2002 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY length
[x] Cancel search: lengthPage 423 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-30 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Glow plug warning lamp
The glow plug warning lamp is located in the instrument cluster. It illuminates to alert the driver that the glow plugs
are being heated prior to the engine being started. The length of time that the lamp illuminates and the glow plugs
are operating prior to cranking is the pre-heat period, which is subject to battery voltage and ECT sensor signal
controlled by the ECM.
Input/Output
The instrument cluster supplies battery voltage to the glow plug warning lamp. The ECM provides an earth path to
illuminate the lamp. The earth path is via pin 30 of ECM connector C0658.
Glow plugs
The 4 glow plugs are located in the engine block on the inlet side, in cylinder 1 to 4. Cylinder 5 has no glow plug. The
glow plugs are a vital part of the engine starting strategy.
Page 424 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 18-1-31
The purpose of the glow plugs is:
lAssist cold engine start.
lReduce exhaust emissions at low engine load/speed.
The main part of the glow plug is a tubular heating element that protrudes into the combustion chamber of the engine.
The heating element contains a spiral filament that is encased in magnesium oxide powder. At the tip of the tubular
heating element is the heater coil. Behind the heater coil and connected in series is a control coil. The control coil
regulates the heater coil to ensure that it does not overheat and cause a possible failure. The glow plug circuit has its
own control relay located in the engine compartment fuse box.
Pre-heat is the length of time the glow plugs operate prior to engine cranking. The ECM controls the pre-heat time of
the glow plugs based on battery voltage and coolant temperature information via the glow plug relay.
Post-heat is the length of time the glow plugs operate after the engine starts. The ECM controls the post-heat time
based on ECT information. If the ECT fails the ECM will operate pre/post-heat time strategies with default values from
its memory. The engine will be difficult to start.
Input/Output
The glow plugs receive voltage from the glow plug relay that is controlled by the ECM. The ECM provides the earth
path for the relay coil closing the relay contacts and supplying the glow plugs with battery voltage. The supply voltage
heats the coils to approximately 1000
°C (1832 °F). The glow plug circuit is wired in parallel, the body of each glow
plug is screwed directly into the engine block which provides each glow plug with an earth path.
The glow plugs can fail in the following ways:
lHeater coil open circuit.
lControl coil open circuit.
lPoor earth quality.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lWiring loom fault.
lRelay windings open circuit.
lIncorrect relay fitted.
In the event of a glow plug failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lDifficult starting.
lExcessive smoke emissions after engine start.
Page 431 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-38 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Operation
Engine management
The ECM controls the operation of the engine using stored information within its memory. This guarantees optimum
performance from the engine in terms of torque delivery, fuel consumption and exhaust emissions in all operating
conditions, while still giving optimum driveability.
The ECM will receive information from its sensors under all operating conditions, especially during:
lCold starting.
lHot starting.
lIdle.
lWide open throttle.
lAcceleration.
lAdaptive strategy.
lBackup strategy for sensor failures.
The ECM receives information from various sensors to determine the current operating state of the engine. The ECM
then refers this information to stored values in its memory and makes any necessary changes to optimise air/fuel
mixture and fuel injection timing. The ECM controls the air/fuel mixture and fuel injection timing via the Electronic Unit
Injectors (EUI), by the length of time the EUI's are to inject fuel into the cylinder. This is a rolling process and is called
adaptive strategy. By using this adaptive strategy the ECM is able to control the engine to give optimum driveability
under all operating conditions.
During cold start conditions the ECM uses ECT information to allow more fuel to be injected into the cylinders, this
combined with the glow plug timing strategy supplied by the ECM facilitates good cold starting.
During hot start conditions the ECM uses ECT and FT information to implement the optimum fuelling strategy to
facilitate good hot starting.
During idle and wide open throttle conditions the ECM uses mapped information within its memory to respond to input
information from the throttle pedal position sensor to implement the optimum fuelling strategy to facilitate idle and wide
open throttle.
To achieve an adaptive strategy for acceleration the ECM uses input information from the CKP sensor, TP sensor,
ECT sensor, MAP/ IAT sensor, and the FT sensor. This is compared to mapped information within its memory to
implement the optimum fuelling strategy to facilitate acceleration.
Immobilisation system
When the starter switch is turned on, the BCU sends a unique security code to the ECM. The ECM must accept this
code before it will allow the engine to operate. If the ECM receives no security code or the ECM receives the incorrect
security code, then the ECM allows the engine to run for 0.5 seconds only. During this operation all other ECM
functions remain as normal.
The ECM operates immobilisation in three states:
l'New.'
l'Secure'.
l'No Code'.
When an ECM is unconfigured it will operate in the 'New' state. When an unconfigured ECM is installed the engine
can be started and operated once only, then the ECM has to be re-configured to either 'secure' or 'no code'
configuration depending on whether a security system is fitted to the vehicle. This is achieved by using TestBook.
Page 505 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8
18-2-48 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Misfire detection
Due to increasing legislation, all new vehicles must be able to detect two specific levels of misfire.
Conditions
The ECM is able to carry out misfire detection as part of the OBD system using the following component parts:
lFlywheel reluctor adaptation.
lCalculation of engine roughness.
lDetection of excess emissions misfire.
lDetection of catalyst damaging misfire.
Function
The flywheel/ reluctor ring is divided into four segments 90
° wide. The ECM misfire detection system uses information
generated by the CKP to determine crankshaft speed and position. If a misfire occurs, there will be an instantaneous
slight decrease in engine speed. The ECM misfire detection system is able to compare the length of time each 90
°
segment takes and is therefore able to pinpoint the source of the misfire.
For the ECM misfire detection system to be calibrated for the tolerances of the reluctor tooth positions, the flywheel/
reluctor ring must be 'adapted' as follows:
l1800 - 3000 rev/min = speed range 1.
l3000 - 3800 rev/min = speed range 2.
l3800 - 4600 rev/min = speed range 3.
l4600 - 5400 rev/min = speed range 4.
The ECM carries out flywheel/ reluctor ring adaptions across all the above speed ranges and can be monitored by
TestBook. The test should be carried out as follows:
lEngine at normal operating temperature.
lSelect second gear (for both automatic and manual transmission vehicles).
lAccelerate until engine rev limiter is operational.
lRelease throttle smoothly to allow engine to decelerate throughout the speed ranges.
lRepeat process as necessary until all adaptations are complete.
TestBook is able to retrieve the following misfire detection fault codes:
P Code J2012 Description Land Rover Description
P0300 Random/multiple cylinder misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire on more than one
cylinder
P0301 Cylinder 1 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.1
P0302 Cylinder 2 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.2
P0303 Cylinder 3 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.3
P0304 Cylinder 4 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.4
P0305 Cylinder 5 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.5
P0306 Cylinder 6 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.6
P0307 Cylinder 7 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.7
P0308 Cylinder 8 misfire detected Excess emissions level of misfire detected on cylinder
No.8
Page 774 of 1672

TRANSFER BOX - LT230SE
OVERHAUL 41-41
4.Using a micrometer, measure the width of each
bearing inner track.
5.Record each reading as measurement 'A' and
'B', both measurements should fall within the
range of 21.95 to 22.00 mm (0.864 to 0.866 in).
6.Fit inner bearing track 'A' onto tool LRT-41-017
and position intermediate gear cluster onto
bearing 'A'.
7.Fit inner bearing track 'B' to intermediate gear,
apply finger pressure to bearing inner track
and rotate intermediate gear 5 to 10 turns to
settle in bearing rollers. 8.Attach a DTI to base of tool LRT-41-017 , zero
gauge on top of tool post and take 2
measurements at 180
° of the step height
between the top of the tool post and the
bearing inner track. Take an average of the two
readings and record this as measurement 'C'.
Measurement 'C' should be in the range of 0.15
to 0.64 mm (0.006 to 0.025 in).
9.Using the formula 103.554 mm (4.0769 in) -'A'-
'B'-'C', calculate the length of bearing spacer
required. From the result of the calculation
round DOWN to the nearest length of spacer
available to give a correct bearing pre-load of
0.005 mm (0.002 in). 40 spacers are
available ranging in length from 58.325 mm
(2.296 in) to 59.300 mm (2.335 in) rising in
increments of 0.025 mm (0.001 in).
10.Remove intermediate gear assembly from tool
LRT-41-017.
11.Lubricate and fit bearings and selected spacer
to intermediate gear.
12.Position tool LRT-41-004 through bearings
and spacer.
13.Lubricate and fit 'O' rings to main casing and
intermediate shaft.
14.With assistance, position intermediate gear
assembly and fit intermediate shaft.
15.Rotate shaft until retaining plate can be located
on flat on shaft.
16.Apply Loctite 290 to threads of retaining plate
bolt, tighten bolt to 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
17.Fit new intermediate shaft Patchlok nut and
tighten to 88 Nm (65 lbf.ft).Do not stake nut at
this stage.
Page 781 of 1672
TRANSFER BOX - LT230SE
41-48 OVERHAUL
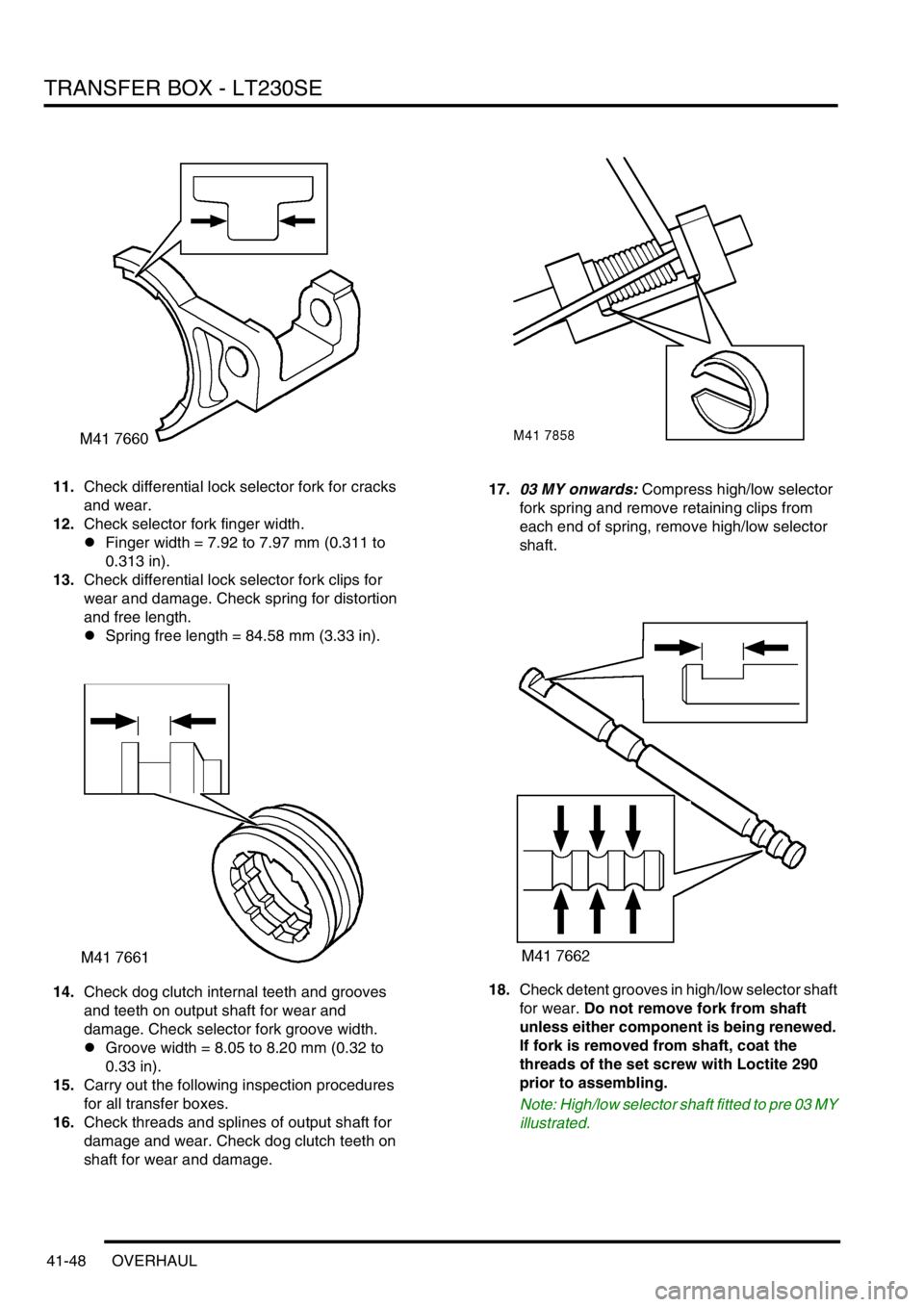
11.Check differential lock selector fork for cracks
and wear.
12.Check selector fork finger width.
lFinger width = 7.92 to 7.97 mm (0.311 to
0.313 in).
13.Check differential lock selector fork clips for
wear and damage. Check spring for distortion
and free length.
lSpring free length = 84.58 mm (3.33 in).
14.Check dog clutch internal teeth and grooves
and teeth on output shaft for wear and
damage. Check selector fork groove width.
lGroove width = 8.05 to 8.20 mm (0.32 to
0.33 in).
15.Carry out the following inspection procedures
for all transfer boxes.
16.Check threads and splines of output shaft for
damage and wear. Check dog clutch teeth on
shaft for wear and damage.17.03 MY onwards: Compress high/low selector
fork spring and remove retaining clips from
each end of spring, remove high/low selector
shaft.
18.Check detent grooves in high/low selector shaft
for wear. Do not remove fork from shaft
unless either component is being renewed.
If fork is removed from shaft, coat the
threads of the set screw with Loctite 290
prior to assembling.
Note: High/low selector shaft fitted to pre 03 MY
illustrated.
Page 782 of 1672
TRANSFER BOX - LT230SE
OVERHAUL 41-49
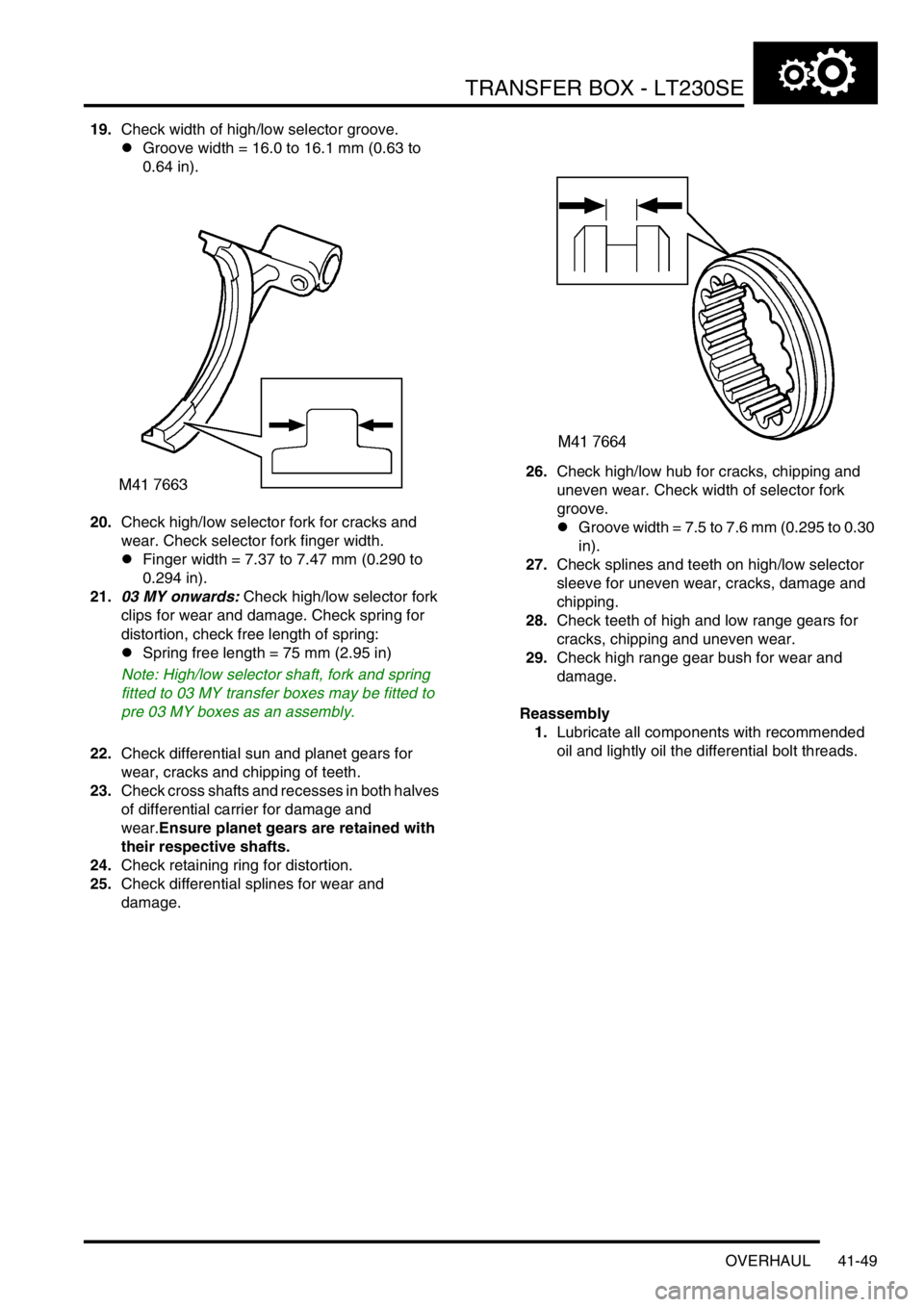
19.Check width of high/low selector groove.
lGroove width = 16.0 to 16.1 mm (0.63 to
0.64 in).
20.Check high/low selector fork for cracks and
wear. Check selector fork finger width.
lFinger width = 7.37 to 7.47 mm (0.290 to
0.294 in).
21.03 MY onwards: Check high/low selector fork
clips for wear and damage. Check spring for
distortion, check free length of spring:
lSpring free length = 75 mm (2.95 in)
Note: High/low selector shaft, fork and spring
fitted to 03 MY transfer boxes may be fitted to
pre 03 MY boxes as an assembly.
22.Check differential sun and planet gears for
wear, cracks and chipping of teeth.
23.Check cross shafts and recesses in both halves
of differential carrier for damage and
wear.Ensure planet gears are retained with
their respective shafts.
24.Check retaining ring for distortion.
25.Check differential splines for wear and
damage.26.Check high/low hub for cracks, chipping and
uneven wear. Check width of selector fork
groove.
lGroove width = 7.5 to 7.6 mm (0.295 to 0.30
in).
27.Check splines and teeth on high/low selector
sleeve for uneven wear, cracks, damage and
chipping.
28.Check teeth of high and low range gears for
cracks, chipping and uneven wear.
29.Check high range gear bush for wear and
damage.
Reassembly
1.Lubricate all components with recommended
oil and lightly oil the differential bolt threads.
Page 783 of 1672

TRANSFER BOX - LT230SE
41-50 OVERHAUL
2.Secure rear half of differential carrier in a soft
jawed vice.
3.Fit each planet gear to its respective cross
shaft, fit new dished thrust washer to each
gear.
4.Fit cross shafts, planet gears and dished thrust
washers in rear half of carrier.Ensure that
cross shafts are fitted correctly. Do not fit
the sun gear into the rear half carrier at this
stage.
5.Fit retaining ring.
6.Fit a 1.05 mm (0.04 in) thrust washer to sun
gear from front half of carrier. Position gear in
front half of carrier.
7.Ensuring that assembly marks are aligned, fit
both halves of carrier together.
8.Fit the differential carrier bolts and, working in a
diagonal sequence, tighten the bolts to 60 Nm,
(44 lbf.ft).9.Insert the front output shaft into the front half of
the carrier and check that the gears rotate
freely.
10.Fit output flange on to the splines of the output
shaft, but do not fit flange nut at this stage.
11.Fit transmission brake drum to output flange
and secure the drum using 2 nuts.
12.Secure a length of cord around the drum and
attach one end of the cord to a spring balance.
13.Pull on the spring balance and note the load at
which the brake drum starts to turn. Used
gears should rotate smoothly, while new
gears will have a 'notchy' feel as they rotate.
14.Compare the figure obtained with the following.
lUsed gears = 0.45 kg (1.0 lb)
lNew gears = 1.72 kg (3.8 lb)
15.If the load to turn figure is below the specified
limits, proceed as follows.
16.Remove the front output shaft and brake drum.
17.Remove the 8 bolts securing the two halves of
the differential carrier
18.Separate the differential carrier and remove the
sun gear and thrust washer from the front half.
19.Select a thicker thrust washer from the range
available. 5 different thrust washers are
available, rising in increments of 0.10 mm
(0.004 in) from 1.05 mm to 1.45 mm (0.04 to
0.06 in).
20.Repeat steps 7 to 19 as necessary until the
load to turn figure is as specified
21.When specified load to turn is obtained,
proceed as follows.
22.Remove the front output shaft and brake drum.
23.Remove the 8 bolts securing the two halves of
the differential carrier
24.Separate the differential carrier and remove the
sun gear and thrust washer from the front
half.Retain the selected thrust washer with
its sun gear.