2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Time
[x] Cancel search: TimePage 1776 of 2199
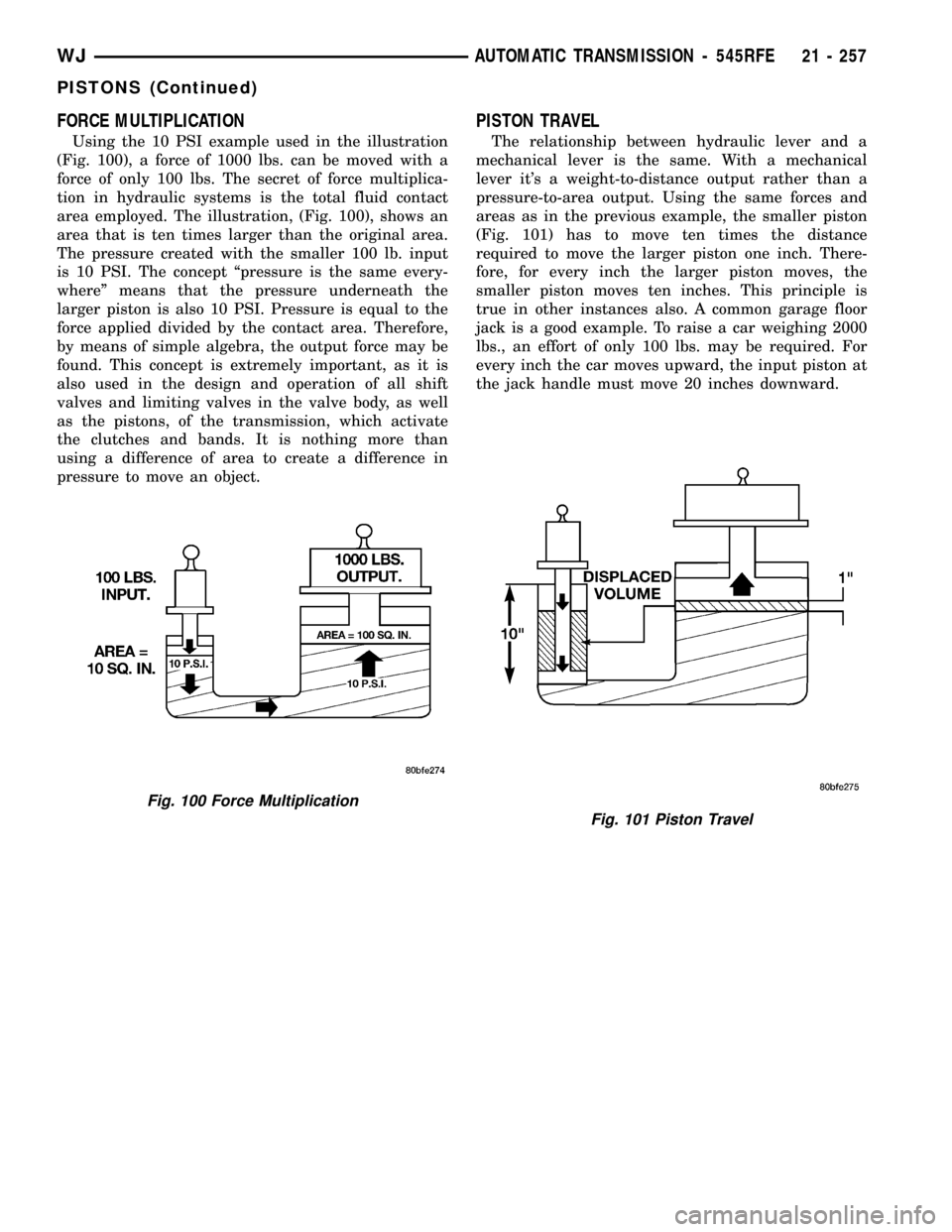
FORCE MULTIPLICATION
Using the 10 PSI example used in the illustration
(Fig. 100), a force of 1000 lbs. can be moved with a
force of only 100 lbs. The secret of force multiplica-
tion in hydraulic systems is the total fluid contact
area employed. The illustration, (Fig. 100), shows an
area that is ten times larger than the original area.
The pressure created with the smaller 100 lb. input
is 10 PSI. The concept ªpressure is the same every-
whereº means that the pressure underneath the
larger piston is also 10 PSI. Pressure is equal to the
force applied divided by the contact area. Therefore,
by means of simple algebra, the output force may be
found. This concept is extremely important, as it is
also used in the design and operation of all shift
valves and limiting valves in the valve body, as well
as the pistons, of the transmission, which activate
the clutches and bands. It is nothing more than
using a difference of area to create a difference in
pressure to move an object.
PISTON TRAVEL
The relationship between hydraulic lever and a
mechanical lever is the same. With a mechanical
lever it's a weight-to-distance output rather than a
pressure-to-area output. Using the same forces and
areas as in the previous example, the smaller piston
(Fig. 101) has to move ten times the distance
required to move the larger piston one inch. There-
fore, for every inch the larger piston moves, the
smaller piston moves ten inches. This principle is
true in other instances also. A common garage floor
jack is a good example. To raise a car weighing 2000
lbs., an effort of only 100 lbs. may be required. For
every inch the car moves upward, the input piston at
the jack handle must move 20 inches downward.
Fig. 100 Force Multiplication
Fig. 101 Piston Travel
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 257
PISTONS (Continued)
Page 1782 of 2199

INSTALLATION
(1) Place the floor shifter lever in PARK position.
(2) Loosen the adjustment screw on the shift cable.
(3) Verify that the park lock cable adjustment tab
is pulled upward to the unlocked position.
(4) Install wiring harness to the shifter assembly
bracket. Engage any wire connectors removed from
the shifter assembly.
(5) Install the transfer case shift cable to the
shifter assembly bracket. Install clip to hold cable to
the bracket.
(6) Snap the transfer case shift cable, if equipped,
onto the transfer case shift lever pin.
(7) Install the park lock cable into the shifter
assembly bracket and into the shifter BTSI lever.(Re-
fer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC/SHIFT INTERLOCK MECHANISM -
ADJUSTMENTS)
(8) Install the shift cable to the shifter assembly
bracket. Push cable into the bracket until secure.
(9) Install shifter assembly onto the shifter assem-
bly studs on the floor pan.
(10) Install the nuts to hold the shifter assembly
onto the floor pan. Tighten nuts to 28 N´m (250
in.lbs.).
(11) Snap the shift cable onto the shift lever pin.
(12) Verify that the shift lever is in the PARK posi-
tion.
(13) Tighten the adjustment screw to 7 N´m (65
in.lbs.).
(14) Place the key in the accessory position.
(15) Push downward on the park lock cable adjust-
ment tab to lock the adjustment.
(16) Verify correct shifter, park lock, and BTSI
operation.
(17) Install any console parts removed for access to
shift lever assembly and shift cables. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - INSTALLA-
TION)
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The Solenoid Switch Valve (SSV) is located in the
valve body and controls the direction of the transmis-
sion fluid when the L/R-TCC solenoid is energized.
OPERATION
The Solenoid Switch Valve controls line pressure
from the LR-TCC solenoid. In 1st gear, the SSV will
be in the downshifted position, thus directing fluid to
the L/R clutch circuit. In 2nd, 3rd, 4th,and 5th gears,
the solenoid switch valve will be in the upshifted
position and directs the fluid into the torque con-
verter clutch (TCC) circuit.When shifting into 1st gear, a special hydraulic
sequence is performed to ensure SSV movement into
the downshifted position. The L/R pressure switch is
monitored to confirm SSV movement. If the move-
ment is not confirmed (the L/R pressure switch does
not close), 2nd gear is substituted for 1st. A DTC will
be set after three unsuccessful attempts are made to
get into 1st gear in one given key start.
SOLENOIDS
DESCRIPTION
The typical electrical solenoid used in automotive
applications is a linear actuator. It is a device that
produces motion in a straight line. This straight line
motion can be either forward or backward in direc-
tion, and short or long distance.
A solenoid is an electromechanical device that uses
a magnetic force to perform work. It consists of a coil
of wire, wrapped around a magnetic core made from
steel or iron, and a spring loaded, movable plunger,
which performs the work, or straight line motion.
The solenoids used in transmission applications
are attached to valves which can be classified asnor-
mally openornormally closed. Thenormally
opensolenoid valve is defined as a valve which
allows hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is
applied to the solenoid. Thenormally closedsole-
noid valve is defined as a valve which does not allow
hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is applied
to the solenoid. These valves perform hydraulic con-
trol functions for the transmission and must there-
fore be durable and tolerant of dirt particles. For
these reasons, the valves have hardened steel pop-
pets and ball valves. The solenoids operate the valves
directly, which means that the solenoids must have
very high outputs to close the valves against the siz-
able flow areas and line pressures found in current
transmissions. Fast response time is also necessary
to ensure accurate control of the transmission.
The strength of the magnetic field is the primary
force that determines the speed of operation in a par-
ticular solenoid design. A stronger magnetic field will
cause the plunger to move at a greater speed than a
weaker one. There are basically two ways to increase
the force of the magnetic field:
1. Increase the amount of current applied to the
coil or
2. Increase the number of turns of wire in the coil.
The most common practice is to increase the num-
ber of turns by using thin wire that can completely
fill the available space within the solenoid housing.
The strength of the spring and the length of the
plunger also contribute to the response speed possi-
ble by a particular solenoid design.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 263
SHIFT MECHANISM (Continued)
Page 1786 of 2199

STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 112) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 113).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 114) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock-free power transfer, it is
natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impeller
and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston with friction material was added to the tur-
bine assembly to provide this mechanical lock-up.
In order to reduce heat build-up in the transmission
and buffer the powertrain against torsional vibrations,
the TCM can duty cycle the L/R-CC Solenoid to achieve
a smooth application of the torque converter clutch.
This function, referred to as Electronically Modulated
Converter Clutch (EMCC) can occur at various times
depending on the following variables:
²Shift lever position
²Current gear range
²Transmission fluid temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Input speed
²Throttle angle
²Engine speed
Fig. 112 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 113 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 114 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 267
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1790 of 2199

TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/
TRS ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
The transmission solenoid/TRS assembly is inter-
nal to the transmission and mounted on the valve
body assembly (Fig. 118). The assembly consists of
six solenoids that control hydraulic pressure to the
six friction elements (transmission clutches), and the
torque converter clutch. The pressure control sole-
noid is located on the side of the solenoid/TRS assem-
bly. The solenoid/TRS assembly also contains five
pressure switches that feed information to the TCM.
OPERATION
SOLENOIDS
Solenoids are used to control the L/R, 2C, 4C, OD,
and UD friction elements. The reverse clutch is con-
trolled by line pressure and the position of the man-
ual valve in the valve body. All the solenoids are
contained within the Solenoid and Pressure Switch
Assembly. The solenoid and pressure switch assembly
contains one additional solenoid, Multi-Select (MS),
which serves primarily to provide 2nd and 3rd gear
limp-in operation.The solenoids receive electrical power from the
Transmission Control Relay through a single wire.
The TCM energizes or operates the solenoids individ-
ually by grounding the return wire of the solenoid as
necessary. When a solenoid is energized, the solenoid
valve shifts, and a fluid passage is opened or closed
(vented or applied), depending on its default operat-
ing state. The result is an apply or release of a fric-
tional element.
The MS and UD solenoids are normally applied to
allow transmission limp-in in the event of an electri-
cal failure.
The continuity of the solenoids and circuits are
periodically tested. Each solenoid is turned on or off
depending on its current state. An inductive spike
should be detected by the TCM during this test. If no
spike is detected, the circuit is tested again to verify
the failure. In addition to the periodic testing, the
solenoid circuits are tested if a speed ratio or pres-
sure switch error occurs.
PRESSURE SWITCHES
The TCM relies on five pressure switches to moni-
tor fluid pressure in the L/R, 2C, 4C, UD, and OD
hydraulic circuits. The primary purpose of these
switches is to help the TCM detect when clutch cir-
cuit hydraulic failures occur. The switches close at 23
psi and open at 11 psi, and simply indicate whether
or not pressure exists. The switches are continuously
monitored by the TCM for the correct states (open or
closed) in each gear as shown in the following chart:
GEAR L/R 2C 4C UD OD
ROP OP OP OP OP
P/NCL OP OP OP OP
1STCL* OP OP CL OP
2NDOP CL OP CL OP
2ND
PRIMEOP OP CL CL OP
DOP OP OP CL CL
4THOP OP CL OP CL
5THOP CL OP OP CL
*L/R is closed if output speed is below 100 rpm in
Drive and Manual 2. L/R is open in Manual 1.
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will set if the
TCM senses any switch open or closed at the wrong
time in a given gear.
Fig. 118 Transmission Solenoid/TRS Assembly
1 - PRESSURE CONTROL SOLENOID
2 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SELECTOR PLATE
3 - 23-WAY CONNECTOR
4 - SOLENOID PACK
5 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
6 - VALVE BODY
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 271
Page 1791 of 2199

REMOVAL
(1) Remove the valve body from the transmission
(Fig. 119).
(2) Remove the screws holding the transmission
solenoid/TRS assembly onto the valve body (Fig. 120).
(3) Separate the transmission solenoid/TRS assem-
bly from the valve body.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place TRS selector plate in the PARK position.
(2) Position the transmission solenoid/TRS assem-
bly onto the valve body. Be sure that both alignment
dowels are fully seated in the valve body and that
the TRS switch contacts are properly positioned in
the selector plate
(3) Install the screws to hold the transmission
solenoid/TRS assembly onto the valve body.
(4) Tighten the solenoid assembly screws adjacent
to the arrows cast into the bottom of the valve body
first. Tighten the screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in.lbs.).
(5) Tighten the remainder of the solenoid assembly
screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in.lbs.).
(6) Install the valve body into the transmission.
TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The transmission temperature sensor is a ther-
mistor that is integral to the Transmission Range
Sensor (TRS).
OPERATION
The transmission temperature sensor is used by
the TCM to sense the temperature of the fluid in the
sump. Since fluid temperature can affect transmis-
sion shift quality and convertor lock up, the TCM
requires this information to determine which shift
schedule to operate in.
Calculated Temperature
A failure in the temperature sensor or circuit will
result in calculated temperature being substituted for
actual temperature. Calculated temperature is a pre-
dicted fluid temperature which is calculated from a
combination of inputs:
²Battery (ambient) temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²In-gear run time since start-up
Fig. 119 Valve Body Bolts
1 - VALVE BODY TO CASE BOLT (6)
Fig. 120 Ttransmission Solenoid/TRS Assembly
Screws
1 - SOLENOID PACK BOLTS (15)
21 - 272 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1799 of 2199
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DESCRIPTION........................280
OPERATION..........................281
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER
CASE - NV242.......................281
REMOVAL............................282
DISASSEMBLY........................282
CLEANING...........................292
INSPECTION.........................293
ASSEMBLY...........................295
INSTALLATION........................307
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV242.............308
SPECIAL TOOLS
TRANSFER CASE - NV242.............308
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID DRAIN/
REFILL............................310FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL............................310
INSTALLATION........................310
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................311
OPERATION..........................311
REMOVAL............................312
INSTALLATION........................312
REAR RETAINER BUSHING AND SEAL -
NV242HD
REMOVAL............................312
INSTALLATION........................312
SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL............................313
INSTALLATION........................313
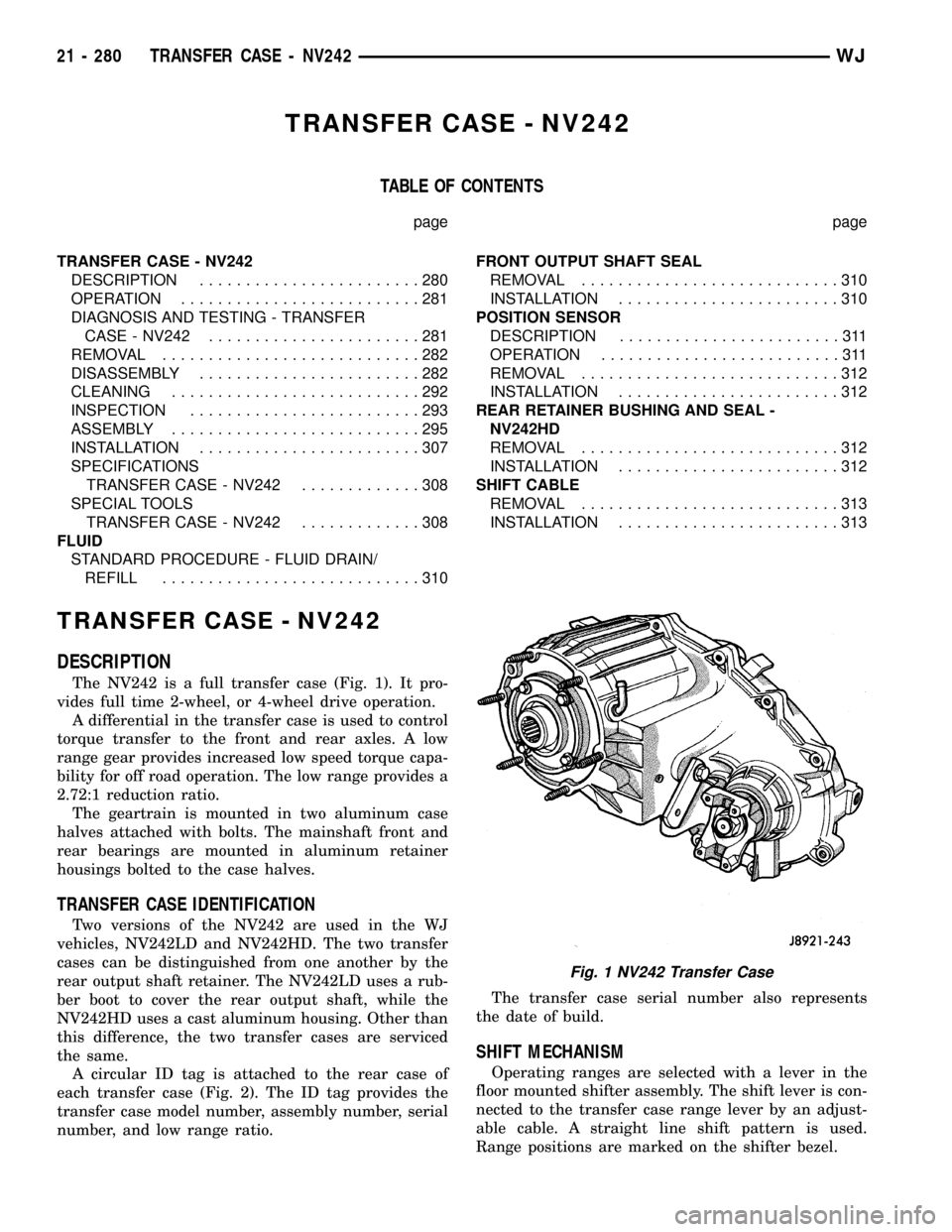
TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DESCRIPTION
The NV242 is a full transfer case (Fig. 1). It pro-
vides full time 2-wheel, or 4-wheel drive operation.
A differential in the transfer case is used to control
torque transfer to the front and rear axles. A low
range gear provides increased low speed torque capa-
bility for off road operation. The low range provides a
2.72:1 reduction ratio.
The geartrain is mounted in two aluminum case
halves attached with bolts. The mainshaft front and
rear bearings are mounted in aluminum retainer
housings bolted to the case halves.
TRANSFER CASE IDENTIFICATION
Two versions of the NV242 are used in the WJ
vehicles, NV242LD and NV242HD. The two transfer
cases can be distinguished from one another by the
rear output shaft retainer. The NV242LD uses a rub-
ber boot to cover the rear output shaft, while the
NV242HD uses a cast aluminum housing. Other than
this difference, the two transfer cases are serviced
the same.
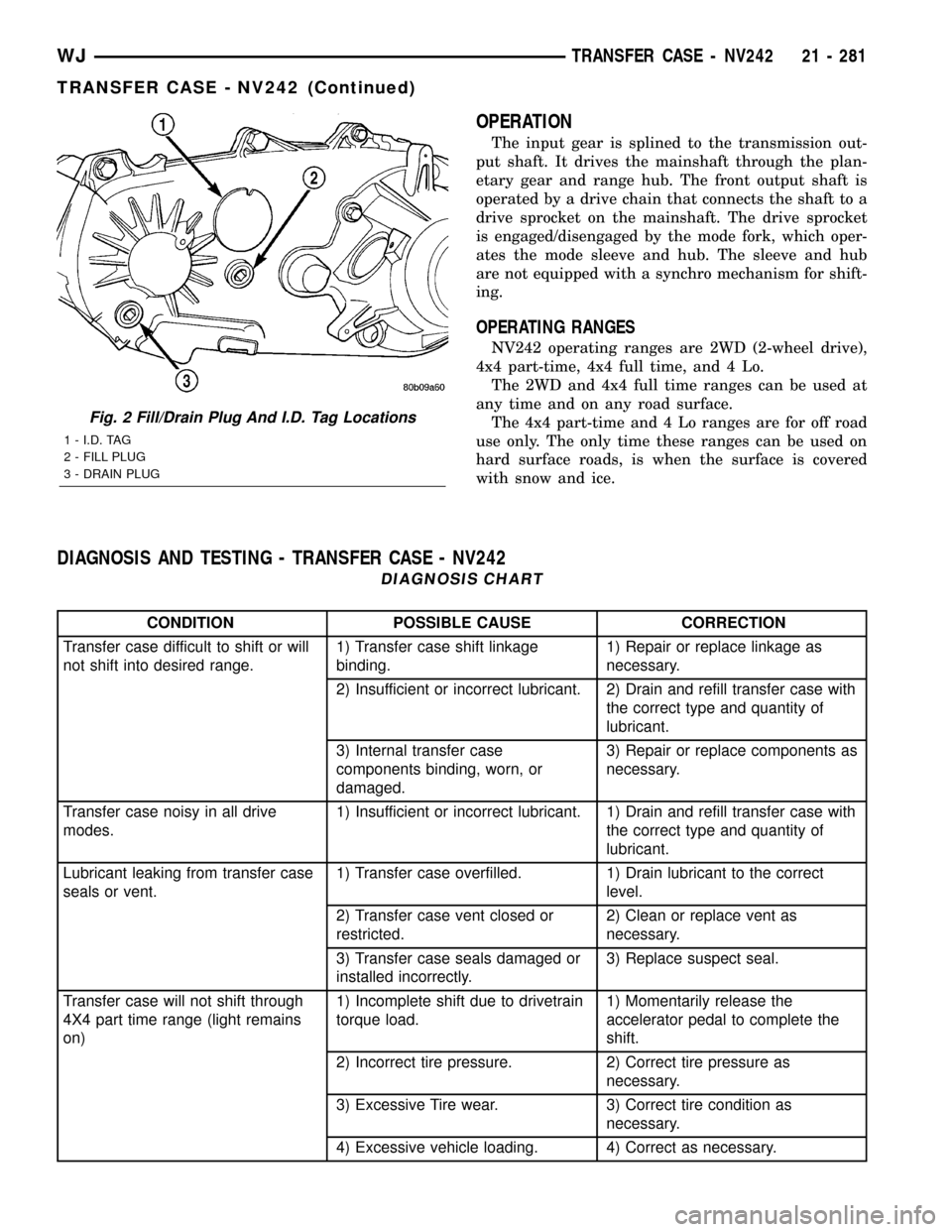
A circular ID tag is attached to the rear case of
each transfer case (Fig. 2). The ID tag provides the
transfer case model number, assembly number, serial
number, and low range ratio.The transfer case serial number also represents
the date of build.
SHIFT MECHANISM
Operating ranges are selected with a lever in the
floor mounted shifter assembly. The shift lever is con-
nected to the transfer case range lever by an adjust-
able cable. A straight line shift pattern is used.
Range positions are marked on the shifter bezel.
Fig. 1 NV242 Transfer Case
21 - 280 TRANSFER CASE - NV242WJ
Page 1800 of 2199
OPERATION
The input gear is splined to the transmission out-
put shaft. It drives the mainshaft through the plan-
etary gear and range hub. The front output shaft is
operated by a drive chain that connects the shaft to a
drive sprocket on the mainshaft. The drive sprocket
is engaged/disengaged by the mode fork, which oper-
ates the mode sleeve and hub. The sleeve and hub
are not equipped with a synchro mechanism for shift-
ing.
OPERATING RANGES
NV242 operating ranges are 2WD (2-wheel drive),
4x4 part-time, 4x4 full time, and 4 Lo.
The 2WD and 4x4 full time ranges can be used at
any time and on any road surface.
The 4x4 part-time and 4 Lo ranges are for off road
use only. The only time these ranges can be used on
hard surface roads, is when the surface is covered
with snow and ice.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER CASE - NV242
DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Transfer case difficult to shift or will
not shift into desired range.1) Transfer case shift linkage
binding.1) Repair or replace linkage as
necessary.
2) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 2) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct type and quantity of
lubricant.
3) Internal transfer case
components binding, worn, or
damaged.3) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Transfer case noisy in all drive
modes.1) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 1) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct type and quantity of
lubricant.
Lubricant leaking from transfer case
seals or vent.1) Transfer case overfilled. 1) Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2) Transfer case vent closed or
restricted.2) Clean or replace vent as
necessary.
3) Transfer case seals damaged or
installed incorrectly.3) Replace suspect seal.
Transfer case will not shift through
4X4 part time range (light remains
on)1) Incomplete shift due to drivetrain
torque load.1) Momentarily release the
accelerator pedal to complete the
shift.
2) Incorrect tire pressure. 2) Correct tire pressure as
necessary.
3) Excessive Tire wear. 3) Correct tire condition as
necessary.
4) Excessive vehicle loading. 4) Correct as necessary.
Fig. 2 Fill/Drain Plug And I.D. Tag Locations
1 - I.D. TAG
2 - FILL PLUG
3 - DRAIN PLUG
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 281
TRANSFER CASE - NV242 (Continued)
Page 1830 of 2199
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
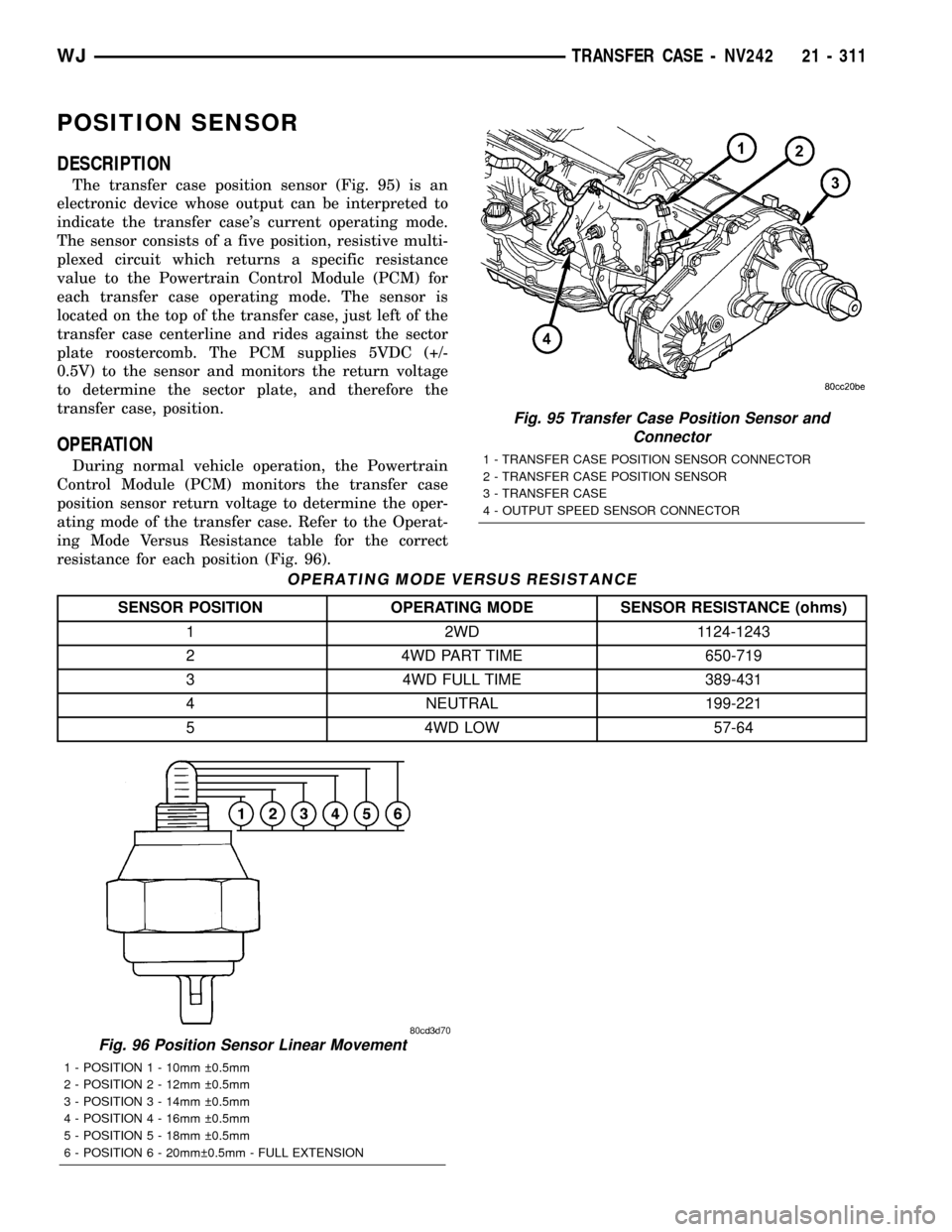
The transfer case position sensor (Fig. 95) is an
electronic device whose output can be interpreted to
indicate the transfer case's current operating mode.
The sensor consists of a five position, resistive multi-
plexed circuit which returns a specific resistance
value to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) for
each transfer case operating mode. The sensor is
located on the top of the transfer case, just left of the
transfer case centerline and rides against the sector
plate roostercomb. The PCM supplies 5VDC (+/-
0.5V) to the sensor and monitors the return voltage
to determine the sector plate, and therefore the
transfer case, position.
OPERATION
During normal vehicle operation, the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) monitors the transfer case
position sensor return voltage to determine the oper-
ating mode of the transfer case. Refer to the Operat-
ing Mode Versus Resistance table for the correct
resistance for each position (Fig. 96).
OPERATING MODE VERSUS RESISTANCE
SENSOR POSITION OPERATING MODE SENSOR RESISTANCE (ohms)
1 2WD 1124-1243
2 4WD PART TIME 650-719
3 4WD FULL TIME 389-431
4 NEUTRAL 199-221
5 4WD LOW 57-64
Fig. 96 Position Sensor Linear Movement
1 - POSITION 1 - 10mm 0.5mm
2 - POSITION 2 - 12mm 0.5mm
3 - POSITION 3 - 14mm 0.5mm
4 - POSITION 4 - 16mm 0.5mm
5 - POSITION 5 - 18mm 0.5mm
6 - POSITION 6 - 20mm 0.5mm - FULL EXTENSION
Fig. 95 Transfer Case Position Sensor and
Connector
1 - TRANSFER CASE POSITION SENSOR CONNECTOR
2 - TRANSFER CASE POSITION SENSOR
3 - TRANSFER CASE
4 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 311