2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE park neutral
[x] Cancel search: park neutralPage 1629 of 2199

(2) Install new seal on switch and install switch in
case. Tighten switch to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Test continuity of new switch with 12V test
lamp.
(4) Connect switch wires and lower vehicle.
(5) Top off transmission fluid level.
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION
There are several sizes and types of pistons used in
an automatic transmission. Some pistons are used to
apply clutches. They all have in common the fact
that they are round or circular in shape, located
within a smooth walled cylinder, which is closed at
one end and converts fluid pressure into mechanical
movement. The fluid pressure exerted on the piston
is contained within the system through the use of
piston rings or seals.
OPERATION
The principal which makes this operation possible
is known as Pascal's Law. Pascal's Law can be stated
as: ªPressure on a confined fluid is transmitted
equally in all directions and acts with equal force on
equal areas.º
PRESSURE
Pressure (Fig. 199) is nothing more than force
(lbs.) divided by area (in or ft.), or force per unit
area. Given a 100 lb. block and an area of 100 sq. in.
on the floor, the pressure exerted by the block is: 100lbs. 100 in or 1 pound per square inch, or PSI as it is
commonly referred to.
PRESSURE ON A CONFINED FLUID
Pressure is exerted on a confined fluid (Fig. 200)
by applying a force to some given area in contact
with the fluid. A good example of this is a cylinder
filled with fluid and equipped with a piston that is
closely fitted to the cylinder wall. If a force is applied
to the piston, pressure will be developed in the fluid.
Of course, no pressure will be created if the fluid is
not confined. It will simply ªleakº past the piston.
There must be a resistance to flow in order to create
pressure. Piston sealing is extremely important in
hydraulic operation. Several kinds of seals are used
to accomplish this within a transmission. These
include but are not limited to O-rings, D-rings, lip
seals, sealing rings, or extremely close tolerances
between the piston and the cylinder wall. The force
exerted is downward (gravity), however, the principle
remains the same no matter which direction is taken.
The pressure created in the fluid is equal to the force
applied, divided by the piston area. If the force is 100
lbs., and the piston area is 10 sq. in., then the pres-
sure created equals 10 PSI. Another interpretation of
Pascal's Law is that regardless of container shape or
size, the pressure will be maintained throughout, as
long as the fluid is confined. In other words, the
pressure in the fluid is the same everywhere within
the container.
Fig. 198 Park/Neutral Position Switch
1 - NEUTRAL CONTACT
2 - MANUAL LEVER AND SWITCH PLUNGER IN REVERSE
POSITION
3 - PARK CONTACT
4 - SWITCH
Fig. 199 Force and Pressure Relationship
21 - 110 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1642 of 2199

ASSEMBLY
(1) Lubricate piston and guide seals (Fig. 235)
with petroleum jelly. Lubricate other servo parts with
MopartATF +4, type 9602, transmission fluid.
(2) Install new seal ring on servo piston.
(3) Assemble piston, plug, spring and new snap-
ring.
(4) Lubricate piston seal lip with petroleum jelly.
SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION
The gear shift mechanism provides six shift posi-
tions which are:
²PARK (P)
²REVERSE (R)
²NEUTRAL (N)
²DRIVE (D)
²Manual SECOND (2)
²Manual LOW (1)
OPERATION
Manual LOW (1) range provides first gear only.
Overrun braking is also provided in this range. Man-
ual SECOND (2) range provides first and second gear
only.
DRIVE range provides first, second third and over-
drive fourth gear ranges. The shift into overdrive
fourth gear range occurs only after the transmission
has completed the shift into D third gear range. No
further movement of the shift mechanism is required
to complete the 3-4 shift.
The fourth gear upshift occurs automatically when
the overdrive selector switch is in the ON position.
No upshift to fourth gear will occur if any of the fol-
lowing are true:
²The transmission fluid temperature is below 10É
C (50É F) or above 121É C (250É F).
²The shift to third is not yet complete.
²Vehicle speed is too low for the 3-4 shift to occur.
²Battery temperature is below -5É C (23É F).
REMOVAL
(1) Remove any necessary console parts for access
to shift lever assembly and shifter cables. (Refer to
23 - BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE -
REMOVAL)
(2) Shift transmission into PARK.
(3) Disconnect the transmission shift cable at shift
lever and shifter assembly bracket (Fig. 236).
(4) Disconnect the park lock cable from the shifter
BTSI lever and the shifter assembly bracket. (Fig.
237)
(5) Disconnect the transfer case shift cable from
the transfer case shift lever pin (Fig. 238), if
equipped.
(6) Remove the clip holding the transfer case shift
cable to the shifter assembly bracket, if equipped.
(7) Remove the transfer case shift cable from the
shifter assembly bracket, if equipped.
Fig. 234 Rear Servo Components
1 - SNAP-RING
2 - PISTON SEAL
3 - PISTON PLUG
4 - SPRING RETAINER
5 - SNAP-RING
6 - PISTON SPRING
7 - CUSHION SPRING
8 - PISTON
Fig. 235 Rear Servo Components
1 - SNAP-RING
2 - PISTON SEAL
3 - PISTON PLUG
4 - SPRING RETAINER
5 - SNAP-RING
6 - PISTON SPRING
7 - CUSHION SPRING
8 - PISTON
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 123
REAR SERVO (Continued)
Page 1673 of 2199
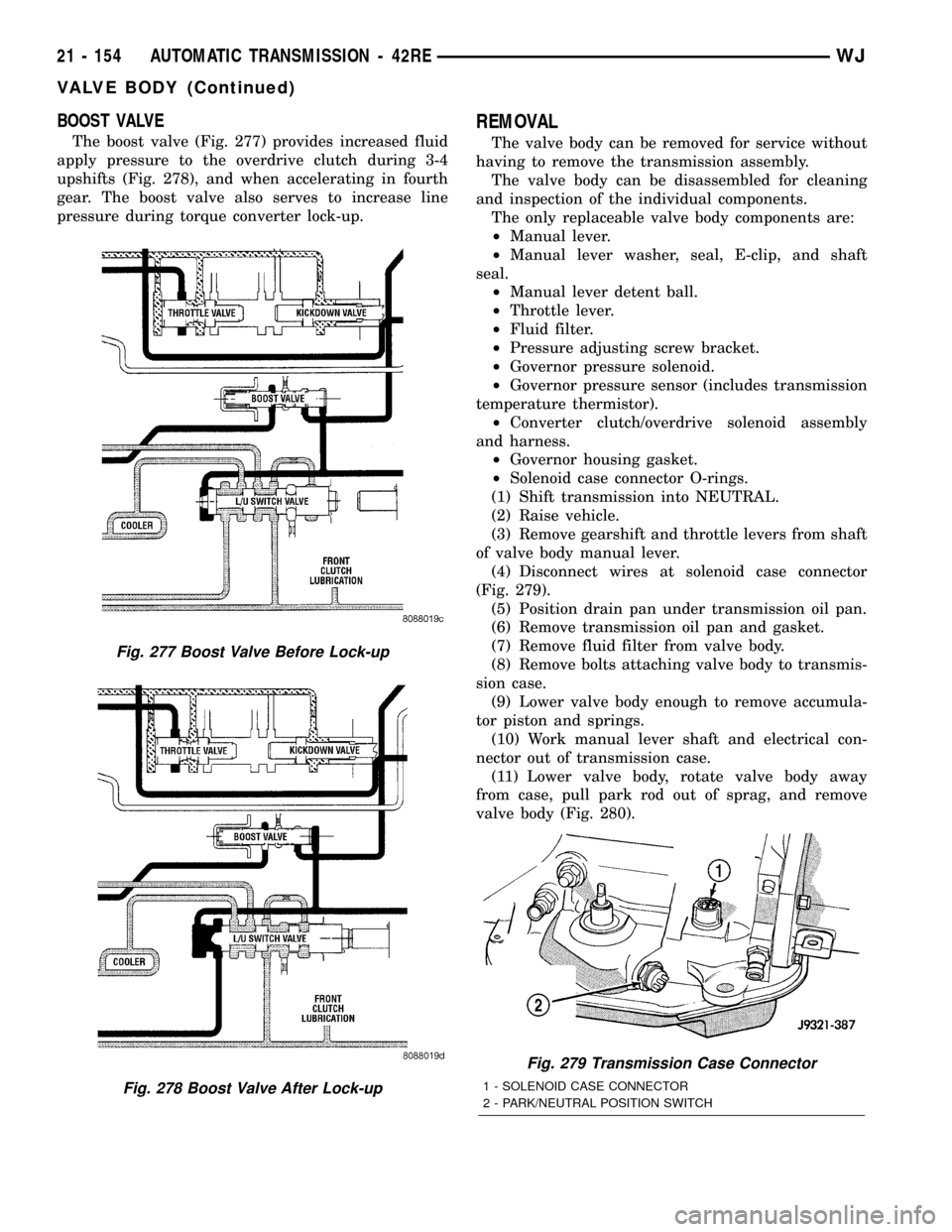
BOOST VALVE
The boost valve (Fig. 277) provides increased fluid
apply pressure to the overdrive clutch during 3-4
upshifts (Fig. 278), and when accelerating in fourth
gear. The boost valve also serves to increase line
pressure during torque converter lock-up.
REMOVAL
The valve body can be removed for service without
having to remove the transmission assembly.
The valve body can be disassembled for cleaning
and inspection of the individual components.
The only replaceable valve body components are:
²Manual lever.
²Manual lever washer, seal, E-clip, and shaft
seal.
²Manual lever detent ball.
²Throttle lever.
²Fluid filter.
²Pressure adjusting screw bracket.
²Governor pressure solenoid.
²Governor pressure sensor (includes transmission
temperature thermistor).
²Converter clutch/overdrive solenoid assembly
and harness.
²Governor housing gasket.
²Solenoid case connector O-rings.
(1) Shift transmission into NEUTRAL.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Remove gearshift and throttle levers from shaft
of valve body manual lever.
(4) Disconnect wires at solenoid case connector
(Fig. 279).
(5) Position drain pan under transmission oil pan.
(6) Remove transmission oil pan and gasket.
(7) Remove fluid filter from valve body.
(8) Remove bolts attaching valve body to transmis-
sion case.
(9) Lower valve body enough to remove accumula-
tor piston and springs.
(10) Work manual lever shaft and electrical con-
nector out of transmission case.
(11) Lower valve body, rotate valve body away
from case, pull park rod out of sprag, and remove
valve body (Fig. 280).
Fig. 277 Boost Valve Before Lock-up
Fig. 278 Boost Valve After Lock-up
Fig. 279 Transmission Case Connector
1 - SOLENOID CASE CONNECTOR
2 - PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH
21 - 154 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1698 of 2199
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan
sealing surface (Fig. 1). Refer to this information
when ordering replacement parts. A label is attached
to the transmission case above the stamped numbers.
The label gives additional information which may
also be necessary for identification purposes.
GEAR RATIOS The 545RFE gear ratios are:
1st .................................3.00:1
2nd.................................1.67:1
2nd Prime............................1.50:1
3rd .................................1.00:1
4th .................................0.75:1
5th .................................0.67:1
Reverse..............................3.00:1
OPERATION
The 545RFE offers full electronic control of all auto-
matic up and downshifts, and features real-time adap-
tive closed-loop shift and pressure control. Electronic
shift and torque converter clutch controls help protect
the transmission from damage due to high tempera-
tures, which can occur under severe operating condi-
tions. By altering shift schedules, line pressure, and
converter clutch control, these controls reduce heat gen-
eration and increase transmission cooling.
To help reduce efficiency-robbing parasitic losses,
the transmission includes a dual-stage transmission
fluid pump with electronic output pressure control.
Under most driving conditions, pump output pres-
sure greatly exceeds that which is needed to keep the
clutches applied. The 545RFE pump-pressure controlsystem monitors input torque and adjusts the pump
pressure accordingly. The primary stage of the pump
works continuously; the second stage is bypassed
when demand is low. The control system also moni-
tors input and output speed and, if incipient clutch
slip is observed, the pressure control solenoid duty
cycle is varied, increasing pressure in proportion to
demand.
A high-travel torque converter damper assembly
allows earlier torque converter clutch engagement to
reduce slippage. Needle-type thrust bearings reduce
internal friction. The 545RFE is packaged in a one-
piece die-cast aluminum case. To reduce NVH, the
case has high lateral, vertical and torsional stiffness.
It is also designed to maximize the benefit of the
structural dust cover that connects the bottom of the
bell housing to the engine bedplate, enhancing over-
all power train stiffness. Dual filters protect the
pump and other components. A pump return filter is
added to the customary main sump filter. Indepen-
dent lubrication and cooler circuits assure ample
pressure for normal transmission operation even if
the cooler is obstructed or the fluid cannot flow due
to extremely low temperatures.
The hydraulic control system design (without elec-
tronic assist) provides the transmission with PARK,
REVERSE, NEUTRAL, SECOND, and THIRD gears,
based solely on driver shift lever selection. This
design allows the vehicle to be driven (in ªlimp-inº
mode) in the event of a electronic control system fail-
ure, or a situation that the Transmission Control
Module (TCM) recognizes as potentially damaging to
the transmission.
The TCM also performs certain self-diagnostic
functions and provides comprehensive information
(sensor data, DTC's, etc.) which is helpful in proper
diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed
with the DRB scan tool.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
CAUTION: Before attempting any repair on a
545RFE automatic transmission, check for Diagnos-
tic Trouble Codes with the DRBTscan tool.
Transmission malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions:
²Poor engine performance
²Improper adjustments
²Hydraulic malfunctions
²Mechanical malfunctions
²Electronic malfunctions
Fig. 1 Transmission Part And Serial Number
Location
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 179
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1699 of 2199

Diagnosis of these problems should always begin
by checking the easily accessible variables: fluid level
and condition, gearshift cable adjustment. Then per-
form a road test to determine if the problem has been
corrected or if more diagnosis is necessary. If the
problem persists after the preliminary tests and cor-
rections are completed, hydraulic pressure checks
should be performed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure for
vehicles that are drivable and an alternate procedure for
disabled vehicles (will not back up or move forward).
VEHICLE IS DRIVABLE
(1) Check for transmission fault codes using DRBt
scan tool.
(2) Check fluid level and condition.
(3) Adjust gearshift cable if complaint was based
on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts.
(4) Road test and note how transmission upshifts,
downshifts, and engages.
(5) Perform stall test if complaint is based on slug-
gish acceleration. Or, if abnormal throttle opening is
needed to maintain normal speeds with a properly
tuned engine.
(6) Perform hydraulic pressure test if shift prob-
lems were noted during road test.
(7)
Perform air-pressure test to check clutch operation.
VEHICLE IS DISABLED
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2)
Check for broken or disconnected gearshift cable.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose
or missing pressure-port plugs.(4) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands,
start engine, shift transmission into gear, and note
following:
(a) If propeller shaft turns but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged driveplate, converter,
oil pump, or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic-pressure test to
determine if problem is hydraulic or mechanical.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TESTING
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and con-
trol cable adjustments have been checked and
adjusted if necessary. Verify that all diagnostic trou-
ble codes have been resolved.
Observe engine performance during the road test.
A poorly tuned engine will not allow accurate analy-
sis of transmission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for shift variations and engine flare which indicates
slippage. Note if shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed,
early, or if part throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Slippage indicated by engine flare, usually means
clutch, overrunning clutch, or line presure problems.
A slipping clutch can often be determined by com-
paring which internal units are applied in the vari-
ous gear ranges. The Clutch Application chart
provides a basis for analyzing road test results.
CLUTCH APPLICATION CHART
SLP UD OD R 2C 4C L/R OVERRUNNING
P±PARKON
R±REVERSEON ON
N-NEUTRALON
D±OVERDRIVE
FIRSTON ON* ON
SECONDON ON
SECOND PRIMEON ON
THIRDON ON
FOURTHON ON
FIFTHON ON
LIMP-INON ON
2±FIRSTON ON* ON
SECONDON ON
LIMP-INON ON
1±LOWON ON ON
*L/R clutch is on only with the output shaft speed below 150 rpm.
21 - 180 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1745 of 2199
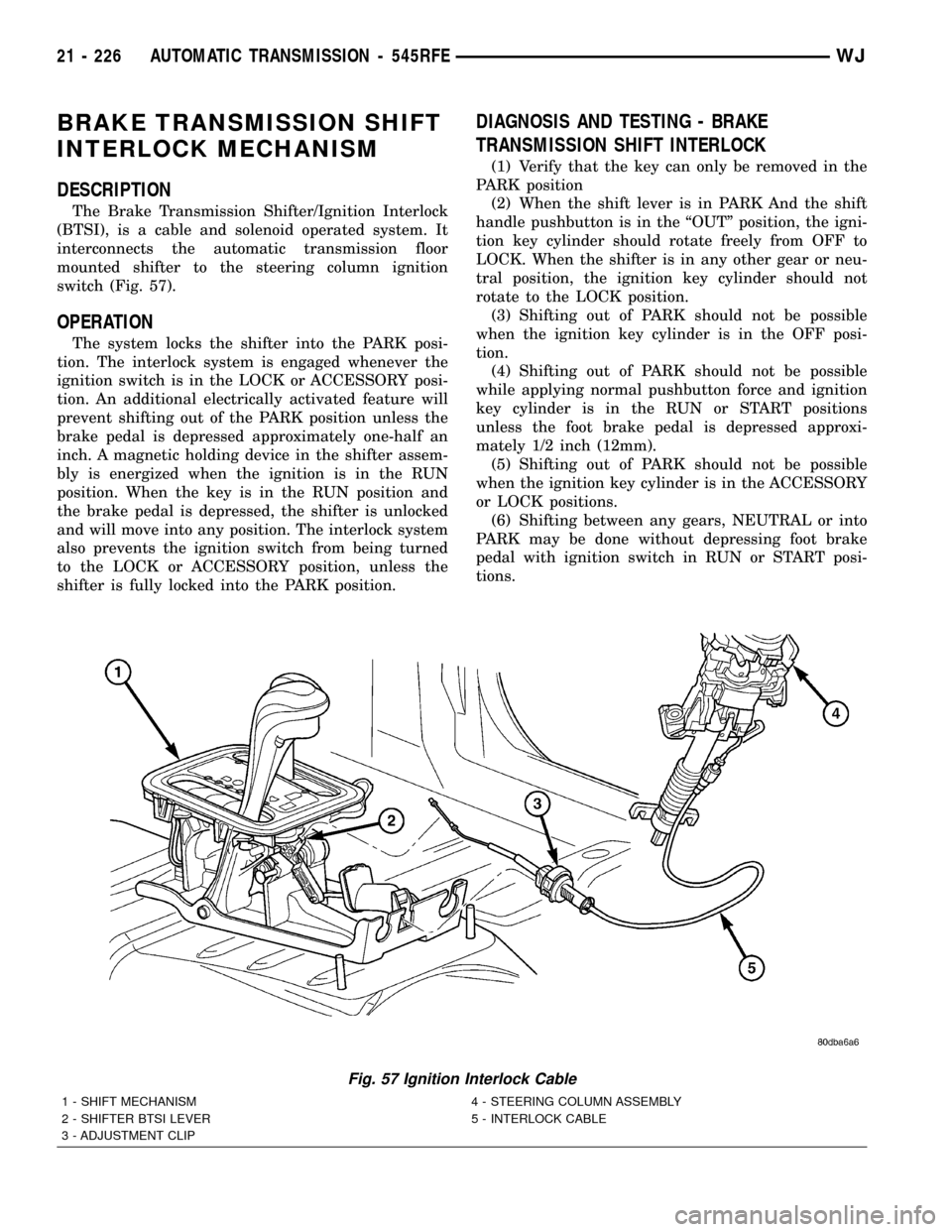
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT
INTERLOCK MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION
The Brake Transmission Shifter/Ignition Interlock
(BTSI), is a cable and solenoid operated system. It
interconnects the automatic transmission floor
mounted shifter to the steering column ignition
switch (Fig. 57).
OPERATION
The system locks the shifter into the PARK posi-
tion. The interlock system is engaged whenever the
ignition switch is in the LOCK or ACCESSORY posi-
tion. An additional electrically activated feature will
prevent shifting out of the PARK position unless the
brake pedal is depressed approximately one-half an
inch. A magnetic holding device in the shifter assem-
bly is energized when the ignition is in the RUN
position. When the key is in the RUN position and
the brake pedal is depressed, the shifter is unlocked
and will move into any position. The interlock system
also prevents the ignition switch from being turned
to the LOCK or ACCESSORY position, unless the
shifter is fully locked into the PARK position.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
(1) Verify that the key can only be removed in the
PARK position
(2) When the shift lever is in PARK And the shift
handle pushbutton is in the ªOUTº position, the igni-
tion key cylinder should rotate freely from OFF to
LOCK. When the shifter is in any other gear or neu-
tral position, the ignition key cylinder should not
rotate to the LOCK position.
(3) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
when the ignition key cylinder is in the OFF posi-
tion.
(4) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
while applying normal pushbutton force and ignition
key cylinder is in the RUN or START positions
unless the foot brake pedal is depressed approxi-
mately 1/2 inch (12mm).
(5) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
when the ignition key cylinder is in the ACCESSORY
or LOCK positions.
(6) Shifting between any gears, NEUTRAL or into
PARK may be done without depressing foot brake
pedal with ignition switch in RUN or START posi-
tions.
Fig. 57 Ignition Interlock Cable
1 - SHIFT MECHANISM 4 - STEERING COLUMN ASSEMBLY
2 - SHIFTER BTSI LEVER 5 - INTERLOCK CABLE
3 - ADJUSTMENT CLIP
21 - 226 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
Page 1746 of 2199

ADJUSTMENTS - BRAKE TRANSMISSION
SHIFT INTERLOCK
The park interlock cable is part of the brake/shift
lever interlock system. Correct cable adjustment is
important to proper interlock operation. The gear
shift and park lock cables must both be correctly
adjusted in order to shift out of PARK.
ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
(1) Remove floor console as necessary for access to
the brake transmission shift interlock cable. (Refer to
23 - BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE -
REMOVAL)
(2) Shift the transmission into the PARK position.
(3) Turn ignition switch to LOCK position.Be
sure ignition key cylinder is in the LOCK posi-
tion. Cable will not adjust correctly in any
other position.
(4) Pull cable lock button up to release cable (Fig.
58).
(5) Ensure that the cable is free to self-adjust by
pushing cable rearward and releasing.
(6) Push lock button down until it snaps in place.
BTSI FUNCTION CHECK
(1) Verify removal of ignition key allowed in PARK
position only.
(2) When the shift lever is in PARK, and the shift
handle push-button is in the out position, the igni-
tion key cylinder should rotate freely from off to lock.
When the shifter is in any other position, the ignition
key should not rotate from off to lock.
(3) Shifting out of PARK should be possible when
the ignition key cylinder is in the off position.
(4) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
while applying normal push-button force, and igni-
tion key cylinder is in the run or start positions,
unless the foot brake pedal is depressed approxi-
mately 1/2 inch (12mm).
(5) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
when the ignition key cylinder is in the accessory or
lock position.
(6) Shifting between any gear and NEUTRAL, or
PARK, may be done without depressing foot brake
with ignition switch in run or start positions.
(7) The floor shifter lever and gate positions
should be in alignment with all transmission detent
positions.
Fig. 58 Brake Transmission Shift Interlock Cable
1 - SHIFT MECHANISM 4 - STEERING COLUMN ASSEMBLY
2 - SHIFTER BTSI LEVER 5 - INTERLOCK CABLE
3 - ADJUSTMENT CLIP
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 227
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK MECHANISM (Continued)
Page 1747 of 2199

(8) Engine starts must be possible with shifter
lever in PARK or NEUTRAL gate positions only.
Engine starts must not be possible in any other gate
positions other than PARK or NEUTRAL.
(9) With shifter lever handle push-button not
depressed and lever detent in:
²PARK position- apply forward force on center of
handle and remove pressure. Engine start must be
possible.
²PARK position- apply rearward force on center
of handle and remove pressure. Engine start must be
possible.
²NEUTRAL position- engine start must be possi-
ble.
²NEUTRAL position, engine running and brakes
applied- Apply forward force on center of shift han-
dle. Transmission should not be able to shift into
REVERSE detent.
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has three primary causes.
(1) Internal clutch slippage, usually caused by low
line pressure, inadequate clutch apply pressure, or
clutch seal failure.
(2) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.(3) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to reverse flush cooler and lines after
repair
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The transmission cooler and lines should be
reverse flushed whenever a malfunction generates
sludge and/or debris. The torque converter should
also be replaced at the same time.
Failure to flush the cooler and lines will result in
recontamination. Flushing applies to auxiliary cool-
ers as well. The torque converter should also be
replaced whenever a failure generates sludge and
debris. This is necessary because normal converter
flushing procedures will not remove all contami-
nants.
21 - 228 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK MECHANISM (Continued)