2002 JEEP LIBERTY wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 1313 of 1803
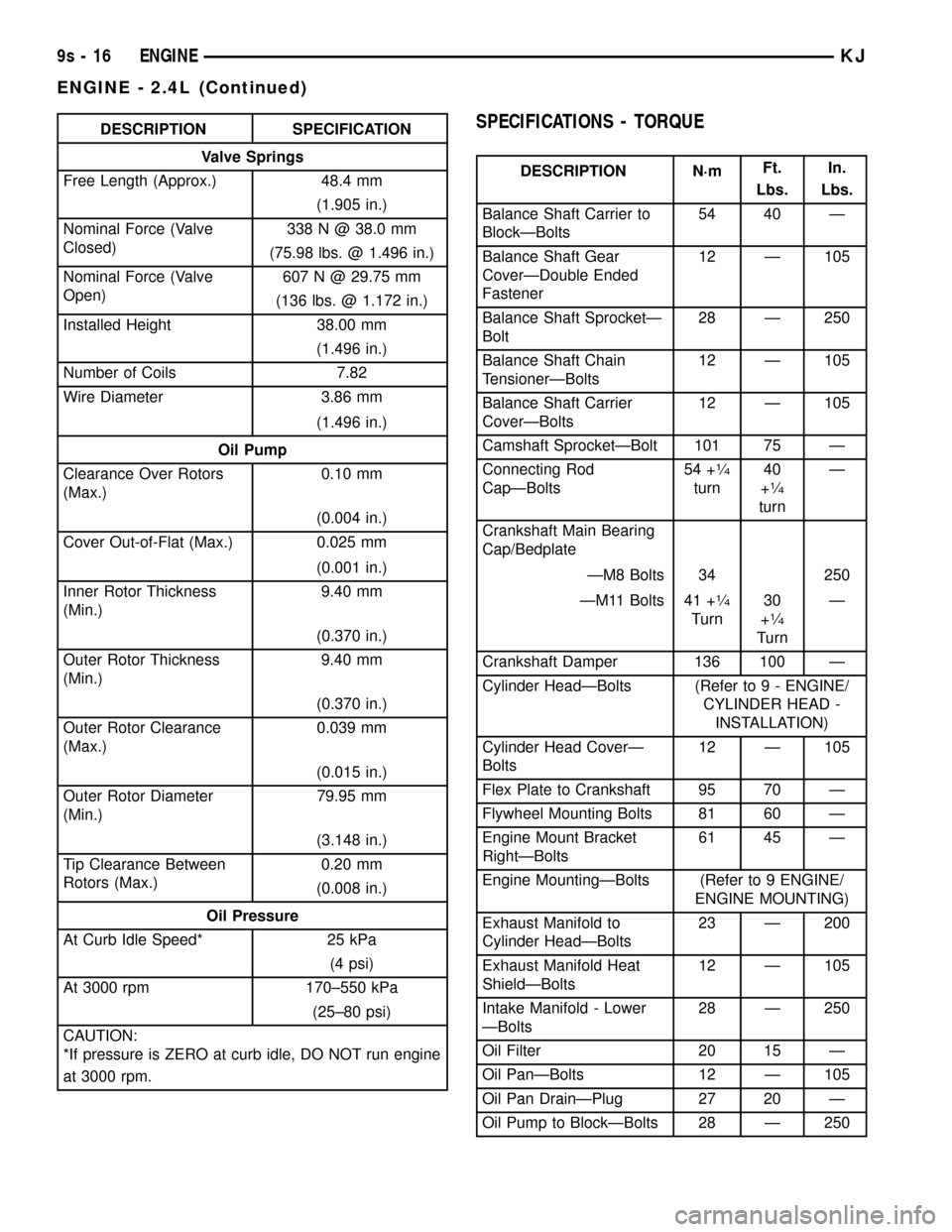
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Valve Springs
Free Length (Approx.) 48.4 mm
(1.905 in.)
Nominal Force (Valve
Closed)338 N @ 38.0 mm
(75.98 lbs. @ 1.496 in.)
Nominal Force (Valve
Open)607 N @ 29.75 mm
(136 lbs. @ 1.172 in.)
Installed Height 38.00 mm
(1.496 in.)
Number of Coils 7.82
Wire Diameter 3.86 mm
(1.496 in.)
Oil Pump
Clearance Over Rotors
(Max.)0.10 mm
(0.004 in.)
Cover Out-of-Flat (Max.) 0.025 mm
(0.001 in.)
Inner Rotor Thickness
(Min.)9.40 mm
(0.370 in.)
Outer Rotor Thickness
(Min.)9.40 mm
(0.370 in.)
Outer Rotor Clearance
(Max.)0.039 mm
(0.015 in.)
Outer Rotor Diameter
(Min.)79.95 mm
(3.148 in.)
Tip Clearance Between
Rotors (Max.)0.20 mm
(0.008 in.)
Oil Pressure
At Curb Idle Speed* 25 kPa
(4 psi)
At 3000 rpm 170±550 kPa
(25±80 psi)
CAUTION:
*If pressure is ZERO at curb idle, DO NOT run engine
at 3000 rpm.SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Balance Shaft Carrier to
BlockÐBolts54 40 Ð
Balance Shaft Gear
CoverÐDouble Ended
Fastener12 Ð 105
Balance Shaft SprocketÐ
Bolt28 Ð 250
Balance Shaft Chain
TensionerÐBolts12 Ð 105
Balance Shaft Carrier
CoverÐBolts12 Ð 105
Camshaft SprocketÐBolt 101 75 Ð
Connecting Rod
CapÐBolts54 +
1¤4
turn40
+1¤4
turnÐ
Crankshaft Main Bearing
Cap/Bedplate
ÐM8 Bolts 34 250
ÐM11 Bolts 41 +
1¤4
Turn30
+1¤4
TurnÐ
Crankshaft Damper 136 100 Ð
Cylinder HeadÐBolts (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD -
INSTALLATION)
Cylinder Head CoverÐ
Bolts12 Ð 105
Flex Plate to Crankshaft 95 70 Ð
Flywheel Mounting Bolts 81 60 Ð
Engine Mount Bracket
RightÐBolts61 45 Ð
Engine MountingÐBolts (Refer to 9 ENGINE/
ENGINE MOUNTING)
Exhaust Manifold to
Cylinder HeadÐBolts23 Ð 200
Exhaust Manifold Heat
ShieldÐBolts12 Ð 105
Intake Manifold - Lower
ÐBolts28 Ð 250
Oil Filter 20 15 Ð
Oil PanÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Oil Pan DrainÐPlug 27 20 Ð
Oil Pump to BlockÐBolts 28 Ð 250
9s - 16 ENGINEKJ
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1330 of 1803

OPERATION
The crankshaft transfers force generated by com-
bustion within the cylinder to the flywheel or flex-
plate.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CRANKSHAFT END
PLAY
(1) Using Dial Indicator C-3339 and Mounting
Post L-4438, attach to front of engine, locating probe
perpendicular on nose of crankshaft (Fig. 40).
(2) Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel.
(3) Zero the dial indicator.
(4) Move crankshaft all the way to the front and
read the dial indicator. Refer to Engine Specifica-
tions.
REMOVAL
NOTE: Crankshaft can not be removed when engine
is in vehicle.
(1) Remove engine assembly from vehicle. (Refer to
9 - ENGINE - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove flex plate and crankshaft rear oil seal.
(3) Mount engine on a repair stand.
(4) Drain engine oil and remove oil filter.
(5) Remove the oil pan. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL)
(6) Remove the timing belt covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)(7) Remove the timing belt. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL)
(8) Remove the oil pump. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - REMOVAL)
(9) Remove balance shafts and housing assembly.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/BALANCE
SHAFT - REMOVAL)
(10) Remove all bedplate bolts from the engine
block (Fig. 41).
(11) Using a mallet gently tap the bedplate loose
from the engine block dowel pins.
CAUTION: Do not pry up on one side of the bed-
plate. Damage may occur to cylinder block to bed-
plate alignment and thrust bearing.
(12) Bedplate should be removed evenly from the
cylinder block dowel pins to prevent damage to the
dowel pins and thrust bearing.
(13) Lift out crankshaft from cylinder block. Do
not damage the main bearings or journals when
removing the crankshaft.
Fig. 39 Crankshaft - Typical
1 - MAIN BEARING JOURNALS
2 - COUNTER BALANCE WEIGHTS
Fig. 40 CHECKING CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
Fig. 41 Bedplate Bolt Tightenening Sequence
KJENGINE9s-33
CRANKSHAFT (Continued)
Page 1374 of 1803

FRAMES & BUMPERS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FRONT FASCIA
REMOVAL.............................1
INSTALLATION..........................2
REAR FASCIA
REMOVAL.............................2
INSTALLATION..........................2
REAR FASCIA SUPPORT
REMOVAL.............................3
INSTALLATION..........................3
FRAME
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - FRAME DIMENSIONS . . . 3
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE.............6
FRONT SKID PLATE
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................6
ENGINE CRADLE CROSSMEMBER
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................6TRANSFER CASE SKID PLATE
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................7
REAR CROSSMEMBER
REMOVAL.............................7
INSTALLATION..........................7
FRONT TOW HOOK
REMOVAL.............................8
INSTALLATION..........................8
REAR TOW HOOK
REMOVAL.............................8
INSTALLATION..........................8
TRAILER HITCH
REMOVAL.............................9
INSTALLATION..........................9
FUEL TANK SKID PLATE
REMOVAL.............................9
INSTALLATION..........................9
FRONT FASCIA
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the grille. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTE-
RIOR/GRILLE - REMOVAL)
(2) Raise and support vehicle.
(3) Remove the front wheel opening flare moldings.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/FRONT WHEEL
OPENING FLARE MOLDINGS - REMOVAL)
(4) Remove the four screws through the lower air
dam (Fig. 1).
(5) Disconnect the electrical connectors:
²Fascia to grille opening reinforcement. (Fig. 1)
²Side repeater lights, both sides, if equipped.
(Fig. 2)
(6) Remove the six push pins from the grill sup-
port.
(7) Remove the rivets attaching the air dam to the
wheelhouse splash shield.
(8) Release the support tabs beneath the head-
lamps.
(9) Release the inner support clips from within the
fascia between the lights (Fig. 2).
(10) Remove the fascia.
Fig. 1 FRONT FASCIA
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - PUSH PINS
3 - FRONT FASCIA ASSEMBLY
4 - LOWER SCREWS
5 - PLASTIC RIVETS (2)
6 - INNER SUPPORT CLIPS
7 - SUPPORT TABS
KJFRAMES & BUMPERS 13 - 1
Page 1375 of 1803

INSTALLATION
(1) Install the fascia.
(2) Connect the electrical connectors.
²Side repeater lights, both sides, if equipped.
²Fascia to grille opening reinforcement.
(3) Install the six push pin fasteners into the grill
support.
(4) Install the four screws through the lower air
damn.
(5) Install new rivets attaching the air dam to the
wheelhouse splash shield.
(6) Install the front wheel opening flare moldings.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/WHEEL OPENING
FLARE MOLDING - INSTALLATION)
(7) Install the grille. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERI-
OR/GRILLE - INSTALLATION)
REAR FASCIA
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the wheel flares (rear). (Refer to 23 -
BODY/EXTERIOR/REAR WHEEL OPENING
FLARE MOLDINGS - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove the rear lamp units. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/
REAR LAMP UNIT - REMOVAL)(3) Remove the four side bolts. (Fig. 3)
(4) Remove the four bottom rivets.
(5) Remove the 3 bolts along the upper edge.
(6) Separate the side plastic retainers and remove
the fascia from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Fascia must be pushed completely forward
to allow the plastic retainers full engagement in
their respective slots.
(1) Install the fascia and insert the plastic retain-
ers.
(2) Install the three upper bolts.
(3) Install the four side bolts.
(4) Install four bottom rivets.
(5) Install the rear lamp units. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/REAR
LAMP UNIT - INSTALLATION)
(6) Install the rear half wheel opening flares.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/WHEEL OPENING
FLARE MOLDING - INSTALLATION)
Fig. 2 FASCIA INNER SUPPORT
1 - INNER SUPPORT CLIP
2 - SIDE REPEATER CONNECTOR (IF EQUIPPED)
3 - FASCIA ASSEMBLY
4 - FOG LAMP
Fig. 3 REAR FASCIA
1 - REAR FASCIA ASSEMBLY
2 - PLASTIC RETAINERS
3 - FASCIA SUPPORT BRACKET
4 - SIDE BOLTS
5 - RIVETS
6 - UPPER BOLTS
13 - 2 FRAMES & BUMPERSKJ
FRONT FASCIA (Continued)
Page 1413 of 1803

OPERATION
2.4L
Engine speed and crankshaft position are provided
through the CKP (Crankshaft Position) sensor. The
sensor generates pulses that are the input sent to the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The PCM inter-
prets the sensor input to determine the crankshaft
position. The PCM then uses this position, along with
other inputs, to determine injector sequence and igni-
tion timing.
The sensor is a hall effect device combined with an
internal magnet. It is also sensitive to steel within a
certain distance from it.
A tonewheel (targetwheel) is a part of the engine
crankshaft (Fig. 4). This tonewheel has sets of
notches at its outer edge.
The notches cause a pulse to be generated when
they pass under the sensor. The pulses are the input
to the PCM.
3.7L
Engine speed and crankshaft position are provided
through the CKP (Crankshaft Position) sensor. The
sensor generates pulses that are the input sent to the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The PCM inter-
prets the sensor input to determine the crankshaft
position. The PCM then uses this position, along with
other inputs, to determine injector sequence and igni-
tion timing.
The sensor is a hall effect device combined with an
internal magnet. It is also sensitive to steel within a
certain distance from it.A tonewheel (targetwheel) is bolted to the engine
crankshaft (Fig. 5). This tonewheel has sets of
notches at its outer edge (Fig. 5).
The notches cause a pulse to be generated when
they pass under the sensor. The pulses are the input
to the PCM.
REMOVAL
2.4L
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is mounted
into the right front side of the cylinder block (Fig. 6).
It is positioned and bolted into a machined hole.
(1) Disconnect sensor electrical connector.
(2) Remove sensor bolt.
(3) Carefully pry sensor from cylinder block in a
rocking action.
(4) Check condition of sensor o-ring (Fig. 7).
3.7L
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is mounted
into the right rear side of the cylinder block (Fig. 8).
It is positioned and bolted into a machined hole.
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Disconnect sensor electrical connector.
(3) Remove sensor mounting bolt (Fig. 8).
(4) Carefully remove sensor from cylinder block in
a rocking and twisting action.
(5) Check condition of sensor o-ring.
Fig. 4 CKP OPERATION-2.4L
1 - NOTCHES
2 - CRANKSHAFT
Fig. 5 CKP OPERATION-3.7L
1 - TONEWHEEL
2 - NOTCHES
3 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
4 - CRANKSHAFT
KJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 31
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1431 of 1803
STEERING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STEERING
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
STEERING SYSTEM....................1DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
STEERING FLOW AND PRESSURE........3
COLUMN...............................5
GEAR.................................13
LINKAGE..............................16
PUMP.................................17
STEERING
DESCRIPTION
Power steering systems consist of:
²Steering column & Intermediate Shaft
²Rack and pinion steering gear
²Belt driven hydraulic steering pump
²Pump pressure, supply and return hoses
²Oil Cooler
OPERATION
The steering column intermediate shaft attaches
the steering column to the gear pinion. The rotation
of the pinion moves the gear rack from side-to-side.
This lateral action of the rack pushes and pulls the
tie rods to change the direction of the front wheels.
Power assist is provided by an engine mounted
hydraulic pump. The pump supplies hydraulic fluid
to the steering gear. All vehicles are equipped with
an oil cooler.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER STEERING SYSTEM
STEERING NOISE
There is some noise in all power steering systems. One of the most common is a hissing sound evident at a
standstill/parking, or when the steering is at the end of it's travel. Hiss is a high frequency noise similar to that
of a water tap being closed slowly. The noise is present in all valves that have a high velocity fluid passing through
an orifice. There is no relationship between this noise and steering performance.
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OBJECTIONAL HISS OR
WHISTLE1. Steering intermediate shaft to dash panel
seal.1. Check and repair seal at dash
panel.
2. Noisy valve in power steering gear. 2. Replace steering gear.
1. Gear mounting bolts loose. 1. Tighten bolts to specification.
2. Loose or damaged suspension
components.2. Inspect and repair suspension.
3. Internal gear noise. 3. Replace steering gear.
4. Loose or damaged intermediate shaft or
column.4. Inspect and repair or replace.
MOAN Pressure hose in contact with other
components.Reposition hose.
CHIRP OR SQUEAL 1. Loose belt. 1. Adjust or replace.
KJSTEERING 19 - 1
Page 1432 of 1803
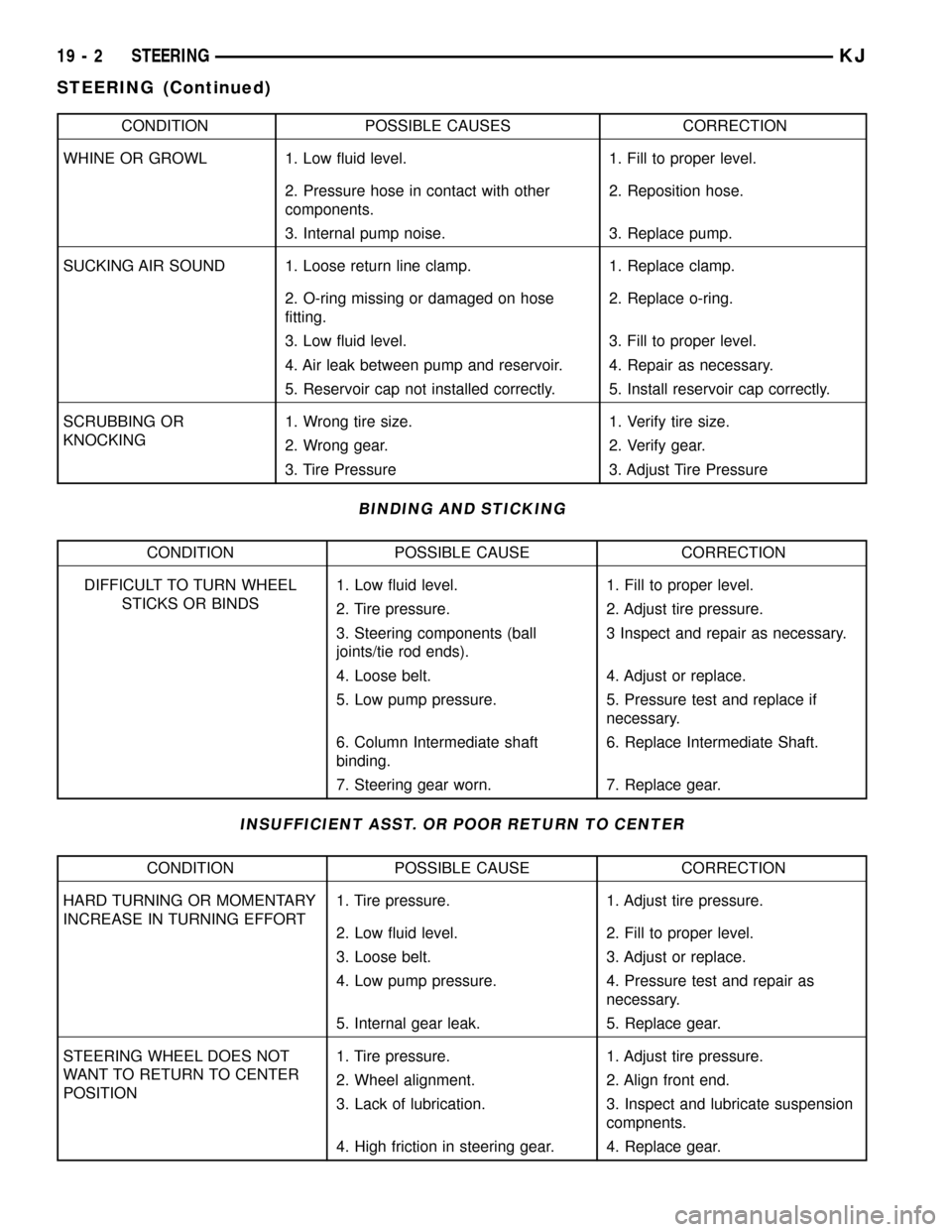
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
WHINE OR GROWL 1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill to proper level.
2. Pressure hose in contact with other
components.2. Reposition hose.
3. Internal pump noise. 3. Replace pump.
SUCKING AIR SOUND 1. Loose return line clamp. 1. Replace clamp.
2. O-ring missing or damaged on hose
fitting.2. Replace o-ring.
3. Low fluid level. 3. Fill to proper level.
4. Air leak between pump and reservoir. 4. Repair as necessary.
5. Reservoir cap not installed correctly. 5. Install reservoir cap correctly.
SCRUBBING OR
KNOCKING1. Wrong tire size. 1. Verify tire size.
2. Wrong gear. 2. Verify gear.
3. Tire Pressure 3. Adjust Tire Pressure
BINDING AND STICKING
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
DIFFICULT TO TURN WHEEL
STICKS OR BINDS1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill to proper level.
2. Tire pressure. 2. Adjust tire pressure.
3. Steering components (ball
joints/tie rod ends).3 Inspect and repair as necessary.
4. Loose belt. 4. Adjust or replace.
5. Low pump pressure. 5. Pressure test and replace if
necessary.
6. Column Intermediate shaft
binding.6. Replace Intermediate Shaft.
7. Steering gear worn. 7. Replace gear.
INSUFFICIENT ASST. OR POOR RETURN TO CENTER
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
HARD TURNING OR MOMENTARY
INCREASE IN TURNING EFFORT1. Tire pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Low fluid level. 2. Fill to proper level.
3. Loose belt. 3. Adjust or replace.
4. Low pump pressure. 4. Pressure test and repair as
necessary.
5. Internal gear leak. 5. Replace gear.
STEERING WHEEL DOES NOT
WANT TO RETURN TO CENTER
POSITION1. Tire pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Wheel alignment. 2. Align front end.
3. Lack of lubrication. 3. Inspect and lubricate suspension
compnents.
4. High friction in steering gear. 4. Replace gear.
19 - 2 STEERINGKJ
STEERING (Continued)
Page 1433 of 1803
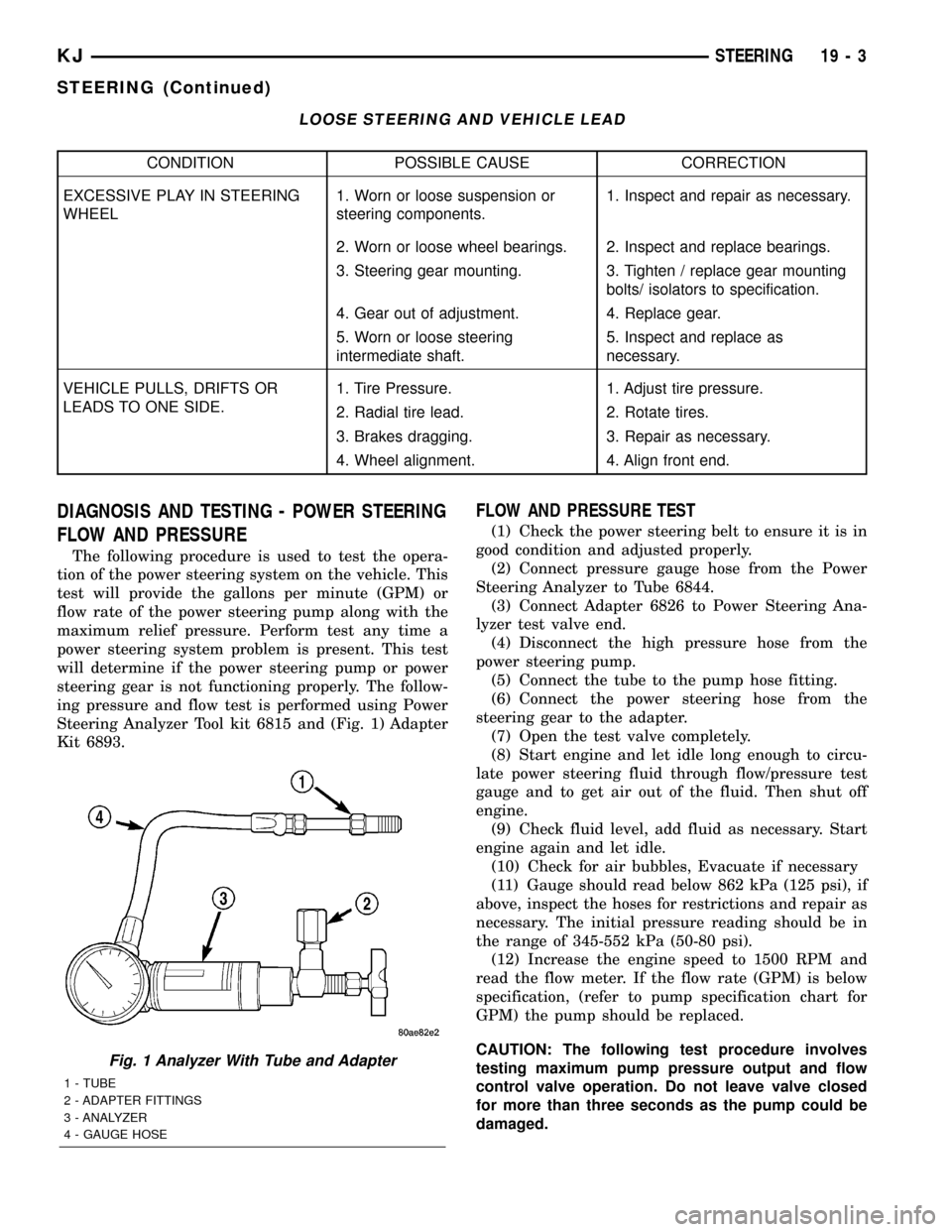
LOOSE STEERING AND VEHICLE LEAD
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE PLAY IN STEERING
WHEEL1. Worn or loose suspension or
steering components.1. Inspect and repair as necessary.
2. Worn or loose wheel bearings. 2. Inspect and replace bearings.
3. Steering gear mounting. 3. Tighten / replace gear mounting
bolts/ isolators to specification.
4. Gear out of adjustment. 4. Replace gear.
5. Worn or loose steering
intermediate shaft.5. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
VEHICLE PULLS, DRIFTS OR
LEADS TO ONE SIDE.1. Tire Pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Radial tire lead. 2. Rotate tires.
3. Brakes dragging. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Wheel alignment. 4. Align front end.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER STEERING
FLOW AND PRESSURE
The following procedure is used to test the opera-
tion of the power steering system on the vehicle. This
test will provide the gallons per minute (GPM) or
flow rate of the power steering pump along with the
maximum relief pressure. Perform test any time a
power steering system problem is present. This test
will determine if the power steering pump or power
steering gear is not functioning properly. The follow-
ing pressure and flow test is performed using Power
Steering Analyzer Tool kit 6815 and (Fig. 1) Adapter
Kit 6893.
FLOW AND PRESSURE TEST
(1) Check the power steering belt to ensure it is in
good condition and adjusted properly.
(2) Connect pressure gauge hose from the Power
Steering Analyzer to Tube 6844.
(3) Connect Adapter 6826 to Power Steering Ana-
lyzer test valve end.
(4) Disconnect the high pressure hose from the
power steering pump.
(5) Connect the tube to the pump hose fitting.
(6) Connect the power steering hose from the
steering gear to the adapter.
(7) Open the test valve completely.
(8) Start engine and let idle long enough to circu-
late power steering fluid through flow/pressure test
gauge and to get air out of the fluid. Then shut off
engine.
(9) Check fluid level, add fluid as necessary. Start
engine again and let idle.
(10) Check for air bubbles, Evacuate if necessary
(11) Gauge should read below 862 kPa (125 psi), if
above, inspect the hoses for restrictions and repair as
necessary. The initial pressure reading should be in
the range of 345-552 kPa (50-80 psi).
(12) Increase the engine speed to 1500 RPM and
read the flow meter. If the flow rate (GPM) is below
specification, (refer to pump specification chart for
GPM) the pump should be replaced.
CAUTION: The following test procedure involves
testing maximum pump pressure output and flow
control valve operation. Do not leave valve closed
for more than three seconds as the pump could be
damaged.
Fig. 1 Analyzer With Tube and Adapter
1 - TUBE
2 - ADAPTER FITTINGS
3 - ANALYZER
4 - GAUGE HOSE
KJSTEERING 19 - 3
STEERING (Continued)