2002 JEEP LIBERTY reset
[x] Cancel search: resetPage 599 of 1803

²STEP
²C/T - Compass/Temperature
²US/M - English/Metric
²RESET
1. STEP BUTTON
Pressing the STEP button selects one of the follow-
ing 6 displays:
²Average fuel economy
²Distance to empty
²Instantaneous fuel economy
²Trip odometer
²Elapsed time
²Blank Screen
2. C/T (COMPASS/TEMPERATURE)
BUTTON
Pressing the C/T button selects the Compass/Tem-
perature display.
3. US/M (ENGLISH/METRIC
MEASUREMENT) BUTTON
Pressing the US/M button switches the display
units between English and Metric readings.
4. RESET BUTTON
Pressing the RESET button resets the function on
the display, provided that function can be reset. The
functions which can be reset are Average fuel econ-
omy, Trip odometer and Elapsed time.
Global ResetThis feature allows all three dis-
plays (Average fuel economy, Trip odometer and
Elapsed time) to be reset easily, by pressing the
RESET button twice within three seconds with any
of the screens in display. This eliminates the need to
reset each display individually.
The RESET button is also used to set the variance
and/or calibrate the compass. Refer to the Variance
Procedure and Calibration Procedure in this section.
For more information on the features, control func-
tions and setting procedures for the CMTC module,
see the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMPASS
MINI-TRIP COMPUTER
The following diagnostic procedure can be used if
the compass mini-trip computer is not operational in
any way. If the problem is specific to a individual
CMTC display, go to the appropriate display title
noted below and diagnose using the information pro-
vided on how these displays are generated.
(1) Remove the overhead console from the head-
liner (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD CON-
SOLE - REMOVAL).
(2) Using a ohmmeter, check the ground circuit
cavity of the compass mini-trip computer electricalconnector for proper continuity to ground. Continuity
should be present, If OK go to Step 3, If not OK
repair the open or shorted ground circuit as required.
NOTE: Connect the negative battery cable before
proceeding.
(3) Using a voltmeter, check the fused (B+) circuit
cavity of the compass mini-trip computer electrical
connector for 12v. Voltage should be present, If OK go
to Step 4, If not OK repair the open or shorted fused
(B+) circuit as required.
(4) Using a voltmeter, check the fused ignition
switch output circuit cavity of the compass mini-trip
computer electrical connector for 12v with Key ON.
Voltage should be present, If OK, replace the inoper-
ative CMTC module, If not OK repair the open or
shorted fused ignition switch output circuit as
required.
TEMPERATURE
The compass mini-trip computer receives Program-
mable Communications Interface bus (PCI bus) mes-
sages from the Body Control Module (BCM) for all
displayed information except the compass display. If
a dash (-) is displayed, the compass mini-trip com-
puter is not receiving a PCI bus message from the
BCM. To check out the PCI bus line and the BCM,
use the DRB llltscan tool and proper Body Diagnos-
tic Procedure Manual.
If the compass mini-trip computer displays a tem-
perature more than 54É C (130É F), check for a short
circuit between the temperature sensor and the
BCM.
If the compass mini-trip computer displays a tem-
perature less than -40É C (-67É F), check for an open
circuit between the temperature sensor and the
BCM.
AVERAGE FUEL ECONOMY
The compass mini-trip computer receives average
fuel economy information from the BCM over the PCI
bus line. If the compass mini-trip computer displays
-.- instead of an average fuel economy value, it is not
receiving a PCI bus message for the average fuel
economy from the BCM. To check out the PCI bus
line and the BCM use the DRB llltscan tool and
proper Body Diagnostic Procedure Manual.
DISTANCE TO EMPTY
The compass mini-trip computer receives distance
to empty information from the BCM over the PCI bus
line. If compass mini-trip computer displays a dash
(-) instead of a distance to empty value, it is not
receiving a PCI bus message for the distance to
empty from the BCM. To check out the PCI bus line
8M - 6 MESSAGE SYSTEMSKJ
COMPASS/MINI-TRIP COMPUTER (Continued)
Page 617 of 1803
POWER SEATS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
POWER SEATS
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER SEATS . . 15
SEAT TRACK
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SEAT TRACK....16
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
LEFT POWER SEAT SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................16OPERATION...........................17
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - LEFT POWER
SEAT SWITCH........................17
REMOVAL.............................18
INSTALLATION.........................18
RIGHT POWER SEAT SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................19
OPERATION...........................19
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RIGHT POWER
SEAT SWITCH........................19
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................20
POWER SEATS
DESCRIPTION
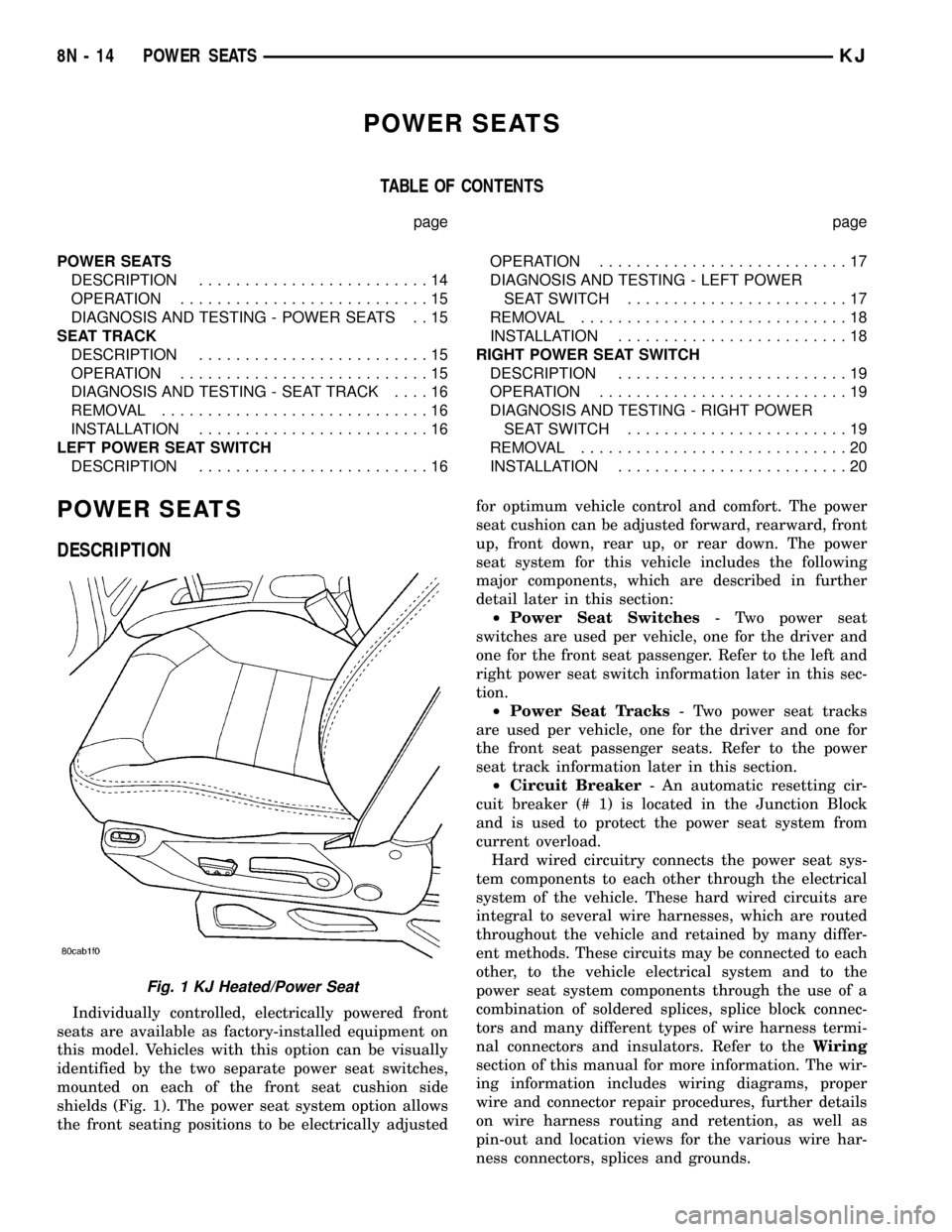
Individually controlled, electrically powered front
seats are available as factory-installed equipment on
this model. Vehicles with this option can be visually
identified by the two separate power seat switches,
mounted on each of the front seat cushion side
shields (Fig. 1). The power seat system option allows
the front seating positions to be electrically adjustedfor optimum vehicle control and comfort. The power
seat cushion can be adjusted forward, rearward, front
up, front down, rear up, or rear down. The power
seat system for this vehicle includes the following
major components, which are described in further
detail later in this section:
²Power Seat Switches- Two power seat
switches are used per vehicle, one for the driver and
one for the front seat passenger. Refer to the left and
right power seat switch information later in this sec-
tion.
²Power Seat Tracks- Two power seat tracks
are used per vehicle, one for the driver and one for
the front seat passenger seats. Refer to the power
seat track information later in this section.
²Circuit Breaker- An automatic resetting cir-
cuit breaker (# 1) is located in the Junction Block
and is used to protect the power seat system from
current overload.
Hard wired circuitry connects the power seat sys-
tem components to each other through the electrical
system of the vehicle. These hard wired circuits are
integral to several wire harnesses, which are routed
throughout the vehicle and retained by many differ-
ent methods. These circuits may be connected to each
other, to the vehicle electrical system and to the
power seat system components through the use of a
combination of soldered splices, splice block connec-
tors and many different types of wire harness termi-
nal connectors and insulators. Refer to theWiring
section of this manual for more information. The wir-
ing information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and location views for the various wire har-
ness connectors, splices and grounds.
Fig. 1 KJ Heated/Power Seat
8N - 14 POWER SEATSKJ
Page 618 of 1803

OPERATION
The power seat system receives battery current
through a fuse in the Power Distribution Center
(PDC) and a circuit breaker in the Junction Block,
regardless of the ignition switch position.
When a power seat switch control knob or knobs
are actuated, a battery feed and a ground path are
applied through the switch contacts to the appropri-
ate power seat track adjuster motor. The selected
adjuster motor operates to move the seat track
through its drive unit in the selected direction until
the switch is released, or until the travel limit of the
seat track is reached. When the switch is moved in
the opposite direction, the battery feed and ground
path to the motor are reversed through the switch
contacts. This causes the adjuster motor to run in the
opposite direction.
Refer to the owner's manual in the vehicle glove
box for more information on the features, use and
operation of the power seat system.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER SEATS
Before any testing of the power seat system is
attempted, the battery should be fully-charged and
all wire harness connections and pins cleaned and
tightened to ensure proper continuity and grounds.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The wir-
ing information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and joint connector location views for the var-
ious wire harness connectors, splices and grounds.
(1) If all power seats are inoperative, check the
automatic resetting circuit breaker in the Junction
Block. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER DISTRI-
BUTION/CIRCUIT BREAKER - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
(2) With the dome lamp on, apply the power seat
switch in the direction of the failure.
(3) If the dome lamp dims, the seat or the power
seat track may be jammed. Check under and behind
the seat for binding or obstructions.
(4) If the dome lamp does not dim, proceed with
testing of the individual power seat system compo-
nents and circuits.
SEAT TRACK
DESCRIPTION
The six-way power seat option includes a power
seat track assembly located under each front seat
(Fig. 2). The power seat track assembly replaces the
standard manually operated seat tracks. The lower
half of the power seat track is secured at the frontwith two bolts to the floor panel seat cross member,
and at the rear with one bolt and one nut to the floor
panel. Four bolts secure the bottom of the seat cush-
ion frame to the upper half of the power seat track
unit.
The power seat track assembly cannot be repaired,
and is serviced only as a complete assembly. If any
component in this assembly is faulty or damaged, the
entire power seat track must be replaced.
OPERATION
The power seat track unit includes three reversible
electric motors that are secured to the upper half of
the track unit. Each motor moves the seat adjuster
through a combination of worm-drive gearboxes and
screw-type drive units. Each of the three driver side
power seat track motors also has a position potenti-
ometer integral to the motor assembly, which elec-
tronically monitors the motor position.
The front and rear of the seat are operated by two
separate vertical adjustment motors. These motors
can be operated independently of each other, tilting
the entire seat assembly forward or rearward; or,
they can be operated in unison by selecting the
proper power seat switch functions, which will raise
or lower the entire seat assembly. The third motor is
the horizontal adjustment motor, which moves the
seat track in the forward and rearward directions.
Fig. 2 Power Seat Track - Typical
1 - POWER SEAT ADJUSTER AND MOTORS
2 - SEAT CUSHION FRAME
3 - POWER SEAT TRACK ASSEMBLY
KJPOWER SEATS 8N - 15
POWER SEATS (Continued)
Page 620 of 1803

The individual switches internal to the power seat
switch cannot be repaired. If one switch is damaged
or faulty, the entire power seat switch unit must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The power seat tracks can be adjusted in six differ-
ent ways using the power seat switches. See the own-
er's manual in the vehicle glove box for more
information on the power seat switch functions and
the seat adjusting procedures.
When a power seat switch control knob or knobs
are actuated, a battery feed and a ground path are
applied through the switch contacts to the power seat
track adjuster motor. The selected adjuster motor
operates to move the seat track through its drive
unit in the selected direction until the switch is
released, or until the travel limit of the seat track is
reached. When the switch is moved in the opposite
direction, the battery feed and ground path to the
motor are reversed through the switch contacts. This
causes the adjuster motor to run in the opposite
direction.
No power seat switch should be held applied in any
direction after the seat track has reached its travel
limit. The power seat adjuster motors each contain a
self-resetting circuit breaker to protect them from
overload. However, consecutive or frequent resetting
of the circuit breaker must not be allowed to con-
tinue, or the motor may be damaged.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - LEFT POWER
SEAT SWITCH
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toPower
Seatin Wiring Diagrams.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the power seat switch from the out-
board seat cushion side shield.
(3) Use an ohmmeter to test the continuity of the
power seat switch in each switch position. See the
Power Seat Switch Continuity chart (Fig. 5) and
switch (Fig. 6) below. If OK, refer toDiagnosis and
Testing the Power Seat Trackin this section. If
not OK, replace the faulty power seat switch unit.
Fig. 5 SIX-WAY POWER SEAT SWITCH CONTINUITY
Fig. 6 DIAGNOSING POWER SEAT SWITCH
1-UP
2 - REARWARD
3 - DOWN
4 - FORWARD
5 - FRONT RISER SWITCH
6 - CENTER SEAT SWITCH
7 - REAR RISER SWITCH
KJPOWER SEATS 8N - 17
LEFT POWER SEAT SWITCH (Continued)
Page 622 of 1803

RIGHT POWER SEAT SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with the power seat option uti-
lize a six-way power seat switch. This six-way power
seat switch features one seat cushion shaped knob,
visible on the outboard seat cushion side shield.
The switch is secured to the back of the seat cush-
ion side shield with two screws. However, the control
knob must be removed before the seat switch can be
removed from the side shield.
The individual switches internal to the power seat
switch cannot be repaired. If one switch is damaged
or faulty, the entire power seat switch unit must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The power seat tracks can be adjusted in six differ-
ent ways using the power seat switches. See the own-
er's manual in the vehicle glove box for more
information on the power seat switch functions and
the seat adjusting procedures.
When a power seat switch control knob or knobs
are actuated, a battery feed and a ground path are
applied through the switch contacts to the power seat
track adjuster motor. The selected adjuster motor
operates to move the seat track through its drive
unit in the selected direction until the switch is
released, or until the travel limit of the seat track is
reached. When the switch is moved in the opposite
direction, the battery feed and ground path to the
motor are reversed through the switch contacts. This
causes the adjuster motor to run in the opposite
direction.
No power seat switch should be held applied in any
direction after the seat track has reached its travel
limit. The power seat adjuster motors each contain a
self-resetting circuit breaker to protect them from
overload. However, consecutive or frequent resetting
of the circuit breaker must not be allowed to con-
tinue, or the motor may be damaged.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RIGHT POWER
SEAT SWITCH
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toPower
Seatin Wiring Diagrams.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the power seat switch from the out-
board seat cushion side shield.(3) Use an ohmmeter to test the continuity of the
power seat switch in each switch position. See the
Power Seat Switch Continuity chart (Fig. 8) and
switch (Fig. 9) below. If OK, refer toDiagnosis and
Testing the Power Seat Trackin this section. If
not OK, replace the faulty power seat switch unit.
Fig. 8 SIX-WAY POWER SEAT SWITCH CONTINUITY
Fig. 9 DIAGNOSING POWER SEAT SWITCH
1-UP
2 - REARWARD
3 - DOWN
4 - FORWARD
5 - FRONT RISER SWITCH
6 - CENTER SEAT SWITCH
7 - REAR RISER SWITCH
KJPOWER SEATS 8N - 19
Page 705 of 1803

²Intermittent Wipe Mode- The control knob on
the right (wiper) control stalk of the multi-function
switch has five minor detent intermittent wipe posi-
tions. When selected, these switch positions will
cause the front wiper system to operate with one of
five delay intervals between complete wipe cycles.
²Mist Wipe Mode- The right (wiper) control
stalk of the multi-function switch has a momentary
Mist position. When selected, this switch position
will operate the front wipers in a low speed continu-
ous cycle for as long as the switch is held closed,
then will complete the current wipe cycle and park
the front wiper blades near the base of the wind-
shield when the switch is released.
²Washer Mode- When the momentary front
wash position of the right (wiper) control stalk of the
multi-function switch is selected with the front wiper
system operating in a continuous wipe mode, washer
fluid will be dispensed onto the windshield glass
through the washer nozzles for as long as the washer
switch is held closed. When the front washer switch
is actuated with the front wiper system operating in
an intermittent wipe mode, washer fluid is still dis-
pensed until the switch is released; however, the
front wipers will operate in a low speed continuous
cycle from the time the washer switch is closed until
several wipe cycles after the switch is released,
before returning to the selected intermittent wipe
mode.
²Wipe-After-Wash Mode- When the momentary
front wash position of the right (wiper) control stalk
of the multi-function switch is selected with the front
wiper system turned Off, the internal circuitry of the
BCM provides a wipe-after-wash feature. When
selected, this feature will operate the washer pump/
motor and the front wipers for as long as the front
washer switch is held closed, then provide several
additional wipe cycles after the switch is released
before parking the front wiper blades near the base
of the windshield.
OPERATION
The front wiper and washer system is designed to
provide the vehicle operator with a convenient, safe,
and reliable means of maintaining visibility through
the windshield glass. The various components of this
system are designed to convert electrical energy pro-
duced by the vehicle electrical system into the
mechanical action of the wiper blades to wipe the
outside surface of the glass, as well as into the
hydraulic action of the washer system to apply
washer fluid stored in an on-board reservoir to the
area of the glass to be wiped. When combined, these
components provide the means to effectively main-
tain clear visibility for the vehicle operator by remov-
ing excess accumulations of rain, snow, bugs, mud, orother minor debris from the outside windshield glass
surface that might be encountered while driving the
vehicle under numerous types of inclement operating
conditions.
The vehicle operator initiates all front wiper and
washer system functions with the right (wiper) con-
trol stalk of the multi-function switch that extends
from the right side of the steering column, just below
the steering wheel. Rotating the control knob on the
end of the control stalk, selects the Off, Delay, Low,
or High front wiper system operating modes. In the
Delay mode, the control knob also allows the vehicle
operator to select from one of five intermittent wipe
Delay intervals. Pulling the right control stalk down-
wards actuates the momentary front wiper system
Mist mode switch, while pulling the right control
stalk towards the steering wheel actuates the
momentary front washer system switch. The multi-
function switch provides hard wired resistor multi-
plexed inputs to the Body Control Module (BCM) for
all of the front wiper system functions, as well as a
separate hard wired sense input to the BCM for the
front washer system function.
The front wiper and washer system will only oper-
ate when the ignition switch is in the Accessory or
On positions. Battery current is directed from a B(+)
fuse in the Power Distribution Center (PDC) to the
wiper and washer system circuit breaker in the Junc-
tion Block (JB) through a fused ignition switch out-
put (run-acc) circuit. The automatic resetting circuit
breaker then provides battery current through a
fused ignition switch output (run-acc) circuit to the
wiper high/low relay, the wiper on/off relay, and the
park switch within the front wiper motor. A separate
fuse in the JB provides battery current through
another fused ignition switch output (run-acc) circuit
to the multi-function switch. The multi-function
switch circuitry uses this battery feed and a ground
circuit input to directly control the operation and
direction of the reversible electric washer pump/mo-
tor unit. The BCM uses low side drivers to control
front wiper system operation by energizing or de-en-
ergizing the wiper high/low and wiper on/off relays.
The hard wired circuits and components of the
front wiper and washer system may be diagnosed
and tested using conventional diagnostic tools and
procedures. However, conventional diagnostic meth-
ods may not prove conclusive in the diagnosis of the
Body Control Module (BCM), or the inputs to or out-
puts from the BCM that control the front wiper and
washer system operating modes. The most reliable,
efficient, and accurate means to diagnose the BCM,
or the BCM inputs and outputs related to the various
front wiper and washer system operating modes
requires the use of a DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information.
8R - 4 FRONT WIPERS/WASHERSKJ
FRONT WIPERS/WASHERS (Continued)
Page 716 of 1803

FRONT WIPER MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The front wiper module bracket is secured with
two nuts below the wiper motor through rubber insu-
lators to two weld studs on the bottom of the cowl
plenum panel beneath the cowl plenum cover/grille
panel (Fig. 14). Two screws secure the top of the
module bracket to the cowl plenum panel through
rubber insulators located on the outboard end of each
pivot bracket. The ends of the wiper pivot shafts that
protrude through dedicated openings in the cowl ple-
num cover/grille panel to drive the wiper arms and
blades are the only visible components of the front
wiper module. The front wiper module consists of the
following major components:
²Bracket- The front wiper module bracket con-
sists of a long tubular steel main member that has a
die cast pivot bracket formation near each end where
the two wiper pivots are secured. A stamped steel
mounting plate for the wiper motor is secured with
welds near the center of the main member. A short
stamped steel tab that extends laterally from one
side of the mounting plate provides a mounting loca-
tion for the wiper motor pigtail wire connector.
²Crank Arm- The front wiper motor crank arm
is a stamped steel unit with a slotted hole on thedriven end that is secured to the wiper motor output
shaft with a nut, and has a ball stud secured to the
drive end.
²Linkage- Two stamped steel drive links con-
nect the wiper motor crank arm to the wiper pivot
lever arms. The right side drive link has a plastic
socket-type bushing on each end. The left side drive
link has a plastic socket-type bushing on one end,
and a plastic sleeve-type bushing on the other end.
The socket-type bushing on one end of each drive
link is snap-fit over the ball stud on the lever arm of
its respective pivot. The left side drive link sleeve-
type bushing end is then fit over the motor crank
arm ball stud, and the other socket-type bushing of
the right side drive link is snap-fit over the exposed
end of the wiper motor crank arm ball stud.
²Motor- The front wiper motor is secured with
three screws to the motor mounting plate near the
center of the wiper module bracket. The wiper motor
output shaft passes through a hole in the module
bracket, where a nut secures the wiper motor crank
arm to the motor output shaft. The two-speed perma-
nent magnet wiper motor features an integral trans-
mission, an internal park switch, and an internal
automatic resetting circuit breaker. A molded plastic
shield covers the top of the motor.
²Pivots- The two front wiper pivots are secured
within the die cast pivot brackets on the outboard
ends of the wiper module main member. The lever
arms that extend from the center of the pivot shafts
each have a ball stud on their end. The upper end of
each pivot shaft where the wiper arms will be fas-
tened each is tapered and serrated with a threaded
stud formation at the tip. The lower ends of the pivot
shafts are installed through lubricated bushings in
the pivot brackets and are secured with snap rings. A
molded plastic shield covers each pivot shaft where it
enters the pivot bracket.
The front wiper module cannot be adjusted or
repaired. If any component of the module is faulty or
damaged, the entire front wiper module unit must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The front wiper module operation is controlled by
the battery current inputs received by the wiper
motor from the wiper on/off and wiper high/low
relays. The wiper motor speed is controlled by cur-
rent flow to either the low speed or the high speed
set of brushes. The park switch is a single pole, sin-
gle throw, momentary switch within the wiper motor
that is mechanically actuated by the wiper motor
transmission components. The park switch alter-
nately closes the wiper park switch sense circuit to
ground or to battery current, depending upon the
position of the wipers on the glass. This feature
Fig. 14 Front Wiper Module
1 - PIVOT BRACKET (2)
2 - MOTOR COVER
3 - MOTOR BRACKET
4 - LINKAGE BUSHING (4)
5 - DRIVE LINK (2)
6 - PIVOT SHAFT (2)
7 - INSULATOR (4)
8 - PIVOT CRANK ARM (2)
9 - PIVOT COVER
10 - MOTOR CRANK ARM
11 - PIGTAIL WIRE CONNECTOR
KJFRONT WIPERS/WASHERS 8R - 15
Page 717 of 1803

allows the motor to complete its current wipe cycle
after the wiper system has been turned Off, and to
park the wiper blades in the lowest portion of the
wipe pattern. The automatic resetting circuit breaker
protects the motor from overloads. The wiper motor
crank arm, the two wiper linkage members, and the
two wiper pivots mechanically convert the rotary out-
put of the wiper motor to the back and forth wiping
motion of the wiper arms and blades on the glass.
REMOVAL
(1) Unlatch and open the hood.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(3) Remove both front wiper arms from the wiper
pivots. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASH-
ERS - FRONT/FRONT WIPER ARM - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the cowl plenum cover/grille panel
from over the cowl plenum. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EX-
TERIOR/COWL GRILLE - REMOVAL).
(5) Disconnect the headlamp and dash wire har-
ness connector for the front wiper motor from the
motor pigtail wire connector (Fig. 15).
(6) Remove the two screws that secure the front
wiper module to the top of the cowl plenum panel at
the pivot brackets.
(7) Remove the two nuts that secure the front
wiper module to the two weld studs on the bottom of
the cowl plenum panel.
(8) Lift the front wiper module up from the cowl
plenum panel far enough to disengage the two lower
insulators from the weld studs on the bottom of the
plenum panel.(9) Remove the front wiper module from the cowl
plenum panel as a unit.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the front wiper module to the cowl ple-
num as a unit (Fig. 15).
(2) Lower the front wiper module lower mounting
insulators over the two weld studs on the bottom of
the cowl plenum panel.
(3) Install the two screws that secure the front
wiper module to the top of the cowl plenum panel at
the pivot brackets. Tighten the screw on the driver
side, followed by the screw on the passenger side.
Tighten the screws to 8 N´m (72 in. lbs.).
(4) Install and tighten the two nuts that secure
the front wiper module to the two weld studs on the
bottom of the cowl plenum panel. Tighten the nuts to
8 N´m (72 in. lbs.).
(5) Reconnect the headlamp and dash wire harness
connector for the front wiper motor to the motor pig-
tail wire connector.
(6) Reinstall the cowl plenum cover/grille panel
over the cowl plenum. (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERI-
OR/COWL GRILLE - INSTALLATION).
(7) Close and latch the hood.
(8) Reinstall both front wiper arms onto the wiper
pivots. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/FRONT WIPERS/
WASHERS/FRONT WIPER ARM - INSTALLATION).
(9) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
FRONT WIPER/WASHER
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The front wiper and washer switches are integral
to the right (wiper) control stalk of the multi-function
switch. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHT-
ING - EXTERIOR/MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH -
DESCRIPTION).
OPERATION
The front wiper and washer switches are integral
to the right (wiper) control stalk of the multi-function
switch. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHT-
ING - EXTERIOR/MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH -
OPERATION).
Fig. 15 Front Wiper Module Remove/Install
1 - NUT (2)
2 - SCREW (2)
3 - FRONT WIPER MODULE
4 - STUD (2)
5 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
8R - 16 FRONT WIPERS/WASHERSKJ
FRONT WIPER MODULE (Continued)