealer or a professional towing service
if you need to have your disabled vehicle towed.
See
Roadside Assistance Program on page 7-6.
Recreational Vehicle Towing
Recreational vehicle towing means towing your vehicle
behind another vehicle Ð such as behind a motorhome.
The two most common types of recreational vehicle
towing are known as ªdinghy towingº (towing your
vehicle with all four wheels on the ground) and ªdolly
towingº (towing your vehicle with two wheels on
the ground and two wheels up on a device known as
a ªdollyº).
Your vehicle was not designed to be towed with any of
its wheels on the ground. If your vehicle must be
towed, see ªTowing Your Vehicleº earlier in this section.
Loading Your Vehicle
Two labels on your vehicle show how much weight it
may properly carry. The Tire-Loading Information
label found on the rear edge of the driver's door tells
you the proper size, speed rating and recommended
in¯ation pressures for the tires on your vehicle. It also
gives you important information about the number
of people that can be in your vehicle and the total weight
that you can carry. This weight is called the vehicle
capacity weight and includes the weight of all occupants,
cargo and all nonfactory-installed options.
4-33