Page 587 of 1672
COOLING SYSTEM - TD5
26-1-4 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Cooling system coolant flow
Coolant flow diagram
aEU 3 Models
bPre EU3 Models
Page 949 of 1672
FRONT SUSPENSION
60-10 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ACE system control diagram
1Upper accelerometer
2Lower accelerometer
3Pressure transducer
4Directional control valve
5Directional control valve
6Pressure control valve
7Instrument pack warning lamp
8Diagnostic socket9Reverse lamp switch
10SLABS ECU
11Engine Control Module (ECM)
12Ignition feed
13ACE relay
14Battery supply
15ACE ECU
M60 0589B
12
5
4
3
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Page 964 of 1672
FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 60-25
Operation
Hydraulic circuit diagram
1Pressure transducer
2Directional control valve 2
3Front torsion bar assembly
4Actuator
5Actuator
6Rear torsion bar assembly
7Directional control valve 18Valve block
9Pressure control valve
10Reservoir
11Filter
12High pressure filter
13Hydraulic pump
14Attenuator hose
Vehicle not moving
When the engine is running and the vehicle is not moving, both DCV's are closed, locking fluid in each side of the
actuator pistons. The hydraulic pump draws fluid from the reservoir and passes it at very low pressure to the valve
block. Because both DCV's are closed, after the fluid passes through the high pressure filter, it is directed through the
pressure control valve to the reservoir. The pressure control valve is open fully to allow the full flow to pass to the
reservoir. The DCV's will remain closed until the ECU detects a need to operate.
Page 1015 of 1672
REAR SUSPENSION
64-10 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
SLS system control diagram
Page 1025 of 1672
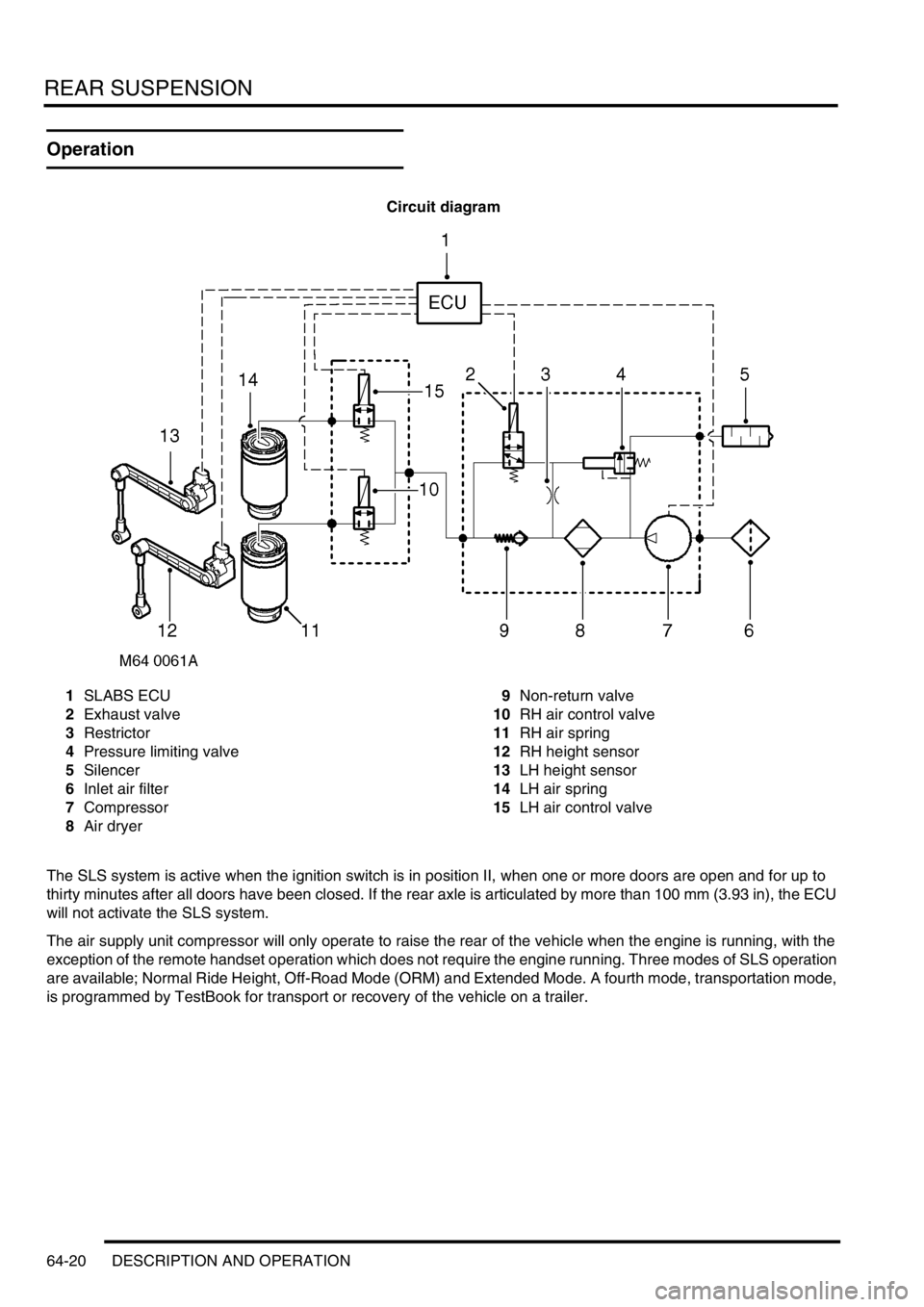
REAR SUSPENSION
64-20 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Operation
Circuit diagram
1SLABS ECU
2Exhaust valve
3Restrictor
4Pressure limiting valve
5Silencer
6Inlet air filter
7Compressor
8Air dryer9Non-return valve
10RH air control valve
11RH air spring
12RH height sensor
13LH height sensor
14LH air spring
15LH air control valve
The SLS system is active when the ignition switch is in position II, when one or more doors are open and for up to
thirty minutes after all doors have been closed. If the rear axle is articulated by more than 100 mm (3.93 in), the ECU
will not activate the SLS system.
The air supply unit compressor will only operate to raise the rear of the vehicle when the engine is running, with the
exception of the remote handset operation which does not require the engine running. Three modes of SLS operation
are available; Normal Ride Height, Off-Road Mode (ORM) and Extended Mode. A fourth mode, transportation mode,
is programmed by TestBook for transport or recovery of the vehicle on a trailer.
Page 1047 of 1672
BRAKES
70-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Brake system control diagram
Page 1065 of 1672

BRAKES
70-20 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Operation
Refer to illustration.
+ BRAKES, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Brake system control diagram.
When the ignition is switched on, the SLABS ECU performs a check of the brake related warning lamps as part of the
power up procedure. The warning lamps are illuminated for approximately 3 seconds and then extinguished. If a fault
warning lamp remains illuminated after the lamp check, a fault has been detected and repair action is required.
ABS
The ABS function prevents the road wheels locking during brake application, thus maintaining vehicle stability even
under emergency conditions.
WARNING: ABS is an aid to retaining steering control and stability while braking:
lABS cannot defy the natural laws of physics acting on the vehicle.
lABS will not prevent accidents resulting from excessive cornering speeds, following another vehicle too
closely, aquaplaning, etc.
lThe additional control provided by ABS must never be exploited in a dangerous or reckless manner
which could jeopardise the safety of driver or other road users.
lThe fitting of ABS does not imply that the vehicle will always stop in a shorter distance.
NOTE: During normal braking the feel of the brake pedal on vehicles equipped with ABS will be the same as that on
non ABS vehicles. During anti-lock braking operation the driver will experience feedback in the form of a pulsating
brake pedal and solenoid/pump motor noise from the ABS modulator.
The anti-lock braking function is automatically enabled whenever the ABS modulator is in the normal braking mode.
While the anti-lock braking function is enabled, if the SLABS ECU detects a wheel decelerating faster than the
average and at the calibrated wheel slip limit for ABS operation, it operates the ABS modulator in the ABS braking
mode for the affected wheel.
EBD
The EBD function optimises the distribution of hydraulic pressure between the front and rear axles, under all vehicle
load configurations and road conditions, to maintain vehicle stability during braking. EBD operates in forward and
reverse and is automatically enabled whenever the ABS modulator is in the normal braking mode at vehicle
deceleration rates of 0.3 g and above (i.e. medium to high brake pedal loads). EBD operation is similar to that of ABS,
but is calibrated to intervene at lower wheel slip limits and operates the brakes in axle pairs instead of individually.
During braking, if the SLABS ECU detects the wheels of one axle going slower than those of the other axle, i.e. a
potential wheel slip situation, it signals the ABS modulator to close the inlet solenoid valve for the brakes of the slower
wheels. This prevents any further increase in hydraulic pressure to those brakes, while allowing the hydraulic pressure
to the brakes on the other axle to increase and so maximise the overall braking effort. If the wheel speeds of the axle
being subjected to EBD control return within the calibrated wheel slip limits, the SLABS ECU signals a stepped
opening of the inlet solenoid valves, which allows a progressive increase of hydraulic pressure to the related brakes.
Operation of EBD is detectable from a stiffening of brake pedal movement as the inlet solenoid valves close and a
slight pulsing of the brake pedal as the inlet solenoid valves open. EBD operation ceases immediately the brake pedal
is released.
The wheel slip limit for EBD operation varies with vehicle speed. During normal operation, the inlet solenoid valves
always operate in axle pairs, with only one axle pair closed at any one time. Since the most lightly loaded wheel during
a braking manoeuvre will usually be the first to reach the slip limit, under most vehicle load configurations and road
conditions EBD control occurs on the trailing axle. However, EBD control can occur on the leading axle or switch
between axles during the braking manoeuvre.
Page 1097 of 1672
RESTRAINT SYSTEMS
75-2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
SRS block diagram
1DCU
2SRS warning lamp
3Driver airbag module
4Driver seat belt pretensioner
5Passenger airbag module
6Passenger seat belt pretensioner