2002 MAZDA 6 light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 430 of 909

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–15
K2
X : Available
End Of SiePOWERTRAIN DESCRIPTIONA6E571401030207Outline
•In the powertrain system, the hydraulic pressure transported by the control valve operates the clutch, and
brake, and the planetary gear changes the gear ratio according to the driving conditions.
Structure
•The powertrain system consists of seven pairs of clutches, brake, brake band, two pairs of one-way clutches,
and simple type planetary gears.
Duty
typePressure
control
solenoidXX XX X
2-4 brake
solenoid
valveXX XX X
High
clutch
solenoid
valveXX XX X
TCC
solenoid
valveXXX
CAN
signalReduce
torque
signalXXX
Range
signalX
Turbine
speed
signalX
ATF
temperatu
re signalX
TCC
signalXX
Racing
select
signalX
MIL
indicate
request
signalX
AT
warning
light
request
signalX ComponentControl item
Shift
controlLine
pressure
controlReverse
inhibition
controlShift
transient
controlFeedbac
k controlTCC
controlN-D
select
controlSlope
mode
controlOBD
system
Page 456 of 909

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–41
K2
OIL PUMP DESCRIPTIONA6E571419220201Outline
•The light-weight, compact, and quiet trochoid type oil pump reduces pump driving torque.
•The direct drive type oil pump is placed behind the torque converter.
Structure/Operation
•The outer rotor and inner rotor are installed in the oil pump housing.
•The inner rotor in the oil pump housing is driven by the torque converter.
•When the inner rotor in the oil pump rotates, the ATF is drawn to the oil pump. The discharge amount is
proportional to the rotating speed of the torque converter.
End Of Sie
AMU0517S015
AMU0517S016
Page 465 of 909

K2–50
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
CONTROLLER AREA NETWORK (CAN) DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901201Outline
•The TCM transmits/receives information using the CAN system. See Section T for detailed information
regarding the CAN system.
Structure/Operation
•The PCM inputs throttle opening angle, engine speed, engine torque, engine coolant temperature. to the TCM.
•The TCM operates shift and TCC controls based on the throttle opening angle, and controls line pressure and
other based on the throttle opening angle and the engine torque.
•The TCM outputs reduce torque signal, range signal, turbine speed, ATF temperature signal, and TCC signal to
the PCM.
•If there is an open or short circuit in the CAN wiring, the system determines that the CAN is abnormal and
switches to fail-safe mode.
Input
•Throttle position
•Engine torque (without torque down)
•Engine torque (with torque down)
•Engine torque (loss torque)
•Torque reduction request
•ECT
•Engine speed
•Buttery reconnection
Output
•Range position
•Turbine speed
•ATF temperature
•TCC
•Racing select
•Gear position
•Desired torque
•Desired gear position
•Upper torque limit
•Traveled distance
•MIL indicate request
•AT warning light indicate request
End Of Sie
Page 467 of 909

K2–52
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
Operation
Range determination
•Each range is determined by operating the selector lever, and switching ON/OFF the switch in the TR switch
internal circuit. The present range is detected according to the ON/OFF signal of the switch.
•The following switches are built into the TR switch, and determine each range when the switch is on.
P position switch
R position switch
N position switch
D range switch
End Of Sie
MANUAL MODE SHIFT CONTROL DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901204Outline
Features
•The manual mode shift control is activated by moving the selector lever from the D to M range position (selector
lever is shifted over toward front passenger side).
•Manual mode shift control with a manual shifting system allowing selection of gear positions by manual
operation of the selector lever forward (-) and back (+) has been adopted. Moreover, engine braking for all
gears in manual mode according to the gear ratio is available.
— Shifting between 1GR and 2GR when the vehicle is stopped is possible.
— When shifting from the D to M range while driving, the same gear position is maintained.
— Consecutive shifting in the M range has been adopted. When shifting down from M range 4GR or 3GR, one
gear can be skipped over by rapidly tapping the selector lever two times in the down-shift (-) direction.
•Selector lever position and gear position indicator lights, built into the instrument cluster, have been adopted.
— The selector indicator light includes a selector lever position indicator that displays selector lever positions
and, a gear position indicator light that displays gear positions.
Construction (system diagram)
.
9
8
7
5
43
12
10
18
17
15
16
14
1311
12
6
A6E5714W065
1PCM
2TCM
3Output
4 Ignition timing signal
5 Line pressure control signal
6 Clutch pressure control signal7Engine
8ATX
9 Indication
10 Selector indicator light
11 Gear position indicator light
12 AT warning light
Page 468 of 909

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–53
K2
Operation
Manual mode shift
•When the selector lever is shifted over from the D to M range position, the M range switch in the selector lever
component turns on, sending a manual mode command signal to the PCM which activates the manual mode
shift control.
•When in manual mode and the selector lever is operated in the back (+) direction, the up switch in the selector
lever component is turned on and an up-shift command signal is inputted to the PCM.
—The PCM, triggered by the up-shift command signal, carries out shifting by outputting an operation signal to
the shift solenoid if the ATF temperature is not low (for 3GR only), vehicle speed is higher than the set
speed and the gear position is 3GR or lower.
•Conversely, when the selector lever is operated in the forward (-) direction, the down switch in the selector lever
component turns on, and a down-shift command signal is inputted to the PCM.
—The PCM, triggered by the down-shift command signal, carries out shifting by outputting an operation
signal to the shift solenoid if the vehicle speed is less than the set speed and the gear position is 2GR or
above.
•The PCM utilizes a specialized M range automatic shift diagram when down shifting. This restriction of manual
downshifting is carried out to reduce load on the ATX and prevent engine over-revving.
13 Instrument cluster
14 Input15 Selector lever component
-M range switch
-Up switch
-Down switch
16 TR switch
17 ABS HU/CM or DSC HU/CM
18 TFT sensor
Condition Shift control Note
2GR→3GR up-shift command
at low speed•To reduce load on the ATX, upshifting is
inhibited until vehicle reaches speed
possible for upshifting
— 3GR→4GR up-shift command
at low speed
3GR→4GR up-shift command,
low ATF temperature•To reduce load on the ATX, upshifting to
4GR is inhibited
4GR→3GR down-shift
command, above set speed•To prevent engine over-rev, downshifting is
inhibited until vehicle reaches speed
possible for downshifting•Selector indicator “M” light and gear
position indicator light flash to alert
driver
3GR→2GR down-shift
command, above set speed
2GR→1GR down-shift
command, above set speed
In 4GR deceleration, speed
goes below coast-down set
speed (deceleration down-
shift)•To assure drive stability, automatically
downshifts from 4GR to 3GR
— In 3GR deceleration, speed
goes below coast-down set
speed (deceleration down-
shift)•To assure drive stability, automatically
downshifts from 3GR to 1GR
In 2GR deceleration, speed
goes below coast-down set
speed (deceleration down-
shift)•To assure driving stability, automatically
downshifts from 2GR to 1GR
Page 479 of 909
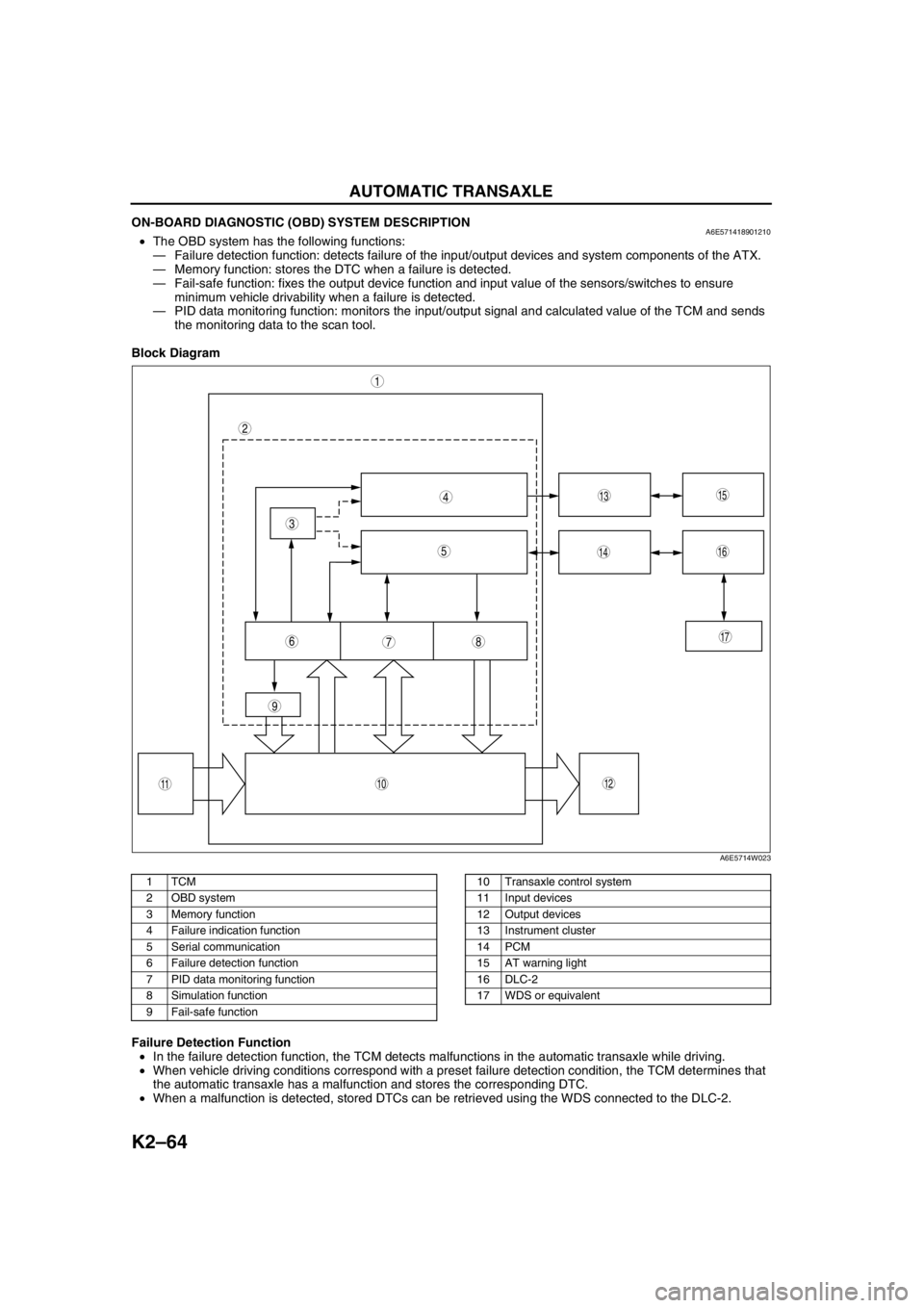
K2–64
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC (OBD) SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901210•The OBD system has the following functions:
—Failure detection function: detects failure of the input/output devices and system components of the ATX.
—Memory function: stores the DTC when a failure is detected.
—Fail-safe function: fixes the output device function and input value of the sensors/switches to ensure
minimum vehicle drivability when a failure is detected.
—PID data monitoring function: monitors the input/output signal and calculated value of the TCM and sends
the monitoring data to the scan tool.
Block Diagram
.
Failure Detection Function
•In the failure detection function, the TCM detects malfunctions in the automatic transaxle while driving.
•When vehicle driving conditions correspond with a preset failure detection condition, the TCM determines that
the automatic transaxle has a malfunction and stores the corresponding DTC.
•When a malfunction is detected, stored DTCs can be retrieved using the WDS connected to the DLC-2.
9
87
5
4
3
1
2
10
17
15
1614
13
1112
6
A6E5714W023
1TCM
2 OBD system
3 Memory function
4 Failure indication function
5 Serial communication
6 Failure detection function
7 PID data monitoring function
8 Simulation function
9 Fail-safe function10 Transaxle control system
11 Input devices
12 Output devices
13 Instrument cluster
14 PCM
15 AT warning light
16 DLC-2
17 WDS or equivalent
Page 480 of 909

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–65
K2
Memory Function
•The memory function stores failure information detected in the failure detection function. Once failure
information is stored, the memory will not be cleared even when the ignition switch is turned off (LOCK
position) or the malfunction is repaired.
•The stored memory (failure information) can be cleared by using the WDS or disconnecting the negative
battery cable.
Failure Indication Function
•The failure indication function illuminates the AT warning lights when the failure detection function determines
there is a malfunction.
DTC Table
X : Available
CCM:Continuous monitor
Fail-safe Function
•In the fail-safe function, minimum vehicle drivability is obtained by changing the signals that are determined as
malfunctions by the failure detection function to the preset values, and limiting the TCM control.
DTC No. On-board diagnostic function MILAT warning
light
indicationDCMonitor
itemMemory
function
P0705 TR switch circuit malfunction (Power short circuit) X X 2 CCM X
P0706 TR switch circuit malfunction (Open/ground short circuit) X X 2 CCM X
P0711 TFT sensor malfunction (Stuck) X–2 CCM X
P0712 TFT sensor circuit malfunction (Short circuit) X X 2 CCM X
P0713 TFT sensor circuit malfunction (Open circuit) X X 2 CCM X
P0715 Input/turbine speed sensor circuit malfunction X X 2 CCM X
P0720 Vehicle speedometer sensor circuit malfunction X X 2 CCM X
P0740 TCC system X–2 CCM X
P0743 TCC solenoid valve malfunction (Open/short) X X 1 CCM X
P0748 Pressure control solenoid malfunction (Open/short)–X–CCM X
P0751 Shift solenoid A malfunction (Stuck off) X–2 CCM X
P0752 Shift solenoid A malfunction (Stuck on) X–2 CCM X
P0753 Shift solenoid A malfunction (Open/short) X X 1 CCM X
P0756 Shift solenoid B malfunction (Stuck off) X–2 CCM X
P0757 Shift solenoid B malfunction (Stuck on) X–2 CCM X
P0758 Shift solenoid B malfunction (Open/short) X X 1 CCM X
P0761 Shift solenoid C malfunction (Stuck off) X–2 CCM X
P0762 Shift solenoid C malfunction (Stuck on) X–2 CCM X
P0763 Shift solenoid C malfunction (Open/short) X X 1 CCM X
P0768 Reduction timing solenoid malfunction (Open/short)–X–CCM X
P0773 Neutral shift solenoid malfunction (Open/short)–X–CCM X
P0778 2-4 brake solenoid malfunction (Open/short)–X–CCM X
P0791 Intermediate sensor malfunction (Open/short) X X 2 CCM X
P0798 High clutch solenoid malfunction (Open/short)–X–CCM X
P1710 GND return malfunction–––Other X
U0073 CAN BUS OFF X X 1 CCM X
U0100 TCM cannot receive any signals from PCM X X 1 CCM X
DTC
No.On-board diagnostic function Detection condition Fail-safe TCC
P0705Transaxle range (TR) switch
circuit malfunction (power short
circuit)•Two or more range signals
are inputted from TR switch
for 5 seconds or more•TR switch priority
D > N > P > R
•Inhibits feedback control,
SLOPE mode, torque
reduction controlAvailable
P0706Transaxle range (TR) switch
circuit malfunction (open/ground
short circuit)•No range signal is inputted
from TR switch for 100
seconds or more•Inhibits feedback control,
SLOPE mode, torque
reduction controlAvailable
Page 483 of 909

K2–68
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
Parameter Identification (PID) Access
Monitor item table
End Of Sie
Display on the
testerDefinitionUnit/
ConditionTCM
terminal
2-4 B Duty 2-4 brake solenoid valve control signal in TCM ON/OFF 2V
BOO Brake switch ON/OFF 1U
DWN_SW Down switch ON/OFF 1S
GEAR Calculated gear range in TCM1ST/2ND/
3RD/4TH/5TH–
H/C Duty High clutch solenoid valve control signal in TCM % 2U
LPS Pressure control solenoid control signal in TCM % 2Y
MNL_SW M range switch ON/OFF 1AA
NSFT TIM Neutral shift solenoid valve control signal in TCM ON/OFF 2D
OSS Intermediate sensor rpm 1K, 1X
PNP TR switch (P/N position switch) ON/OFF–
RDCN TIM Reduction timing solenoid valve control signal in TCM ON/OFF 2G
RPM Engine speed rpm–
SSA/SS1 Shift solenoid A control signal in TCM ON/OFF–
SSB/SS2 Shift solenoid B control signal in TCM ON/OFF–
SSC/SS3 Shift solenoid C control signal in TCM ON/OFF–
TCCC TCC solenoid valve control signal in TCM % 2S
TCIL AT warning light control signal in TCM ON/OFF 1E
TFT ATF temperature°C1B, 1F
TFTV ATF temperature signal voltage V 1B, 1F
THOP Throttle position %–
TRD Tr switch (D range switch) ON/OFF 1Z
TRR TR switch (R position switch) ON/OFF 1W
TSS Input/turbine speed sensor rpm 1N, 2F
UP_SW Up switch ON/OFF 2C
VPWR Battery voltage V 1P
VSS Vehicle speed km/h 1V, 1M