2002 JEEP LIBERTY Cooling
[x] Cancel search: CoolingPage 1451 of 1803

HOSES
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - PRESSURE HOSE
(1) Siphon the power steering fluid from the reser-
voir.
(2) Remove the radiator crossmember (Refer to 23
- BODY/EXTERIOR/RADIATOR CROSSMEMBER -
REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the fan (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the fan shroud.
(5) Remove the serpentine belt (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - REMOV-
AL).
(6) Remove the pressure hose at the pump.
(7) Disconnect the pressure switch electrical con-
nector from the pressure hose.
(8) Remove the pressure hose from the gear.
(9) Remove the pressure hose mounting bracket
bolts from behind the headlamp assembly. (Fig. 6)
(10) Remove the pressure hose from the vehicle
and transfer power steering pressure switch if neces-
sary.
REMOVAL - RETURN HOSE (GEAR TO THE
COOLER)
(1) Siphon the power steering fluid from the reser-
voir.
(2) Remove the radiator crossmember (Refer to 23
- BODY/EXTERIOR/RADIATOR CROSSMEMBER -
REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the fan (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE/RADIATOR FAN - REMOVAL).(4) Remove the fan shroud.
(5) Remove the serpentine belt (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - REMOV-
AL).
(6) Remove the return hose from the gear.
(7) Remove the return hose at the cooler.
(8) Remove the return hose mounting bracket bolts
from the front cradle. (Fig. 7)
(9) Remove the return hose from the vehicle.
REMOVAL - RETURN HOSE (RESERVOIR TO
THE COOLER)
(1) Siphon the power steering fluid from the reser-
voir.
(2) Remove the return hose from the pump reser-
voir.
(3) Remove the return hose at the cooler.
(4) Remove the return hose from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - PRESSURE HOSE
(1) Install the pressure hose to the vehicle. (Fig. 8)
(2) Install the pressure hose mounting bracket
bolts behind the headlamp assembly. Tighten to to 12
N´m (9 ft.lbs.).
(3) Install the pressure hose to the gear. Tighten
the hose to28 N´m (21 ft.lbs.).
(4) Install the pressure switch electrical connector.
(5) Install the pressure hose at the pump. Tighten
the hose to28 N´m (21 ft.lbs.).
Fig. 6 MOUNTING BRACKET
1 - HIGH PRESSURE POWER STEERING HOSE
2 - MOUNTING BRACKET
Fig. 7 RETURN HOSE TO COOLER
1 - MOUNTING BRACKETS
2 - FLUID COOLER
3 - PRESSURE SWITCH
4 - RETURN HOSE
KJPUMP 19 - 21
Page 1452 of 1803

(6) Install the serpentine belt (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTAL-
LATION).
(7) Install the fan shroud.
(8) Install the fan (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE/RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLATION).
(9) Install the radiator crossmember (Refer to 23 -
BODY/EXTERIOR/RADIATOR CROSSMEMBER -
INSTALLATION).
(10) Refill the power steering fluid (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
INSTALLATION - RETURN HOSE (GEAR TO THE
COOLER)
(1) Install the return hose to the vehicle. (Fig. 7)
(2) Install the return hose mounting bracket bolts
to the front cradle.
(3) Install the return hose at the cooler.
(4) Install the return hose at the gear 28 N´m (21
ft.lbs.).
(5) Install the serpentine belt (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTAL-
LATION).
(6) Install the fan shroud.
(7) Install the fan (Refer to 7 - COOLING/EN-
GINE/RADIATOR FAN - INSTALLATION).
(8) Install the radiator crossmember (Refer to 23 -
BODY/EXTERIOR/RADIATOR CROSSMEMBER -
INSTALLATION).
(9) Refill the power steering fluid (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
INSTALLATION - RETURN HOSE (RESERVOIR
TO THE COOLER)
(1) Install the return hose to the vehicle.
(2) Install the return hose to the pump reservoir.
(3) Install the return hose at the cooler.
(4) Refill the power steering fluid (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/PUMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
POWER STEERING PRESSURE
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
A pressure sensing switch is used in the power
steering system. It is mounted on the high-pressure
steering hose. This switch will be used with both
2.4L and 3.7L engines.
OPERATION
The switch is used on both the 2.4L 4±cylinder and
3.7L V-6 engines.
The power steering pressure switch provides an
input to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). This
input is provided during periods of high steering
pump load and low engine rpm; such as during park-
ing maneuvers. The PCM increases the idle speed
through the Idle Air Control (IAC) motor. This is
done to prevent the engine from stalling under the
increased load.
When steering pump pressure exceeds 3275 kPa
690 kPa (475 psi 100 psi), the Normally Closed
(NC) switch will open and the PCM will increase the
engine idle speed. This will prevent the engine from
stalling.
When pump pressure drops to approximately 1379
kPa (200 psi), the switch circuit will re-close and
engine idle speed will return to its previous setting.
REMOVAL
The power steering pressure switch is installed in
the power steering high-pressure hose (Fig. 9).
(1) Remove the high pressure power steering
hose(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP/HOSES -
REMOVAL).
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from power
steering pressure switch.
(3) Place a small container or shop towel beneath
switch to collect any excess fluid.
(4) Remove switch. Use back-up wrench on power
steering line to prevent line bending.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install power steering switch into power steer-
ing line. (Fig. 9)
(2) Tighten to 9.6 N´m (85 in. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 8 HIGH PRESSURE HOSE ASSEMBLY
1 - HIGH PRESSURE POWER STEERING HOSE
2 - MOUNTING BRACKET
3 - POWER STEERING PRESURE SWITCH
19 - 22 PUMPKJ
HOSES (Continued)
Page 1653 of 1803

HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER........................1
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
REQUIREMENTS.......................1
DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT........................2
OPERATION
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER........................2
OPERATION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT........................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE.......................2DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE.......................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VACUUM
SYSTEM.............................6
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DIODE
REPLACEMENT.......................9
SPECIFICATIONS
A/C APPLICATION TABLE................9
SPECIFICATIONS.....................10
CONTROLS.............................11
DISTRIBUTION..........................29
PLUMBING.............................38
HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER
All vehicles are equipped with a common HVAC
housing assembly (Fig. 1). The system combines air
conditioning, heating, and ventilating capabilities in
a single unit housing mounted under the instrument
panel. On heater-only systems, the evaporator coil is
omitted from the housing.
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
REQUIREMENTS
To maintain the performance level of the HVAC
system, the engine cooling system must be properly
maintained. The use of a bug screen is not recom-
mended. Any obstructions in front of the radiator or
condenser will reduce the performance of the air con-
ditioning and engine cooling systems.
The engine cooling system includes the heater core
and the heater hoses. Refer to Engine Cooling for
more information before the opening of, or attempt-
ing any service to the engine cooling system.
Fig. 1 Blend Door
1 - DEFROSTER DOOR
2- HEATER CORE
3- BLEND DOORS
4- BLOWER MOTOR HOUSING
5- EVAPORATOR (A/C ONLY)
6- LOWER HVAC CASE ASSEMBLY
KJHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 1
Page 1657 of 1803
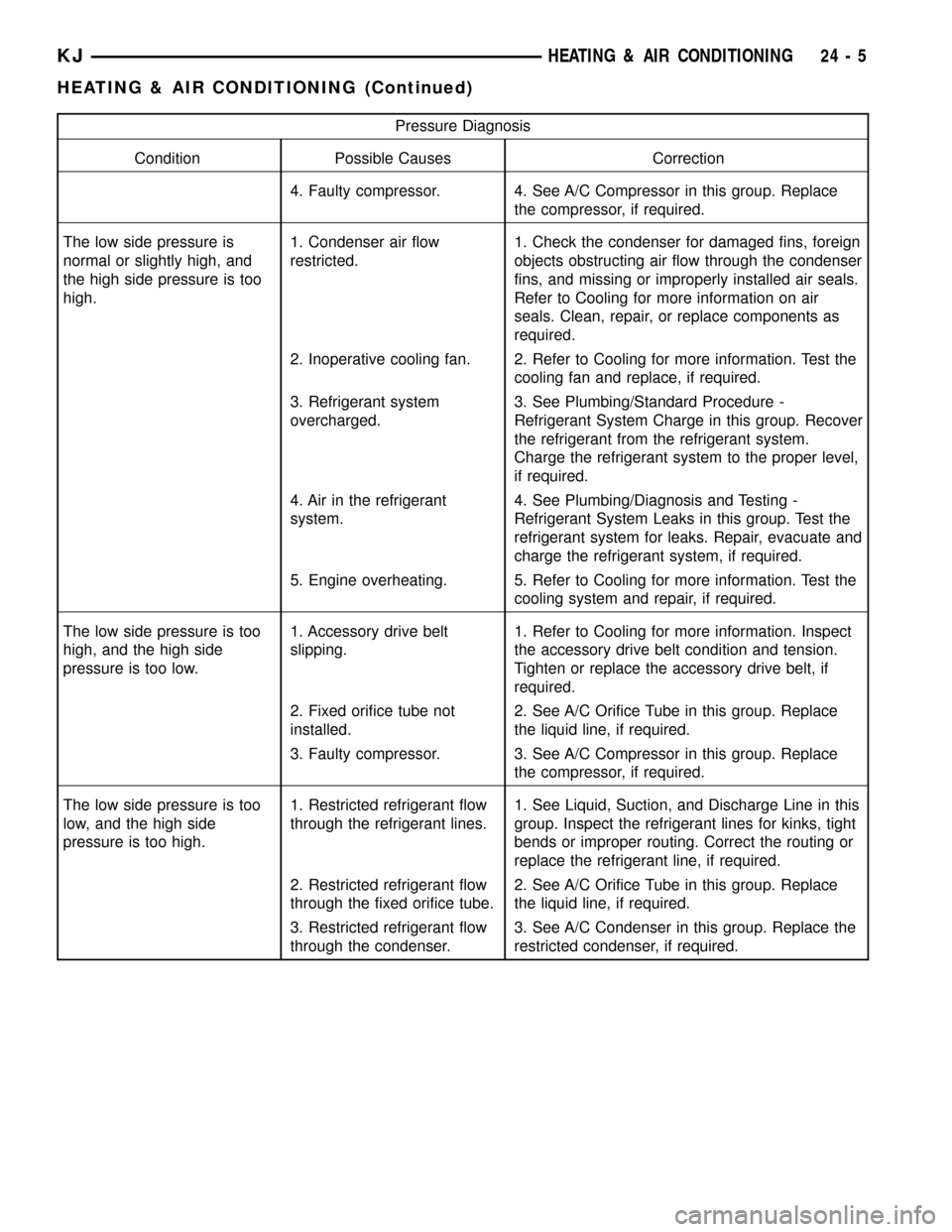
Pressure Diagnosis
Condition Possible Causes Correction
4. Faulty compressor. 4. See A/C Compressor in this group. Replace
the compressor, if required.
The low side pressure is
normal or slightly high, and
the high side pressure is too
high.1. Condenser air flow
restricted.1. Check the condenser for damaged fins, foreign
objects obstructing air flow through the condenser
fins, and missing or improperly installed air seals.
Refer to Cooling for more information on air
seals. Clean, repair, or replace components as
required.
2. Inoperative cooling fan. 2. Refer to Cooling for more information. Test the
cooling fan and replace, if required.
3. Refrigerant system
overcharged.3. See Plumbing/Standard Procedure -
Refrigerant System Charge in this group. Recover
the refrigerant from the refrigerant system.
Charge the refrigerant system to the proper level,
if required.
4. Air in the refrigerant
system.4. See Plumbing/Diagnosis and Testing -
Refrigerant System Leaks in this group. Test the
refrigerant system for leaks. Repair, evacuate and
charge the refrigerant system, if required.
5. Engine overheating. 5. Refer to Cooling for more information. Test the
cooling system and repair, if required.
The low side pressure is too
high, and the high side
pressure is too low.1. Accessory drive belt
slipping.1. Refer to Cooling for more information. Inspect
the accessory drive belt condition and tension.
Tighten or replace the accessory drive belt, if
required.
2. Fixed orifice tube not
installed.2. See A/C Orifice Tube in this group. Replace
the liquid line, if required.
3. Faulty compressor. 3. See A/C Compressor in this group. Replace
the compressor, if required.
The low side pressure is too
low, and the high side
pressure is too high.1. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the refrigerant lines.1. See Liquid, Suction, and Discharge Line in this
group. Inspect the refrigerant lines for kinks, tight
bends or improper routing. Correct the routing or
replace the refrigerant line, if required.
2. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the fixed orifice tube.2. See A/C Orifice Tube in this group. Replace
the liquid line, if required.
3. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the condenser.3. See A/C Condenser in this group. Replace the
restricted condenser, if required.
KJHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 5
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1658 of 1803

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE
Before performing the following tests, refer to Cool-
ing for the procedures to check the radiator coolant
level, serpentine drive belt tension, radiator air flow
and the radiator fan operation. Also be certain that
the accessory vacuum supply line is connected at the
engine intake manifold.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT
Engine coolant is delivered to the heater core
through two heater hoses. With the engine idling atnormal operating temperature, set the temperature
control knob in the full hot position, the mode control
switch knob in the floor heat position, and the blower
motor switch knob in the highest speed position.
Using a test thermometer, check the temperature of
the air being discharged at the HVAC housing floor
outlets. Compare the test thermometer reading to the
Temperature Reference chart.
Temperature Reference
Ambient Air Temperature15.5É C
(60É F)21.1É C
(70É F)26.6É C
(80É F)32.2É C
(90É F)
Minimum Air Temperature at
Floor Outlet52.2É C
(126É F)56.1É C
(133É F)59.4É C
(139É F)62.2É C
(144É F)
If the floor outlet air temperature is too low, refer
to Cooling to check the engine coolant temperature
specifications. Both of the heater hoses should be hot
to the touch. The coolant return heater hose should
be slightly cooler than the coolant supply heater
hose. If the return hose is much cooler than the sup-
ply hose, locate and repair the engine coolant flow
obstruction in the cooling system. Refer to Cooling
for the procedures.
OBSTRUCTED COOLANT FLOW Possible loca-
tions or causes of obstructed coolant flow:
²Pinched or kinked heater hoses.
²Improper heater hose routing.
²Plugged heater hoses or supply and return ports
at the cooling system connections.
²A plugged heater core.
If proper coolant flow through the cooling system is
verified, and heater outlet air temperature is still
low, a mechanical problem may exist.
MECHANICAL PROBLEMS Possible locations or
causes of insufficient heat:
²An obstructed cowl air intake.
²Obstructed heater system outlets.
²A blend door not functioning properly.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL
If the heater outlet air temperature cannot be
adjusted with the temperature control knob on theA/C Heater control panel, the following could require
service:
²The A/C Heater control.
²The blend door actuator.
²The blend door.
²Improper engine coolant temperature.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VACUUM SYSTEM
Vacuum control is used to operate the mode doors
in the heater-only and a/c heater housings. Testing of
the heater-only and A/C Heater mode control switch
operation will determine if the vacuum, electrical,
and mechanical controls are functioning. However, it
is possible that a vacuum control system that oper-
ates perfectly at engine idle (high engine vacuum)
may not function properly at high engine speeds or
loads (low engine vacuum). This can be caused by
leaks in the vacuum system, or a faulty vacuum
check valve.
A vacuum system test will help to identify the
source of poor vacuum system performance or vac-
uum system leaks. Before starting this test, stop the
engine and make certain that the problem is not a
disconnected vacuum supply tube at the engine
intake manifold vacuum tap or at the vacuum reser-
voir.
24 - 6 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGKJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1661 of 1803
(5) Connect the test set hose or probe to the open
end of the leaking circuit. The test set gauge should
return to the 27 kPa (8 in. Hg.) setting shortly after
each connection is made. If OK, replace the faulty
disconnected component. If not OK, go to Step 6.
(6)
To locate a leak in a vacuum line, leave one end
of the line plugged and connect the test set hose or
probe to the other end of the line. Run your fingers
slowly along the line while watching the test set gauge.
The vacuum reading will fluctuate when your fingers
contact the source of the leak. To repair the vacuum
line, cut out the leaking section of the line. Then, insert
the loose ends of the line into a suitable length of 3 mil-
limeter (0.125 inch) inside diameter rubber hose.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DIODE
REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable and iso-
late it.
(2) Locate the diode in the harness, and remove
the protective covering.
(3) Remove the diode from the harness, pay atten-
tion to the current flow direction (Fig. 5).
(4) Remove the insulation from the wires in the
harness. Only remove enough insulation to solder in
the new diode.
(5) Install the new diode in the harness, making
sure current flow is correct. If necessary refer to the
appropriate wiring diagram for current flow.
(6) Solder the connection together using rosin core
type solder only.Do not use acid core solder.
(7) Tape the diode to the harness using electrical
tape making, sure the diode is completely sealed
from the elements.
(8) Re-connect the battery negative cable, and test
affected systems.
SPECIFICATIONS
A/C APPLICATION TABLE
Item Description Notes
Vehicle KJ- Liberty
System R134a w/ fixed
orifice tube
Compressor Sanden PXF-18 SP-10 PAG oil
Freeze±up
ControlA/C low
pressure switchaccumulator
mounted
Low psi Control opens < 25 psi
- resets > 43
psi
High psi Control switch - opens
> 450-490 psi -
resets <
270-330 psidischarge line
Control Head manual type
Mode Door vacuum
Blend Door electric
Recirculation
Doorvacuum
Blower Motor hardwired to
control headresistor block
Cooling Fan viscous for
cooling, single
speed electric
for A/C
Clutch Electro-
mechanical
Control relay PCM
Draw 2 - 3.7 amps @
12V 0.5V @ 70É F
Gap 0.0169- 0.0319
DRB IIIT
Reads TPS, RPM, A/C
switch test
Actuators clutch and fan
relay
Fig. 5 DIODE IDENTIFICATION
1 - CURRENT FLOW
2 - BAND AROUND DIODE INDICATES CURRENT FLOW
3 - DIODE AS SHOWN IN THE DIAGRAMS
KJHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 9
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 1665 of 1803

to 2000 rpm. This procedure (burnishing) will seat
the opposing friction surfaces and provide a higher
compressor clutch torque capability.
REMOVAL
The refrigerant system can remain fully-charged
during compressor clutch, rotor, or coil replacement.
The compressor clutch can be serviced in the vehicle.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the serpentine drive belt(Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(3) Unplug the compressor clutch coil wire harness
connector.
(4) Remove the four bolts that secure the compres-
sor to the mounting bracket.
(5) Remove the compressor from the mounting
bracket. Support the compressor in the engine com-
partment while servicing the clutch.
(6) Insert the two pins of the spanner wrench
(Special Tool C-4489 or equivalent) into the holes of
the clutch plate. Hold the clutch plate stationary and
remove the hex nut (Fig. 2).(7) Remove the clutch plate.
(8) Remove the compressor clutch shims.
(9) Remove the external front housing snap ring
with snap ring pliers (Fig. 3).
(10) Install the lip of the rotor puller (Special Tool
C-6141-1 or equivalent) into the snap ring groove
exposed in the previous step, and install the shaft
protector (Special Tool C-6141-2 or equivalent) (Fig.
4).
Fig. 2 CLUTCH NUT REMOVE
1 - CLUTCH PLATE
2 - SPANNER
Fig. 3 EXTERNAL SNAP RING REMOVE
1 - PULLEY
2 - SNAP RING PLIERS
Fig. 4 SHAFT PROTECTOR AND PULLER
1 - PULLER JAW
2 - SHAFT PROTECTOR
KJCONTROLS 24 - 13
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1670 of 1803

electric cooling fan operations. The switch is located
on the discharge line near the compressor. The
switch is screwed onto a fitting that contains a
Schrader-type valve, which allows the switch to be
serviced without discharging the refrigerant system.
The discharge line fitting is equipped with an O-ring
to seal the switch connection.
OPERATION
The A/C high pressure switch is connected in series
electrically with the A/C low pressure switch between
ground and the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
The switch contacts open and close causing the PCM
to turn the compressor clutch on and off. This pre-
vents compressor operation when the discharge line
pressure approaches high levels, and also reduces
electrical surging from compressor clutch engage-
ment.
The A/C high pressure switch controls the electric
cooling fan operation by monitoring refrigerant line
pressures. When the discharge line pressure rises
above 1900 to 2200 kPa (280 to 320 psi) the fan will
turn on. The cooling fan will turn off when the dis-
charge line pressure drops to 1600 kPa (235 psi).
The A/C high pressure switch controls the A/C
clutch operation by disengaging the clutch when the
discharge line pressure rises above 3100 to 3375 kPa
(450 to 490 psi). The switch contacts will close and
allow A/C clutch engagement when the discharge line
pressure drops to 1860 to 2275 kPa (270 to 330 psi).
The A/C high pressure switch is a factory-cali-
brated unit. The switch cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C HIGH
PRESSURE SWITCH
Before performing diagnosis of the A/C high pres-
sure switch, verify that the refrigerant system has
the correct refrigerant charge. (Refer to 24 - HEAT-
ING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
CHARGE)
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information).
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unplug the A/C high pressure switch wire har-
ness connector from the switch on the refrigerant
system fitting.
(3) On the four terminal A/C high pressure switch,
check for continuity between terminals C and D. On
the two terminal A/C high pressure switch, check for
continuity between both terminals of the switch.
There should be continuity. If OK, test and repair theA/C switch sense circuit as required. If not OK,
replace the faulty switch.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Unplug the wire harness connector from the
A/C high pressure switch, which is mounted to a fit-
ting on the non-flexible section of the discharge line
nearest the compressor.
(3) Unscrew the A/C high pressure switch from the
discharge line fitting.
(4) Remove the A/C high pressure switch from the
vehicle.
(5) Remove the O-ring seal from the discharge line
fitting and discard.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate a new O-ring seal with clean refrig-
erant oil and install it on the discharge line fitting.
Use only the specified O-rings as they are made of a
special material for the R-134a system. Use only
refrigerant oil of the type recommended for the com-
pressor in the vehicle(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING - SPECIFICATIONS). (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/RE-
FRIGERANT OIL - DESCRIPTION)
(2) Install and tighten the a/c high pressure switch
on the discharge line fitting. The switch should be
hand-tightened onto the discharge line fitting.
(3) Plug the wire harness connector into the a/c
high pressure switch.
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
A/C LOW PRESSURE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The a/c low pressure switch is located on the top of
the accumulator. The switch is screwed onto an accu-
mulator fitting that contains a Schrader-type valve,
which allows the switch to be serviced without dis-
charging the refrigerant system. The accumulator fit-
ting is equipped with an O-ring to seal the switch
connection.
OPERATION
The a/c low pressure switch is connected in series
electrically with the a/c high pressure switch,
between ground and the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The switch contacts open and close causing
the PCM to turn the a/c compressor clutch on and
off. This regulates the refrigerant system pressure
and controls evaporator temperature. Controlling the
evaporator temperature prevents condensate water
24 - 18 CONTROLSKJ
A/C HIGH PRESSURE SWITCH (Continued)