2002 JEEP LIBERTY replace head gasket
[x] Cancel search: replace head gasketPage 1265 of 1803
90É turn. DO NOT rotate crankshaft. Plastigage will
smear, resulting in inaccurate indication.
(6) Remove the bearing cap and determine amount
of bearing-to-journal clearance by measuring the
width of compressed Plastigage. Refer to Engine
Specifications for the proper clearance.Plastigage
should indicate the same clearance across the
entire width of the insert. If the clearance var-
ies, it may be caused by either a tapered jour-
nal, bent connecting rod or foreign material
trapped between the insert and cap or rod.
(7) If the correct clearance is indicated, replace-
ment of the bearing inserts is not necessary. Remove
the Plastigage from crankshaft journal and bearing
insert. Proceed with installation.
(8) If bearing-to-journal clearance exceeds the
specification, determin which services bearing set to
use the bearing sizes are as follows:
Bearing
MarkSIZE USED WITH
JOURNAL SIZE
.025 US.025 mm 57.871-57.879 mm
(.001 in.) (2.2783-2.2786 in.)
Std.STANDARD 57.896-57.904 mm
(2.2793-2.2810 in.)
.250 US.250 mm 57.646-57.654 mm
(.010 in.) (2.2695-2.2698 in.)
(9) Repeat the Plastigage measurement to verify
your bearing selection prior to final assembly.
(10) Once you have selected the proper insert,
install the insert and cap. Tighten the connecting rod
bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus a 90É turn.
Slide snug-fitting feeler gauge between the con-
necting rod and crankshaft journal flange. Refer to
Engine Specifications for the proper clearance.
Replace the connecting rod if the side clearance is
not within specification.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON FITTING
(1) To correctly select the proper size piston, a cyl-
inder bore gauge, capable of reading in 0.003 mm (
.0001 in.) INCREMENTS is required. If a bore gauge
is not available, do not use an inside micrometer.
(2) Measure the inside diameter of the cylinder
bore at a point 38.0 mm (1.5 inches) below top of
bore. Start perpendicular (across or at 90 degrees) to
the axis of the crankshaft at point A and then take
an additional bore reading 90 degrees to that at point
B (Fig. 54).
(3) The coated pistons will be serviced with the
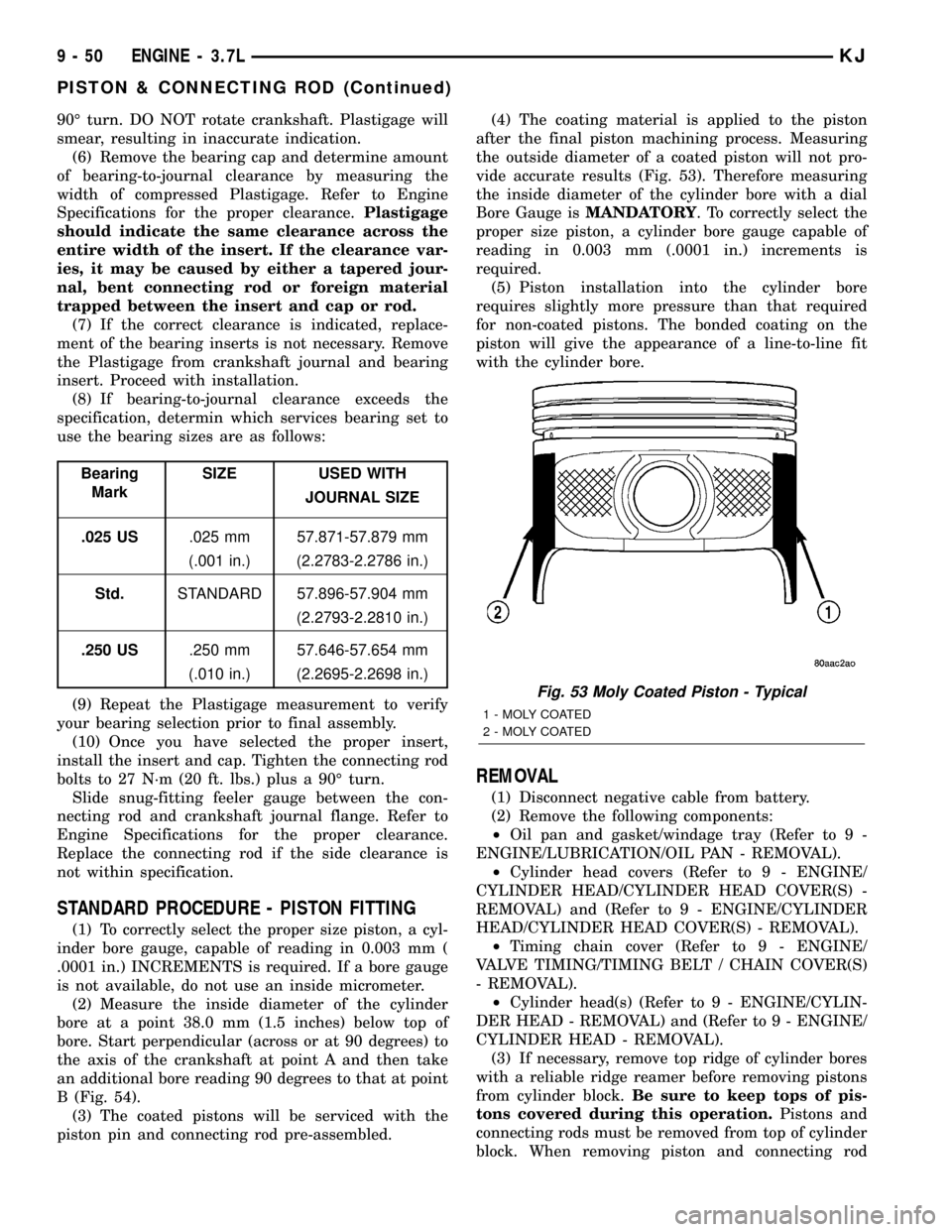
piston pin and connecting rod pre-assembled.(4) The coating material is applied to the piston
after the final piston machining process. Measuring
the outside diameter of a coated piston will not pro-
vide accurate results (Fig. 53). Therefore measuring
the inside diameter of the cylinder bore with a dial
Bore Gauge isMANDATORY. To correctly select the
proper size piston, a cylinder bore gauge capable of
reading in 0.003 mm (.0001 in.) increments is
required.
(5) Piston installation into the cylinder bore
requires slightly more pressure than that required
for non-coated pistons. The bonded coating on the
piston will give the appearance of a line-to-line fit
with the cylinder bore.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the following components:
²Oil pan and gasket/windage tray (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
²Cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) -
REMOVAL) and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
²Timing chain cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
- REMOVAL).
²Cylinder head(s) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLIN-
DER HEAD - REMOVAL) and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(3) If necessary, remove top ridge of cylinder bores
with a reliable ridge reamer before removing pistons
from cylinder block.Be sure to keep tops of pis-
tons covered during this operation.Pistons and
connecting rods must be removed from top of cylinder
block. When removing piston and connecting rod
Fig. 53 Moly Coated Piston - Typical
1 - MOLY COATED
2 - MOLY COATED
9 - 50 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1267 of 1803

ton into cylinder bore and carefully position connect-
ing rod guides over crankshaft journal.
(9) Tap piston down in cylinder bore using a ham-
mer handle. While at the same time, guide connect-
ing rod into position on rod journal.
CAUTION: Connecting Rod Bolts are Torque to
Yield Bolts and Must Not Be Reused. Always
replace the Rod Bolts whenever they are loosened
or removed.
(10) Lubricate rod bolts and bearing surfaces with
engine oil. Install connecting rod cap and bearing.
Tighten bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus 90É.
(11) Install the following components:
²Cylinder head(s). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLIN-
DER HEAD - INSTALLATION).
²Timing chain and cover. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S)
- INSTALLATION).²Cylinder head covers (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) -
INSTALLATION).
²Oil pan and gasket/windage tray. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLA-
TION).
(12) Fill crankcase with proper engine oil to cor-
rect level.
(13) Connect negative cable to battery.
PISTON RINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING
Before reinstalling used rings or installing new
rings, the ring clearances must be checked.
(1) Wipe the cylinder bore clean.
(2) Insert the ring in the cylinder bore.
NOTE: The ring gap measurement must be made
with the ring positioned at least 12mm (0.50 inch.)
from bottom of cylinder bore.
(3) Using a piston, to ensure that the ring is
squared in the cylinder bore, slide the ring downward
into the cylinder.
(4) Using a feeler gauge check the ring end gap
(Fig. 57). Replace any rings not within specification.
PISTON RING SIDE CLEARANCE
Fig. 55 Piston and Connecting Rod - Installation -
Typical
1 - ªFº TOWARD FRONT OF ENGINE
2 - OIL SLINGER SLOT
3 - RING COMPRESSOR
4 - SPECIAL TOOL 8507
Fig. 56 Piston and Connecting Rod Orientation
1 - MAJOR THRUST SIDE OF PISTON
2 - OIL SLINGER SLOT
9 - 52 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1302 of 1803

crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, replace compo-
nent(s) as necessary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).Refer to the Engine Mechanical and the Engine
Performance diagnostic charts, for possible causes
and corrections of malfunctions (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MECHANICAL)
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
- PERFORMANCE).
For fuel system diagnosis, (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
²Lash Adjuster (Tappet) Noise Diagnosis
²Engine Oil Leak Inspection
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery. 1. Test battery. Charge or replace
as necessary. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. Test starting system. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/STARTING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
4. Faulty coil(s) or control unit. 4. Test and replace as needed.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. Set gap. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL
- SPECIFICATIONS)
6. Contamination in fuel system. 6. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
7. Faulty fuel pump. 7. Test fuel pump and replace as
needed. (Refer to Appropriate
Diagnostic Information)
8. Incorrect engine timing. 8. Check for a skipped timing
belt/chain.
KJENGINE9s-5
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1303 of 1803

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE STALLS OR IDLES
ROUGH1. Idle speed too low. 1. Test minimum air flow. (Refer to
Appropriate Diagnostic Information)
2. Incorrect fuel mixture. 2. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
3. Intake manifold leakage. 3. Inspect intake manifold, manifold
gasket, and vacuum hoses.
4. Faulty ignition coil(s). 4. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
ENGINE LOSS OF POWER 1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped plugs. 1. Clean plugs and set gap.
2. Contamination in fuel system. 2. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
3. Faulty fuel pump. 3. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
4. Incorrect valve timing. 4. Correct valve timing.
5. Leaking cylinder head gasket. 5. Replace cylinder head gasket.
6. Low compression. 6. Test compression of each
cylinder.
7. Burned, warped, or pitted valves. 7. Replace valves.
8. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system.8. Perform exhaust restriction test.
(Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) Install
new parts, as necessary.
9. Faulty ignition coil(s). 9. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs.1. Clean spark plugs and set gap.
2. Contamination in Fuel System. 2. Clean fuel system and replace
fuel filter.
3. Burned, warped, or pitted valves. 3. Replace valves.
4. Faulty ignition coil(s). 4. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
ENGINE MISSES AT HIGH SPEED 1. Dirty or incorrect spark plug gap. 1. Clean spark plugs and set gap.
2. Faulty ignition coil(s). 2. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
3. Dirty fuel injector(s). Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
4. Contamination in fuel system. 4. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
9s - 6 ENGINEKJ
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1316 of 1803

AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL - 2.4L
Housing removal is not necessary for element (fil-
ter) replacement.
(1) Disconnect air intake duct at side of element
cover.
(2) Pry up 2 spring clips from front of housing
cover (spring clips retain cover to housing).
(3) Release housing cover from locating tabs
located on rear of housing, and remove cover.
(4) Remove air cleaner element (filter) from hous-
ing.
(5) Clean inside of housing before replacing ele-
ment.
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Install element into housing.
(2) Position housing cover into housing locating
tabs.
(3) Pry up spring clips and lock cover to housing.
(4) Connect air intake duct.
If any air filter, air resonator, air intake tubes or
air filter housing clamps had been loosened or
removed, tighten them to 5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The cross flow designed, aluminum cylinder head
contains dual over-head camshafts with four valves
per cylinder (Fig. 5). The valves are arrange in two
in-line banks. The intake valves face toward the left
side of the vehicle. The exhaust valves face the right
side. The cylinder head incorporates powdered metalvalve guides and seats. The cylinder head is sealed to
the block using a multi-layer steel head gasket and
retaining bolts.
Integral oil galleries providing lubrication passages
to the hydraulic lash adjusters, camshafts, and valve
mechanisms.
OPERATION
The cylinder head closes the combustion chamber,
allowing the pistons to compress the fuel/air mixture
for ignition. The valves are actuated by the lobe pro-
files on the camshaft to open and close at specified
duration to either allow clean air in the combustion
chamber or the exhaust gases out; depending on the
stroke of the engine.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Combustion Leak Tester C-3685-A
Cylinder Compression Pressure Adaptor 8116
Fig. 5 Cylinder Head and Camshafts
CAM PLUG - NOT SHOWN
1 - CAMSHAFT BEARING CAPS
2 - PLUG
3 - CAMSHAFT
4 - CYLINDER HEAD
5 - CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL
KJENGINE9s-19
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1318 of 1803

Remove all gasket material from cylinder head and
block (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE). Be careful not to gouge or scratch the alumi-
num head sealing surface.
Clean all engine oil passages.
INSPECTION
(1) Cylinder head must be flat within 0.1 mm
(0.004 in.) (Fig. 6).
(2) Inspect camshaft bearing journals for scoring.
(3) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from
inside of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
(4) Using a small hole gauge and a micrometer,
measure valve guides in 3 places top, middle and bot-
tom (Fig. 7). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICA-
TIONS) Replace guides if they are not within
specification.
(5) Check valve guide height (Fig. 8).
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD
NOTE: The Cylinder head bolts should be examined
BEFORE reuse. If the threads are necked down, the
bolts must be replaced (Fig. 9).
Necking can be checked by holding a scale or
straight edge against the threads. If all the threads
do not contact the scale, the bolt should be replaced.
(1) Before installing the bolts, the threads should
be coated with engine oil.
(2) Position cylinder head gasket on engine block
(Fig. 10).
(3) Install cylinder head on engine block.
(4) Tighten the cylinder head bolts in the sequence
shown in (Fig. 11). Using the 4 step torque turn
method, tighten according to the following values:
²First All to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.)
²Second All to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.)
Fig. 6 Checking Cylinder Head Flatness
1 - FEELER GAUGE
2 - STRAIGHT EDGE
Fig. 7 Checking Wear on Valve GuideÐTypical
1-TOP
2 - MIDDLE
3 - BOTTOM
4 - CUT AWAY VIEW OF VALVE GUIDE MEASUREMENT
LOCATIONS
Fig. 8 Valve Guide Height
1 - VALVE GUIDE
2 - 13.25 - 13.75 MM (.521 - .541 IN.)
3 - SPRING SEAT
Fig. 9 Checking Bolts for Stretching (Necking)
1 - STRETCHED BOLT
2 - THREADS ARE NOT STRAIGHT ON LINE
3 - THREADS ARE STRAIGHT ON LINE
4 - UNSTRETCHED BOLT
KJENGINE9s-21
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1322 of 1803

INSPECTION
(1) Inspect camshaft bearing journals for damage
and binding (Fig. 19). If journals are binding, check
the cylinder head for damage. Also check cylinder
head oil holes for clogging.
(2) Check the cam lobe and bearing surfaces for
abnormal wear and damage. Replace camshaft if
defective.
NOTE: If camshaft is replaced due to lobe wear or
damage, always replace the rocker arms.
(3) Measure the lobe actual wear (unworn area -
wear zone = actual wear) (Fig. 19) and replace cam-
shaft if out of limit. Standard value is 0.0254 mm
(0.001 in.), wearlimitis 0.254 mm (0.010 in.).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Ensure that NONE of the pistons are at
top dead center when installing the camshafts.
(1) Lubricate all camshaft bearing journals, rocker
arms and camshaft lobes.
(2) Install all rocker arms in original positions, if
reused.
(3) Position camshafts on cylinder head bearing
journals. Install right and left camshaft bearing caps
No.2±5andright No. 6. Tighten M6 fasteners to 12
N´m (105 in. lbs.) in sequence shown in (Fig. 20).
(4) Apply MopartGasket Maker to No. 1 and No.
6 bearing caps (Fig. 21). Install bearing caps and
tighten M8 fasteners to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).NOTE: Bearing end caps must be installed before
seals can be installed.
(5) Install camshaft oil seals. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CAMSHAFT OIL
SEAL(S) - INSTALLATION)
(6) Install camshaft target magnet and camshaft
position sensor.
(7) Install cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
(8) Install timing belt rear cover and camshaft
sprocket. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) - INSTALLA-
TION)
(9) Install timing belt. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT/CHAIN AND
SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION)
Fig. 19 Checking Camshaft(s) for Wear
1 - UNWORN AREA
2 - ACTUAL WEAR
3 - BEARING JOURNAL
4 - LOBE
5 - WEAR ZONE
Fig. 20 Camshaft Bearing Cap Tightening Sequence
Fig. 21 Camshaft Bearing Cap Sealing
1 - 1.5 mm (.060 in.) DIAMETER BEAD OF MOPAR GASKET
MAKER
KJENGINE9s-25
CAMSHAFT(S) (Continued)
Page 1323 of 1803
CYLINDER HEAD COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove intake manifold. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL)
(2) Remove ignition coil and spark plug wires.
(3) Disconnect PCV and make-up air hoses from
cylinder head cover.
(4) Remove cylinder head cover bolts.
(5) Remove cylinder head cover from cylinder
head.
CLEANING
Clean cylinder head and cover mating surfaces
using a suitable solvent.
INSPECTION
Inspect cover rails for flatness.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Replace spark plug well seals and bolt
assemblies when installing a new cylinder head
cover gasket.
(1) Install new cylinder head cover gaskets and
spark plug well seals (Fig. 22).
(2) Replace cylinder head cover bolt assemblies
(Fig. 23).
CAUTION: Do not allow oil or solvents to contact
the timing belt as they can deteriorate the rubber
and cause tooth skipping.(3) Apply MopartEngine RTV GEN II at the
camshaft cap corners and at the top edges of the 1/2
round seal (Fig. 24).
Fig. 22 Spark Plug Well Seals
Fig. 23 Cylinder Head Cover Bolt Assembly
Fig. 24 Sealer Locations - Typical
1 ± SEALER LOCATION
9s - 26 ENGINEKJ