2002 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 472 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-15
Input/Output
Electrical input to the camshaft position sensor is from fuse 2 located in engine compartment fuse box. One output is
sensor earth, the other is the signal output to the ECM via pin 20 of connector C0636.
The CMP sensor can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lSensor open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle battery supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lIncorrect fitting of the sensor.
lExcessive camshaft gear wheel tolerance.
lExcessive camshaft endfloat.
lCamshaft and crankshaft misalignment.
lSpeed signal correlation with CKP sensor signal.
lCam wheel magnetised / residual magnetism
In the event of a CMP sensor signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lIgnition timing reverts to default values from ECM memory.
lLoss of cylinder correction.
lLoss of active knock control.
lLoss of active knock control diagnostics.
lLoss of cylinder identification for misfire diagnostics.
lLoss of quick synchronisation of crankshaft and camshaft for cranking/ start up.
lFuel injection could be 360
° out of phase.
lFront HO
2S sensor ageing period diagnostic disabled (NAS only)
Should a malfunction of the component occur the following fault code may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook:
The fault condition has to be detected for more than 100 cam pulses (25 revolutions) when the engine speed is greater
than 500 rev/min.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor (C0196)
The ECT sensor is located at the front of the engine adjacent to the coolant outlet pipe. The ECT sensor forms a vital
part of the ECM operating strategy, and therefore the optimum control of the running of the engine. Richer air/ fuel
ratio is required at lower coolant temperatures such as cold starting. Coolant temperature information from the ECT
sensor is also vital to enable the ECM to weaken the air/ fuel mixture as temperature rises to maintain low emissions
and optimum performance.
P code J2012 description Land Rover description
P0340 Camshaft position sensor circuit malfunction Open/short circuit to vehicle supply or earth
Page 473 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-16 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
For NAS vehicles with secondary air injection, the signal from the ECT sensor is monitored at engine start, to
determine whether the conditions are cold enough to warrant secondary air injection to be employed. The ECT sensor
is then monitored to switch off the secondary air injection when the required engine coolant temperature has been
attained.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Secondary air injection system.
The ECT works as a Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) sensor. As temperature rises, the resistance in the
sensor decreases, as temperature decreases, the resistance in the sensor increases. The ECT sensor forms part of
a voltage divider chain with a pull up resistor within the ECM. Consequently as the ECT sensor resistance changes,
the analogue voltage at the input signal from the ECT sensor to the ECM will be adjusted which corresponds to the
temperature of the engine coolant. With this information, the ECM can implement the correct strategies for cold start,
warm up etc. The ECM supplies the instrument cluster with a pulse width modulated (PWM) coolant temperature
signal to drive the temperature gauge.
Input/Output
The electrical input and output to and from the ECT sensor are reference voltage and sensor earth. The ECM provides
the ECT sensor with a 5 volt reference via pin 22 of connector C0636 of the ECM, and earth via pin 21 of connector
C0636 of the ECM. The normal operating parameters of the ECT sensor are as follows
Should the sensor fail the ECM has a back up strategy that uses a changing default value during warm up based on
the signal from the inlet air temperature sensor. When the strategy default value reaches 60
°C (140 °F), the ECM
implements a fixed default value of 85
°C (185 °F). It will also illuminate the MIL.
M124704A
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
4.5
5
VkΩ
kΩ
V
°C
145-50-35-20-5102540557085100115130
Page 476 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-19
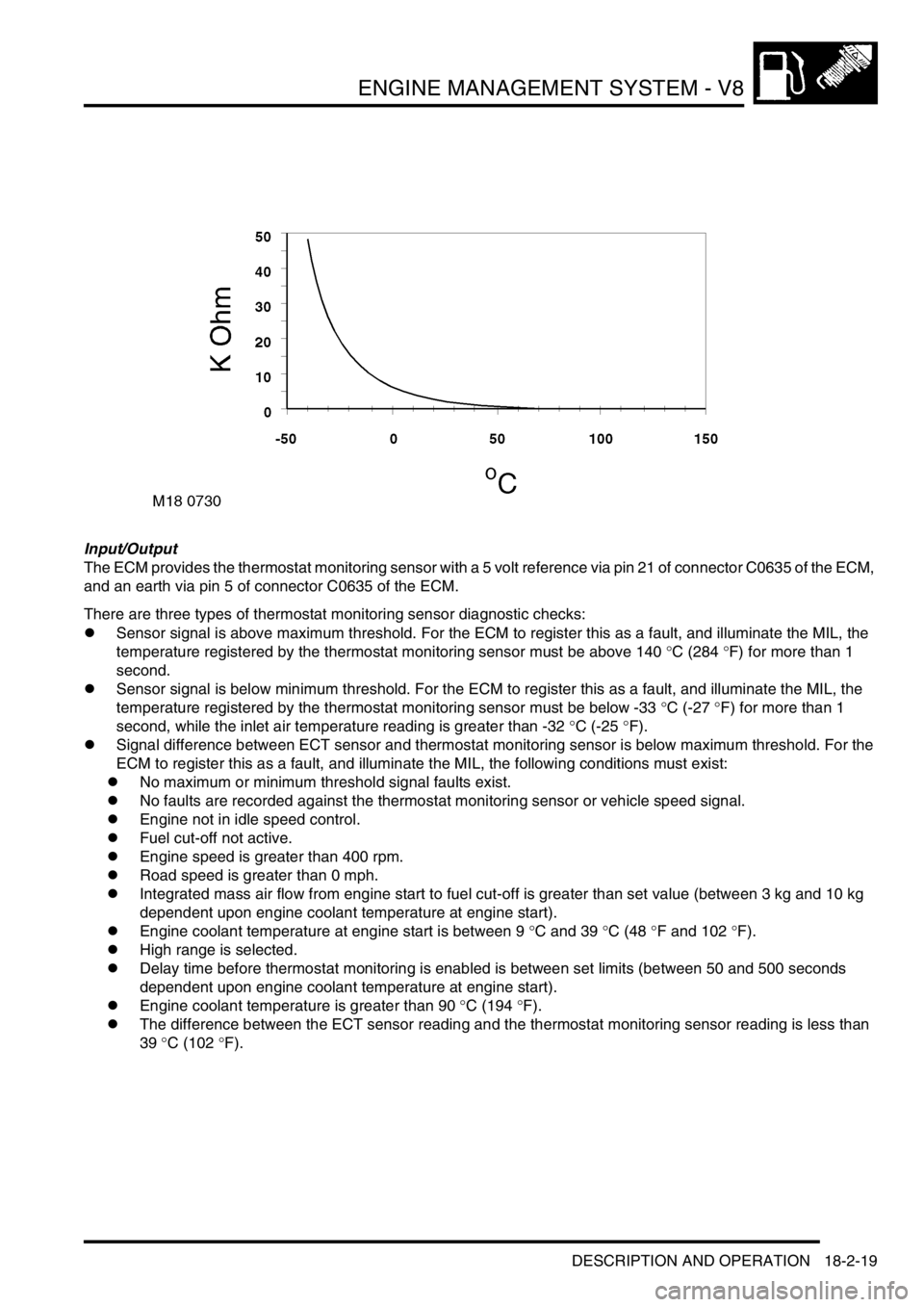
Input/Output
The ECM provides the thermostat monitoring sensor with a 5 volt reference via pin 21 of connector C0635 of the ECM,
and an earth via pin 5 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
There are three types of thermostat monitoring sensor diagnostic checks:
lSensor signal is above maximum threshold. For the ECM to register this as a fault, and illuminate the MIL, the
temperature registered by the thermostat monitoring sensor must be above 140
°C (284 °F) for more than 1
second.
lSensor signal is below minimum threshold. For the ECM to register this as a fault, and illuminate the MIL, the
temperature registered by the thermostat monitoring sensor must be below -33
°C (-27 °F) for more than 1
second, while the inlet air temperature reading is greater than -32
°C (-25 °F).
lSignal difference between ECT sensor and thermostat monitoring sensor is below maximum threshold. For the
ECM to register this as a fault, and illuminate the MIL, the following conditions must exist:
lNo maximum or minimum threshold signal faults exist.
lNo faults are recorded against the thermostat monitoring sensor or vehicle speed signal.
lEngine not in idle speed control.
lFuel cut-off not active.
lEngine speed is greater than 400 rpm.
lRoad speed is greater than 0 mph.
lIntegrated mass air flow from engine start to fuel cut-off is greater than set value (between 3 kg and 10 kg
dependent upon engine coolant temperature at engine start).
lEngine coolant temperature at engine start is between 9
°C and 39 °C (48 °F and 102 °F).
lHigh range is selected.
lDelay time before thermostat monitoring is enabled is between set limits (between 50 and 500 seconds
dependent upon engine coolant temperature at engine start).
lEngine coolant temperature is greater than 90
°C (194 °F).
lThe difference between the ECT sensor reading and the thermostat monitoring sensor reading is less than
39
°C (102 °F).
Page 484 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-27
The HO2S uses zirconium contained in a galvanic cell surrounded by a gas permeable ceramic, this produces an
output voltage proportional to the ratio difference between the oxygen in the exhaust gases and to the ambient
oxygen.
The HO
2S operates at approximately 350 °C (662 °F). To achieve this temperature the HO2S incorporate a heating
element which is controlled by a PWM signal from the ECM. The elements are activated immediately after engine
starts and also under low engine load conditions when the exhaust gas temperature is insufficient to maintain the
required HO
2S temperature. If the heater fails, the ECM will not allow closed loop fuelling to be implemented until the
sensor has achieved the required temperature.
This value equates to an HO
2S output of 450 to 500 mV. A richer mixture can be shown as λ = 0.97, this pushes the
HO
2S output voltage towards 1000 mV. A leaner mixture can be shown as λ = 1.10, this pushes the HO2S output
voltage towards 100 mV.
From cold start, the ECM runs an open loop fuelling strategy. The ECM keeps this strategy in place until the HO
2S is
at a working temperature of 350
°C (662 °F). At this point the ECM starts to receive HO2S information and it can then
switch into closed loop fuelling as part of its adaptive strategy. The maximum working temperature of the tip of the
HO
2S is 930 °C (1706 °F), temperatures above this will damage the sensor.
HO
2S age with use, this increases their response time to switch from rich to lean and from lean to rich. This can lead
to increased exhaust emissions over a period of time. The switching time of the upstream sensors are monitored by
the ECM. If a pre-determined threshold is exceeded, a failure is detected and the MIL illuminated.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Exhaust emission control system.
Input/Output
The upstream and downstream HO
2S are colour coded to prevent incorrect fitting. The tips of the upstream sensors
are physically different to the tips of the downstream sensors.
The HO
2S are colour coded as follows:
lUpstream sensors (both banks) - orange.
lDownstream sensors (both banks) - grey.
The four HO
2S have a direct battery supply to the heater via fuse 2 located in the engine compartment fuse box.
The heater is driven by the ECM providing an earth path for the circuit as follows:
lUpstream LH bank via pin 19 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lUpstream RH bank via pin 13 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream LH bank via pin 7 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream RH bank via pin 1 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
The HO
2S output signal is measured by the ECM as follows:
lUpstream LH bank via pin 15 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lUpstream RH bank via pin 16 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream LH bank via pin 17 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream RH bank via pin 14 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
The HO
2S earth path for the signal is supplied by the ECM as follows:
lUpstream LH bank via pin 9 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lUpstream RH bank via pin 10 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream LH bank via pin 11 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
lDownstream RH bank via pin 8 of connector C0635 of the ECM.
The HO
2S voltage is difficult to measure using a multimeter, the output can be monitored using TestBook. A rich
mixture would read 500 to 1000 mV, a weak mixture would read 100 mV to 500 mV, the reading should switch from
rich to weak. The open loop default voltage is 450 mV, this is used by the ECM to set the air/ fuel ratio until the tip of
the HO
2S reaches operating temperature.
Page 489 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-32 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Idle Air Control Valve (IACV) (C0641)
The IACV is located on the side of the air inlet pipe on top of the engine. The IACV is used to maintain good quality
idle speed under all operating conditions.
When an engine is running at idle it is subject to a combination of internal and external loads that can affect idle speed.
These loads include engine friction, water pump, alternator operation, and air conditioning.
The IACV acts as an air bypass valve. The ECM uses the IACV to enable the closed loop idle speed calculation to be
made by the ECM. This calculation regulates the amount of air flow into the engine at idle, therefore compensating
for any internal or external loads that may affect idle speed.
The IACV utilises two coils that use opposing PWM signals to control the position of opening/closing of a rotary valve.
If one of the circuits that supply the PWM signal fails, the ECM closes down the remaining signal preventing the IACV
from working at its maximum/ minimum setting. If this should occur, the IACV automatically resumes a default idle
position. In this condition, the engine idle speed is raised and maintained at 1200 rev/min with no load placed on the
engine.
The idle speed in cold start condition is held at 1200 rev/min in neutral for 20 seconds and ignition timing is retarded
as a catalyst heating strategy. The cold start idle speed and the default idle position give the same engine speed 1200
rev/min, and although they are the same figure they must not be confused with each other as they are set separately
by the ECM.
Note that the rotary valve must not be forced to move by mechanical means. The actuator can not be
serviced; if defective, the entire IACV must be replaced.
Input/Output
The input to the IACV is a 12 volt signal from fuse 2 located in the engine compartment fuse box. The output earth
signal to open and close the actuator is controlled by the ECM as follows:
lIACV (open signal) - via pin 42 of connector C0636 of the ECM
lIACV (closed signal) - via pin 43 of connector C0636 of the ECM
The IACV can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lActuator faulty.
lRotary valve seized.
lWiring loom fault.
lConnector fault.
lIntake system air leak.
lBlocked actuator port or hoses.
lRestricted or crimped actuator port or hoses.
Page 490 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-33
In the event of an IACV signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEither low or high idle speed.
lEngine stalls.
lDifficult starting.
lIdle speed in default condition.
There are eight IACV diagnostic checks performed by the ECM:
lOutput short circuit to earth – opening coil
lOutput short circuit to battery supply – opening coil
lOutput open circuit – opening coil
lOutput short circuit to earth – closing coil
lOutput short circuit to battery voltage – closing coil
lOutput open circuit – closing coil
lBlocked IACV – rev/min error low (engine speed must be 100 rev/min less than the target speed, engine load
less than 2.5 and the measured air flow more than 10 kg/h less than the expected air flow for a fault condition to
be flagged).
lBlocked IACV – rev/min error high (the engine speed must be more than 180 rev/min greater than the target
speed and the measured air flow more than 10 kg/h greater than the expected air flow for a fault condition to be
flagged).
Should a malfunction of the component occur, the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
Fuel pump relay
The fuel pump relay is located in the engine compartment fuse box. It is a 4 pin normally open relay. Input from the
ECM allows the fuel pump relay to control the electrical input to the fuel pump, regulating the fuel supply to the fuel
injectors. When the ignition is switched on and the engine is cranked, the fuel pump relay is activated by the ECM,
allowing the fuel system to be pressurised to 3.5 bar (52 lbf.in
2). The ECM then deactivates the relay until the engine
has started.
If the fuel pump runs, but the fuel pressure is out of limits, adaptive fuel faults will be stored.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1510 IACV opening coil malfunction Short circuit to battery supply - opening winding
P1513 IACV opening coil malfunction Short circuit to earth - opening winding
P1514 IACV opening coil malfunction Open circuit - opening winding
P1553 IACV closing coil malfunction Short circuit to battery supply - closing winding
P1552 IACV closing coil malfunction Short circuit to earth - closing winding
P1551 IACV closing coil malfunction Open circuit - closing winding
P0505 Idle control system malfunction Blocked IACV - high or low rev/min error
Page 497 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-40 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Air Temperature Control (ATC) request
The ATC request comes via the ATC switch located in the facia panel. When the driver operates the switch it acts as
a request from the ATC ECU to engage the ATC clutch to drive the system.
During periods of high driver demand such as hard acceleration or maximum rev/min the ATC clutch will be disabled
for a short time. This is to reduce the load on the engine.
+ AIR CONDITIONING, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description.
Input/Output
The operation of the ATC request is via a switch being connected to earth. Voltage is supplied via pin 38 of connector
C0637 of the ECM, at the point at when the switch is pressed the connection is made and the ATC clutch is engaged.
The ATC request can fail as follows:
lOpen circuit.
lShort circuit to voltage supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lWiring loom fault.
In the event of an ATC request failure, the ATC system does not work.
Should a malfunction of the component occur the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
ATC compressor clutch relay
The ATC compressor clutch relay is located in the engine compartment fuse box. It is a four pin normally open relay.
The relay must be energised to drive the ATC compressor clutch.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1535 Air conditioning compressor request
malfunctionATC requested when not in standby mode
Page 498 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-2-41
Input/Output
The ECM provides the earth for the relay coil to allow the relay contacts to close and the ATC clutch drive to receive
battery voltage. The ECM uses a transistor as a switch to generate an open circuit in the earth path of the relay coil.
When the ECM opens the earth path, the return spring in the relay will pull the contacts apart to shut down the ATC
clutch drive.
Input to the ATC clutch relay switching contacts is via fuse 6 located in the engine compartment fuse box. The relay
coils are supplied with battery voltage from the main relay, also located in the engine compartment fuse box. The earth
path for the relay coil is via pin 29 of the ECM C0657 connector. When the relay is energised the output from the
switching contacts goes directly to the ATC compressor clutch.
The ATC clutch relay can fail in the following ways:
lRelay open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lBroken return spring.
In the event of an ATC clutch relay failure, the ATC does not work.
Should a malfunction of the component occur, the following fault codes may be evident and can be retrieved by
TestBook.
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P1536 Air conditioning compressor request range/
performanceATC compressor clutch relay open circuit
P1537 Air conditioning compressor request low input ATC compressor clutch relay short to earth
P1538 Air conditioning compressor request high input ATC compressor clutch relay short to battery supply