2002 JEEP LIBERTY wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 1278 of 1803

OIL FILTER
REMOVAL
All engines are equipped with a high quality full-
flow, disposable type oil filter. DaimlerChrysler Cor-
poration recommends a Mopartor equivalent oil
filter be used.
(1) Position a drain pan under the oil filter.
(2) Using a suitable oil filter wrench loosen filter.
(3) Rotate the oil filter counterclockwise (Fig. 73)to
remove it from the cylinder block oil filter boss.
(4) When filter separates from cylinder block oil
filter boss, tip gasket end upward to minimize oil
spill. Remove filter from vehicle.
NOTE: Make sure filter gasket was removed with fil-
ter.
(5) With a wiping cloth, clean the gasket sealing
surface of oil and grime.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lightly lubricate oil filter gasket with engine
oil.
(2) Thread filter onto adapter nipple. When gasket
makes contact with sealing surface, (Fig. 74)hand
tighten filter one full turn, do not over tighten.
(3) Add oil, verify crankcase oil level and start
engine. Inspect for oil leaks.
OIL PAN
DESCRIPTION
The engine oil pan is made of laminated steel and
has a single plane sealing surface. The sandwich
style oil pan gasket has an integrated windage tray
and steel carrier (Fig. 75). The sealing area of the
gasket is molded with rubber and is designed to be
reused as long as the gasket is not cut, torn or
ripped.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the engine (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
REMOVAL).
(2) Position the engine in a suitable engine stand.
NOTE: Do not pry on oil pan or oil pan gasket. Gas-
ket is integral to engine windage tray and does not
come out with oil pan (Fig. 76).
(3) Remove the oil pan mounting bolts and oil pan.
(4) Unbolt oil pump pickup tube and remove tube.
(5) Remove the oil pan gasket/windage tray
assemblyfrom engine.
CLEANING
(1) Clean oil pan in solvent and wipe dry with a
clean cloth.
(2) Clean the oil pan gasket surface.DO NOTuse
a grinder wheel or other abrasive tool to clean seal-
ing surface.
(3) Clean oil screen and tube thoroughly in clean
solvent.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect oil drain plug and plug hole for
stripped or damaged threads. Repair as necessary.
Fig. 73 Oil Filter - 3.7L Engine
1 - ENGINE OIL FILTER
Fig. 74 Oil Filter Sealing SurfaceÐTypical
1 - SEALING SURFACE
2 - RUBBER GASKET
3 - OIL FILTER
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 63
Page 1286 of 1803

(1) Position the engine exhaust manifold and gas-
ket on the two studs located on the cylinder head.
Install conical washers and nuts on these studs.
(2) Install remaining conical washers. Starting at
the center arm and working outward, tighten the
bolts and nuts to 25 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install the exhaust heat shields.
(4) Raise and support the vehicle.
CAUTION: Over tightening heat shield fasteners,
may cause shield to distort and/or crack.
(5) Assemble exhaust pipe to manifold and secure
with bolts, nuts and retainers. Tighten the bolts and
nuts to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
LEFT EXHAUST MANIFOLD
CAUTION: If the studs came out with the nuts when
removing the engine exhaust manifold, install new
studs. Apply sealer on the coarse thread ends.
Water leaks may develop at the studs if this precau-
tion is not taken.
(1) Position the engine exhaust manifold and gas-
ket on the two studs located on the cylinder head.
Install conical washers and nuts on these studs.
(2) Install remaining conical washers. Starting at
the center arm and working outward, tighten the
bolts and nuts to 25 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install the exhaust heat shields.
(4) Raise and support the vehicle.
CAUTION: Over tightening heat shield fasteners,
may cause shield to distort and/or crack.
(5) Assemble exhaust pipe to manifold and secure
with bolts, nuts and retainers. Tighten the bolts and
nuts to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
VALVE TIMING
DESCRIPTION
The timing drive system has been designed to pro-
vide quiet performance and reliability to support a
non-free wheelingengine. Specifically the intake
valves are non-free wheeling and can be easily dam-
aged with forceful engine rotation if camshaft-to-
crankshaft timing is incorrect. The timing drive
system consists of a primary chain, two secondary
timing chain drives and a counterbalance shaft drive.
OPERATION
The primary timing chain is a single inverted tooth
chain type. The primary chain drives the large 40
tooth idler sprocket directly from a 20 tooth crank-shaft sprocket. Primary chain motion is controlled by
a pivoting leaf spring tensioner arm and a fixed
guide. The arm and the guide both use nylon plastic
wear faces for low friction and long wear. The pri-
mary chain receives oil splash lubrication from the
secondary chain drive and designed oil pump leak-
age. The idler sprocket assembly connects the pri-
mary chain drive, secondary chain drives, and the
counterbalance shaft. The idler sprocket assembly
consists of two integral 26 tooth sprockets a 40 tooth
sprocket and a helical gear that is press-fit to the
assembly. The spline joint for the 40 tooth sprocket is
a non ± serviceable press fit anti rattle type. A spiral
ring is installed on the outboard side of the fifty
tooth sprocket to prevent spline disengagement. The
idler sprocket assembly spins on a stationary idler
shaft. The idler shaft is a light press-fit into the cyl-
inder block. A large washer on the idler shaft bolt
and the rear flange of the idler shaft are used to con-
trol sprocket thrust movement. Pressurized oil is
routed through the center of the idler shaft to pro-
vide lubrication for the two bushings used in the
idler sprocket assembly.
There are two secondary drive chains, both are
roller type, one to drive the camshaft in each SOHC
cylinder head. There are no shaft speed changes in
the secondary chain drive system. Each secondary
chain drives a 26 tooth cam sprocket directly from
the 26 tooth sprocket on the idler sprocket assembly.
A fixed chain guide and a hydraulic oil damped ten-
sioner are used to maintain tension in each second-
ary chain system. The hydraulic tensioners for the
secondary chain systems are fed pressurized oil from
oil reservoir pockets in the block. Each tensioner
incorprates a controled leak path through a device
known as a vent disc located in the nose of the piston
to manage chain loads. Each tensioner also has a
mechanical ratchet system that limits chain slack if
the tensioner piston bleeds down after engine shut
down. The tensioner arms and guides also utilize
nylon wear faces for low friction and long wear. The
secondary timing chains receive lubrication from a
small orifice in the tensioners. This orifice is pro-
tected from clogging by a fine mesh screen which is
located on the back of the hydraulic tensioners.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
MEASURING TIMING CHAIN WEAR
NOTE: This procedure must be performed with the
timing chain cover removed.
(1) Remove the timing chain cover. Refer to Timing
Chain Cover in this section for procedure.
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 71
EXHAUST MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1287 of 1803

(2) To determine if the secondary timing chains
are worn, rotate the engine clockwise until maximum
tensioner piston extension is obtained. Measure the
distance between the secondary timing chain ten-
sioner housing and the step ledge on the piston. The
measurement at point (A) must be less than 15mm
(.5906 inches).
(3) If the measurement exceeds the specification
the secondary timing chains are worn and require
replacement. Refer to Timing Chain and Sprockets in
this section for procedure.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
TIMING VERIFICATION
CAUTION: The 3.7L is a non free-wheeling design
engine. Therefore, correct engine timing is critical.
NOTE: Components referred to as left hand or right
hand are as viewed from the drivers position inside
the vehicle.
NOTE: The blue link plates on the chains and the
dots on the camshaft drive sprockets may not line
up during the timing verification procedure. The
blue link plates are lined up with the sprocket dots
only when re-timing the complete timing drive.
Once the timing drive is rotated blue link-to-dot
alignment is no longer valid.
Engine base timing can be verified by the following
procedure:
(1) Remove the cylinder head covers. Refer to the
procedure in this section.
(2) Using a mirror, locate the TDC arrow on the
front cover (Fig. 91). Rotate the crankshaft until the
mark on the crankshaft damper is aligned with the
TDC arrow on the front cover. The engine is now at
TDC.
(3) Note the location of the V6 mark stamped into
the camshaft drive gears. If the V6 mark on each
camshaft drive gear is at the twelve o'clock position,
the engine is at TDC on the exhaust stroke. If the V6
mark on each gear is at the six o'clock position, the
engine is at TDC on the compression stroke. (Fig. 95)
(4) If both of the camshaft drive gears are off in
the same or opposite directions, the primary chain or
both secondary chains are at fault. Refer to Timing
Chain and Sprockets procedure in this section.
(5) If only one of the camshaft drive gears is off
and the other is correct, the problem is confined to
one secondary chain. Refer to Single camshaft tim-
ing, in this procedure.(6) If both camshaft drive gear V6 marks are at
the twelve o'clock or the six o' clock position the
engine base timing is correct. Reinstall the cylinder
head covers.
COUNTER BALANCE SHAFT TIMING
(1) Ensure that the engine is at TDC with both
camshaft sprocket marks are in the 12 o'clock posi-
tion. (Fig. 94)
(2) Look down the left cylinder gear chain cavity.
The timing dot on the counter balance shaft drive
gear should be in the 6 o'clock position (Fig. 92).
TIMING - SINGLE CAMSHAFT
NOTE: to adjust the timing on one camshaft, pre-
form the following procedure.
(1) Using Chain Tensioner Wedge, Special Tool
8379, stabilize the secondary chain drive. For refer-
ence purposes, mark the chain-to-sprocket position.
(Fig. 93)
(2) Remove the camshaft drive gear retaining bolt.
(3) Carefully remove the camshaft drive gear from
the camshaft.
(4) Re-index the camshaft drive gear in the chain
until the V6 mark is at the same position as the V6
mark on the opposite camshaft drive gear.
Fig. 91 Engine Top Dead Center (TDC) Indicator
Mark
1 - TIMING CHAIN COVER
2 - CRANKSHAFT TIMING MARKS
9 - 72 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
VALVE TIMING (Continued)
Page 1291 of 1803

INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Do not use oil based liquids to clean tim-
ing cover or block surfaces. Use only rubbing alco-
hol, along with plastic or wooden scrapers. Use no
wire brushes or abrasive wheels or metal scrapers,
or damage to surfaces could result.
(1) Clean timing chain cover and block surface
using rubbing alcohol.
CAUTION: The 3.7L uses a special anerobic sealer
instead of a gasket to seal the timing cover to the
engine block, from the factory. For service repairs,
MoparTEngine RTV must be used as a substitute.
(2) Inspect the water passage o-rings for any dam-
age, and replace as necessary.
(3) Apply MopartEngine RTV sealer to front cover
(Fig. 100).
(4) Install cover. Tighten fasteners in sequence as
shown in (Fig. 101) to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(5) Install crankshaft damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
INSTALLATION).
(6) Install the A/C compressor (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COM-
PRESSOR - INSTALLATION).
(7) Install the generator (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/CHARGING/GENERATOR - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install accessory drive belt tensioner assembly
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/BELT
TENSIONERS - INSTALLATION).
(9) Install radiator upper and lower hoses.
(10) Install both heater hoses.(11) Install electric fan shroud and viscous fan
drive assembly (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/FAN
DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH - INSTALLATION).
(12) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(13) Connect the battery negative cable.
Fig. 99 Timing Chain Cover Fasteners - Typical
Fig. 100 TIMING COVER SEALANT
1 - TIMING CHAIN COVER
2 - WATER PASSAGE ORING
3 - MOPARTENGINE RTV SEALER
Fig. 101 Timing Chain Cover Fasteners - Typical
9 - 76 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) (Continued)
Page 1292 of 1803

IDLER SHAFT
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the primary and secondary timing
chains and sprockets. Refer to procedure in this sec-
tion.
NOTE: To remove the idler shaft, it is necessary to
tap threads into the shaft, to install the removal
tool.
(2) Using a 12 mm X 1.75 tap, cut threads in the
idler shaft center bore.
(3) Cover the radiator core with a suitable cover.
CAUTION: Use care when removing the idler shaft,
Do not strike the radiator cooling fins with the slide
hammer.
(4) Using Special Tool 8517 Slide Hammer, remove
the idler shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Thoroughly clean the idler shaft bore.
(2) Position the idler shaft in the bore.
NOTE: The two lubrication holes in the idler shaft
do not require any special alignment.
NOTE: Before using the retaining bolt to install the
idler shaft, coat the threads and the pilot on the
idler shaft, with clean engine oil.
(3) Using the primary idler sprocket retaining bolt
and washer, carefully draw the idler shaft into the
bore until fully seated.
(4) Coat the idler shaft with clean engine oil.
(5) Install the timing chains and sprockets. Refer
to procedure in this section.
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKET(S
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Drain cooling system. Refer to COOLING SYS-
TEM for procedures.
(3) Remove right and left cylinder head covers.
Refer to CYLINDER HEAD COVER.
(4) Remove radiator fan shroud. Refer to COOL-
ING SYSTEM for procedure.
(5) Rotate engine until timing mark on crankshaft
damper aligns with TDC mark on timing chain cover
(Fig. 103) (#1 cylinder exhaust stroke) and the cam-
shaft sprocket ªV6º marks are at the 12 o'clock posi-
tion (Fig. 102).
CAUTION: The nut on the right side camshaft
sprocket should not be removed for any reason, as
the sprocket and camshaft sensor target wheel is
serviced as an assembly. If the nut was removed
retorque nut to 5 N´m (44 in. lbs.).
(6) Remove power steering pump. Refer to STEER-
ING for procedure.
(7) Remove access plug from left and right cylinder
heads for access to chain guide fasteners (Fig. 104).
(8) Remove the oil fill housing to gain access to the
right side tensioner arm fastener.
(9) Remove crankshaft damper and timing chain
cover. Refer to procedures.
(10) Collapse and pin primary chain tensioner.
CAUTION: Plate behind left secondary chain ten-
sioner could fall into oil pan. Therefore, cover pan
opening.
(11) Remove secondary chain tensioners.
(12) Remove camshaft position and crankshaft
position sensors (Fig. 105) and (Fig. 106).
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 77
Page 1294 of 1803

CAUTION: Care should be taken not to damage
camshaft target wheel. Do not hold target wheel
while loosening or tightening camshaft sprocket.
Do not place the target wheel near a magnetic
source of any kind. A damaged or magnetized tar-
get wheel could cause a vehicle no start condition.
CAUTION: Do not forcefully rotate the camshafts or
crankshaft independently of each other. Damaging
intake valve to piston contact will occur. Ensure
negative battery cable is disconnected to guard
against accidental starter engagement.
(13) Remove left and right camshaft sprocket bolts.
(14) While holding the left camshaft steel tube
with Special Tool 8428 Camshaft Wrench, remove the
left camshaft sprocket. Slowly rotate the camshaft
approximately 5 degrees clockwise to a neutral posi-
tion.
(15) While holding the right camshaft steel tube
with Special Tool 8428 Camshaft Wrench, remove the
right camshaft sprocket.
(16) Remove idler sprocket assembly bolt.
(17) Slide the idler sprocket assembly and crank
sprocket forward simultaneously to remove the pri-
mary and secondary chains.
(18) Remove both pivoting tensioner arms and
chain guides.
(19) Remove chain tensioner.
INSPECTION
Inspect the following components:
²Sprockets for excessive tooth wear. Some tooth
markings are normal and not a cause for sprocket
replacement.
²Idler sprocket assembly bushing and shaft for
excessive wear.
²Idler sprocket assembly spline joint. The joint
should be tight with no backlash or axial movement.
²Chain guides and tensioner arms. Replace these
parts if grooving in plastic face is more than 1 mm
(0.039 in.) deep. If plastic face is severely grooved or
melted, the tensioner lube jet may be clogged. The
tensioner should be replaced.
²Secondary chain tensioner piston and ratcheting
device. Inspect for evidence of heavy contact between
tensioner piston and tensioner arm. If this condition
exist the tensioner tensioner arm and chain should
be replaced.
²Primary chain tensioner plastic faces. Replace as
required.
Fig. 105 CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
1 - CYLINDER HEAD
2 - CAMSAHFT POSITION SENSOR
2 - SCREW
Fig. 106 Crankshaft Position Sensor
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
3 - CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
4 - RIGHT SIDE CYLINDER BLOCK
KJENGINE - 3.7L 9 - 79
TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKET(S (Continued)
Page 1300 of 1803

ENGINE - 2.4L
DESCRIPTION
The 2.4 Liter (148 cu. in.) in-line four cylinder
engine is a double over head camshaft with hydraulic
lifters and four valve per cylinder design. The engine
is free-wheeling; meaning it has provisions for piston-
to-valve clearance. However valve-to-valve interference
can occur, if camshafts are rotated independently.
The cylinders are numbered from front of the
engine to the rear. The firing order is 1±3±4±2.
The engine identification number is located on the
rear of the cylinder block (Fig. 1).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE PRESSURE CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the pressure cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum, with 552 kPa (80 psi) rec-
ommended.
Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage per cylinder.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
(2) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Select a route free from traf-
fic and other forms of congestion, observe all traffic
laws, and accelerate through the gears several times
briskly.
(3) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As spark
plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnor-
mal firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc. Record cyl-
inder number of spark plug for future reference.
(4) Remove the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay from
the PDC.
(5) Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the
compression check.
(6) Insert compression gage adaptor Special Tool
8116 or the equivalent, into the #1 spark plug hole in
cylinder head. Connect the 0±500 psi (Blue) pressure
transducer with cable adaptors to the DRBIIIt.
Fig. 1 ENGINE IDENTIFICATION
1 - ENGINE IDENTIFICATION
KJENGINE9s-3
Page 1305 of 1803
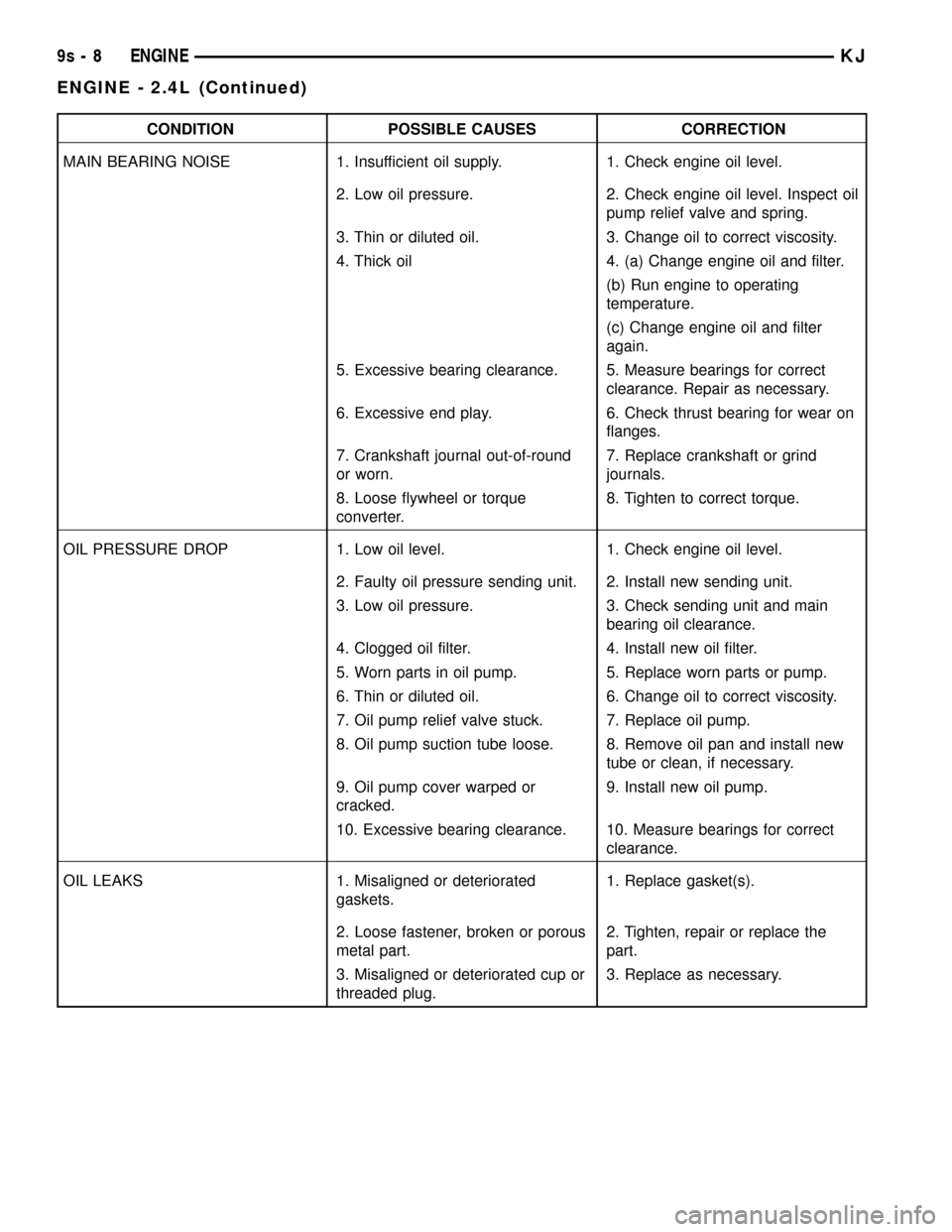
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil
pump relief valve and spring.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Thick oil 4. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
5. Excessive bearing clearance. 5. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary.
6. Excessive end play. 6. Check thrust bearing for wear on
flanges.
7. Crankshaft journal out-of-round
or worn.7. Replace crankshaft or grind
journals.
8. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.8. Tighten to correct torque.
OIL PRESSURE DROP 1. Low oil level. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit. 2. Install new sending unit.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check sending unit and main
bearing oil clearance.
4. Clogged oil filter. 4. Install new oil filter.
5. Worn parts in oil pump. 5. Replace worn parts or pump.
6. Thin or diluted oil. 6. Change oil to correct viscosity.
7. Oil pump relief valve stuck. 7. Replace oil pump.
8. Oil pump suction tube loose. 8. Remove oil pan and install new
tube or clean, if necessary.
9. Oil pump cover warped or
cracked.9. Install new oil pump.
10. Excessive bearing clearance. 10. Measure bearings for correct
clearance.
OIL LEAKS 1. Misaligned or deteriorated
gaskets.1. Replace gasket(s).
2. Loose fastener, broken or porous
metal part.2. Tighten, repair or replace the
part.
3. Misaligned or deteriorated cup or
threaded plug.3. Replace as necessary.
9s - 8 ENGINEKJ
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)