2002 MAZDA 6 diagram
[x] Cancel search: diagramPage 426 of 909

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–11
K2
End Of SieAUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE BLOCK DIAGRAMA6E571401030205
.
17 2-4 brake solenoid valve
18 High clutch solenoid valve
19 TCC solenoid valve
20 Shift solenoid A
21 Shift solenoid B
22 Shift solenoid C
23 Reduction timing solenoid valve24 Neutral shift solenoid valve
25 CAN_L
26 CAN_H
27 Instrument cluster
28 PCM
29 ABS HU/CM or DSC HU/CM
543
12
A6E5714W012
1 Input
2Output
3TCM
4PCM
ABS HU/CM or DSC HU/CM
TFT sensor
Input/turbine speed sensor
Intermediate sensor
VSS
TR switch
M range switch
Up switch
Down switch
Brake switch
Cruise control module5 Pressure control solenoid
2-4 brake solenoid valve
High clutch solenoid valve
TCC solenoid valve
Shift solenoid A
Shift solenoid B
Shift solenoid C
Reduction timing solenoid valve
Neutral shift solenoid valve
AT warning light
Page 427 of 909

K2–12
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
Electronic Control Item and Control
Component Description (Electronic Control)
Control item Contents
Shift control•Detects engine load condition and vehicle speed. Shifts to the best gear
position according to the programmed automatic shift diagram.
Line pressure control•Generates line pressure matching the engine load condition and driving
conditions. Optimizes line pressure for each shift. When the ATF
temperature is low, automatically optimizes line pressure for quick clutch
engagement.
Revers inhibition control•When the shift lever is shifted to R position while the vehicle is running
forward at approx. 30 km/h{19 mph} or more, the TCM turns the neutral
shift solenoid valve on and drains the low and reverse brake hydraulic
pressure. Due to this, the transaxle shifts to neutral.
Shift transient control•Adjusts transient hydraulic pressure according to engine load and
vehicle driving conditions when shifting using the pressure control
solenoid, 2-4 brake solenoid valve, the high clutch solenoid valve, and
each accumulator control valve.
•Temporarily lowers engine torque during shift (up and down) to improve
shift feel
•The lock timing for the reduction brake band is controlled by the control
of the reduction timing solenoid valve ON/OFF timing.
•The lock timing for the clutch brake is controlled by the control of shift
solenoid A, B, and C ON/OFF timing.
Feedback control•Corrects clutch engagement pressure and timing on drain side to
compensate for changes in engine performance and changes in
transaxle
TCC control•Controls TCC according to the programmed TCC points
N-D select control•When a driving range is selected from P/N, the fuel injection amount is
controlled to prevent fluctuation in engine speed.
Slope mode control•Changes the shift point to prevent frequent shifting up/down when
climbing hills
OBD system•Detects and/or memorizes failure of input/output part and transaxle
condition
Part name Function
Input system TR switch•Detects selector lever ranges/positions
Input/turbine speed sensor•Detects reverse clutch drum revolution speed
Intermediate sensor•Detects output gear revolution speed
Vehicle speedometer sensor•Detects parking gear revolution speed
TFT sensor•Detects the ATF temperature
Brake switch•Detects the brake pedal depressed
Cruise control module (in cruise actuator)•When the cruise control is in use, the signal detects when the
difference between the target speed and actual speed
exceeds specification
M range switch•Detects selector lever shifted M range
Up switch•Detects up shift in M range
Down switch•Detects down shift in M range
CAN signal Throttle position signal•Input throttle opening angle from PCM
Engine torque signal
(without torque down)•Input engine torque from PCM
Engine torque signal (with
torque down)•Input engine torque from PCM
Engine torque signal (loss
torque)•Input engine loss torque from PCM
Torque reduced signal•Detects signals indicating torque down availability
Engine coolant
temperature signal•Input engine coolant temperature from PCM
Engine speed signal•Input engine speed from PCM
Battery OFF signal•Detect negative battery cable disconnected
4 wheel speed signal•Input wheel speed from ABS HU/CM or DSC HU/CM
Page 466 of 909
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–51
K2
TRANSAXLE CONTROL MODULE (TCM) DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901202Outline
•The TCM controls the automatic transaxle operations. The TCM outputs a control signal to the transaxle
according to the signal from other sensors and/or switches.
•In driving mode, there are three mode selections: NORMAL, high temp, and SLOPE. The TCM automatically
selects the proper mode according to driving condition.
End Of Sie
SHIFT CONTROL DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901203Outline
Features
•The TCM selects and determines the shift diagram based on the results of the range and driving mode
judgements. Then, based on the shift diagram, the TCM sends the signal to the duty-cycle type solenoid valves
and the ON/OFF type solenoid valves, according to the VSS signal and the throttle opening signal, to perform
shifting.
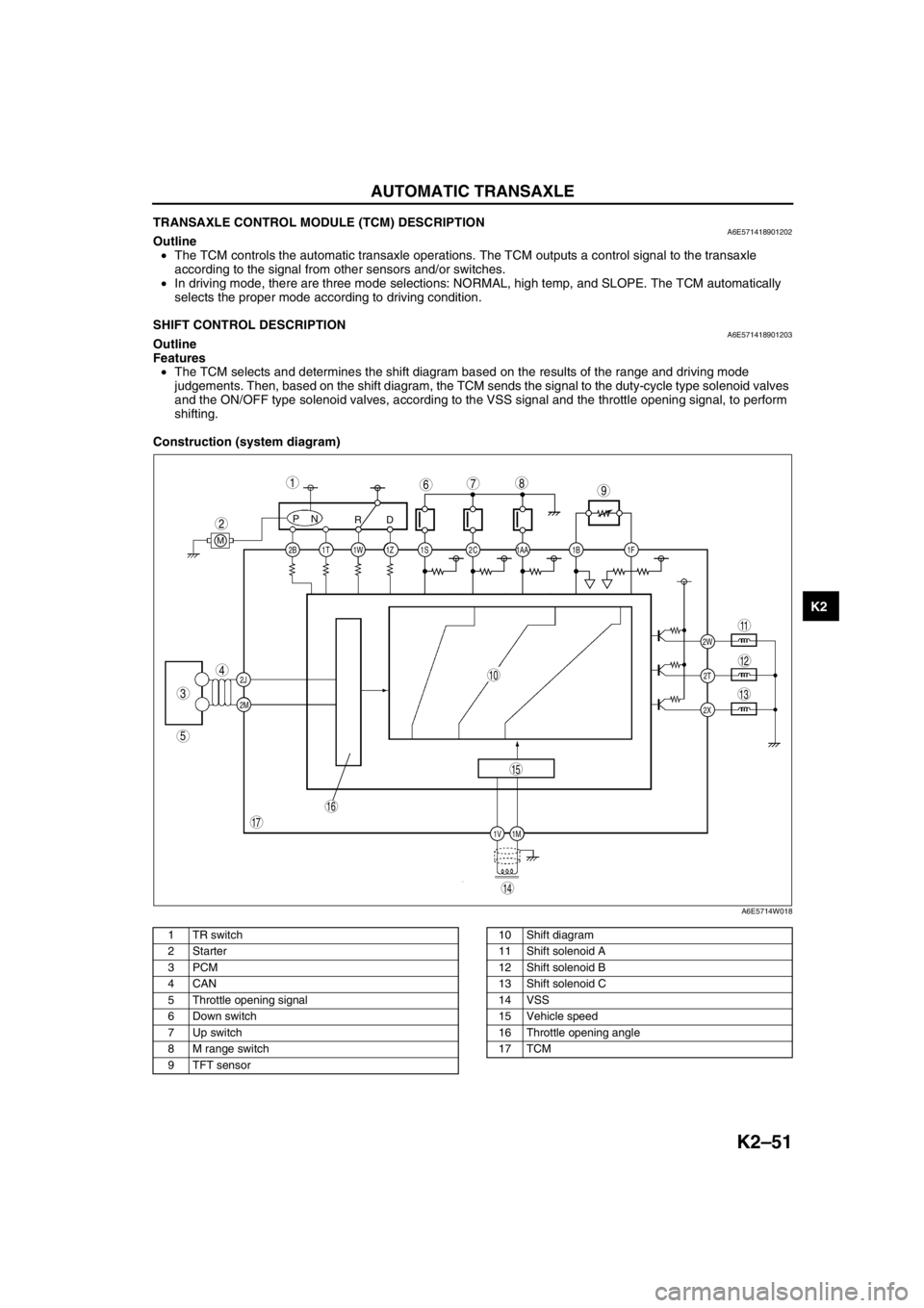
Construction (system diagram)
.
2C 2B
2J
2M1AA 1S 1T 1Z1W 1B 1F
2W
1M 1V2T
2X
PN
RD
M
987
5
4
3
1
2
10
17
15
16
14
13
11
12
6
A6E5714W018
1 TR switch
2Starter
3PCM
4CAN
5 Throttle opening signal
6 Down switch
7 Up switch
8 M range switch
9 TFT sensor10 Shift diagram
11 Shift solenoid A
12 Shift solenoid B
13 Shift solenoid C
14 VSS
15 Vehicle speed
16 Throttle opening angle
17 TCM
Page 467 of 909

K2–52
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
Operation
Range determination
•Each range is determined by operating the selector lever, and switching ON/OFF the switch in the TR switch
internal circuit. The present range is detected according to the ON/OFF signal of the switch.
•The following switches are built into the TR switch, and determine each range when the switch is on.
P position switch
R position switch
N position switch
D range switch
End Of Sie
MANUAL MODE SHIFT CONTROL DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901204Outline
Features
•The manual mode shift control is activated by moving the selector lever from the D to M range position (selector
lever is shifted over toward front passenger side).
•Manual mode shift control with a manual shifting system allowing selection of gear positions by manual
operation of the selector lever forward (-) and back (+) has been adopted. Moreover, engine braking for all
gears in manual mode according to the gear ratio is available.
— Shifting between 1GR and 2GR when the vehicle is stopped is possible.
— When shifting from the D to M range while driving, the same gear position is maintained.
— Consecutive shifting in the M range has been adopted. When shifting down from M range 4GR or 3GR, one
gear can be skipped over by rapidly tapping the selector lever two times in the down-shift (-) direction.
•Selector lever position and gear position indicator lights, built into the instrument cluster, have been adopted.
— The selector indicator light includes a selector lever position indicator that displays selector lever positions
and, a gear position indicator light that displays gear positions.
Construction (system diagram)
.
9
8
7
5
43
12
10
18
17
15
16
14
1311
12
6
A6E5714W065
1PCM
2TCM
3Output
4 Ignition timing signal
5 Line pressure control signal
6 Clutch pressure control signal7Engine
8ATX
9 Indication
10 Selector indicator light
11 Gear position indicator light
12 AT warning light
Page 468 of 909

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–53
K2
Operation
Manual mode shift
•When the selector lever is shifted over from the D to M range position, the M range switch in the selector lever
component turns on, sending a manual mode command signal to the PCM which activates the manual mode
shift control.
•When in manual mode and the selector lever is operated in the back (+) direction, the up switch in the selector
lever component is turned on and an up-shift command signal is inputted to the PCM.
—The PCM, triggered by the up-shift command signal, carries out shifting by outputting an operation signal to
the shift solenoid if the ATF temperature is not low (for 3GR only), vehicle speed is higher than the set
speed and the gear position is 3GR or lower.
•Conversely, when the selector lever is operated in the forward (-) direction, the down switch in the selector lever
component turns on, and a down-shift command signal is inputted to the PCM.
—The PCM, triggered by the down-shift command signal, carries out shifting by outputting an operation
signal to the shift solenoid if the vehicle speed is less than the set speed and the gear position is 2GR or
above.
•The PCM utilizes a specialized M range automatic shift diagram when down shifting. This restriction of manual
downshifting is carried out to reduce load on the ATX and prevent engine over-revving.
13 Instrument cluster
14 Input15 Selector lever component
-M range switch
-Up switch
-Down switch
16 TR switch
17 ABS HU/CM or DSC HU/CM
18 TFT sensor
Condition Shift control Note
2GR→3GR up-shift command
at low speed•To reduce load on the ATX, upshifting is
inhibited until vehicle reaches speed
possible for upshifting
— 3GR→4GR up-shift command
at low speed
3GR→4GR up-shift command,
low ATF temperature•To reduce load on the ATX, upshifting to
4GR is inhibited
4GR→3GR down-shift
command, above set speed•To prevent engine over-rev, downshifting is
inhibited until vehicle reaches speed
possible for downshifting•Selector indicator “M” light and gear
position indicator light flash to alert
driver
3GR→2GR down-shift
command, above set speed
2GR→1GR down-shift
command, above set speed
In 4GR deceleration, speed
goes below coast-down set
speed (deceleration down-
shift)•To assure drive stability, automatically
downshifts from 4GR to 3GR
— In 3GR deceleration, speed
goes below coast-down set
speed (deceleration down-
shift)•To assure drive stability, automatically
downshifts from 3GR to 1GR
In 2GR deceleration, speed
goes below coast-down set
speed (deceleration down-
shift)•To assure driving stability, automatically
downshifts from 2GR to 1GR
Page 469 of 909

K2–54
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
Shift diagram
.
End Of SieLINE PRESSURE CONTROL DESCRIPTIONA6E571418901205Outline
Features
•Line pressure is hydraulic pressure for operating friction elements such as the multiple disc clutches, multiple
disc brakes, and the brake band.
•To adjust to optimal line pressure according to engine load conditions and vehicle driving conditions,
continuous variable line pressure control from the pressure control solenoid is used.
•The line pressure control includes the basic control, line pressure control when shifting, backup control, and
other.
8/8
4/8
0/813
3
1
2 4
4
5 1
2
0{0} 20{12} 40{25} 60{37} 80{50} 100{62} 120{74} 140{87} 160{99}
180{112}200{124}
220{136}
2
3
34 4 5
7
5
43
1
2
6
A6E5714W070
1 TCC operation available
2 Throttle opening
3 TCC operation OFF
4 TCC operation ON5 Vehicle speed (km/h {mph})
6 Down shifting is inhibited until vehicle reaches
speed possible for downshifting
7 When decelerating below set vehicle speed,
executes automatic downshifting
Page 470 of 909

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
K2–55
K2
Construction (System diagram)
.
1T 1Z 1W
1AA
2C 2Y
1S
1H2B 1K
1X
1M
1V
1N
2F
2J
2M
1F
1B
9
8
7
5
4
3
1
2
10
17
15
16
14
13
11
12
6
A6E5714W019
1 Intermediate sensor
2 VSS
3 Input/turbine speed sensor
4 Throttle position signal
5 Engine torque signal
6 TFT sensor
7TCM8TR switch
9 Pressure control solenoid
10 M range switch
11 Up switch
12 Down switch
13 Cruise control module
Page 473 of 909

K2–58
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
Construction (system diagram)
.
1T 1Z 1W
2B
2Y
2V
2U
2P 1K
1X 1M
1V
1N
2F
2J
2M
1F
1B
9
8
7
5
4
3
1
2
10
19
18
17
15
16
14
13
11
12
6
A6E5714W020
1 VSS
2 Input/turbine speed sensor
3 Intermediate sensor
4 Input5 Throttle position signal
Torque reduce signal
Engine torque signal
6Output
7 Reduce torque signal