2002 JEEP LIBERTY Tab 9
[x] Cancel search: Tab 9Page 1298 of 1803

ENGINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ENGINE - 2.4L
DESCRIPTION..........................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST................................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST.........3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
LEAK INSPECTION.....................4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE.......5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE............5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
MECHANICAL.........................7
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE
AND OIL GALLERY PLUGS...............9
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR OF
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS..........9
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HYDROSTATIC
LOCKED ENGINE......................9
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-
PLACE GASKETS AND SEALERS.........10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE
GASKET SURFACE PREPARATION........11
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
BEARING CLEARANCE USING
PLASTIGAGE.........................11
REMOVAL - ENGINE ASSEMBLY...........12
INSTALLATION - ENGINE ASSEMBLY........12
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS - 2.4L ENGINE.........13
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE............16
SPECIAL TOOLS
2.4L ENGINE.........................17
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL - 2.4L........................19
INSTALLATION - 2.4L....................19
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION.........................19
OPERATION...........................19
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER HEAD
GASKET............................19
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD.............20
CLEANING............................20
INSPECTION..........................21
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD..........21CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL(S)
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................22
CAMSHAFT(S)
DESCRIPTION.........................23
OPERATION...........................23
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CAMSHAFT
END-PLAY...........................23
REMOVAL.............................24
CLEANING............................24
INSPECTION..........................25
INSTALLATION.........................25
CYLINDER HEAD COVER
REMOVAL.............................26
CLEANING............................26
INSPECTION..........................26
INSTALLATION.........................26
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS
DESCRIPTION.........................27
CLEANING............................27
VALVE SPRINGS
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD ON.........27
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD OFF........27
INSPECTION..........................28
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD ON.....28
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD OFF....28
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - LASH ADJUSTER
(TAPPET) NOISE DIAGNOSIS............28
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29
ROCKER ARMS
REMOVAL.............................29
INSPECTION..........................30
INSTALLATION.........................30
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION.........................30
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON TO
CYLINDER BORE FITTING..............30
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER
BORE HONING.......................31
CLEANING............................31
INSPECTION..........................32
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE
CONNECTING ROD - FITTING...........32
KJENGINE 9s - 1
Page 1301 of 1803

(7) Crank engine until maximum pressure is
reached on gage. Record this pressure as #1 cylinder
pressure.
(8) Repeat the previous step for all remaining cyl-
inders.
(9) Compression should not be less than 689 kPa
(100 psi) and not vary more than 25 percent from cyl-
inder to cylinder.
(10) If one or more cylinders have abnormally low
compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
(11) If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an
abnormally low reading on the second compression
test, it could indicate the existence of a problem in
the cylinder in question.The recommended com-
pression pressures are to be used only as a
guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
should not be disassembled to determine the
cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL LEAK
INSPECTION
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair as necessary.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24 km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.
(5)If the oil leak source is not positively
identified at this time, proceed with the air leak
detection test method as follows:
²Disconnect the fresh air hose (make-up air) at
the cylinder head cover and plug or cap the nipple on
the cover.
²Remove the PCV valve hose from the cylinder
head cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve nipple on the
cover.
²Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and reg-
ulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.²Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provides the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
²If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil
seal area, refer to the section, Inspection for Rear
Seal Area Leak.
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply.
Remove the air hose, all plugs, and caps. Install the
PCV valve and fresh air hose (make-up air). Proceed
to next step.
(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
NOTE: If oil leakage is observed at the dipstick tube
to block location; remove the tube, clean and reseal
using MoparTStud & Bearing Mount (press fit tube
applications only), and for O-ring style tubes,
remove tube and replace the O-ring seal.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak. If a leak is
present in this area, remove transmission for further
inspection.
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, oil gallery cup
plug, bedplate to cylinder block mating surfaces
and seal bore. See proper repair procedures for
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as previously described.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
9s - 4 ENGINEKJ
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1309 of 1803

NOTE: Plastigage is available in a variety of clear-
ance ranges. Use the most appropriate range for
the specifications you are checking.
(4) Install the proper crankshaft bearings to
achieve the specified bearing clearances. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARINGS - STANDARD PROCEDURE) (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CONNECTING ROD
BEARINGS - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
REMOVAL - ENGINE ASSEMBLY
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Remove hood. Mark hood hinge location for
reinstallation.
(3) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(4) Remove radiator core support bracket.
(5) Remove fan shroud with electric fan assembly.
(6) Remove drive belt.
NOTE: It is NOT necessary to discharge the A/C
system to remove the engine.
(7) Remove A/C compressor and secure away from
engine with lines attached.
(8) Remove generator and secure away from
engine.
NOTE: Do NOT remove the phenolic pulley from the
P/S pump. It is not required for P/S pump removal.
(9) Remove power steering pump with lines
attached and secure away from engine.
(10) Drain cooling system.
(11) Remove coolant bottle.
(12) Disconnect the heater hoses from the engine.
(13) Disconnect heater hoses from heater core and
remove hose assembly.
(14) Disconnect throttle and speed control cables.
(15) Remove upper radiator hose from engine.
(16) Remove lower radiator hose from engine.
(17) Disconnect the engine to body ground straps
at the left side of cowl.
(18) Disconnect the engine wiring harness at the
following points:
²Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor
²Fuel Injectors
²Throttle Position (TPS) Switch
²Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
²Engine Oil Pressure Switch
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Manifold Absolute Pressure MAP) Sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Coil Over Plugs
²Crankshaft Position Sensor
(19) Remove coil over plugs.
(20) Release fuel rail pressure.(21) Remove fuel rail and secure away from
engine.
(22) Remove the PCV hose.
(23) Remove the breather hoses.
(24) Remove the vacuum hose for the power brake
booster.
(25) Disconnect knock sensors.
(26) Secure the left and right engine wiring har-
nesses away from engine.
(27) Raise vehicle.
(28) Disconnect oxygen sensor wiring.
(29) Disconnect crankshaft postion sensor.
(30) Disconnect the engine block heater power
cable, if equipped.
(31) Disconnect the front propshaft at the front
differential and secure out of way.
(32) Remove the starter.
(33) Remove the ground straps from the engine
(34) Disconnect the exhaust pipes at the manifold.
(35) Remove the structural cover, if equipped.
(36) Remove torque convertor bolts, and mark
location for reassembly.
(37) Remove transmission bellhousing to engine
bolts.
(38) Loosen left and right engine mount thru bolts.
NOTE: It is not necessary to completely remove
engine mount thru bolts, for engine removal.
(39) Lower the vehicle.
(40) Support the transmission with a suitable jack.
(41) Connect a suitable engine hoist to the engine.
CAUTION: The 2.4L engine with manual transmis-
sions, can be removed without removing the man-
ual transmission. Use caution when attempting this
procedure as the clearance is tight.
(42) Remove engine from vehicle.
INSTALLATION - ENGINE ASSEMBLY
(1) Position the engine in the vehicle.
CAUTION: Use caution when installing 2.4L engine
into vehicle equipped with manual transmission, as
clearance is tight.
(2) Install both left and right side engine mounts
into the frame mounts.
(3) Raise the vehicle.
(4) Install the transmission bellhousing to engine
mounting bolts. Tighten the bolts to 41 N´m (30ft.
lbs.).
(5) Tighten the engine mount thru bolts.
(6) Install the torque convertor bolts.
(7) Connect the ground straps on the left and right
side of the engine.
9s - 12 ENGINEKJ
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1316 of 1803

AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL - 2.4L
Housing removal is not necessary for element (fil-
ter) replacement.
(1) Disconnect air intake duct at side of element
cover.
(2) Pry up 2 spring clips from front of housing
cover (spring clips retain cover to housing).
(3) Release housing cover from locating tabs
located on rear of housing, and remove cover.
(4) Remove air cleaner element (filter) from hous-
ing.
(5) Clean inside of housing before replacing ele-
ment.
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Install element into housing.
(2) Position housing cover into housing locating
tabs.
(3) Pry up spring clips and lock cover to housing.
(4) Connect air intake duct.
If any air filter, air resonator, air intake tubes or
air filter housing clamps had been loosened or
removed, tighten them to 5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The cross flow designed, aluminum cylinder head
contains dual over-head camshafts with four valves
per cylinder (Fig. 5). The valves are arrange in two
in-line banks. The intake valves face toward the left
side of the vehicle. The exhaust valves face the right
side. The cylinder head incorporates powdered metalvalve guides and seats. The cylinder head is sealed to
the block using a multi-layer steel head gasket and
retaining bolts.
Integral oil galleries providing lubrication passages
to the hydraulic lash adjusters, camshafts, and valve
mechanisms.
OPERATION
The cylinder head closes the combustion chamber,
allowing the pistons to compress the fuel/air mixture
for ignition. The valves are actuated by the lobe pro-
files on the camshaft to open and close at specified
duration to either allow clean air in the combustion
chamber or the exhaust gases out; depending on the
stroke of the engine.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Combustion Leak Tester C-3685-A
Cylinder Compression Pressure Adaptor 8116
Fig. 5 Cylinder Head and Camshafts
CAM PLUG - NOT SHOWN
1 - CAMSHAFT BEARING CAPS
2 - PLUG
3 - CAMSHAFT
4 - CYLINDER HEAD
5 - CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL
KJENGINE9s-19
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1320 of 1803

(3) Install timing belt rear cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
NOTE: Target ring tab should provide posative
snap-on fit on the camshaft.
(4) Install exhaust camshaft target ring with the
wordFRONTfacing forward.
(5) Install exhaust camshaft sensor.
(6) Install camshaft sprockets. Hold each sprocket
with Special Tool 6847 and tighten center bolt to 101
N´m (75 ft. lbs.).
(7) Install timing belt and front covers. (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAINAND SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION) (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
CAMSHAFT(S)
DESCRIPTION
Both nodular iron camshafts have six bearing jour-
nal surfaces and two cam lobes per cylinder (Fig. 15).
Flanges at the rear journals control camshaft end
play. Provision for a cam position sensor is located on
the exhaust camshaft on the front of the cylinder
head. A hydrodynamic oil seal is used for oil control
at the front of the camshaft.
OPERATION
The camshaft is driven by the crankshaft via drive
sprockets and belt. The camshaft has precisely
machined lobes to provide accurate valve timing and
duration.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CAMSHAFT
END-PLAY
(1) Oil camshaft journals and install camshaft
WITHOUTcam follower assemblies. Install rear cam
caps and tighten screws to specified torque.
(2) Using a suitable tool, move camshaft as far
rearward as it will go.
(3) Zero dial indicator (Fig. 16).
(4) Move camshaft as far forward as it will go.
(5) Record reading on dial indicator. For end play
specification, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICA-
TIONS).
(6) If end play is excessive, check cylinder head
and camshaft for wear; replace as necessary.
Fig. 12 Camshaft Sprocket - Removal/Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6847
Fig. 13 Camshaft Oil Seal - Removal With C-4679-A
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4679
Fig. 14 Camshaft Seal - Installation
1 - SPECIAL TOOL MD 998306
KJENGINE9s-23
CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL(S) (Continued)
Page 1321 of 1803

REMOVAL
(1) Remove cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove camshaft position sensor and camshaft
target magnet. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNI-
TION CONTROL/CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
REMOVAL)
(3) Remove timing belt. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - REMOVAL)(4) Remove camshaft sprockets and timing belt
rear cover. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(5) Bearing caps are identified for location.
Remove the outside bearing caps first (Fig. 17).
(6) Loosen the camshaft bearing cap attaching
fasteners in sequence shown (Fig. 18) one camshaft
at a time.
CAUTION: Camshafts are not interchangeable. The
intake cam number 6 thrust bearing face spacing is
wider.
(7) Identify the camshafts before removing from
the head. The camshafts are not interchangeable.
(8) Remove camshafts from cylinder head.
NOTE: If removing rocker arms, identify for reinstal-
lation in the original position.
CLEANING
Clean camshaft with a suitable solvent.
Fig. 15 Camshafts
CAM PLUG - NOT SHOWN
1 - CAMSHAFT BEARING CAPS
2 - PLUG
3 - CAMSHAFT
4 - CYLINDER HEAD
5 - CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL
Fig. 16 Camshaft End Play - Typical
Fig. 17 Camshaft Bearing Cap Identification
Fig. 18 Camshaft Bearing Cap - Removal
1 - REMOVE OUTSIDE BEARING CAPS FIRST
9s - 24 ENGINEKJ
CAMSHAFT(S) (Continued)
Page 1323 of 1803
CYLINDER HEAD COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove intake manifold. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL)
(2) Remove ignition coil and spark plug wires.
(3) Disconnect PCV and make-up air hoses from
cylinder head cover.
(4) Remove cylinder head cover bolts.
(5) Remove cylinder head cover from cylinder
head.
CLEANING
Clean cylinder head and cover mating surfaces
using a suitable solvent.
INSPECTION
Inspect cover rails for flatness.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Replace spark plug well seals and bolt
assemblies when installing a new cylinder head
cover gasket.
(1) Install new cylinder head cover gaskets and
spark plug well seals (Fig. 22).
(2) Replace cylinder head cover bolt assemblies
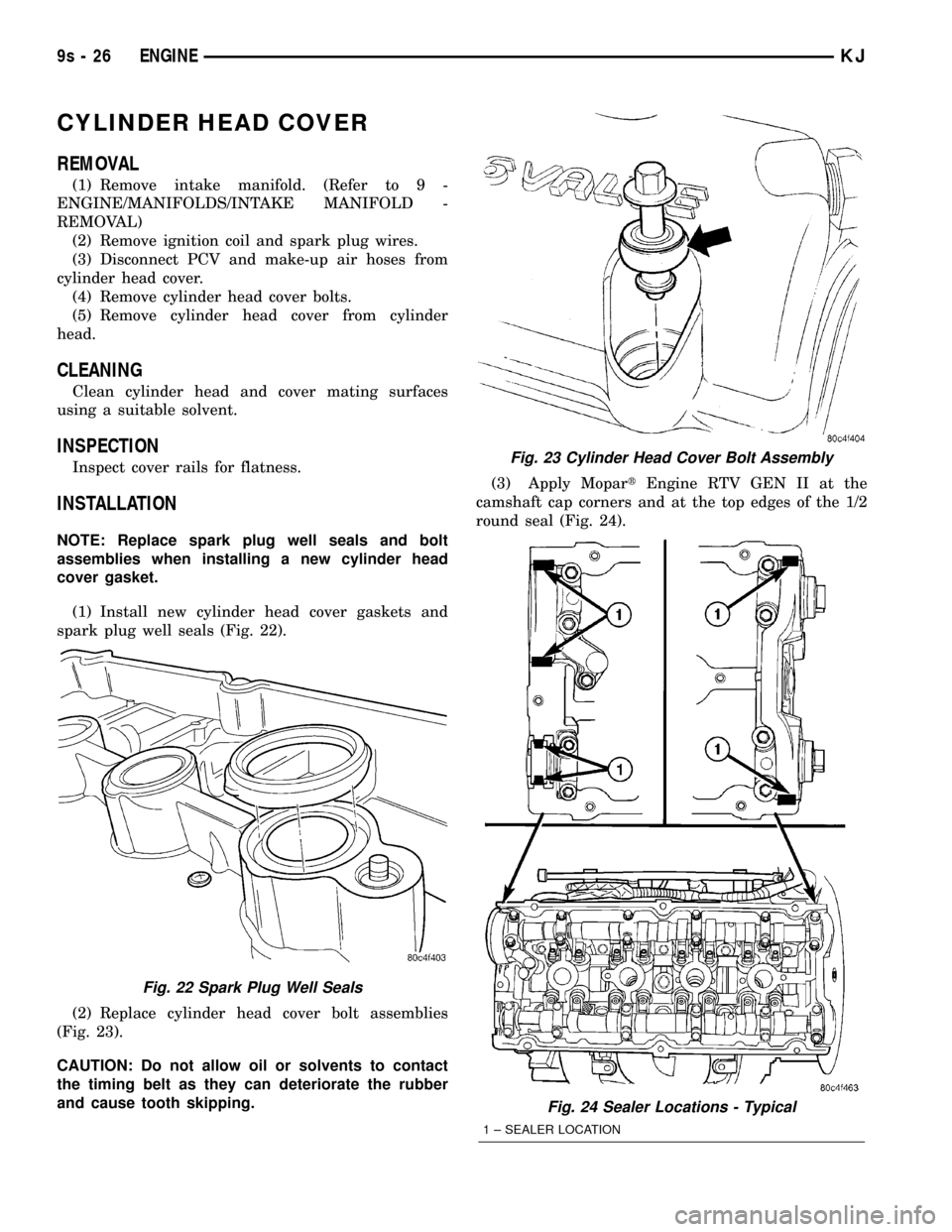
(Fig. 23).
CAUTION: Do not allow oil or solvents to contact
the timing belt as they can deteriorate the rubber
and cause tooth skipping.(3) Apply MopartEngine RTV GEN II at the
camshaft cap corners and at the top edges of the 1/2
round seal (Fig. 24).
Fig. 22 Spark Plug Well Seals
Fig. 23 Cylinder Head Cover Bolt Assembly
Fig. 24 Sealer Locations - Typical
1 ± SEALER LOCATION
9s - 26 ENGINEKJ
Page 1328 of 1803

shown in (Fig. 34). Refer to for Engine Specifications
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS). Correct
piston to bore clearance must be established in order
to assure quiet and economical operation.
NOTE: Pistons and cylinder bores should be mea-
sured at normal room temperature, 21ÉC (70ÉF).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE
HONING
(1) Used carefully, the cylinder bore resizing hone,
recommended tool C-823 or equivalent, equipped
with 220 grit stones, is the best tool for this honing
procedure. In addition to deglazing, it will reduce
taper and out-of-round as well as removing light
scuffing, scoring or scratches. Usually a few strokes
will clean up a bore and maintain the required lim-
its.
(2) Deglazing of the cylinder walls may be done
using a cylinder surfacing hone, recommended toolC-3501 or equivalent, equipped with 280 grit stones,
if the cylinder bore is straight and round. 20±60
strokes depending on the bore condition, will be suf-
ficient to provide a satisfactory surface. Use a light
honing oil.Do not use engine or transmission oil,
mineral spirits or kerosene.Inspect cylinder walls
after each 20 strokes.
(3) Honing should be done by moving the hone up
and down fast enough to get a cross-hatch pattern.
When hone marksintersectat 40-60 degrees, the
cross hatch angle is most satisfactory for proper seat-
ing of rings (Fig. 36).
(4) A controlled hone motor speed between
200±300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 40±60
degree angle. Faster up and down strokes increase
the cross-hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned again to remove all traces of abrasive.
CAUTION: Ensure all abrasives are removed from
engine parts after honing. It is recommended that a
solution of soap and hot water be used with a
brush and the parts then thoroughly dried. The bore
can be considered clean when it can be wiped
clean with a white cloth and cloth remains clean.
Oil the bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
CLEANING
Clean cylinder block thoroughly using a suitable
cleaning solvent.
Fig. 34 Checking Cylinder Bore -Typical
Fig. 35 Piston Measurement - Typical
Fig. 36 Cylinder Bore Cross-Hatch Pattern
1 - CROSS-HATCH PATTERN
2 - 40ɱ60É
KJENGINE9s-31
ENGINE BLOCK (Continued)