2002 MAZDA 6 oil
[x] Cancel search: oilPage 159 of 909

OUTLINE
F2–7
F2
End Of Sie
11 Generator
12 Oil pressure switch
13 Sedimentor switch
14 Instrument cluster
15 Neutral switch
16 Clutch switch
17 Coil
18 Brake switch
19 Brake switch 2
20 Cruise control switch
21 With cruise control system
22 PCM control relay
23 MAF/IAT sensor
24 Calibration resistor No.1
25 Fuel injector No.1
26 Calibration resistor No.2
27 Fuel injector No.2
28 Calibration resistor No.3
29 Fuel injector No.3
30 Calibration resistor No.4
31 Fuel injector No.4
32 CMP sensor
33 CKP sensor
34 EGR solenoid valve (vacuum)
35 EGR solenoid valve (vent)
36 VSC solenoid valve
37 Intake shutter solenoid valve (half)38 Intake shutter solenoid valve (full)
39 VBC solenoid valve
40 EGR control solenoid valve
41 Boost sensor
42 Accelerator position sensor
43 Idle switch
44 Fuel pressure sensor
45 ECT sensor
46 Fuel temperature sensor
47 Suction control valve
48 IAT sensor No.2
49 Cooling fan relay No.2
50 Cooling fan No.1
51 Refrigerant pressure switch (middle)
52 A/C switch
53 A/C amplifier
54 Cooling fan relay No.1
55 Cooling fan No.2
56 A/C relay
57 Refrigerant pressure switch (HI and LO)
58 Magnetic clutch
59 With A/C
60 Glow plug relay
61 Glow plug
62 Vacuum switch
63 Fuel warmer
64 With fuel warmer
Page 190 of 909
F2–38
INTAKE-AIR SYSTEM
TURBOCHARGER INSPECTIONA6E401013700201
Note
•If the following problems exist, diagnosis the turbocharger using the following symptom troubleshooting
procedures.
1. Lack of power: perform “NO.12 LACK/LOSS OF POWER”. (See F2–195 NO.12 LACK/LOSS OF POWER-
ACCELERATION/CRUISE.)
2. Oil leak: perform “NO.16 HIGH OIL CONSUMPTION/LEAKAGE”. (See F2–209 NO.16 HIGH OIL
CONSUMPTION/LEAKAGE.)
3. Noise: perform “NO. 21 ENGINE NOISE”. (See F2–217 NO.21 ENGINE NOISE.)
Compressor Wheel Inspection
1. Remove the air pipe between the air cleaner and the turbocharger. (See F2–36 INTAKE-AIR SYSTEM
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION.)
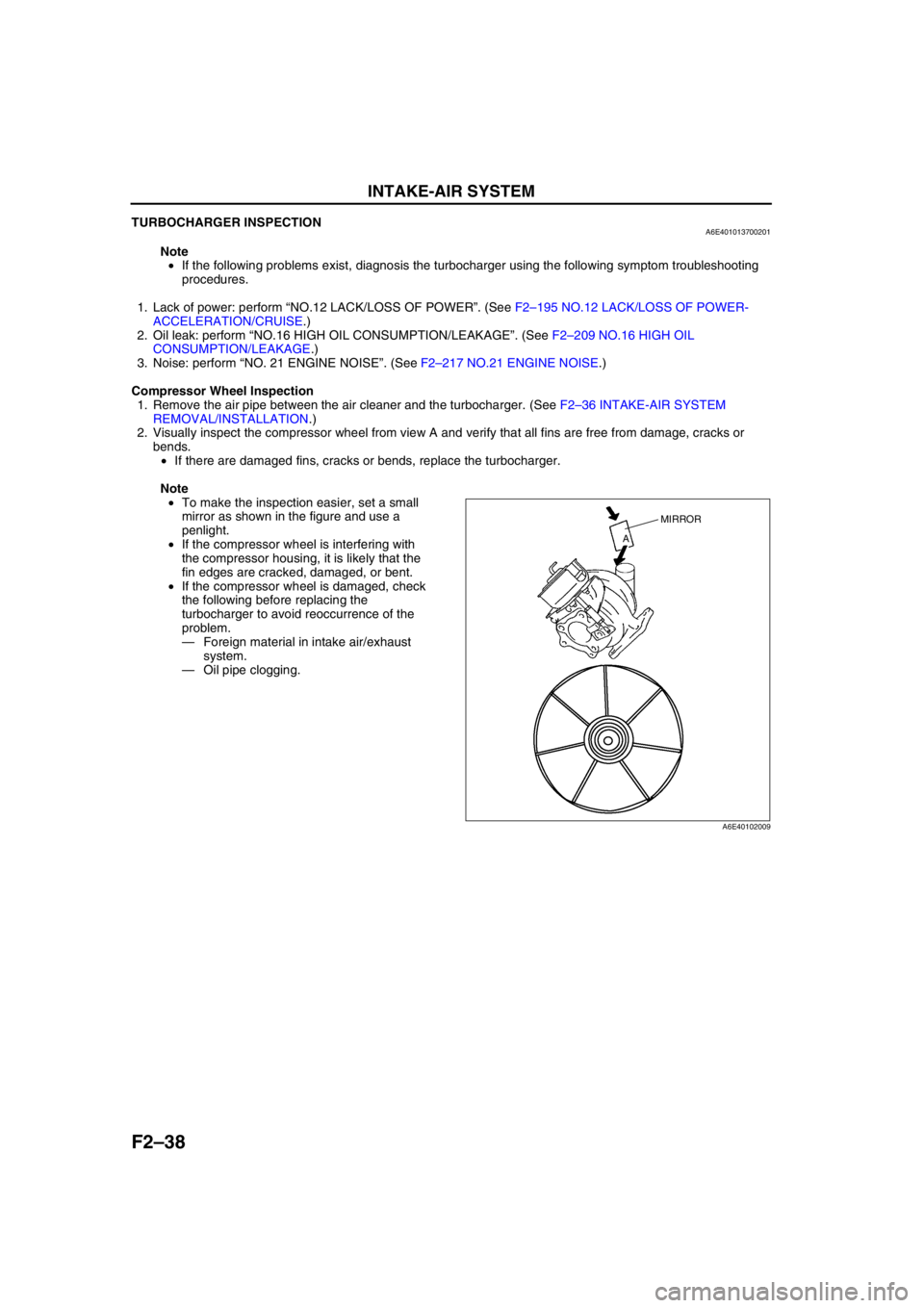
2. Visually inspect the compressor wheel from view A and verify that all fins are free from damage, cracks or
bends.
•If there are damaged fins, cracks or bends, replace the turbocharger.
Note
•To make the inspection easier, set a small
mirror as shown in the figure and use a
penlight.
•If the compressor wheel is interfering with
the compressor housing, it is likely that the
fin edges are cracked, damaged, or bent.
•If the compressor wheel is damaged, check
the following before replacing the
turbocharger to avoid reoccurrence of the
problem.
—Foreign material in intake air/exhaust
system.
—Oil pipe clogging.
MIRROR
A
A6E40102009
Page 191 of 909
INTAKE-AIR SYSTEM
F2–39
F2
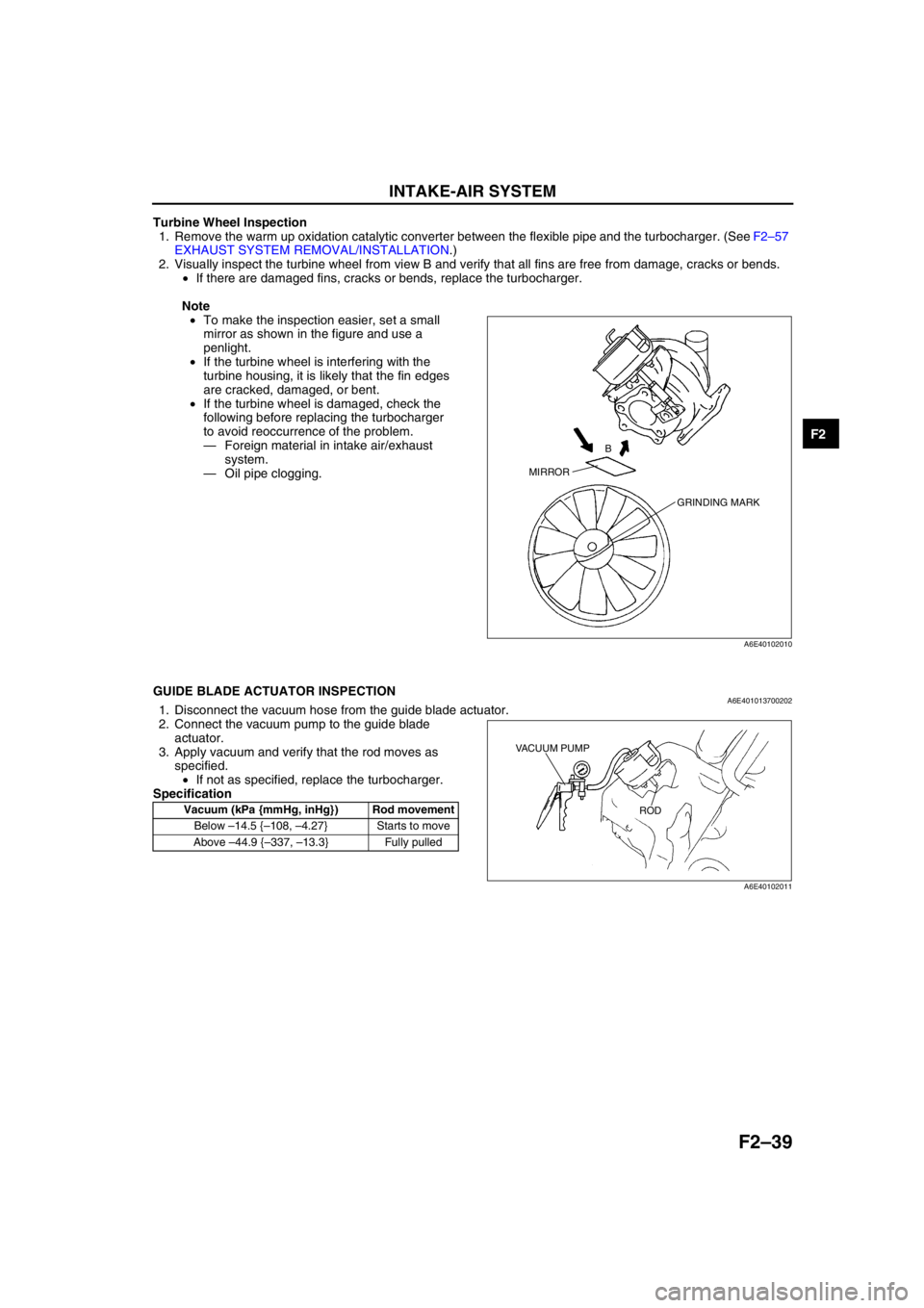
Turbine Wheel Inspection
1. Remove the warm up oxidation catalytic converter between the flexible pipe and the turbocharger. (See F2–57
EXHAUST SYSTEM REMOVAL/INSTALLATION.)
2. Visually inspect the turbine wheel from view B and verify that all fins are free from damage, cracks or bends.
•If there are damaged fins, cracks or bends, replace the turbocharger.
Note
•To make the inspection easier, set a small
mirror as shown in the figure and use a
penlight.
•If the turbine wheel is interfering with the
turbine housing, it is likely that the fin edges
are cracked, damaged, or bent.
•If the turbine wheel is damaged, check the
following before replacing the turbocharger
to avoid reoccurrence of the problem.
—Foreign material in intake air/exhaust
system.
—Oil pipe clogging.
End Of Sie
GUIDE BLADE ACTUATOR INSPECTIONA6E4010137002021. Disconnect the vacuum hose from the guide blade actuator.
2. Connect the vacuum pump to the guide blade
actuator.
3. Apply vacuum and verify that the rod moves as
specified.
•If not as specified, replace the turbocharger.
Specification
End Of Sie
MIRRORB
GRINDING MARK
A6E40102010
Vacuum (kPa {mmHg, inHg}) Rod movement
Below –14.5 {–108, –4.27} Starts to move
Above –44.9 {–337, –13.3} Fully pulled
VACUUM PUMP
ROD
A6E40102011
Page 201 of 909

FUEL SYSTEM
F2–49
F2
(2) Apply a slight amount of clean engine oil to
the sealing surface of the fuel pump unit.
(3) Align the fuel pipe on the fuel pump unit and
quick release connector so that the tabs of the
retainer are correctly fitted into the quick
release connector. Push the quick release
connector straight into the retainer until a click
is heard.
(4) Lightly pull and push the quick release
connector a few times by hand and verify that
it can move 2.0—3.0 mm {0.08—0.11 in} and
it is connected securely.
•If the quick release connector does not
move at all, verify that O-ring is not
damaged of that is has not slipped, and reconnect the quick release connector.
2. When the retainer is removed, perform the following procedure.
End Of Sie
FUEL TANK INSPECTIONA6E401242110202
Caution
•Disconnecting/connecting the quick release connector without cleaning it may possibly cause
damage to the fuel pipe and quick release connector. Always clean the quick release connector
joint area before disconnecting/connecting using a cloth or soft brush, and make sure that it is
free of foreign material.
Note
•This inspection is for two rollover valves and check valve (two-way) integrated in the fuel tank.
1. Remove the fuel tank with the fuel gauge sender unit. (See F2–45 FUEL TANK REMOVAL/INSTALLATION.)
2. Plug the fuel pipe of the fuel gauge sender unit.
3. Plug port C.
4. Connect the pump to port B.
5. Level the fuel tank.
6. Apply pressure of +2.0 kpa {+34 mmHg, +1.3
inHg} to port B.
(1) Verify there is airflow from port A.
•If there is no airflow, replace the fuel tank.
7. Apply pressure of –5.9 kPa {–44 mmHg, –1.7
inHg} to port B.
•If there is no vacuum, replace the fuel tank.
•If there is vacuum, turn the fuel tank
upside-down and proceed to next step.
8. Apply pressure of +2.0 kPa {+15 mmHg, +0.6
inHg} to port B.
(1) Verify there is no airflow from port A.
•If there is airflow, replace the fuel tank.
End Of Sie
OILOIL
PLASTIC FUEL HOSE QUICK RELEASE
CONNECTOR SEALING
SURFACE
A6E3912W006
B
C
APLUG
PLUG
CHECK VALVE
(TWO-WAY)
FUEL GAUGE SENDER UNIT
ROLLOVER VALVE
A6E40122034
B CA
PLUGPLUG
CHECK VALVE
(TWO-WAY)
FUEL GAUGE SENDER UNIT
ROLLOVER VALVE
A6E40122035
Page 210 of 909

F2–58
EXHAUST SYSTEM
Warm Up Oxidation Catalytic Converter Removal Note
1. Support the crossmember using a jack before
removing the crossmember bracket.
2. Loosen the jack and lower the crossmember.
3. Remove the warm up oxidation catalytic
converter.
Water Hose Removal Note
1. Drain the engine coolant.
Turbocharger Removal Note
1. Remove the air pipe and the air hose before
removing the turbocharger. (See F2–36
INTAKE-AIR SYSTEM REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION.)
Exhaust Manifold Removal Note
1. Remove the EGR pipe before removing the exhaust manifold. (See F2–59 EGR VALVE REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION.)
Exhaust Manifold Installation Note
1. Tighten the exhaust manifold installation nuts in
the order shown.
Water Pipe Installation Note
1. Install the connector bolt before installing the
water pipe bracket.
Oil Pipe (Supply) Installation Note
1. Install the connector bolt before installing the
water pipe bracket.
End Of Sie
8 Exhaust manifold insulator
9 Oil pipe (supply)
(See F2–58 Oil Pipe (Supply) Installation Note)
10 Oil pipe (return)
11 Water hose
(See F2–58 Water Hose Removal Note)12 Water pipe
(See F2–58 Water Pipe Installation Note)
13 Turbocharger
(See F2–58 Turbocharger Removal Note)
14 Exhaust manifold
(See F2–58 Exhaust Manifold Removal Note)
(See F2–58 Exhaust Manifold Installation Note)
FRONT
CROSSMEMBER
CROSSMEMBER
BRACKET FRONT
A6E0612W107
87
5436
12
A6E40142003
Page 232 of 909

F2–80
CONTROL SYSTEM
CAMSHAFT POSITION (CMP) SENSOR REMOVAL/INSTALLATIONA6E404018200201
Caution
•When foreign material, such as iron chips, gets on the CMP sensor, it can cause abnormal output
from the sensor because of flux turbulence and adversely affect engine control. Be sure there is
no foreign material on the CMP sensor when replacing.
•Do not forcefully pull the wiring harness of the CMP sensor. Doing so will break the harness.
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the engine cover.
3. Remove in the order indicated in the table.
4. Install in the reverse order of removal.
O-ring Installation Note
1. Apply engine oil to new O-ring thinly and install it
as does not damage.
End Of Sie
CAMSHAFT POSITION (CMP) SENSOR INSPECTIONA6E404018200202
Note
•Perform the following test only when directed.
Caution
•When foreign material, such as iron chips, gets on the CMP sensor, it can cause abnormal output
from the sensor because of flux turbulence and adversely affect engine control. Be sure there is
no foreign material on the CMP sensor when replacing.
•Do not forcefully pull the wiring harness of the CMP sensor. Doing so will break the harness.
Visual Inspection
1. Verify that the CMP sensor and the pulsar are free of any metallic shavings or particles.
•If any are found on the CMP sensor and the pulsar, clean them off.
Air Gap Inspection
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the gear cover.
3. Verify that clearance A between the CMP sensor
and the pulsar is within the specification.
•If not as specified, replace the CMP sensor.
Clearance A
0.5—1.5 mm {0.020—0.059 in}
1 CMP sensor installation bolt
2 CMP sensor
3 O-ring
(See F2–80 O-ring Installation Note)
N·m {kgf·cm, in·lbf}
3
127.8—10.8
{80—110, 69.1—95.5}
R
OILOIL
A6E40702050
CMP SENSOR
CLEARANCE A
PULSAR
A6E40702051
Page 317 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
F2–165
F2
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSTIC INDEXA6E408018881201
TROUBLESHOOTING
No. TROUBLESHOOTING ITEM DESCRIPTION PAGE
1 Melting of main or other fuses—(See F2–173 NO.1 MELTING
OF MAIN OR OTHER FUSES)
2 MIL illuminates MIL is illuminated incorrectly.(See F2–174 NO.2 MIL
ILLUMINATES)
3 Will not crank Starter does not work.(See F2–174 NO.3 WILL NOT
CRANK)
4Hard start/long crank/erratic start/
erratic crankStarter cranks engine at normal speed but
engine requires excessive cranking time
before starting.(See F2–176 NO.4 HARD
START/LONG CRANK/
ERRATIC START/ERRATIC
CRANK)
5 Engine stalls After start/at idleEngine stops unexpectedly at idle and/or
after start.(See F2–178 NO.5 ENGINE
STALLS-AFTER START/AT
IDLE)
6 Cranks normally but will not startStarter cranks engine at normal speed but
engine will not run.(See F2–181 NO.6 CRANKS
NORMALLY BUT WILL NOT
START)
7 Slow return to idleEngine takes more time than normal to
return to idle speed.(See F2–184 NO.7 SLOW
RETURN TO IDLE)
8 Engine runs rough/rolling idleEngine speed fluctuates between specified
idle speed and lower speed and engine
shakes excessively.(See F2–186 NO.8 ENGINE
RUNS ROUGH/ROLLING
IDLE)
9 Fast idle/runs onEngine speed continues at fast idle after
warm-up.
Engine runs after engine switch is turned to
OFF.(See F2–189 NO.9 FAST
IDLE/RUNS ON)
10 Low idle/stalls during decelerationEngine stops unexpectedly at beginning of
deceleration or recovery from deceleration.(See F2–190 NO.10 LOW
IDLE/STALLS DURING
DECELERATION)
11Engine stalls/quitsAcceleration/
cruiseEngine stops unexpectedly at beginning of
acceleration or during acceleration.
Engine stops unexpectedly while cruising.
(See F2–192 NO.11 ENGINE
STALLS/QUITS, ENGINE
RUNS ROUGH, MISSES,
BUCK/JERK, HESITATION/
STUMBLE, SURGES) Engine runs roughAcceleration/
cruiseEngine speed fluctuates during acceleration
or cruising.
MissesAcceleration/
cruiseEngine misses during acceleration or
cruising.
Buck/jerkAcceleration/
cruise/
decelerationVehicle bucks/jerks during acceleration,
cruising, or deceleration.
Hesitation/stumble AccelerationMomentary pause at beginning of
acceleration or during acceleration.
SurgesAcceleration/
cruiseMomentary minor irregularity in engine
output.
12 Lack/loss of powerAcceleration/
cruisePerformance is poor under load (e.g. power
down when climbing hills).(See F2–195 NO.12 LACK/
LOSS OF POWER-
ACCELERATION/CRUISE)
13 Knocking/pingingExcessive shrilly knocking sound from
engine.(See F2–199 NO.13
KNOCKING/PINGING)
14 Poor fuel economy Fuel economy is unsatisfactory.(See F2–202 NO.14 POOR
FUEL ECONOMY)
15 Emissions compliance Fails emissions test.(See F2–205 NO.15
EMISSION COMPLIANCE)
16 High oil consumption/leakage Oil consumption is excessive.(See F2–209 NO.16 HIGH OIL
CONSUMPTION/LEAKAGE)
17Cooling system
concernsOverheatingEngine runs at higher than normal
temperature/overheats.(See F2–210 NO.17 COOLING
SYSTEM CONCERNS-
OVERHEATING)
Page 319 of 909

TROUBLESHOOTING
F2–167
F2
SYMPTOM QUICK DIAGNOSIS CHARTA6E408018881202
×: Applicable
Troubleshooting item
1 Melting of main or other fuses
2 MIL illuminates
3 Will not crank×× ×× × ×
4 Hard start/long crank/erratic start/erratic crank×× ×
5 Engine stalls After start/at idle××
6 Cranks normally but will not start××
7 Slow return to idle
8 Engine runs rough/rolling idle××
9 Fast idle/runs on
10 Low idle/stalls during deceleration××
11Engine stalls/quits Acceleration/cruise××
Engine runs rough Acceleration/cruise××
Misses Acceleration/cruise××
Buck/jerk Acceleration/cruise/ deceleration××
Hesitation/stumble Acceleration××
Surges Acceleration/cruise××
12 Lack/loss of power Acceleration/cruise××
13 Knocking/pinging××
14 Poor fuel economy××
15 Emissions compliance×× ×
16 High oil consumption/leakage××××
17 Cooling system concerns Overheating××
18 Cooling system concerns Runs cold
19 Excessive black smoke×
20 Fuel odor (in engine compartment)
21 Engine noise×× × ×
22 Vibration concerns (engine)×
23 A/C does not work sufficiently
24 A/C always on or A/C compressor runs continuously
25 A/C does not cut off under wide open throttle conditions
26 Constant voltage
Starter motor malfunction (Mechanical or electrical)Starter circuit including engine switch is openImproper engine oil levelLow or dead bateryCharging system malfunctionLow engine compressionImproper valve timingHydrolocked egineImproper engine oil viscosityImproper dipstickBase engine malfunctionSeized flywheelImproper tension or damaged drivebelts