2002 JEEP LIBERTY maintenance
[x] Cancel search: maintenancePage 400 of 1803

gle plug displaying an abnormal condition indicates
that a problem exists in the corresponding cylinder.
Replace spark plugs at the intervals recommended in
the Lubrication and Maintenance section.
Spark plugs that have low mileage may be cleaned
and reused if not otherwise defective, carbon or oil
fouled. Also refer to Spark Plug Conditions.
CAUTION: Never use a motorized wire wheel brush
to clean the spark plugs. Metallic deposits will
remain on the spark plug insulator and will cause
plug misfire.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SPARK PLUG
CONDITIONS
NORMAL OPERATING
The few deposits present on the spark plug will
probably be light tan or slightly gray in color. This is
evident with most grades of commercial gasoline
(Fig. 21). There will not be evidence of electrode
burning. Gap growth will not average more than
approximately 0.025 mm (.001 in) per 3200 km (2000
miles) of operation. Spark plugs that have normal
wear can usually be cleaned, have the electrodes
filed, have the gap set and then be installed.
Some fuel refiners in several areas of the United
States have introduced a manganese additive (MMT)
for unleaded fuel. During combustion, fuel with MMT
causes the entire tip of the spark plug to be coated
with a rust colored deposit. This rust color can be
misdiagnosed as being caused by coolant in the com-bustion chamber. Spark plug performance may be
affected by MMT deposits.
COLD FOULING/CARBON FOULING
Cold fouling is sometimes referred to as carbon
fouling. The deposits that cause cold fouling are basi-
cally carbon (Fig. 21). A dry, black deposit on one or
two plugs in a set may be caused by sticking valves
or defective spark plug cables. Cold (carbon) fouling
of the entire set of spark plugs may be caused by a
clogged air cleaner element or repeated short operat-
ing times (short trips).
WET FOULING OR GAS FOULING
A spark plug coated with excessive wet fuel or oil
is wet fouled. In older engines, worn piston rings,
leaking valve guide seals or excessive cylinder wear
can cause wet fouling. In new or recently overhauled
engines, wet fouling may occur before break-in (nor-
mal oil control) is achieved. This condition can usu-
ally be resolved by cleaning and reinstalling the
fouled plugs.
OIL OR ASH ENCRUSTED
If one or more spark plugs are oil or oil ash
encrusted (Fig. 22), evaluate engine condition for the
cause of oil entry into that particular combustion
chamber.
ELECTRODE GAP BRIDGING
Electrode gap bridging may be traced to loose
deposits in the combustion chamber. These deposits
accumulate on the spark plugs during continuous
stop-and-go driving. When the engine is suddenly
Fig. 21 Normal Operation and Cold (Carbon) Fouling
1 - NORMAL
2 - DRY BLACK DEPOSITS
3 - COLD (CARBON) FOULING
Fig. 22 Oil or Ash Encrusted
KJIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 13
SPARK PLUG (Continued)
Page 1219 of 1803
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either per-
formance (e.g., engine idles rough and stalls) or
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING)ÐPERFORMANCE and (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)ÐMECHANICAL for
possible causes and corrections of malfunctions.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) and (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) for the fuel system diagnosis.Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following diagnosis:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TEST-
ING).
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING).
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
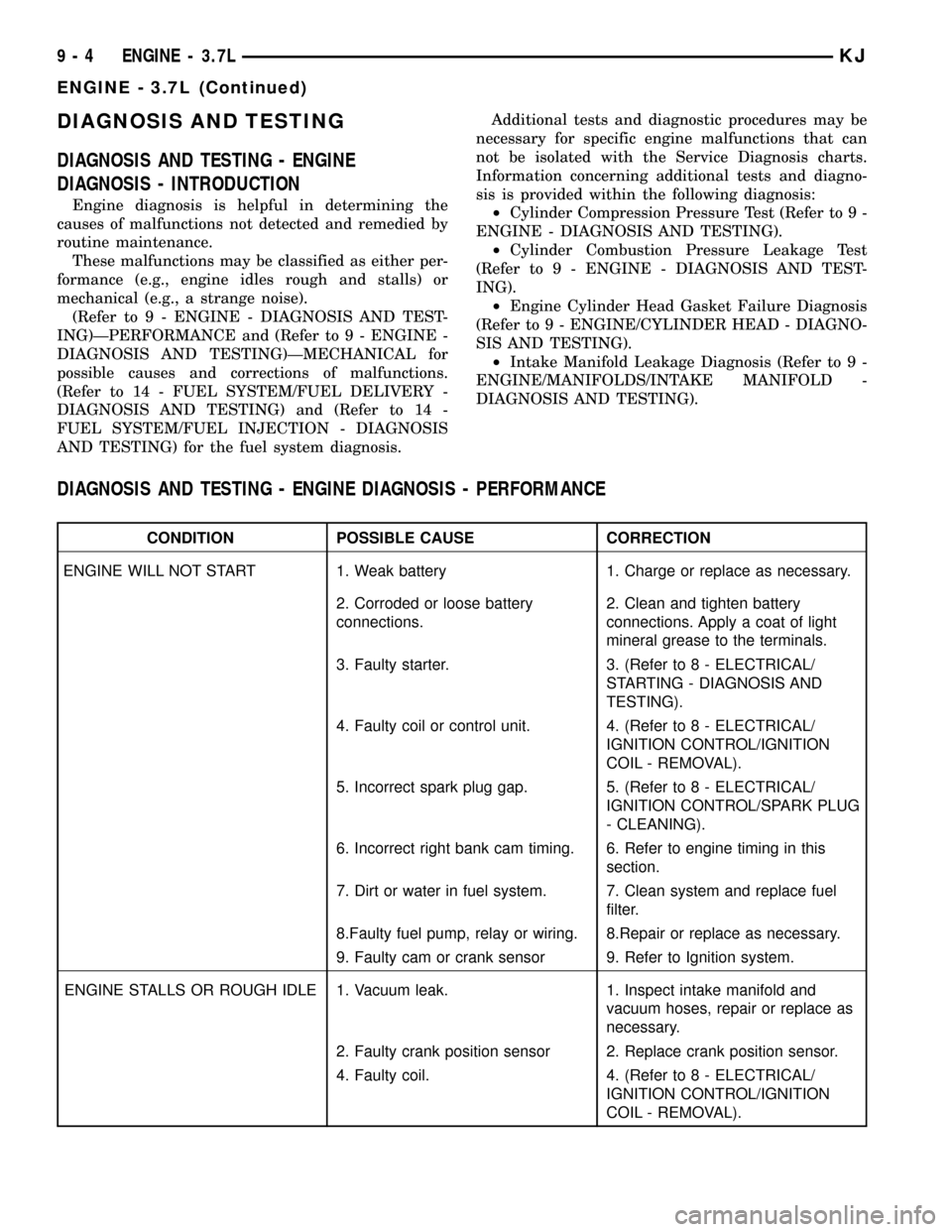
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery 1. Charge or replace as necessary.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to the terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
4. Faulty coil or control unit. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING).
6. Incorrect right bank cam timing. 6. Refer to engine timing in this
section.
7. Dirt or water in fuel system. 7. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
8.Faulty fuel pump, relay or wiring. 8.Repair or replace as necessary.
9. Faulty cam or crank sensor 9. Refer to Ignition system.
ENGINE STALLS OR ROUGH IDLE 1. Vacuum leak. 1. Inspect intake manifold and
vacuum hoses, repair or replace as
necessary.
2. Faulty crank position sensor 2. Replace crank position sensor.
4. Faulty coil. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION
COIL - REMOVAL).
9 - 4 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)
Page 1221 of 1803
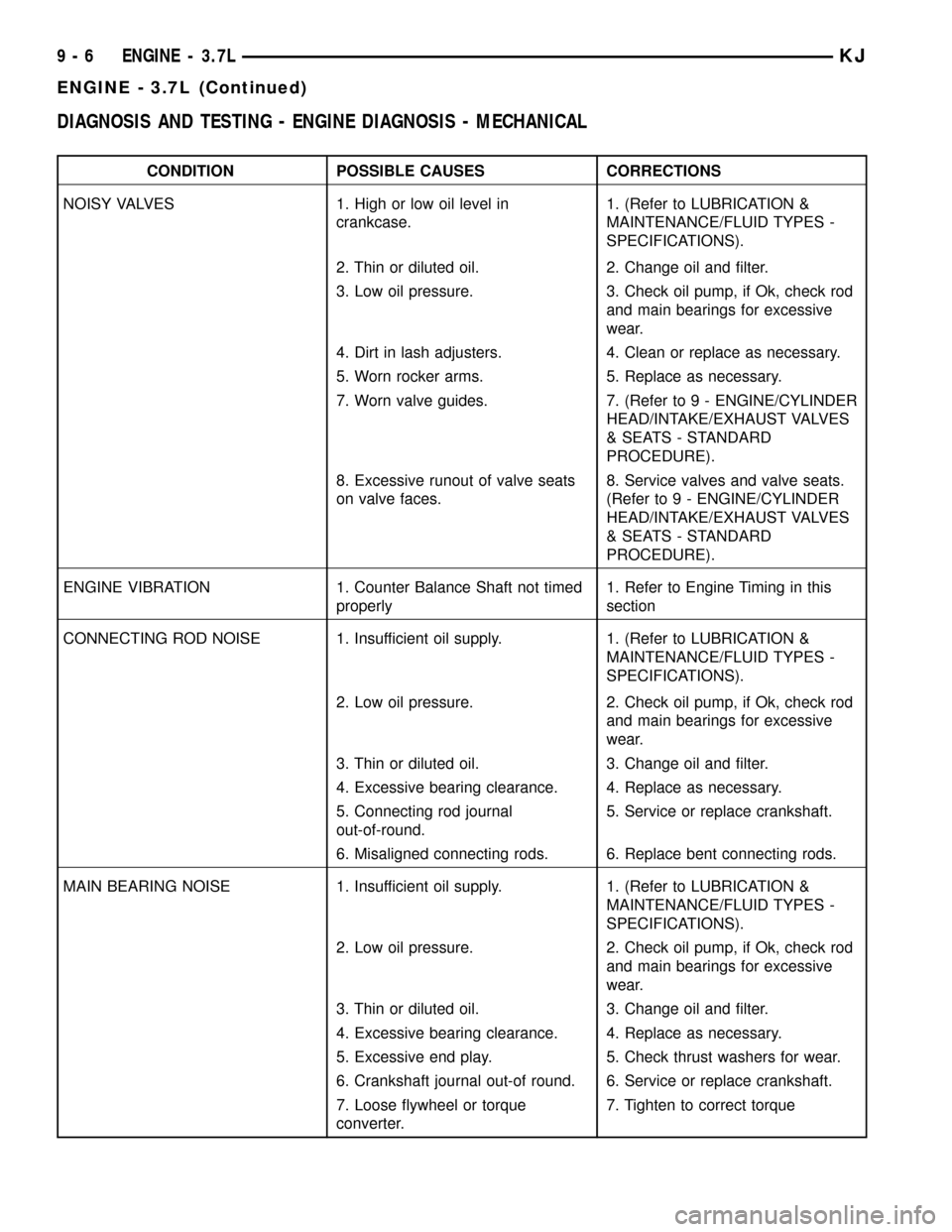
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTIONS
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
SPECIFICATIONS).
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil and filter.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
4. Dirt in lash adjusters. 4. Clean or replace as necessary.
5. Worn rocker arms. 5. Replace as necessary.
7. Worn valve guides. 7. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
8. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.8. Service valves and valve seats.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES
& SEATS - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
ENGINE VIBRATION 1. Counter Balance Shaft not timed
properly1. Refer to Engine Timing in this
section
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
SPECIFICATIONS).
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.5. Service or replace crankshaft.
6. Misaligned connecting rods. 6. Replace bent connecting rods.
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
SPECIFICATIONS).
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check oil pump, if Ok, check rod
and main bearings for excessive
wear.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil and filter.
4. Excessive bearing clearance. 4. Replace as necessary.
5. Excessive end play. 5. Check thrust washers for wear.
6. Crankshaft journal out-of round. 6. Service or replace crankshaft.
7. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.7. Tighten to correct torque
9 - 6 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
ENGINE - 3.7L (Continued)
Page 1277 of 1803

ple viscosities such as 5W-30 or 10W-30 in the 3.7L
engines. These are specified with a dual SAE viscos-
ity grade which indicates the cold-to-hot temperature
viscosity range. Select an engine oil that is best
suited to your particular temperature range and vari-
ation (Fig. 71).
ENERGY CONSERVING OIL
An Energy Conserving type oil is recommended for
gasoline engines. The designation of ENERGY CON-
SERVING is located on the label of an engine oil con-
tainer.
CONTAINER IDENTIFICATION
Standard engine oil identification notations have
been adopted to aid in the proper selection of engine
oil. The identifying notations are located on the label
of engine oil plastic bottles and the top of engine oil
cans (Fig. 72).
OIL LEVEL INDICATOR (DIPSTICK)
The engine oil level indicator is located on the
right side of the the 3.7L engine.
CRANKCASE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION
CAUTION: Do not overfill crankcase with engine oil,
pressure loss or oil foaming can result.Inspect engine oil level approximately every 800
kilometers (500 miles). Unless the engine has exhib-
ited loss of oil pressure, run the engine for about five
minutes before checking oil level. Checking engine oil
level on a cold engine is not accurate.
To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the
engine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level.
The acceptable levels are indicated between the ADD
and SAFE marks on the engine oil dipstick.
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.
(2) With engine OFF, allow approximately ten min-
utes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase, remove
engine oil dipstick.
(3) Wipe dipstick clean.
(4) Install dipstick and verify it is seated in the
tube.
(5) Remove dipstick, with handle held above the
tip, take oil level reading.
(6) Add oil if level is below the SAFE ZONE on
dipstick.
ENGINE OIL CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in Maintenance Schedules.
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Remove oil fill cap.
(3) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain.
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow
oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for
stretching or other damage. Replace drain plug if
damaged.
(6) Install drain plug in crankcase.
(7) Remove oil filter (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL FILTER - REMOVAL).
(8) Install a new oil filter.
(9) Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with 5 quarts
of the specified type of engine oil described in this
section.
(10) Install oil fill cap.
(11) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(12) Stop engine and inspect oil level.
USED ENGINE OIL DISPOSAL
Care should be exercised when disposing used
engine oil after it has been drained from a vehicle
engine. Refer to the WARNING at beginning of this
section.
Fig. 71 Temperature/Engine Oil Viscosity - 3.7L
Engine
Fig. 72 Engine Oil Container Standard Notations
9 - 62 ENGINE - 3.7LKJ
OIL (Continued)
Page 1302 of 1803

crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, replace compo-
nent(s) as necessary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).Refer to the Engine Mechanical and the Engine
Performance diagnostic charts, for possible causes
and corrections of malfunctions (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MECHANICAL)
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
- PERFORMANCE).
For fuel system diagnosis, (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
²Lash Adjuster (Tappet) Noise Diagnosis
²Engine Oil Leak Inspection
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery. 1. Test battery. Charge or replace
as necessary. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. Test starting system. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/STARTING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
4. Faulty coil(s) or control unit. 4. Test and replace as needed.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. Set gap. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL
- SPECIFICATIONS)
6. Contamination in fuel system. 6. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
7. Faulty fuel pump. 7. Test fuel pump and replace as
needed. (Refer to Appropriate
Diagnostic Information)
8. Incorrect engine timing. 8. Check for a skipped timing
belt/chain.
KJENGINE9s-5
ENGINE - 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1344 of 1803

(6) Install oil pressure switch and connector. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PRESSURE
SENSOR/SWITCH - INSTALLATION)
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE
ENGINE OIL LEVEL CHECK
The best time to check engine oil level is after it
has sat overnight, or if the engine has been running,
allow the engine to be shut off for at least 5 minutes
before checking oil level.
Checking the oil while the vehicle is on level
ground will improve the accuracy of the oil level
reading. Remove dipstick and observe oil level. Add
oil only when the level is at or below the ADD mark
(Fig. 78).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL AND
FILTER CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in the Maintenance Schedule. (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTE-
NANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION)
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY. CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR GOVERN-
MENT AGENCY FOR LOCATION OF COLLECTION
CENTER IN YOUR AREA.
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.(2) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
Refer to Hoisting and Jacking Recommendations.
(Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/HOIST-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(3) Remove oil fill cap.
(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain.
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow
oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for
stretching or other damage. Replace drain plug and
gasket if damaged.
(6) Remove oil filter. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL FILTER - REMOVAL)
(7) Install and tighten drain plug in crankcase.
(8) Install new oil filter. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL FILTER - INSTALLATION)
(9) Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified
type and amount of engine oil. (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION)
(10) Install oil fill cap.
(11) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(12) Stop engine and inspect oil level.
NOTE: Care should be exercised when disposing
used engine oil after it has been drained from a
vehicle engine. Refer to the WARNING listed above.
OIL FILTER
DESCRIPTION
The engine oil filter is a high quality full-flow, dis-
posable type. Replace the oil filter with a Mopartor
the equivalent.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Position an oil collecting container under oil fil-
ter location.
CAUTION: When servicing the oil filter avoid
deforming the filter can by installing the remove/in-
stall tool band strap against the can to base lock
seam. The lock seam joining the can to the base is
reinforced by the base plate.
(3) Using a suitable filter wrench, turn oil filter
counterclockwise to remove (Fig. 79).
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean and check filter mounting surface. The
surface must be smooth, flat and free of debris or
pieces of gasket.
(2) Lubricate new oil filter gasket with clean
engine oil.
Fig. 78 Oil Level
1 - ENGINE OIL LEVEL DIPSTICK
KJENGINE9s-47
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1385 of 1803

OPERATION
Fuel is picked up in the fuel tank by the fuel pump
module. This module is located on the bottom of the
fuel tank.
A fuel return system is provided within the fuel
pump module using check valves. A separate fuel
return line from the engine to the tank is not used.
The fuel pressure regulator and the main fuel filter
are not combined. They are separate items.
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
fuel pump module assembly, fuel pump module lock
ring/gasket, ORVR components. Refer to 25, Emis-
sion Control System for ORVR information.
A fuel filler/vent tube assembly using a pressure/
vacuum, 1/4 turn fuel filler cap is used. The fuel
filler tube contains a flap door located below the fuel
fill cap. A one-way check valve is installed into the
tanks fuel fill fitting.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system and ORVR system. This
is designed to reduce the emission of fuel vapors into
the atmosphere. The description and function of the
Evaporative Control System is found in 25, Emission
Control Systems.
Both fuel filters (mounted to front of fuel tank, and
inside the bottom fuel pump module) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. The bottom section of the fuel
pump module (with included filter) should only be
replaced if a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
Also, the fuel filter mounted to the front of the fuel
tank should only be replaced if a diagnostic proce-
dure indicates to do so.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL PRESSURE
LEAK DOWN TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Pressure Test and Fuel Pump Capacity Test.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
Abnormally long periods of cranking to restart a
hotengine that has been shut down for a short
period of time may be caused by:
²Fuel pressure bleeding past a fuel injector(s).²Fuel pressure bleeding past the check valve in
the fuel pump module.
(1) Disconnect the fuel inlet line at fuel rail. Refer
to Quick Connect Fittings for procedures. On some
engines, air cleaner housing removal may be neces-
sary before fuel line disconnection.
(2) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Tool Hose. Tool number 6539 is used for 5/16º fuel
lines and tool number 6631 is used for 3/8º fuel lines.
(3) Connect correct Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Tool Hose between disconnected fuel line
and fuel rail (Fig. 2).
(4) Connect the 0-414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure
test gauge (from Gauge Set 5069) to the test port on
the appropriate Adaptor Tool.The DRBtIII Scan
Tool along with the PEP module, the 500 psi
pressure transducer, and the transducer-to-test
port adapter may also be used in place of the
fuel pressure gauge.
The fittings on both tools must be in good
condition and free from any small leaks before
performing the proceeding test.
(5) Start engine and bring to normal operating
temperature.
(6) Observe test gauge. Normal operating pressure
should be 339 kPa +/±34 kPa (49.2 psi +/±5 psi).
(7) Shut engine off.
Fig. 2 CONNECTING ADAPTER TOOLÐTYPICAL
1 - VEHICLE FUEL LINE
2 - TEST PORT ªTº
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 6923, 6631, 6541 OR 6539
4 - FUEL PRESSURE TEST GAUGE
5 - FUEL LINE CONNECTION AT RAIL
6 - FUEL RAIL
KJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 3
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
Page 1467 of 1803

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WATER LEAKS
Water leaks can be caused by poor sealing,
improper body component alignment, body seam
porosity, missing plugs, or blocked drain holes. Cen-
trifugal and gravitational force can cause water to
drip from a location away from the actual leak point,
making leak detection difficult. All body sealing
points should be water tight in normal wet-driving
conditions. Water flowing downward from the front of
the vehicle should not enter the passenger or luggage
compartment. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal water tight under all conditions. At
times, side glass or door seals will allow water to
enter the passenger compartment during high pres-
sure washing or hard driving rain (severe) condi-
tions. Overcompensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop a water leak that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After completing
a repair, water test vehicle to verify leak has stopped
before returning vehicle to use.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE WATER LEAK TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place, body
drains are clear, and body components are properly
aligned and sealed. If component alignment or seal-
ing is necessary, refer to the appropriate section of
this group for proper procedures.
WATER LEAK TESTS
WARNING: DO NOT USE ELECTRIC SHOP LIGHTS
OR TOOLS IN WATER TEST AREA. PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT.
When the conditions causing a water leak have
been determined, simulate the conditions as closely
as possible.
²If a leak occurs with the vehicle parked in a
steady light rain, flood the leak area with an open-
ended garden hose.
²If a leak occurs while driving at highway speeds
in a steady rain, test the leak area with a reasonable
velocity stream or fan spray of water. Direct the
spray in a direction comparable to actual conditions.
²If a leak occurs when the vehicle is parked on an
incline, hoist the end or side of the vehicle to simu-
late this condition. This method can be used when
the leak occurs when the vehicle accelerates, stops or
turns. If the leak occurs on acceleration, hoist the
front of the vehicle. If the leak occurs when braking,
hoist the back of the vehicle. If the leak occurs on left
turns, hoist the left side of the vehicle. If the leak
occurs on right turns, hoist the right side of the vehi-cle. For hoisting recommendations refer to Group 0,
Lubrication and Maintenance, General Information
section.
WATER LEAK DETECTION
To detect a water leak point-of-entry, do a water
test and watch for water tracks or droplets forming
on the inside of the vehicle. If necessary, remove inte-
rior trim covers or panels to gain visual access to the
leak area. If the hose cannot be positioned without
being held, have someone help do the water test.
Some water leaks must be tested for a considerable
length of time to become apparent. When a leak
appears, find the highest point of the water track or
drop. The highest point usually will show the point of
entry. After leak point has been found, repair the
leak and water test to verify that the leak has
stopped.
Locating the entry point of water that is leaking
into a cavity between panels can be difficult. The
trapped water may splash or run from the cavity,
often at a distance from the entry point. Most water
leaks of this type become apparent after accelerating,
stopping, turning, or when on an incline.
MIRROR INSPECTION METHOD
When a leak point area is visually obstructed, use
a suitable mirror to gain visual access. A mirror can
also be used to deflect light to a limited-access area
to assist in locating a leak point.
BRIGHT LIGHT LEAK TEST METHOD
Some water leaks in the luggage compartment can
be detected without water testing. Position the vehi-
cle in a brightly lit area. From inside the darkened
luggage compartment inspect around seals and body
seams. If necessary, have a helper direct a drop light
over the suspected leak areas around the luggage
compartment. If light is visible through a normally
sealed location, water could enter through the open-
ing.
PRESSURIZED LEAK TEST METHOD
When a water leak into the passenger compart-
ment cannot be detected by water testing, pressurize
the passenger compartment and soap test exterior of
the vehicle. To pressurize the passenger compart-
ment, close all doors and windows, start engine, and
set heater control to high blower in HEAT position. If
engine can not be started, connect a charger to the
battery to ensure adequate voltage to the blower.
With interior pressurized, apply dish detergent solu-
tion to suspected leak area on the exterior of the
vehicle. Apply detergent solution with spray device or
soft bristle brush. If soap bubbles occur at a body
seam, joint, seal or gasket, the leak entry point could
be at that location.
23 - 2 BODYKJ
BODY (Continued)