2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE No RDS
[x] Cancel search: No RDSPage 1474 of 2199

REMOVAL - 4.7L
CAUTION: Be careful not to damage or kink the
cable core wire (within the cable sheathing) while
servicing accelerator pedal or throttle cable.
(1) From inside vehicle, hold up accelerator pedal.
Remove plastic cable retainer (clip) and throttle cable
core wire from upper end of pedal arm (Fig. 16).
Plastic cable retainer (clip) snaps into pedal arm.
(2) Remove cable core wire at pedal arm.
(3) From inside vehicle, remove clip holding cable
to dashpanel (Fig. 16).
(4) Remove air box at throttle body.
(5) Unsnap cable from plenum routing clip.
(6) Remove cable housing from dash panel and
pull into engine compartment.
(7) Using finger pressure only, disconnect accelera-
tor cable connector at throttle body bellcrank pin by
pushing connector off bellcrank pin towards front of
vehicle (Fig. 38).DO NOT try to pull connector
off perpendicular to the bellcrank pin. Connec-
tor will be broken.(8) Lift accelerator cable from top of cable cam
(Fig. 38).
(9) Press tab (Fig. 39) to release plastic cable
mount from bracket.Press on tab only enough to
release cable from bracket. If tab is pressed too
much, it will be broken.Slide plastic mount (Fig.
39) towards passenger side of vehicle to remove cable
from bracket.
(10) Remove throttle cable from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION ± 4.0L
(1) Slide throttle cable through hole in bracket
until release tabs lock into bracket.
(2) Connect cable ball end to throttle body
bellcrank ball (snaps on).
(3) Snap cable into routing clips on engine valve
cover.
(4) Slide rubber grommet away from plastic cable
housing.
(5) Install rubber grommet into dash panel until
seated.
(6) Push cable housing into rubber grommet and
through opening in dash panel.
Fig. 37 Throttle (Accelerator) Cable at Throttle
BodyÐ4.0L Engine
1 - ACCELERATOR CABLE
2 - OFF
3 - OFF
4 - THROTTLE BODY BELLCRANK
5 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
6 - RELEASE TABS
7 - BRACKET
Fig. 38 Accelerator Cable at Bell CrankÐ4.7L V-8
Engine
1 - THROTTLE BODY
2 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE CONNECTOR
3 - OFF
4 - OFF
5 - ACCELERATOR CABLE CONNECTOR
6 - CABLE CAM
7 - BELLCRANK
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 55
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE (Continued)
Page 1498 of 2199

(2) Install lower pitman shaft bearing with the
other side Driver 8294 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 11).
Drive bearing into housing until the bearing shoulder
is seated against the housing.
(3) Coat the oil seal and backup washers withspe-
cial greasesupplied with the new seal.
(4) Install the oil seal with Driver 8294 and Han-
dle C-4171.
(5) Install plastic backup washer.
NOTE: The plastic backup washer has a lip on the
inside diameter that faces down towards the oil
seal.
(6) Install metal backup washer.
(7) Install the retainer ring with snap ring pliers.(8) Coat the dust seal withspecial greasesup-
plied with the new seal.
(9) Install dust seal with Driver 8294 and Handle
C-4171.
(10) Install new pitman shaft cover o-ring.
(11) Install pitman shaft assembly into the hous-
ing.
(12) Install cover bolts and tighten to 62 N´m (46
ft. lbs.).
(13) Perform over-center rotation torque adjust-
ment.
Fig. 8 Oil Seal Retaining Ring
1 - SNAP RING PLIERS
2 - RETAINING RING
Fig. 9 Bearing Driver
1 - UPPER BEARING
2 - LOWER BEARING
3 - DRIVER
Fig. 10 Upper Pitman Shaft Bearing
1 - DRIVER
2 - UPPER BEARING
Fig. 11 Lower Pitman Shaft Bearing
1 - STEERING GEAR
2 - BEARING SHOULDER
3 - DRIVER
4 - LOWER BEARING
WJGEAR 19 - 21
PITMAN SHAFT (Continued)
Page 1499 of 2199

PITMAN SHAFT BEARING
REMOVAL
(1) Clean exposed end of pitman shaft and housing
with a wire brush.
(2) Rotate the stub shaft with a wrench (Fig.
5)from stop to stop and count the number of turns.
(3) Center the stub shaft by rotating it from the
stop 1/2 of the total amount of turns.
NOTE: The pitman shaft will not clear the housing if
it is not centered.
(4) Remove pitman shaft cover bolts and remove
the shaft assembly (Fig. 6).
(5) Remove pitman shaft cover o-ring.
(6) Remove pitman shaft dust seal from the hous-
ing with a Puller 7794-A and Slide Hammer C-637
(Fig. 7).
(7) Remove the pitman shaft oil seal retaining ring
with snap ring pliers (Fig. 8).
(8) Remove oil seal metal backup washer then
plastic backup washer from the housing (Fig. 12).
(9)
Remove pitman shaft oil seal from the housing
with a Puller 7794-A and Slide Hammer C-637 (Fig. 7).
(10) Drop Driver 8277 through the top bearing and
align the driver up with the lower bearing. (Fig. 9).
Install Handle C-4171 into the driver and remove the
lower bearing.
(11) Turn the gear over and remover the upper
bearing with Driver 8277 and Handle C-4171.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install upper pitman shaft bearing, with Driver
8294 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 10). Drive bearing into
housing until the driver bottoms out.NOTE: Install upper pitman shaft bearing with the
part number/letters facing the driver.
(2) Install lower pitman shaft bearing with the
other side Driver 8294 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 11).
Drive bearing into housing until the bearing shoulder
is seated against the housing.
(3) Coat the oil seal and backup washers withspe-
cial greasesupplied with the new seal.
(4) Install the oil seal with Driver 8294 and Han-
dle C-4171.
(5) Install plastic backup washer.
NOTE: The plastic backup washer has a lip on the
inside diameter that faces down towards the oil
seal.
(6) Install metal backup washer.
(7) Install the retainer ring with snap ring pliers.
(8) Coat the dust seal withspecial greasesup-
plied with the new seal.
(9) Install dust seal with Driver 8294 and Handle
C-4171.
(10) Install new pitman shaft cover o-ring.
(11) Install pitman shaft assembly into the hous-
ing.
(12) Install cover bolts and tighten to 62 N´m (46
ft. lbs.).
(13) Perform over-center rotation torque adjust-
ment.
PITMAN SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Clean exposed end of pitman shaft and housing
with a wire brush.
(2) Rotate the stub shaft with a wrench (Fig.
5)from stop to stop and count the number of turns.
(3) Center the stub shaft by rotating it from the
stop 1/2 of the total amount of turns.
NOTE: The pitman shaft will not clear the housing if
it is not centered.
(4) Remove pitman shaft cover bolts and remove
the shaft assembly (Fig. 6).
(5) Remove pitman shaft cover o-ring.
(6) Remove pitman shaft dust seal from the hous-
ing with a Puller 7794-A and Slide Hammer C-637
(Fig. 7).
(7) Remove the pitman shaft oil seal retaining ring
with snap ring pliers (Fig. 8).
(8) Remove oil seal metal backup washer then
plastic backup washer from the housing (Fig. 12).
Fig. 12 Backup Washers
1 - METAL BACK UP WASHER
2 - PLASTIC BACK UP WASHER
19 - 22 GEARWJ
Page 1500 of 2199

(9) Remove pitman shaft oil seal from the housing
with a Puller 7794-A and Slide Hammer C-637 (Fig.
7).
(10) Drop Driver 8277 through the top bearing and
align the driver up with the lower bearing. (Fig. 9).
Install Handle C-4171 into the driver and remove the
lower bearing.
(11) Turn the gear over and remover the upper
bearing with Driver 8277 and Handle C-4171.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install upper pitman shaft bearing, with Driver
8294 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 10). Drive bearing into
housing until the driver bottoms out.
NOTE: Install upper pitman shaft bearing with the
part number/letters facing the driver.
(2) Install lower pitman shaft bearing with the
other side Driver 8294 and Handle C-4171 (Fig. 11).
Drive bearing into housing until the bearing shoulder
is seated against the housing.
(3) Coat the oil seal and backup washers withspe-
cial greasesupplied with the new seal.
(4) Install the oil seal with Driver 8294 and Han-
dle C-4171.
(5) Install plastic backup washer.
NOTE: The plastic backup washer has a lip on the
inside diameter that faces down towards the oil
seal.
(6) Install metal backup washer.
(7) Install the retainer ring with snap ring pliers.
(8) Coat the dust seal withspecial greasesup-
plied with the new seal.
(9) Install dust seal with Driver 8294 and Handle
C-4171.
(10) Install new pitman shaft cover o-ring.
(11) Install pitman shaft assembly into the hous-
ing.
(12) Install cover bolts and tighten to 62 N´m (46
ft. lbs.).
(13) Perform over-center rotation torque adjust-
ment.
RACK PISTON/VALVE
ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the steering gear (Refer to 19 -
STEERING/GEAR - REMOVAL).
(2) Clean exposed end of pitman shaft and housing
with a wire brush.
(3) Rotate the stub shaft with a wrench (Fig.
5)from stop to stop and count the number of turns.(4) Center the stub shaft by rotating it from the
stop 1/2 of the total amount of turns.
NOTE: The pitman shaft will not clear the housing if
it is not centered.
(5) Remove pitman shaft cover bolts and remove
the shaft assembly (Fig. 6).
(6) Remove the pitman shaft cover o-ring.
(7) Remove stub shaft housing bolts (Fig. 13).
(8) Remove the housing from the stub shaft (Fig.
14).
Fig. 13 Stub Shaft Housing
1 - STUB SHAFT HOUSING
2 - BOLTS
3 - STUB SHAFT
Fig. 14 Housing Removal
1 - STEERING GEAR
2 - STUB SHAFT HOUSING
WJGEAR 19 - 23
PITMAN SHAFT SEAL (Continued)
Page 1629 of 2199

(2) Install new seal on switch and install switch in
case. Tighten switch to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Test continuity of new switch with 12V test
lamp.
(4) Connect switch wires and lower vehicle.
(5) Top off transmission fluid level.
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION
There are several sizes and types of pistons used in
an automatic transmission. Some pistons are used to
apply clutches. They all have in common the fact
that they are round or circular in shape, located
within a smooth walled cylinder, which is closed at
one end and converts fluid pressure into mechanical
movement. The fluid pressure exerted on the piston
is contained within the system through the use of
piston rings or seals.
OPERATION
The principal which makes this operation possible
is known as Pascal's Law. Pascal's Law can be stated
as: ªPressure on a confined fluid is transmitted
equally in all directions and acts with equal force on
equal areas.º
PRESSURE
Pressure (Fig. 199) is nothing more than force
(lbs.) divided by area (in or ft.), or force per unit
area. Given a 100 lb. block and an area of 100 sq. in.
on the floor, the pressure exerted by the block is: 100lbs. 100 in or 1 pound per square inch, or PSI as it is
commonly referred to.
PRESSURE ON A CONFINED FLUID
Pressure is exerted on a confined fluid (Fig. 200)
by applying a force to some given area in contact
with the fluid. A good example of this is a cylinder
filled with fluid and equipped with a piston that is
closely fitted to the cylinder wall. If a force is applied
to the piston, pressure will be developed in the fluid.
Of course, no pressure will be created if the fluid is
not confined. It will simply ªleakº past the piston.
There must be a resistance to flow in order to create
pressure. Piston sealing is extremely important in
hydraulic operation. Several kinds of seals are used
to accomplish this within a transmission. These
include but are not limited to O-rings, D-rings, lip
seals, sealing rings, or extremely close tolerances
between the piston and the cylinder wall. The force
exerted is downward (gravity), however, the principle
remains the same no matter which direction is taken.
The pressure created in the fluid is equal to the force
applied, divided by the piston area. If the force is 100
lbs., and the piston area is 10 sq. in., then the pres-
sure created equals 10 PSI. Another interpretation of
Pascal's Law is that regardless of container shape or
size, the pressure will be maintained throughout, as
long as the fluid is confined. In other words, the
pressure in the fluid is the same everywhere within
the container.
Fig. 198 Park/Neutral Position Switch
1 - NEUTRAL CONTACT
2 - MANUAL LEVER AND SWITCH PLUNGER IN REVERSE
POSITION
3 - PARK CONTACT
4 - SWITCH
Fig. 199 Force and Pressure Relationship
21 - 110 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1653 of 2199

TORQUE CONVERTER
DRAINBACK VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The drainback valve is located in the transmission
cooler outlet (pressure) line.
OPERATION
The valve prevents fluid from draining from the
converter into the cooler and lines when the vehicle
is shut down for lengthy periods. Production valves
have a hose nipple at one end, while the opposite end
is threaded for a flare fitting. All valves have an
arrow (or similar mark) to indicate direction of flow
through the valve.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TORQUE
CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE
The converter drainback check valve is located in
the cooler outlet (pressure) line near the radiator
tank. The valve prevents fluid drainback when the
vehicle is parked for lengthy periods. The valve check
ball is spring loaded and has an opening pressure of
approximately 2 psi.
The valve is serviced as an assembly; it is not
repairable. Do not clean the valve if restricted, or
contaminated by sludge, or debris. If the valve fails,
or if a transmission malfunction occurs that gener-
ates significant amounts of sludge and/or clutch par-
ticles and metal shavings, the valve must be
replaced.
The valve must be removed whenever the cooler
and lines are reverse flushed. The valve can be flow
tested when necessary. The procedure is exactly the
same as for flow testing a cooler.
If the valve is restricted, installed backwards, or in
the wrong line, it will cause an overheating condition
and possible transmission failure.
CAUTION: The drainback valve is a one-way flow
device. It must be properly oriented in terms of flow
direction for the cooler to function properly. The
valve must be installed in the pressure line. Other-
wise flow will be blocked and would cause an over-
heating condition and eventual transmission failure.
TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Transmission fluid temperature readings are sup-
plied to the transmission control module by the ther-
mistor (Fig. 254). The temperature readings are used
to control engagement of the fourth gear overdrive
clutch, the converter clutch, and governor pressure.
Normal resistance value for the thermistor at room
temperature is approximately 2000 ohms.
The thermistor is part of the governor pressure
sensor assembly and is immersed in transmission
fluid at all times.
OPERATION
The PCM prevents engagement of the converter
clutch and overdrive clutch, when fluid temperature
is below approximately 10ÉC (50ÉF).
If fluid temperature exceeds 126ÉC (260ÉF), the
PCM causes a 4-3 downshift and engage the con-
verter clutch. Engagement is according to the third
gear converter clutch engagement schedule.
The overdrive OFF lamp in the instrument panel
illuminates when the shift back to third occurs. The
transmission will not allow fourth gear operation
until fluid temperature decreases to approximately
110ÉC (230ÉF).
Fig. 254 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
21 - 134 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
Page 1775 of 2199
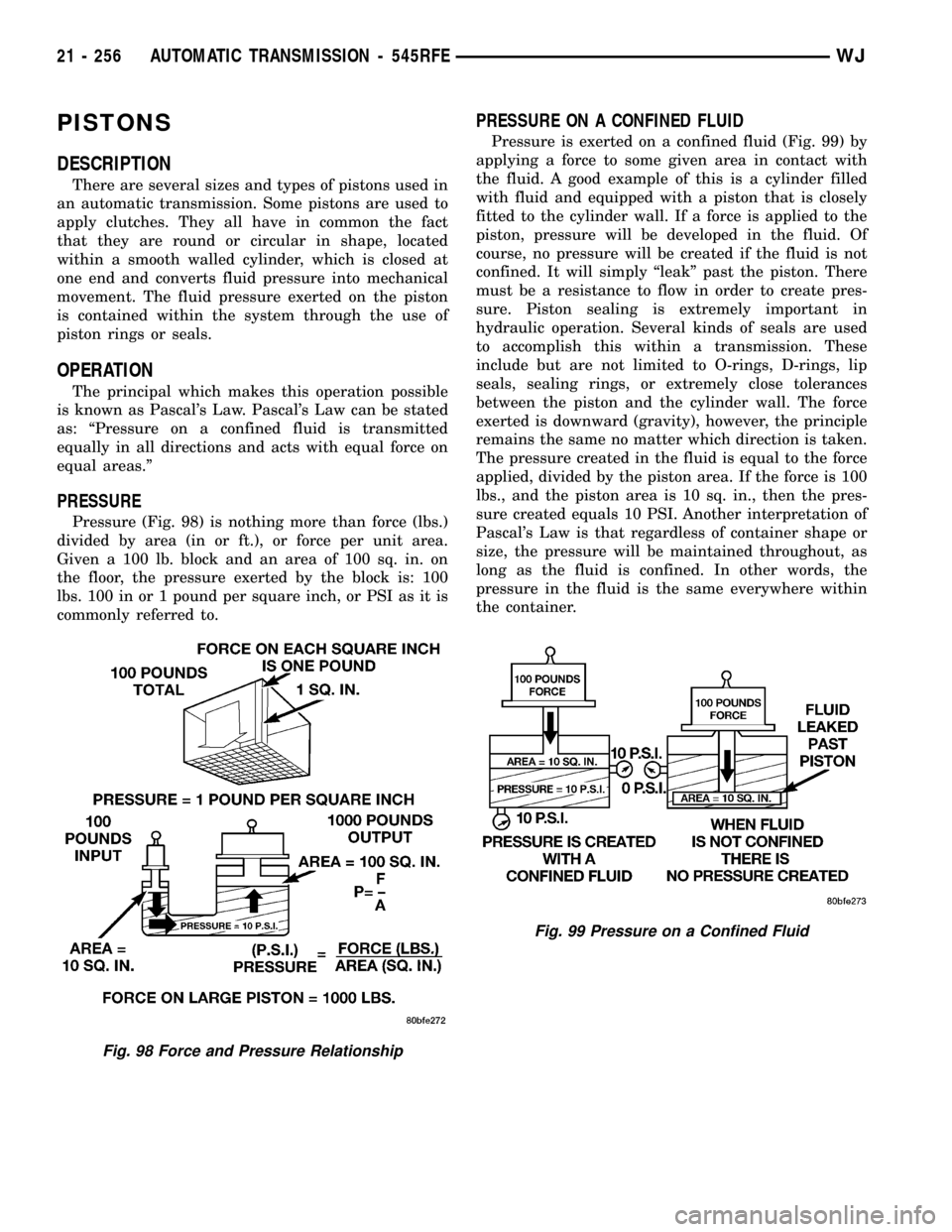
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION
There are several sizes and types of pistons used in
an automatic transmission. Some pistons are used to
apply clutches. They all have in common the fact
that they are round or circular in shape, located
within a smooth walled cylinder, which is closed at
one end and converts fluid pressure into mechanical
movement. The fluid pressure exerted on the piston
is contained within the system through the use of
piston rings or seals.
OPERATION
The principal which makes this operation possible
is known as Pascal's Law. Pascal's Law can be stated
as: ªPressure on a confined fluid is transmitted
equally in all directions and acts with equal force on
equal areas.º
PRESSURE
Pressure (Fig. 98) is nothing more than force (lbs.)
divided by area (in or ft.), or force per unit area.
Given a 100 lb. block and an area of 100 sq. in. on
the floor, the pressure exerted by the block is: 100
lbs. 100 in or 1 pound per square inch, or PSI as it is
commonly referred to.
PRESSURE ON A CONFINED FLUID
Pressure is exerted on a confined fluid (Fig. 99) by
applying a force to some given area in contact with
the fluid. A good example of this is a cylinder filled
with fluid and equipped with a piston that is closely
fitted to the cylinder wall. If a force is applied to the
piston, pressure will be developed in the fluid. Of
course, no pressure will be created if the fluid is not
confined. It will simply ªleakº past the piston. There
must be a resistance to flow in order to create pres-
sure. Piston sealing is extremely important in
hydraulic operation. Several kinds of seals are used
to accomplish this within a transmission. These
include but are not limited to O-rings, D-rings, lip
seals, sealing rings, or extremely close tolerances
between the piston and the cylinder wall. The force
exerted is downward (gravity), however, the principle
remains the same no matter which direction is taken.
The pressure created in the fluid is equal to the force
applied, divided by the piston area. If the force is 100
lbs., and the piston area is 10 sq. in., then the pres-
sure created equals 10 PSI. Another interpretation of
Pascal's Law is that regardless of container shape or
size, the pressure will be maintained throughout, as
long as the fluid is confined. In other words, the
pressure in the fluid is the same everywhere within
the container.
Fig. 98 Force and Pressure Relationship
Fig. 99 Pressure on a Confined Fluid
21 - 256 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
Page 1868 of 2199

CLEANING
Remove the protective coating on the tires before
delivery of a vehicle. This coating may cause deteri-
oration of the tires.
To remove the protective coating, apply warm
water and let it soak for a few minutes. Afterwards,
scrub the coating away with a soft bristle brush.
Steam cleaning may also be used to remove the coat-
ing.
NOTE: DO NOT use gasoline, mineral oil, oil-based
solvent or a wire brush for cleaning.
SPECIFICATIONS
TIRES
SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
TIRE P225/75R16
TIRE P245/70R16
TIRE P235/65R17
SPECIFICATIONS -
SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION - RIM SPECIFICATION - TIRE
BASE LAREDO (2.7L &
4.0L)
16x7P225/75R16
OPTIONAL LAREDO
(2.7L, 4.0L, 4.7L)
16x7P245/70R16
LAREDO 4.7L (JAPAN &
AUSTRALIA)
17x7.5P235/65R17
OPTIONAL LAREDO (UP
COUNTRY)
17x7.5P235/65R17
BASE LIMITED
17x7.5P235/65R17
OPTIONAL LIMITED (UP
COUNTRY)
& OVERLAND
17x7.5P235/65R17
BASE WHEEL / SNOW
TIREP235/65R17
Fig. 16 Tire Wear Patterns
Fig. 17 Tire Repair Area
1 - REPAIRABLE AREA
WJTIRES/WHEELS 22 - 9
TIRES (Continued)