2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE engine chart
[x] Cancel search: engine chartPage 1251 of 2199
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise, the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Clean the spark plug recesses with compressed
air.
(2) Remove the spark plugs (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
REMOVAL).
(3) Secure the throttle in the wide-open position.
(4) Disconnect the ignition coil.
(5) Insert a compression pressure gauge and rotate
the engine with the engine starter motor for three
revolutions.
(6) Record the compression pressure on the third
revolution. Continue the test for the remaining cylin-
ders.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS) for the
correct engine compression pressures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing)
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM HOT COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn OFF the
engine.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.
Perform the test procedure on each cylinder accord-
ing to the tester manufacturer's instructions. While
testing, listen for pressurized air escaping through
the throttle body, tailpipe or oil filler cap opening.
Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder CYLINDER COMBUSTION
PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART .
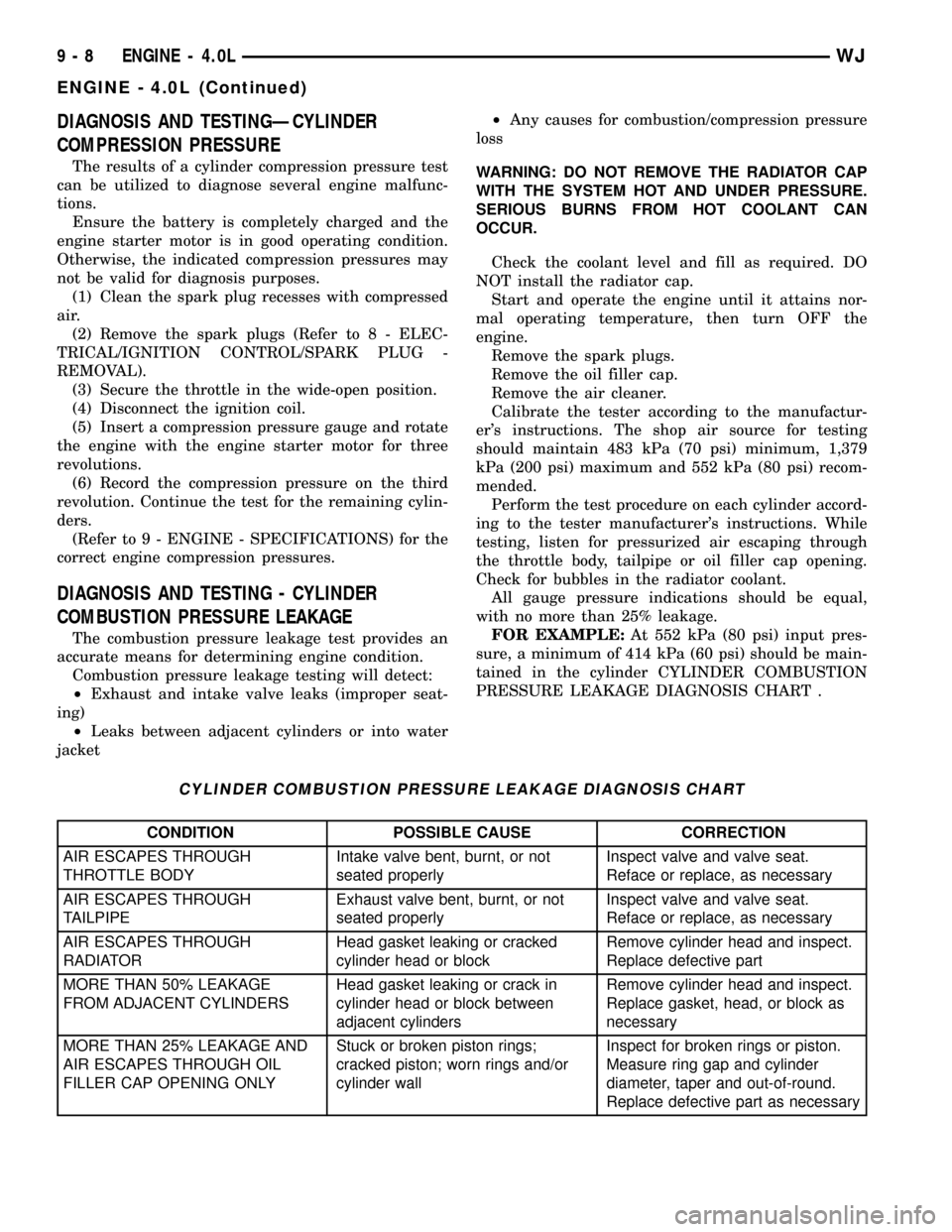
CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
THROTTLE BODYIntake valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
TAILPIPEExhaust valve bent, burnt, or not
seated properlyInspect valve and valve seat.
Reface or replace, as necessary
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH
RADIATORHead gasket leaking or cracked
cylinder head or blockRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace defective part
MORE THAN 50% LEAKAGE
FROM ADJACENT CYLINDERSHead gasket leaking or crack in
cylinder head or block between
adjacent cylindersRemove cylinder head and inspect.
Replace gasket, head, or block as
necessary
MORE THAN 25% LEAKAGE AND
AIR ESCAPES THROUGH OIL
FILLER CAP OPENING ONLYStuck or broken piston rings;
cracked piston; worn rings and/or
cylinder wallInspect for broken rings or piston.
Measure ring gap and cylinder
diameter, taper and out-of-round.
Replace defective part as necessary
9 - 8 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 1278 of 2199
is needed to provide the correct clearance. Refer to
CONNECTING ROD BEARING FITTING CHART .
CONNECTING ROD BEARING FITTING CHART
CRANKSHAFT JOURNAL CORRESPONDING ROD BEARING INSERT
Color Code Diameter Upper Insert Size Lower Insert Size
Yellow53.2257 - 53.2079 mm
Yellow - Standard Yellow - Standard
(2.0955 - 2.0948 in.)
Orange53.2079 - 53.1901 mm
Yellow - StandardBlue - Undersize (2.0948 - 2.0941 in.)
0.0178 mm (0.0007 in.) 0.025 mm (0.001 in.)
Undersize
Blue53.1901 - 53.1724 mm
Blue - Undersize Blue - Undersize (2.0941 - 2.0934 in.)
0.0356 mm (0.0014 in.) 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) 0.025 mm (0.001 in.)
Undersize
Red52.9717 - 52.9539 mm
Red - Undersize Red - Undersize (2.0855 - 2.0848 in.)
0.254 mm (0.010 in.) 0.254 mm (0.010 in.) 0.254 mm (0.010 in.)
Undersize
(11)FOR EXAMPLE:If the initial clearance was
0.0762 mm (0.003 inch), 0.025 mm (0.001 inch)
undersize inserts would reduce the clearance by
0.025 mm (0.001 inch). The clearance would be 0.002
inch and within specification. A 0.051 mm (0.002
inch) undersize insert would reduce the initial clear-
ance an additional 0.013 mm (0.0005 inch). The
clearance would then be 0.038 mm (0.0015 inch).
(12) Repeat the Plastigage measurement to verify
your bearing selection prior to final assembly.
(13) Once you have selected the proper insert,
install the insert and cap. Tighten the connecting rod
bolts to 45 N´m (33 ft. lbs.) torque.
SIDE CLEARANCE MEASUREMENT
Slide snug-fitting feeler gauge between the con-
necting rod and crankshaft journal flange (Fig. 40).
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS). Replace
the connecting rod if the side clearance is not within
specification.
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft is constructed of nodular cast iron.
The crankshaft is a crosshaped four throw design
with eight counterweights for balancing purposes.The crankshaft is supported by seven select main
bearings with the number three serving as the thrust
washer location. The main journals of the crankshaft
are cross drilled to improve rod bearing lubrication.
The select fit main bearing markings are located on
the crankshaft counter weights. The crankshaft rear
oil seal is a two piece design. The front oil seal is a
one piece design retained in the timing chain cover
(Fig. 41).
Fig. 40 Checking Connecting Rod Side Clearance -
Typical
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 35
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1279 of 2199

CRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FITTING
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
FITTING BEARINGS (CRANKSHAFT INSTALLED)
The main bearing caps, numbered (front to rear)
from 1 through 7 have an arrow to indicate the for-
ward position. The upper main bearing inserts are
grooved to provide oil channels while the lower
inserts are smooth.
Each bearing insert pair is selectively fitted to its
respective journal to obtain the specified operating
clearance. In production, the select fit is obtained by
using various-sized color-coded bearing insert pairs
as listed in the Main Bearing Fitting Chart. The
bearing color code appears on the edge of the insert.
The size is not stamped on bearing inserts used
for engine production.
The main bearing journal size (diameter) is identi-
fied by a color-coded paint mark (Fig. 42)on the adja-
cent cheek or counterweight towards the rear of the
crankshaft (flange end). The rear main journal, is
identified by a color-coded paint mark on the crank-
shaft rear flange.
When required, upper and lower bearing inserts of
different sizes may be used as a pair. A standard size
insert is sometimes used in combination with a 0.025
mm (0.001 inch) undersize insert to reduce the clear-
ance by 0.013 mm (0.0005 inch).Never use a pair
of bearing inserts with greater than a 0.025 mm
(0.001 inch) difference in size. Refer to the
Bearing Insert Pair Chart.NOTE: When replacing inserts, the odd size inserts
must be either all on the top (in cylinder block) or
all on the bottom (in main bearing cap).
Once the bearings have been properly fitted, (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT
MAIN BEARINGS - INSTALLATION).
BEARING-TO-JOURNAL CLEARANCE (CRANKSHAFT
INSTALLED)
When using Plastigage, check only one bearing
clearance at a time.
Install the grooved main bearings into the cylinder
block and the non-grooved bearings into the bearing
caps.
Install the crankshaft into the upper bearings dry.
Place a strip of Plastigage across full width of the
crankshaft journal to be checked.
Install the bearing cap and tighten the bolts to 108
N´m (80 ft. lbs.) torque.
NOTE: DO NOT rotate the crankshaft. This will
cause the Plastigage to shift, resulting in an inaccu-
rate reading. Plastigage must not be permitted to
crumble. If brittle, obtain fresh stock.
Remove the bearing cap. Determine the amount of
clearance by measuring the width of the compressed
Plastigage with the scale on the Plastigage envelope
(Fig. 43). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS)
for the proper clearance.
Plastigage should indicate the same clearance
across the entire width of the insert. If clearance var-
ies, it may indicate a tapered journal or foreign
material trapped behind the insert.
If the specified clearance is indicated and there are
no abnormal wear patterns, replacement of the bear-
ing inserts is not necessary. Remove the Plastigage
from the crankshaft journal and bearing insert. Pro-
ceed to (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS -
INSTALLATION).
If the clearance exceeds specification, install a pair
of 0.025 mm (0.001 inch) undersize bearing inserts
and measure the clearance as described in the previ-
ous steps.
The clearance indicate with the 0.025 mm (0.001
inch) undersize insert pair installed will determine if
this insert size or some other combination will pro-
vide the specified clearance.FOR EXAMPLE:If the
clearance was 0.0762 mm (0.003 inch) originally, a
pair of 0.0254 mm (0.001 inch) undersize inserts
would reduce the clearance by 0.0254 mm (0.001
inch). The clearance would then be 0.0508 mm (0.002
inch) and within the specification. A 0.051 mm (0.002
inch) undersize bearing insert and a 0.0254 mm
(0.001 inch) undersize insert would reduce the origi-
Fig. 41 Crankshaft with Select Fit Marking Location
1 - 1/4º LETTERS
2 - (ROD)
3 - (MAIN)
9 - 36 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
CRANKSHAFT (Continued)
Page 1280 of 2199

nal clearance an additional 0.0127 mm (0.0005 inch).
The clearance would then be 0.0381 mm (0.0015
inch).
CAUTION: Never use a pair of inserts that differ
more than one bearing size as a pair.
FOR EXAMPLE:DO NOT use a standard size
upper insert and a 0.051 mm (0.002 inch) undersize
lower insert.If the clearance exceeds specification using a pair
of 0.051 mm (0.002 inch) undersize bearing inserts,
measure crankshaft journal diameter with a
micrometer. If the journal diameter is correct, the
crankshaft bore in the cylinder block may be mis-
aligned, which requires cylinder block replacement or
machining to true bore.
Replace the crankshaft or grind to accept the
appropriate undersize bearing inserts if:
²Journal diameters 1 through 6 are less than
63.4517 mm (2.4981 inches)
²Journal 7 diameter is less than 63.4365 mm
(2.4975 inches).
Once the proper clearances have been obtained,
proceed to (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS - INSTALLA-
TION).
JOURNAL DIAMETER (CRANKSHAFT REMOVED)
Remove the crankshaft from the cylinder block.
Clean the oil off the main bearing journal.
Determine the maximum diameter of the journal
with a micrometer. Measure at two locations 90É
apart at each end of the journal.
The maximum allowable taper and out of round is
0.013 mm (0.0005 inch). Compare the measured
diameter with the journal diameter specification
MAIN BEARING FITTING CHART . Select inserts
required to obtain the specified bearing-to-journal
clearance.
Install the crankshaft into the cylinder block.
Fig. 42 Crankshaft Journal Size Paint I.D. Location
1 - NO. 7 MAIN JOURNAL SIZE PAINT MARK
2 - NO. 6 CONNECTING ROD JOURNAL SIZE PAINT MARK3 - NO. 1 CONNECTING ROD JOURNAL SIZE PAINT MARK
4 - NO. 1 MAIN JOURNAL SIZE PAINT MARK
Fig. 43 Measuring Bearing Clearance with
Plastigage
1 - PLASTIGAGE SCALE
2 - COMPRESSED PLASTIGAGE
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 37
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1281 of 2199
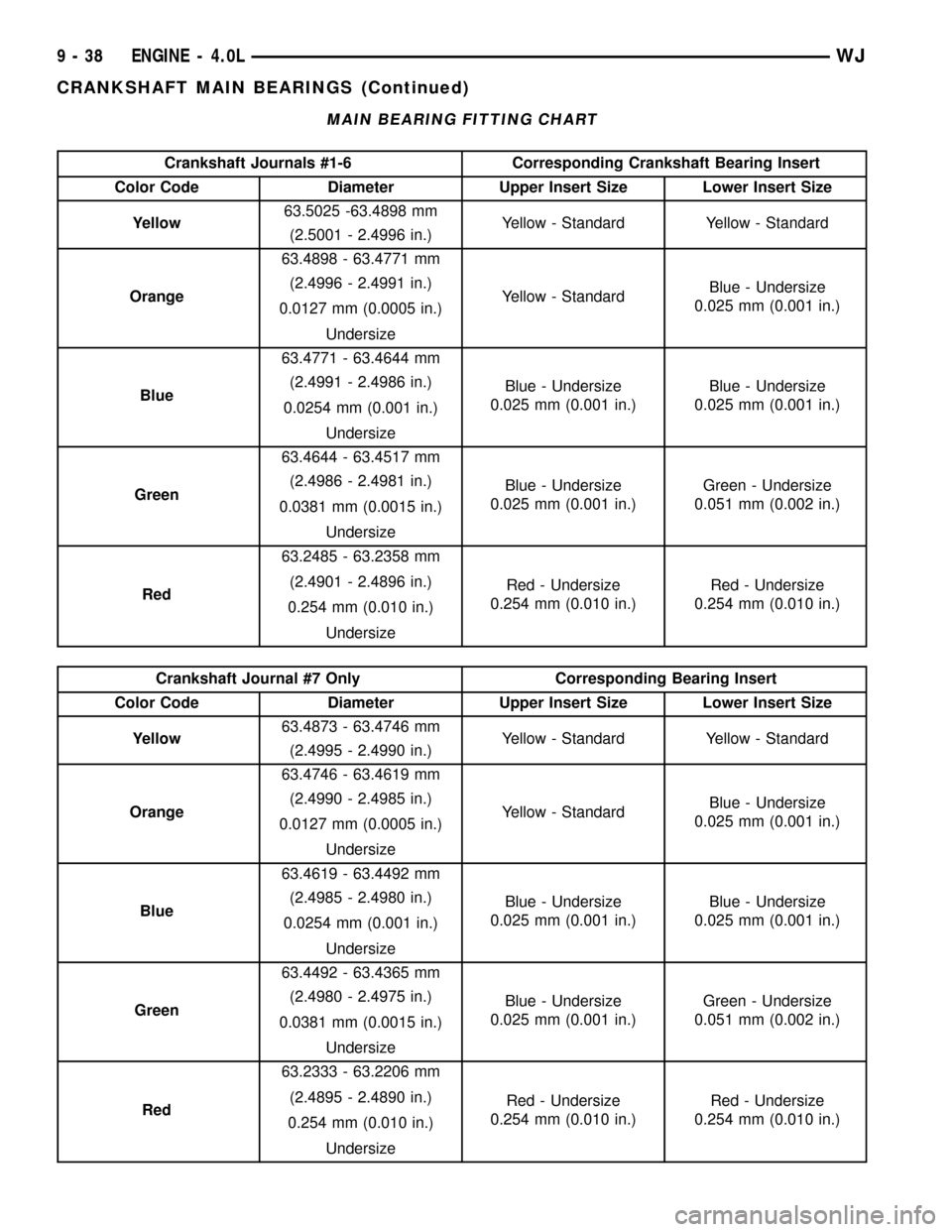
MAIN BEARING FITTING CHART
Crankshaft Journals #1-6 Corresponding Crankshaft Bearing Insert
Color Code Diameter Upper Insert Size Lower Insert Size
Yellow63.5025 -63.4898 mm
Yellow - Standard Yellow - Standard
(2.5001 - 2.4996 in.)
Orange63.4898 - 63.4771 mm
Yellow - StandardBlue - Undersize
0.025 mm (0.001 in.) (2.4996 - 2.4991 in.)
0.0127 mm (0.0005 in.)
Undersize
Blue63.4771 - 63.4644 mm
Blue - Undersize
0.025 mm (0.001 in.)Blue - Undersize
0.025 mm (0.001 in.) (2.4991 - 2.4986 in.)
0.0254 mm (0.001 in.)
Undersize
Green63.4644 - 63.4517 mm
Blue - Undersize
0.025 mm (0.001 in.)Green - Undersize
0.051 mm (0.002 in.) (2.4986 - 2.4981 in.)
0.0381 mm (0.0015 in.)
Undersize
Red63.2485 - 63.2358 mm
Red - Undersize
0.254 mm (0.010 in.)Red - Undersize
0.254 mm (0.010 in.) (2.4901 - 2.4896 in.)
0.254 mm (0.010 in.)
Undersize
Crankshaft Journal #7 Only Corresponding Bearing Insert
Color Code Diameter Upper Insert Size Lower Insert Size
Yellow63.4873 - 63.4746 mm
Yellow - Standard Yellow - Standard
(2.4995 - 2.4990 in.)
Orange63.4746 - 63.4619 mm
Yellow - StandardBlue - Undersize
0.025 mm (0.001 in.) (2.4990 - 2.4985 in.)
0.0127 mm (0.0005 in.)
Undersize
Blue63.4619 - 63.4492 mm
Blue - Undersize
0.025 mm (0.001 in.)Blue - Undersize
0.025 mm (0.001 in.) (2.4985 - 2.4980 in.)
0.0254 mm (0.001 in.)
Undersize
Green63.4492 - 63.4365 mm
Blue - Undersize
0.025 mm (0.001 in.)Green - Undersize
0.051 mm (0.002 in.) (2.4980 - 2.4975 in.)
0.0381 mm (0.0015 in.)
Undersize
Red63.2333 - 63.2206 mm
Red - Undersize
0.254 mm (0.010 in.)Red - Undersize
0.254 mm (0.010 in.) (2.4895 - 2.4890 in.)
0.254 mm (0.010 in.)
Undersize
9 - 38 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1288 of 2199

PISTON SIZE CHART
CYLINDER BORE SIZE PISTON LETTER SIZE
98.438 - 98.448 mm
(3.8755 - 3.8759 in.)A
98.448 - 98.458 mm
(3.8759 - 3.8763 in.)B
98.458 - 98.468 mm
(3.8763 - 3.8767 in.)C
98.468 - 98.478 mm
(3.8767 - 3.8771 in.)D
98.478 - 98.488 mm
(3.8771 - 3.8775 in.)E
98.488 - 98.498 mm
(3.8775 - 3.8779 in.)F
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the engine cylinder head cover. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER
HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the rocker arms, bridges and pivots.
(3) Remove the push rods.
(4) Remove the engine cylinder head. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(5) Position the pistons one at a time near the bot-
tom of the stroke. Use a ridge reamer to remove theridge from the top end of the cylinder walls. Use a
protective cloth to collect the cuttings.
(6) Raise the vehicle.
(7) Drain the engine oil.
(8) Remove the oil pan and gasket. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(9) Remove main bearing cap brace (Fig. 58).
(10) Remove the connecting rod bearing caps and
inserts. Mark the caps and rods with the cylinder
bore location. The connecting rods and caps are
stamped with a two letter combination (Fig. 59).
Fig. 57 Bore Gauge
1 - FRONT
2 - BORE GAUGE
3 - CYLINDER BORE
4 - 49.5 MM (1-15/16 in.)
Fig. 58 Main Bearings Caps and Brace
1 - BLOCK
2 - MAIN BEARING CAP BRACE
Fig. 59 Stamped Connecting Rods and Caps
1 - CONNECTING ROD CAP
2 - CONNECTING ROD
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 45
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1289 of 2199

(11) Lower the vehicle until it is about 2 feet from
the floor.
CAUTION: Ensure that the connecting rod bolts DO
NOT scratch the crankshaft journals or cylinder
walls. Short pieces of rubber hose, slipped over the
rod bolts will provide protection during removal.
(12) Have an assistant push the piston and con-
necting rod assemblies up and through the top of the
cylinder bores (Fig. 60).
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean the cylinder bores thoroughly. Apply a
light film of clean engine oil to the bores with a clean
lint-free cloth.
(2) Install the piston rings on the pistons if
removed (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
PISTON RINGS - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Lubricate the piston and rings with clean
engine oil.
CAUTION: Ensure that connecting rod bolts DO
NOT scratch the crankshaft journals or cylinder
walls. Short pieces of rubber hose slipped over the
connecting rod bolts will provide protection during
installation.(4) Use a piston ring compressor to install the con-
necting rod and piston assemblies through the top of
the cylinder bores (Fig. 61).
(5) Ensure the arrow on the piston top points to
the front of the engine (Fig. 61).
(6) Raise the vehicle.
(7) Each bearing insert is fitted to its respective
journal to obtain the specified clearance between the
bearing and the journal. In production, the select fit
is obtained by using various-sized, color-coded bear-
ing inserts as listed in the Connecting Rod Bearing
Fitting Chart. The color code appears on the edge of
the bearing insert. The size is not stamped on inserts
used for production of engines.
(8) The rod journal is identified during the engine
production by a color-coded paint mark on the adja-
cent cheek or counterweight toward the flange (rear)
end of the crankshaft. The color codes used to indi-
cate journal sizes are listed in the Connecting Rod
Bearing Fitting Chart.
(9) When required, upper and lower bearing
inserts of different sizes may be used as a pair (refer
to Connecting Rod Bearing Fitting Chart). A stan-
dard size insert is sometimes used in combination
with a 0.025 mm (0.001 inch) undersize insert to
reduce clearance 0.013 mm (0.0005 inch).
CAUTION: DO NOT intermix bearing caps. Each
connecting rod and bearing cap are stamped with
the cylinder number. The stamp is located on a
machined surface adjacent to the oil squirt hole
that faces the camshaft side of the cylinder block.
(10) Install the connecting rod bearing caps and
inserts in the same positions as removed.
CAUTION: Verify that the oil squirt holes in the rods
face the camshaft and that the arrows on the pis-
tons face the front of the engine.
(11) Install main bearing cap brace (Fig. 58).
Tighten nuts to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 60 Removal of Connecting Rod and Piston
Assembly
1 - PISTON
2 - CONNECTING ROD
3 - BLOCK
Fig. 61 Rod and Piston Assembly Installation
9 - 46 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1290 of 2199

(12) Install the oil pan and gasket (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLA-
TION).
(13) Lower the vehicle.
(14) Install the engine cylinder head (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION),
push rods, rocker arms, bridges, pivots and engine
cylinder head cover(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER
HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) - INSTALLA-
TION).
(15) Fill the crankcase with engine oil.
PISTON RINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING
(1) Carefully clean the carbon from all ring
grooves. Oil drain openings in the oil ring groove and
pin boss must be clear. DO NOT remove metal from
the grooves or lands. This will change ring-to-groove
clearances and will damage the ring-to-land seating.
(2) Be sure the piston ring grooves are free of
nicks and burrs.
(3) Measure the ring side clearance with a feeler
gauge fitted snugly between the ring land and ring
(Fig. 62) (Fig. 63). Rotate the ring in the groove. It
must move freely around circumference of the groove.
RING SIDE CLEARANCE CHART
ITEM SPECIFICATION
Top Compression Ring 0.042 - 0.084 mm
(0.0017 - 0.0033 in.)
Second Compression
Ring0.042 - 0.084 mm
(0.0017 - 0.0033 in.)
Oil Control Ring 0.06 - 0.21 mm
(0.0024 - 0.0083 in.)
(4) Place ring in the cylinder bore and push down
with inverted piston to position near lower end of the
ring travel. Measure ring gap with a feeler gauge fit-
ting snugly between ring ends (Fig. 64).
RING GAP MEASUREMENT CHART
ITEM SPECIFICATION
Top Compression Ring 0.229 - 0.610 mm
(0.0090 - 0.0240 in.)
Second Compression
Ring0.483 - 0.965 mm
(0.0190 - 0.080 in.)
Oil Control Ring 0.254 - 1.500 mm
(0.010 - 0.060 in.)
Fig. 62 Piston Dimensions
Fig. 63 Ring Side Clearance Measurement
1 - FEELER GAUGE
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 47
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)