2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Rear main seal
[x] Cancel search: Rear main sealPage 1535 of 2199

leaks are generally deposited on the housing and not
on the converter.
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAK POINTS
Possible sources of converter leaks are:
(1) Leaks at the weld joint around the outside
diameter weld (Fig. 12).
(2) Leaks at the converter hub weld (Fig. 12).
CONVERTER HOUSING AREA LEAK CORRECTION
(1) Remove converter.
(2) Tighten front band adjusting screw until band
is tight around front clutch retainer. This prevents
front/rear clutches from coming out when oil pump is
removed.
(3) Remove oil pump and remove pump seal.
Inspect pump housing drainback and vent holes for
obstructions. Clear holes with solvent and wire.
(4) Inspect pump bushing and converter hub. If
bushing is scored, replace it. If converter hub is
scored, either polish it with crocus cloth or replace
converter.(5) Install new pump seal, O-ring, and gasket.
Replace oil pump if cracked, porous or damaged in
any way. Be sure to loosen the front band before
installing the oil pump, damage to the oil pump seal
may occur if the band is still tightened to the front
clutch retainer.
(6) Loosen kickdown lever pin access plug three
turns. Apply LoctiteŸ 592, or PermatextNo.2to
plug threads and tighten plug to 17 N´m (150 in. lbs.)
torque.
(7) Adjust front band.
(8) Lubricate pump seal and converter hub with
transmission fluid or petroleum jelly and install con-
verter.
(9) Install transmission and converter housing
dust shield.
(10) Lower vehicle.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DIAGNOSIS
CHARTS
The diagnosis charts provide additional reference
when diagnosing a transmission fault. The charts
provide general information on a variety of transmis-
sion, overdrive unit and converter clutch fault condi-
tions.
The hydraulic flow charts in the Schematics and
Diagrams section of this group, outline fluid flow and
hydraulic circuitry. Circuit operation is provided for
PARK, NEUTRAL, FIRST, SECOND, THIRD,
FOURTH, MANUAL FIRST, MANUAL SECOND,
and REVERSE gear ranges. Normal working pres-
sures are also supplied for each of the gear ranges.
Fig. 11 Converter Housing Leak Paths
1 - PUMP SEAL
2 - PUMP VENT
3 - PUMP BOLT
4 - PUMP GASKET
5 - CONVERTER HOUSING
6 - CONVERTER
7 - REAR MAIN SEAL LEAK
Fig. 12 Converter Leak Points - Typical
1 - OUTSIDE DIAMETER WELD
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER HUB WELD
3 - STARTER RING GEAR
4 - LUG
21 - 16 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1561 of 2199

(11) Move transmission forward. Then raise, lower
or tilt transmission to align converter housing with
engine block dowels.
(12) Carefully work transmission forward and over
engine block dowels until converter hub is seated in
crankshaft.
(13) Install two bolts to attach converter housing
to engine.
(14) Install the upper transmission bending braces
to the torque converter housing and the overdrive
unit. Tighten the bolts to 41 N´m (30 ft.lbs.).
(15) Install remaining torque converter housing to
engine bolts. Tighten to 68 N´m (50 ft.lbs.).
(16) Install rear transmission crossmember.
Tighten crossmember to frame bolts to 68 N´m (50
ft.lbs.).
(17) Install rear support to transmission. Tighten
bolts to 47 N´m (35 ft.lbs.).
(18) Lower transmission onto crossmember and
install bolts attaching transmission mount to cross-
member. Tighten clevis bracket to crossmember bolts
to 47 N´m (35 ft.lbs.). Tighten the clevis bracket to
rear support bolt to 68 N´m (50 ft.lbs.).
(19) Remove engine support fixture.
(20) Install crankshaft position sensor. (Refer to 14
- FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/CRANKSHAFT
POSITION SENSOR - INSTALLATION)
(21) Install new plastic retainer grommet on any
shift cable that was disconnected. Grommets should
not be reused. Use pry tool to remove rod from grom-
met and cut away old grommet. Use pliers to snap
new grommet into cable and to snap grommet onto
lever.
(22) Connect gearshift and throttle valve cable to
transmission.
(23) Connect wires to park/neutral position switch
and transmission solenoid connector. Be sure trans-
mission harnesses are properly routed.CAUTION: It is essential that correct length bolts be
used to attach the converter to the driveplate. Bolts
that are too long will damage the clutch surface
inside the converter.
(24) Install all torque converter-to-driveplate bolts
by hand.
(25) Verify that the torque converter is pulled
flush to the driveplate. Tighten bolts to 31 N´m (270
in. lbs.).
(26) Install converter housing access cover. Tighten
bolt to 23 N´m (200 in.lbs.).
(27) Install the bell housing brace to the torque
converter cover and the engine to transmission bend-
ing brace. Tighten the bolts and nut to 41 N´m (30
ft.lbs.).
(28) Install starter motor (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/STARTING/STARTER MOTOR - INSTALLA-
TION) and cooler line bracket.
(29) Connect cooler lines to transmission.
(30) Install transmission fill tube. Install new seal
on tube before installation.
(31) Install exhaust components.
(32) Install transfer case. Tighten transfer case
nuts to 35 N´m (26 ft.lbs.).
(33) Install the transfer case shift cable to the
cable support bracket and the transfer case shift
lever.
(34) Align and connect propeller shaft(s).
(35) Adjust gearshift linkage and throttle valve
cable if necessary.
(36) Lower vehicle.
(37) Fill transmission with MopartATF +4, type
9602, fluid.
21 - 42 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1627 of 2199

(8) Install new seals on over drive piston.
(9) Stand transmission case upright on bellhous-
ing.
(10) Position Guide Ring 8114-1 on outer edge of
overdrive piston retainer.
(11) Position Seal Guide 8114-2 on inner edge of
overdrive piston retainer.
(12) Install overdrive piston in overdrive piston
retainer by: aligning locating lugs on overdrive piston
to the two mating holes in retainer.
(a) Aligning locating lugs on overdrive piston to
the two mating holes in retainer.
(b) Lubricate overdrive piston seals with Mopart
Door Ease, or equivalent.
(c) Install piston over Seal Guide 8114-2 and
inside Guide Ring 8114-1.
(d) Push overdrive piston into position in
retainer.
(e) Verify that the locating lugs entered the lug
bores in the retainer.
NOTE: Install the remaining transmission compo-
nents and the overdrive unit.
PARK LOCK CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) Place the shifter in the PARK position.
(2) Lower the steering column cover.
(3) With the ignition switch in the ªRUNº position
depress the park lock cable locking tab, located on
top of the cable connector at the steering column and
pull the park lock cable straight out.
(4) Remove the park lock cable from steering col-
umn (Fig. 197).
(5) Remove the floor console and related trim.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE -
REMOVAL)
(6) Disconnect the park lock cable from the shift
BTSI lever and remove the cable from the shifter
assembly bracket.
(7) Release the park lock cable from any remaining
clips.
(8) Remove park lock cable from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: The gearshift cable must be secured into
position and properly adjusted before the installa-
tion of the Park Lock Cable.
(1) Verify that the shifter is in the PARK position.
(2) Push the park lock cable straight into the
square mounting hole in the steering column until
cable snaps in place.
(3) Route park lock cable to the shifter mecha-
nism.
(4) Install the park lock cable end fitting into
shifter BTSI lever.
(5) Pull rearward on the cable housing to snap
park lock cable adjuster ears into floor shifter
bracket.
(6) Place the ignition key cylinder in the ACCES-
SORY position.
(7) Push the cable adjuster lock clamp downward
to lock it.
(8) Test the park lock cable operation.
(9) Install the floor console and related trim.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE -
INSTALLATION)
Fig. 196 Aligning Overdrive Piston Retainer
1 - PISTON RETAINER
2 - GASKET
3 - RETAINER BOLTS
21 - 108 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH CAM/OVERDRIVE PISTON RETAINER (Continued)
Page 1686 of 2199

²pressure adjusting screw and bracket assembly
²throttle lever
²manual lever and shaft seal
²throttle lever shaft seal, washer, and E-clip
²fluid filter and screws
²detent ball and spring
²valve body screws
²governor pressure solenoid
²governor pressure sensor and retaining clip
²park lock rod and E-clip
ASSEMBLY
CAUTION: Do not force valves or plugs into place
during reassembly. If the valve body bores, valves
and plugs are free of distortion or burrs, the valve
body components should all slide into place easily.
In addition, do not overtighten the transfer plate
and valve body screws during reassembly. Over-
tightening can distort the housings resulting in
valve sticking, cross leakage and unsatisfactory
operation. Tighten valve body screws to recom-
mended torque only.
LOWER HOUSING
(1) Lubricate valves, springs, and the housing
valve and plug bores with clean transmission fluid
(Fig. 309).
(2) Install 3-4 timing valve spring and valve in
lower housing.
(3) Install 3-4 quick fill valve in lower housing.
(4) Install 3-4 quick fill valve spring and plug in
housing.
(5) Install timing valve end plate. Tighten end
plate screws to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
3-4 ACCUMULATOR
(1) Lubricate accumulator piston, seals and hous-
ing piston bore with clean transmission fluid (Fig.
310).
(2) Install new seal rings on accumulator piston.
(3) Install piston and spring in housing.
(4) Install end plate on housing.
TRANSFER PLATE
(1) Install rear clutch and rear servo check balls in
transfer plate (Fig. 311).
(2) Install filter screen in upper housing separator
plate (Fig. 312).
(3) Align and position upper housing separator
plate on transfer plate (Fig. 313).
(4) Install brace plate (Fig. 313). Tighten brace
attaching screws to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install remaining separator plate attaching
screws. Tighten screws to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) torque.
UPPER AND LOWER HOUSING
(1) Position upper housing so internal passages
and check ball seats are facing upward. Then install
check balls in housing (Fig. 314). Eight check balls
are used. The single large check ball is approxi-
mately 8.7 mm (11/32 in.) diameter. The single small
check ball is approximately 4.8 mm (3/16 in.) in
diameter. The remaining 6 check balls are approxi-
mately 6.3 mm (1/4 in.) in diameter.
(2) Position assembled transfer plate and upper
housing separator plate on upper housing (Fig. 315).
Be sure filter screen is seated in proper housing
recess.
Fig. 311 Rear Clutch And Rear Servo Check Ball
Locations
1 - REAR CLUTCH CHECK BALL
2 - REAR SERVO CHECK BALL
3 - TRANSFER PLATE
Fig. 312 Separator Plate Filter Screen Installation
1 - UPPER HOUSING SEPARATOR PLATE
2 - FILTER SCREEN
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 167
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1747 of 2199

(8) Engine starts must be possible with shifter
lever in PARK or NEUTRAL gate positions only.
Engine starts must not be possible in any other gate
positions other than PARK or NEUTRAL.
(9) With shifter lever handle push-button not
depressed and lever detent in:
²PARK position- apply forward force on center of
handle and remove pressure. Engine start must be
possible.
²PARK position- apply rearward force on center
of handle and remove pressure. Engine start must be
possible.
²NEUTRAL position- engine start must be possi-
ble.
²NEUTRAL position, engine running and brakes
applied- Apply forward force on center of shift han-
dle. Transmission should not be able to shift into
REVERSE detent.
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has three primary causes.
(1) Internal clutch slippage, usually caused by low
line pressure, inadequate clutch apply pressure, or
clutch seal failure.
(2) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.(3) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to reverse flush cooler and lines after
repair
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failure
due to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The transmission cooler and lines should be
reverse flushed whenever a malfunction generates
sludge and/or debris. The torque converter should
also be replaced at the same time.
Failure to flush the cooler and lines will result in
recontamination. Flushing applies to auxiliary cool-
ers as well. The torque converter should also be
replaced whenever a failure generates sludge and
debris. This is necessary because normal converter
flushing procedures will not remove all contami-
nants.
21 - 228 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK MECHANISM (Continued)
Page 1749 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
REPLACEMENT
For proper service intervals (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTENANCE SCHED-
ULES - DESCRIPTION).
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) Place a large diameter shallow drain pan
beneath the transmission pan.
(3) Remove bolts holding front and sides of pan to
transmission.
(4)
Loosen bolts holding rear of pan to transmission.
(5) Slowly separate front of pan away from trans-
mission allowing the fluid to drain into drain pan.
(6) Hold up pan and remove remaining bolts hold-
ing pan to transmission.
(7) While holding pan level, lower pan away from
transmission.
(8) Pour remaining fluid in pan into drain pan.
(9)
Remove screw holding filter to valve body (Fig. 60).
(10) Separate filter from valve body and oil pump
and pour fluid in filter into drain pan.
(11) Remove and discard the oil filter seal from the
bottom of the oil pump.
(12) If replacing the cooler return filter, use Oil
Filter Wrench 8321 to remove the filter from the
transmission.
(13) Dispose of used trans fluid and filter(s) prop-
erly.
INSPECTION
Inspect bottom of pan and magnet for excessive
amounts of metal. A light coating of clutch material
on the bottom of the pan does not indicate a problemunless accompanied by a slipping condition or shift
lag. If fluid and pan are contaminated with excessive
amounts of debris, refer to the diagnosis section of
this group.
CLEANING
(1) Using a suitable solvent, clean pan and mag-
net.
(2) Using a suitable gasket scraper, clean original
sealing material from surface of transmission case
and the transmission pan.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install a new primary oil filter seal in the oil
pump inlet bore. Seat the seal in the bore with the
butt end of a hammer, or other suitable tool.
CAUTION: The primary oil filter seal MUST be fully
installed flush against the oil pump body. DO NOT
install the seal onto the filter neck and attempt to
install the filter and seal as an assembly. Damage to
the transmission will result.
(2) Place replacement filter in position on valve
body and into the oil pump.
(3) Install screw to hold filter to valve body (Fig.
60). Tighten screw to 4.5 N´m (40 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install new cooler return filter onto the trans-
mission, if necessary. Torque the filter to 14.12 N´m
(125 in.lbs.).
(5) Place bead of MopartRTV sealant onto the
transmission case sealing surface.
(6) Place pan in position on transmission.
(7) Install bolts to hold pan to transmission.
Tighten bolts to 11.8 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Lower vehicle and fill transmission with
MopartATF +4, type 9602 fluid.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TRANSMISSION
FILL
To avoid overfilling transmission after a fluid
change or overhaul, perform the following procedure:
(1) Remove dipstick and insert clean funnel in
transmission fill tube.
(2) Add following initial quantity of MopartAT F
+4 to transmission:
(a) If only fluid and filter were changed, add10
pints (5 quarts)of ATF +4 to transmission.
(b) If transmission was completely overhauled,
torque converter was replaced or drained, and
cooler was flushed, add24 pints (12 quarts)of
ATF +4 to transmission.
(3) Check the transmission fluid (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC -
45RFE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE) and
adjust as required.
Fig. 60 Transmission Filters - 4X4 Shown
1 - PRIMARY OIL FILTER
2 - COOLER RETURN FILTER
3 - COOLER RETURN FILTER BYPASS VALVE
4 - VALVE BODY
21 - 230 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
FLUID AND FILTER (Continued)
Page 1788 of 2199

position, the clutch will engage after the shift to
third gear, at approximately 56 km/h (35 mph) at
light throttle.
The TCM controls the torque converter by way of
internal logic software. The programming of the soft-
ware provides the TCM with control over the L/R-CC
Solenoid. There are four output logic states that can
be applied as follows:
²No EMCC
²Partial EMCC
²Full EMCC
²Gradual-to-no EMCC
NO EMCC
Under No EMCC conditions, the L/R Solenoid is
OFF. There are several conditions that can result in
NO EMCC operations. No EMCC can be initiated
due to a fault in the transmission or because the
TCM does not see the need for EMCC under current
driving conditions.
PARTIAL EMCC
Partial EMCC operation modulates the L/R Sole-
noid (duty cycle) to obtain partial torque converter
clutch application. Partial EMCC operation is main-
tained until Full EMCC is called for and actuated.
During Partial EMCC some slip does occur. Partial
EMCC will usually occur at low speeds, low load and
light throttle situations.
FULL EMCC
During Full EMCC operation, the TCM increases
the L/R Solenoid duty cycle to full ON after PartialEMCC control brings the engine speed within the
desired slip range of transmission input speed rela-
tive to engine rpm.
GRADUAL-TO-NO EMCC
This operation is to soften the change from Full or
Partial EMCC to No EMCC. This is done at mid-
throttle by decreasing the L/R Solenoid duty cycle.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive flats for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
flats with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if neces-
sary. Verify that the converter hub o-ring is properly
installed and is free from debris. The hub must be
smooth to avoid damaging the pump seal at installa-
tion.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or con-
verter hub o-ring while inserting torque converter
into the front of the transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 117). Surface of converter lugs
should be at least 13 mm (1/2 in.) to rear of straight-
edge when converter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
Fig. 116 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 269
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1799 of 2199
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DESCRIPTION........................280
OPERATION..........................281
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER
CASE - NV242.......................281
REMOVAL............................282
DISASSEMBLY........................282
CLEANING...........................292
INSPECTION.........................293
ASSEMBLY...........................295
INSTALLATION........................307
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV242.............308
SPECIAL TOOLS
TRANSFER CASE - NV242.............308
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID DRAIN/
REFILL............................310FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL............................310
INSTALLATION........................310
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................311
OPERATION..........................311
REMOVAL............................312
INSTALLATION........................312
REAR RETAINER BUSHING AND SEAL -
NV242HD
REMOVAL............................312
INSTALLATION........................312
SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL............................313
INSTALLATION........................313
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DESCRIPTION
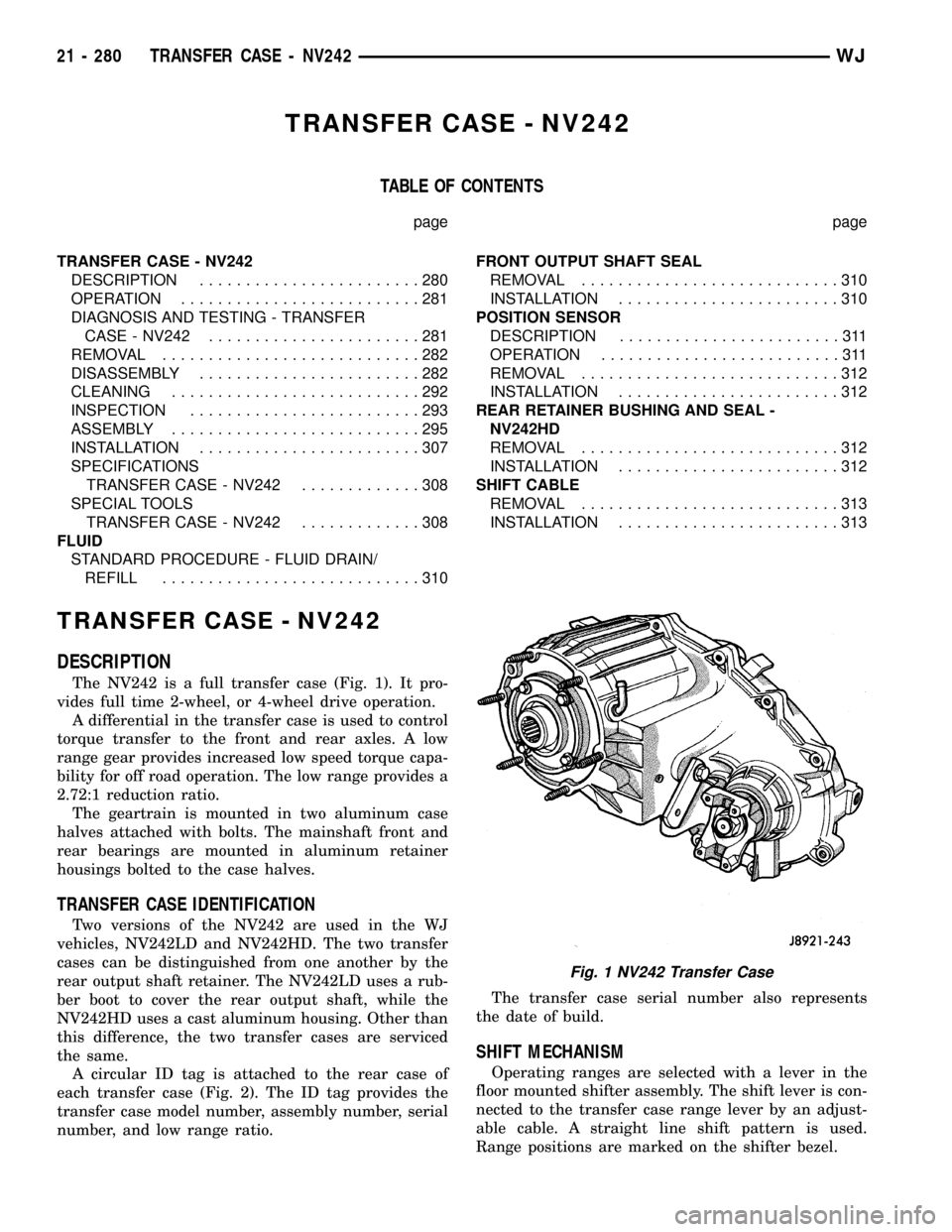
The NV242 is a full transfer case (Fig. 1). It pro-
vides full time 2-wheel, or 4-wheel drive operation.
A differential in the transfer case is used to control
torque transfer to the front and rear axles. A low
range gear provides increased low speed torque capa-
bility for off road operation. The low range provides a
2.72:1 reduction ratio.
The geartrain is mounted in two aluminum case
halves attached with bolts. The mainshaft front and
rear bearings are mounted in aluminum retainer
housings bolted to the case halves.
TRANSFER CASE IDENTIFICATION
Two versions of the NV242 are used in the WJ
vehicles, NV242LD and NV242HD. The two transfer
cases can be distinguished from one another by the
rear output shaft retainer. The NV242LD uses a rub-
ber boot to cover the rear output shaft, while the
NV242HD uses a cast aluminum housing. Other than
this difference, the two transfer cases are serviced
the same.
A circular ID tag is attached to the rear case of
each transfer case (Fig. 2). The ID tag provides the
transfer case model number, assembly number, serial
number, and low range ratio.The transfer case serial number also represents
the date of build.
SHIFT MECHANISM
Operating ranges are selected with a lever in the
floor mounted shifter assembly. The shift lever is con-
nected to the transfer case range lever by an adjust-
able cable. A straight line shift pattern is used.
Range positions are marked on the shifter bezel.
Fig. 1 NV242 Transfer Case
21 - 280 TRANSFER CASE - NV242WJ