2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE low engine oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: low engine oil pressurePage 1380 of 2199
(6) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(7) Disconnect generator electrical connections.
(8) Unbolt the generator and move it away from
the intake manifold for clearance.
(9) Disconnect air conditioning compressor electri-
cal connections.
(10) Unbolt the air conditioning compressor and
move it away from the intake manifold for clearance.
(11) Disconnect left and right radio suppressor
straps.
(12) Disconnect and remove ignition coil towers
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
IGNITION COIL - REMOVAL).
(13) Remove top oil dipstick tube retaining bolt
and ground strap.
(14) Bleed pressure from fuel system (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(15) Remove fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - REMOVAL).
(16) Remove throttle body assembly and mounting
bracket.
(17) Drain cooling system below coolant tempera-
ture level (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(18) Remove coolant temperature sensor (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE COOLANT TEMP
SENSOR - REMOVAL).
(19) Remove cowl to hood seal. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS/COWL WEATHER-
STRIP - REMOVAL).
(20) Remove right side engine lifting stud.
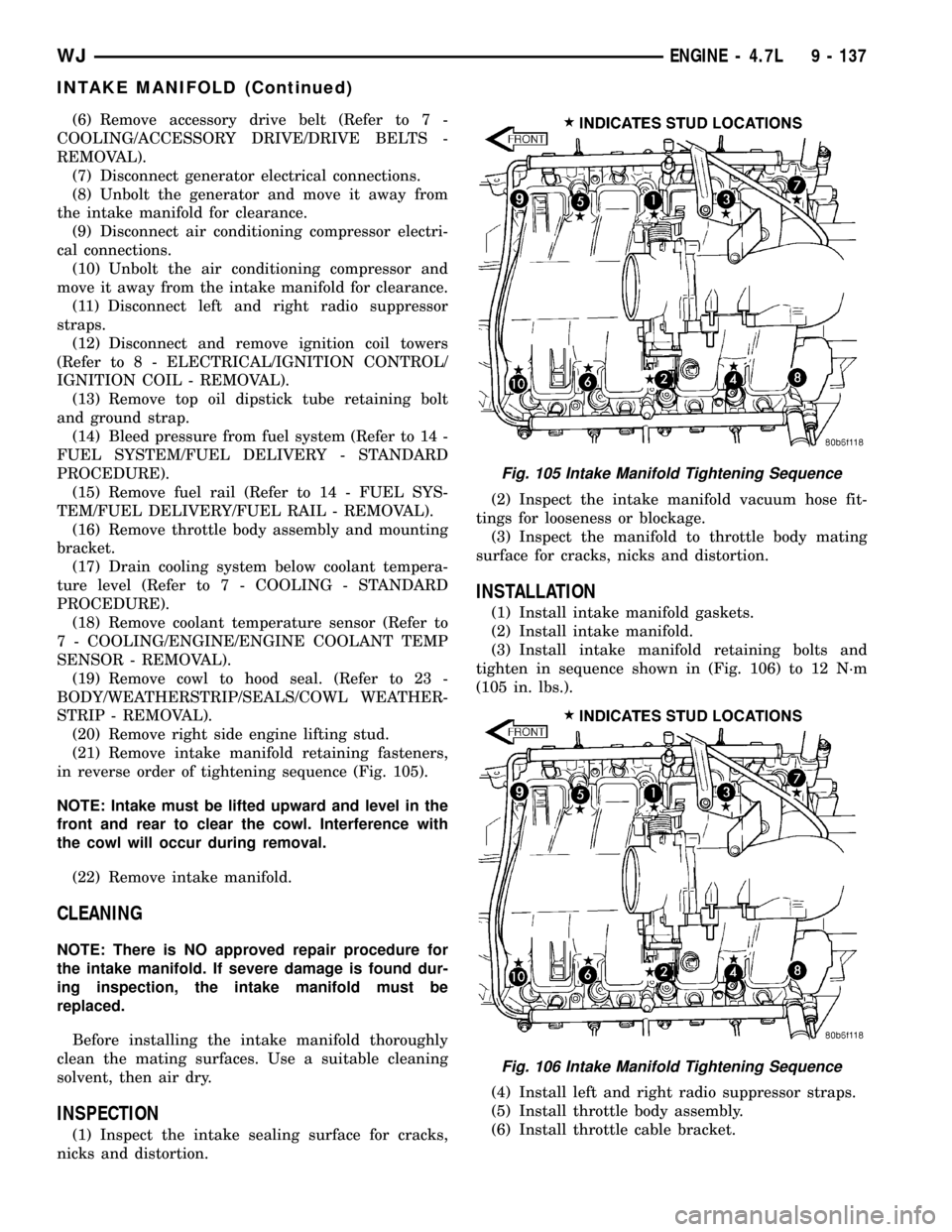
(21) Remove intake manifold retaining fasteners,
in reverse order of tightening sequence (Fig. 105).
NOTE: Intake must be lifted upward and level in the
front and rear to clear the cowl. Interference with
the cowl will occur during removal.
(22) Remove intake manifold.
CLEANING
NOTE: There is NO approved repair procedure for
the intake manifold. If severe damage is found dur-
ing inspection, the intake manifold must be
replaced.
Before installing the intake manifold thoroughly
clean the mating surfaces. Use a suitable cleaning
solvent, then air dry.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect the intake sealing surface for cracks,
nicks and distortion.(2) Inspect the intake manifold vacuum hose fit-
tings for looseness or blockage.
(3) Inspect the manifold to throttle body mating
surface for cracks, nicks and distortion.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install intake manifold gaskets.
(2) Install intake manifold.
(3) Install intake manifold retaining bolts and
tighten in sequence shown in (Fig. 106) to 12 N´m
(105 in. lbs.).
(4) Install left and right radio suppressor straps.
(5) Install throttle body assembly.
(6) Install throttle cable bracket.
Fig. 105 Intake Manifold Tightening Sequence
Fig. 106 Intake Manifold Tightening Sequence
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 137
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1381 of 2199

(7) Connect throttle cable and speed control cable
to throttle body.
(8) Install fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - INSTALLATION).
(9) Install ignition coil towers (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL -
INSTALLATION).
(10) Install coolant temperature sensor (Refer to 7
- COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE COOLANT TEMP
SENSOR - INSTALLATION).
(11) Connect electrical connectors for the following
components:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Coolant Temperature (CTS) Sensor
²Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
²Ignition coil towers
²Fuel injectors
(12) Install top oil dipstick tube retaining bolt and
ground strap.
(13) Install right side engine lifting stud.
(14) Install generator including electrical connec-
tions (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/CHARGING/GEN-
ERATOR - INSTALLATION).
(15) Connect Vapor purge hose, Brake booster
hose, Speed control servo hose, Positive crankcase
ventilation (PCV) hose.
(16) Install air conditioning compressor including
electrical connections.
(17) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(18) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(19) Install cowl to hood seal (Refer to 23 - BODY/
WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS/COWL WEATHERSTRIP -
INSTALLATION).
(20) Install air cleaner housing and throttle body
resonator. Tighten resonator bolts 4.5 N´m (40 in.
lbs.).
(21) Connect negative cable to battery.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD - LEFT
DESCRIPTION
The exhaust manifolds are log style with a pat-
ented flow enhancing design to maximize perfor-
mance. The exhaust manifolds are made of high
silicon molybdenum cast iron. A perforated core
graphite exhaust manifold gasket is used to improve
sealing to the cylinder head. The exhaust manifolds
are covered by a three layer laminated heat shield
for thermal protection and noise reduction. The heat
shields are fastened with a torque prevailing nutthat is backed off slightly to allow for the thermal
expansion of the exhaust manifold.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable for battery.
(2) Hoist vehicle.
(3) Disconnect exhaust pipe at manifold.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Remove air cleaner housing and tube.
(6) Remove the front two exhaust heat shield
retaining fasteners. Raise vehicle and remove the
fasteners at rear of heat shield.
(7) Remove heat shield (Fig. 107).
(8) Lower vehicle and remove the upper exhaust
manifold retaining bolts (Fig. 107).
(9) Raise vehicle and remove the lower exhaust
manifold retaining bolts (Fig. 107).
(10) Remove exhaust manifold and gasket (Fig.
107). Manifold is removed from below the engine
compartment.
CLEANING
(1) Clean the exhaust manifold using a suitable
cleaning solvent, then allow to air dry.
(2) Clean all gasket residue from the manifold
mating surface.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect the exhaust manifold for cracks in the
mating surface and at every mounting bolt hole.
(2) Using a straight edge and a feeler gauge, check
the mating surface for warp and twist.
(3) Inspect the manifold to exhaust pipe mating
surface for cracks, gouges, or other damage that
would prevent sealing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install exhaust manifold and gasket from below
engine compartment.
(2) Install lower exhaust manifold fasteners (Fig.
107). DO NOT tighten until all fasteners are in
place.
(3) Lower vehicle and install upper exhaust mani-
fold fasteners (Fig. 107). Tighten all manifold bolts
starting at center and working outward to 25 N´m
(18 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Over tightening heat shield fasteners,
may cause shield to distort and/or crack.
(4) Install exhaust manifold heat shield (Fig. 107).
Tighten fasteners to 8 N´m (72 in. lbs.), then loosen
45 degrees.
(5) Install air cleaner housing and tube.
(6) Connect exhaust pipe to manifold.
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
9 - 138 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1429 of 2199

(5) Connect (-) and (+) test cable leads into LCS
adapter receptacles. Use10 amp (10A +)receptacle
and common (-) receptacles.
(6) Gain access to MAIN MENU on DRB screen.
(7) Press DVOM button on DRB.
(8) Using left/right arrow keys, highlight CHAN-
NEL 1 function on DRB screen.
(9) Press ENTER three times.
(10) Using up/down arrow keys, highlight RANGE
on DRB screen (screen will default to 2 amp scale).
(11) Press ENTER to change 2 amp scale to 10
amp scale.This step must be done to prevent
damage to DRB scan tool or LCS adapter
(blown fuse).
(12) Remove cover from Power Distribution Center
(PDC).
(13) Remove fuel pump relay from PDC. Refer to
label on PDC cover for relay location.
WARNING: BEFORE PROCEEDING TO NEXT STEP,
NOTE THE FUEL PUMP WILL BE ACTIVATED AND
SYSTEM PRESSURE WILL BE PRESENT. THIS WILL
OCCUR AFTER CONNECTING TEST LEADS FROM
LCS ADAPTER INTO FUEL PUMP RELAY CAVITIES.
THE FUEL PUMP WILL OPERATE EVEN WITH IGNI-
TION KEY IN OFF POSITION. BEFORE ATTACHING
TEST LEADS, BE SURE ALL FUEL LINES AND
FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS ARE CONNECTED.
CAUTION: To prevent possible damage to the vehi-
cle electrical system and LCS adapter, the test
leads must be connected into relay cavities exactly
as shown in following steps.
Depending upon vehicle model, year or engine con-
figuration, three different types of relays may be
used: Type-1, type-2 and type±3.
(14) If equipped withtype±1 relay(Fig. 9), attach
test leads from LCS adapter into PDC relay cavities
number 30 and 87. For location of these cavities,
refer to numbers stamped to bottom of relay (Fig. 9).
(15) If equipped withtype±2 relay(Fig. 10),
attach test leads from LCS adapter into PDC relay
cavities number 30 and 87. For location of these cav-
ities, refer to numbers stamped to bottom of relay
(Fig. 10).
(16) If equipped withtype±3 relay(Fig. 11),
attach test leads from LCS adapter into PDC relay
cavities number 3 and 5. For location of these cavi-
ties, refer to numbers stamped to bottom of relay
(Fig. 11).
(17) When LCS adapter test leads are attached
into relay cavities, fuel pumpwill be activated.
Determine fuel pump amperage on DRB screen.
Amperage should be below 10.0 amps. If amperage is
below 10.0 amps, and specifications for the FuelPump Pressure, Fuel Pump Capacity and Fuel Pres-
sure Leak Down tests were met, the fuel pump mod-
ule is OK.
(18) If amperage is more than 10.0 amps, replace
fuel pump module assembly. The electric fuel pump
is not serviced separately.
Fig. 9 FUEL PUMP RELAY - TYPE 1
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
Fig. 10 FUEL PUMP RELAY - TYPE 2
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
14 - 10 FUEL DELIVERYWJ
FUEL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1430 of 2199

(19) Disconnect test leads from relay cavities
immediately after testing.
FUEL PUMP PRESSURE TEST
Use this test in conjunction with other fuel system
tests. Refer to the Fuel Pump Capacity Test, Fuel
Pressure Leak Down Test and Fuel Pump Amperage
Test.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
The fuel system is equipped with a combination
fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator. The fuel pressure
regulator is not controlled by engine vacuum.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF. BEFORE DISCONNECTING FUEL LINE AT
FUEL RAIL, THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.REFER TO THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
RELEASE PROCEDURE.
(1) Remove pressure test port cap at fuel rail test
port (Fig. 12) or (Fig. 13) . Connect 0±414 kPa (0-60
psi) fuel pressure gauge (from gauge set 5069) to test
port pressure fitting on fuel rail (Fig. 14) .The DRB
III Scan Tool along with the PEP module, the
500 psi pressure transducer, and the transduc-
er-to-test port adapter may also be used in
place of the fuel pressure gauge.
(2) Start and warm engine and note pressure
gauge reading. The DRB scan tool may also be used
to power fuel pump. Fuel pressure should be 339 kPa
34 kPa (49.2 psi 5 psi) at idle.
(3) If engine runs, but pressure is below 44.2 psi,
determine if fuel pump or filter/regulator is defective.
Proceed to next step:
(a) Check for a kinked fuel supply line some-
where between fuel rail and fuel pump module.
Fig. 11 FUEL PUMP RELAY - TYPE 3
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
1 COIL BATTERY
2 COIL GROUND
3 COMMON FEED
4 NORMALLY CLOSED
5 NORMALLY OPEN
Fig. 12 Test Port Cap LocationÐ4.0L Engine
1 - INJ. #1
2 - INJ. #2
3 - INJ. #3
4 - INJ. #4
5 - INJ. #5
6 - INJ. #6
7 - FUEL INJECTOR RAIL
8 - FUEL DAMPER
9 - PRESSURE TEST PORT CAP
10 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
11 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
WJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 11
FUEL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1462 of 2199

(5) Push sensor against flywheel/drive plate. With
sensor pushed against flywheel/drive plate, tighten
mounting bolt to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Route sensor wiring harness into wire shield.
(7) Connect sensor pigtail harness electrical con-
nector to main wiring harness.
INSTALLATION - 4.7L
(1) Clean out machined hole in engine block.
(2) Apply a small amount of engine oil to sensor
o-ring.
(3) Install sensor into engine block with a slight
rocking action. Do not twist sensor into position as
damage to o-ring may result.
CAUTION: Before tightening sensor mounting bolt,
be sure sensor is completely flush to cylinder
block. If sensor is not flush, damage to sensor
mounting tang may result.
(4) Install mounting bolt and tighten to 28 N´m
(21 ft. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
(6) Install starter motor. Refer to Starter Removal/
Installation.
FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION
A separate fuel injector (Fig. 24) is used for each
individual cylinder.
OPERATION
OPERATION
The fuel injectors are electrical solenoids. The
injector contains a pintle that closes off an orifice at
the nozzle end. When electric current is supplied to
the injector, the armature and needle move a short
distance against a spring, allowing fuel to flow out
the orifice. Because the fuel is under high pressure, a
fine spray is developed in the shape of a pencil
stream. The spraying action atomizes the fuel, add-
ing it to the air entering the combustion chamber.
The top (fuel entry) end of the injector (Fig. 24) is
attached into an opening on the fuel rail.
The nozzle (outlet) ends of the injectors are posi-
tioned into openings in the intake manifold just
above the intake valve ports of the cylinder head.
The engine wiring harness connector for each fuel
injector is equipped with an attached numerical tag
(INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.). This is used to identify each fuel
injector.
The injectors are electrically energized, individu-
ally and in a sequential order by the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). The PCM will adjust injector
pulse width by switching the ground path to each
individual injector on and off. Injector pulse width is
the period of time that the injector is energized. The
PCM will adjust injector pulse width based on vari-
ous inputs it receives.
Battery voltage is supplied to the injectors through
the ASD relay.
The PCM determines injector pulse width based on
various inputs.
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT
The nozzle ends of the injectors are positioned into
openings in the intake manifold just above the intake
valve ports of the cylinder head. The engine wiring
harness connector for each fuel injector is equipped
with an attached numerical tag (INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.).
This is used to identify each fuel injector with its
respective cylinder number.
The injectors are energized individually in a
sequential order by the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM will adjust injector pulse width by
switching the ground path to each individual injector
on and off. Injector pulse width is the period of time
that the injector is energized. The PCM will adjust
injector pulse width based on various inputs it
receives.
Battery voltage (12 volts +) is supplied to the injec-
tors through the ASD relay. The ASD relay will shut-
down the 12 volt power source to the fuel injectors if
the PCM senses the ignition is on, but the engine is
not running. This occurs after the engine has not
been running for approximately 1.8 seconds.
Fig. 24 Fuel InjectorÐ4.0L/4.7L Engines
1 - FUEL INJECTOR
2 - NOZZLE
3 - TOP (FUEL ENTRY)
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 43
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1463 of 2199

The PCM determines injector on-time (pulse width)
based on various inputs.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL INJECTOR
To perform a complete test of the fuel injectors and
their circuitry, use the DRB scan tool and refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures man-
ual. To test the injector only, refer to the following:
Disconnect the fuel injector wire harness connector
from the injector. The injector is equipped with 2
electrical terminals (pins). Place an ohmmeter across
the terminals. Resistance reading should be approxi-
mately 12 ohms 1.2 ohms at 20ÉC (68ÉF).
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT PRESSURE EVEN WITH ENGINE OFF.
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL INJECTOR(S), FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
To remove one or more fuel injectors, the fuel rail
assembly must be removed from engine.
(1) Perform Fuel System Pressure Release Proce-
dure.
(2) Remove fuel injector rail. Refer to Fuel Injector
Rail Removal/Installation.
(3) Remove clip(s) retaining injector(s) to fuel rail
(Fig. 25).
(4) Remove injector(s) from fuel rail.
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a small amount of engine oil to each fuel
injector o-ring. This will help in fuel rail installation.
(2) Install injector(s) and injector clip(s) to fuel
rail.
(3) Install fuel rail assembly. Refer to Fuel Injector
Rail Removal/Installation.
(4) Start engine and check for leaks.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The 5±pin, 12±volt, fuel pump relay is located in
the Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to the
label on the PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) energizes
the electric fuel pump through the fuel pump relay.
The fuel pump relay is energized by first applying
battery voltage to it when the ignition key is turned
ON, and then applying a ground signal to the relay
from the PCM.
Whenever the ignition key is turned ON, the elec-
tric fuel pump will operate. But, the PCM will shut-
down the ground circuit to the fuel pump relay in
approximately 1±3 seconds unless the engine is oper-
ating or the starter motor is engaged.
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The IAC stepper motor is mounted to the throttle
body, and regulates the amount of air bypassing the
control of the throttle plate. As engine loads and
ambient temperatures change, engine rpm changes.
A pintle on the IAC stepper motor protrudes into a
passage in the throttle body, controlling air flow
through the passage. The IAC is controlled by the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to maintain the
target engine idle speed.
OPERATION
At idle, engine speed can be increased by retract-
ing the IAC motor pintle and allowing more air to
pass through the port, or it can be decreased by
restricting the passage with the pintle and diminish-
ing the amount of air bypassing the throttle plate.
The IAC is called a stepper motor because it is
moved (rotated) in steps, or increments. Opening the
IAC opens an air passage around the throttle blade
which increases RPM.Fig. 25 Fuel Injector MountingÐTypical (4.7L V-8
Engine Shown)
1 - INLET FITTING
2 - FUEL INJECTOR RAIL
3 - CLIP
4 - FUEL INJECTOR
14 - 44 FUEL INJECTIONWJ
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 1493 of 2199

GEAR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GEAR
DESCRIPTION.........................16
OPERATION...........................16
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
ADJUSTMENTS
STEERING GEAR.....................18
SPECIFICATIONS
POWER STEERING GEAR..............18
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER STEERING GEAR..............19
PITMAN SHAFT
REMOVAL.............................20INSTALLATION.........................20
PITMAN SHAFT BEARING
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................22
PITMAN SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................23
RACK PISTON/VALVE ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL.............................23
INSTALLATION.........................25
STUB SHAFT HOUSING
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................25
GEAR
DESCRIPTION
The power steering gear is a recirculating ball type
gear (Fig. 1) .
The following gear components can be serviced:
²Pitman Shaft and Cover
²Pitman Shaft Bearings
²Pitman Shaft Oil Seal/Dust Seal
²Stud Shaft Housing with Seal
²O-Rings and Teflon Rings
NOTE: If rack piston assembly is damaged the gear
must be replaced.
OPERATION
The gear acts as a rolling thread between the
worm shaft and rack piston. The worm shaft is sup-
ported by a thrust bearing at the lower end and a
bearing assembly at the upper end. When the worm
shaft is turned the rack piston moves. The rack pis-
ton teeth mesh with the pitman shaft. Turning the
worm shaft turns the pitman shaft, which turns the
steering linkage.
REMOVAL
(1) Place the front wheels in the straight ahead
position with the steering wheel centered and locked.
(2) Remove the air cleaner housing,(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER
HOUSING - REMOVAL).
(3) Drain or siphon the power steering system.(4) Remove the pressure and return lines (Fig.
2)from the steering gear. Refer to hose removal in
this section.
(5) Remove the column coupler shaft bolt (Fig.
2)and remove the shaft from the gear.
(6) Raise and support the vehicle.
(7) Remove the left front wheel and tire assembly.
(8) Remove the pitman arm from gear with Puller
C-4150A.
(9) Remove the windshield washer reservoir,(Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WASHER
RESERVOIR - REMOVAL).
(10) Remove the steering gear mounting bolts.
Remove the steering gear out of the engine compart-
ment (Fig. 3).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the steering gear on the frame rail and
install the bolts. Tighten the bolts to 108 N´m (80 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(2) Install the pitman arm and tighten nut to 251
N´m (185 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install windshield washer reservoir,(Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WASHER RES-
ERVOIR - INSTALLATION).
(4) Install the wheel and tire assembly.
(5) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
(6) Install the pressure and return hoses to the
steering gear and tighten to 20-38 N´m (14-28 ft.
lbs.).
(7) Install the column coupler shaft.
(8) Install the air cleaner housing,(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER
HOUSING - INSTALLATION).
19 - 16 GEARWJ
Page 1522 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - TORQUE
CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE........134
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................134
OPERATION..........................134
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION........................135
OPERATION..........................139REMOVAL............................154
DISASSEMBLY........................155
CLEANING...........................165
INSPECTION.........................166
ASSEMBLY...........................167
INSTALLATION........................175
ADJUSTMENTS - VALVE BODY...........175
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION -
42RE
DESCRIPTION
The 42RE is a four speed fully automatic transmis-
sion (Fig. 1) with an electronic governor. The 42RE is
equipped with a lock-up clutch in the torque con-
verter. First through third gear ranges are provided
by the clutches, bands, overrunning clutch, and plan-
etary gear sets in the transmission. Fourth gear
range is provided by the overdrive unit that contains
an overdrive clutch, direct clutch, planetary gear set,
and overrunning clutch.The transmission contains a front, rear, and direct
clutch which function as the input driving compo-
nents. It also contains the kickdown (front) and the
low/reverse (rear) bands which, along with the over-
running clutch and overdrive clutch, serve as the
holding components. The driving and holding compo-
nents combine to select the necessary planetary gear
components, in the front, rear, or overdrive planetary
gear set, transfer the engine power from the input
shaft through to the output shaft.
The valve body is mounted to the lower side of the
transmission and contains the valves to control pres-
sure regulation, fluid flow control, and clutch/band
application. The oil pump is mounted at the front of
the transmission and is driven by the torque con-
verter hub. The pump supplies the oil pressure nec-
essary for clutch/band actuation and transmission
lubrication.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 3