2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE Dif
[x] Cancel search: DifPage 1858 of 2199

REAR RETAINER BUSHING
AND SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove rear propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIF-
FERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/
PROPELLER SHAFT - REMOVAL)
(3) Using a suitable pry tool or slide-hammer
mounted screw, remove the rear retainer seal.
(4) Using Remover 6957, remove bushing from
rear retainer (Fig. 75).
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean fluid residue from sealing surface and
inspect for defects.
(2) Position replacement bushing in rear retainer
with fluid port in bushing aligned with slot in
retainer.
(3) Using Installer 8145, drive bushing into
retainer until installer seats against case (Fig. 76).
(4) Using Installer C-3995-A, install seal in rear
retainer (Fig. 77).
(5) Install rear propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIF-
FERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/
PROPELLER SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(6) Verify proper fluid level.
(7) Lower vehicle.
Fig. 74 Front Output Seal Installation
1 - INSTALLER 6952-A
2 - TRANSFER CASE
Fig. 75 Rear Retainer Bushing Removal
1 - REMOVER 6957
2 - REAR RETAINER BUSHING
Fig. 76 Rear Retainer Bushing Installation
1 - REAR RETAINER BUSHING
2 - INSTALLER 8145
Fig. 77 Install Rear Retainer Seal
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4171
2 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3995-A
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV247 21 - 339
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL (Continued)
Page 1860 of 2199

TIRES/WHEELS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
TIRES/WHEELS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE AND
WHEEL RUNOUT......................1
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE AND
WHEEL BALANCE......................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MATCH
MOUNTING...........................4
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE ROTATION . 5
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WHEEL
INSTALLATION........................5
TIRES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - TIRES..................6
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL±PLY TIRES.......6
DESCRIPTION - TIRE INFLATION
PRESSURES..........................6
DESCRIPTION - TIRE PRESSURE FOR
HIGH SPEED..........................7
DESCRIPTION - REPLACEMENT TIRES.....7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRESSURE
GAUGES.............................8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TREAD WEAR
INDICATORS..........................8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE WEAR
PATTERNS...........................8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE NOISE
OR VIBRATION........................8STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIRING
LEAKS...............................8
CLEANING.............................9
SPECIFICATIONS
TIRES...............................9
SPECIFICATIONS -.....................9
SPARE TIRE
DESCRIPTION - SPARE / TEMPORARY TIRE . . 10
WHEELS
DESCRIPTION.........................10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WHEEL
INSPECTION.........................10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WHEEL
REPLACEMENT.......................10
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE CHART......................11
STUDS
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................11
TIRE PRESSURE MONITORING
DESCRIPTION.........................12
OPERATION...........................12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE PRESSURE
MONITORING SYSTEM.................12
SENSOR
REMOVAL - TIRE PRESSURE SENSOR/
TRANSMITTER.......................12
INSTALLATION - TIRE PRESSURE SENSOR/
TRANSMITTER.......................13
TIRES/WHEELS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE AND WHEEL
RUNOUT
Radial runout is the difference between the high
and low points on the tire or wheel (Fig. 1).
Lateral runout is thewobbleof the tire or wheel.
Radial runout of more than 1.5 mm (.060 inch)
measured at the center line of the tread may cause
the vehicle to shake.
Lateral runout of more than 2.0 mm (.080 inch)
measured near the shoulder of the tire may cause the
vehicle to shake.
Sometimes radial runout can be reduced. Relocate
the wheel and tire assembly on the mounting studs
(See Method 1). If this does not reduce runout to an
acceptable level, the tire can be rotated on the wheel.
(See Method 2).
METHOD 1 (RELOCATE WHEEL ON HUB)
(1) Drive vehicle a short distance to eliminate tire
flat spotting from a parked position.
(2) Check wheel bearings and adjust if adjustable
or replace if necessary.
(3) Check the wheel mounting surface.
(4) Relocate wheel on the mounting, two studs
over from the original position.
(5) Tighten wheel nuts until all are properly
torqued, to eliminate brake distortion.
(6) Check radial runout. If still excessive, mark
tire sidewall, wheel, and stud at point of maximum
runout and proceed to Method 2.
METHOD 2 (RELOCATE TIRE ON WHEEL)
NOTE: Rotating the tire on wheel is particularly
effective when there is runout in both tire and
wheel.
WJTIRES/WHEELS 22 - 1
Page 1864 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - TIRE ROTATION
Tires on the front and rear operate at different
loads and perform different steering, driving, and
braking functions. For these reasons they wear at
unequal rates and tend to develop irregular wear
patterns. These effects can be reduced by rotating
the tires at regular intervals. The benefits of tire
rotation are:
²Increase tread life
²Maintain traction levels
²A smooth, quiet ride
The suggested method of tire rotation is (Fig. 10).
Other rotation methods can be used, but they will
not provide all the tire longevity benefits.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WHEEL
INSTALLATION
The wheel studs and nuts are designed for specific
applications. They must be replaced with equivalent
parts. Do not use replacement parts of lesser quality
or a substitute design. All aluminum and some steel
wheels have wheel stud nuts which feature an
enlarged nose. This enlarged nose is necessary to
ensure proper retention of the aluminum wheels.
NOTE: Do not use chrome plated lug nuts with
chrome plated wheels.
Before installing the wheel, be sure to remove any
build up of corrosion on the wheel mounting surfaces.
Ensure wheels are installed with good metal-to-metal
contact. Improper installation could cause loosening
of wheel nuts. This could affect the safety and han-
dling of your vehicle.
To install the wheel, first position it properly on
the mounting surface. All wheel nuts should then be
tightened just snug. Gradually tighten them in
sequence to the proper torque specification (Fig. 11).
Never use oil or grease on studs or nuts.
Fig. 9 Remount Tire 90 Degrees In Direction of
Arrow
1 - 2ND HIGH SPOT ON TIRE
2 - 1ST HIGH SPOT ON TIRE
Fig. 10 Tire Rotation Pattern
Fig. 11 LUG NUT TIGHTENING PATTERN - TYPICAL
WJTIRES/WHEELS 22 - 5
TIRES/WHEELS (Continued)
Page 1865 of 2199
TIRES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - TIRES
Tires are designed and engineered for each specific
vehicle. They provide the best overall performance
for normal operation. The ride and handling charac-
teristics match the vehicle's requirements. With
proper care they will give excellent reliability, trac-
tion, skid resistance, and tread life.
Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain in most
cases, much greater mileage than severe use or care-
less drivers. A few of the driving habits which will
shorten the life of any tire are:
²Rapid acceleration
²Severe brake applications
²High speed driving
²Excessive speeds on turns
²Striking curbs and other obstacles
Radial-ply tires are more prone to irregular tread
wear. It is important to follow the tire rotation inter-
val shown in the section on Tire Rotation.(Refer to 22
- TIRES/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCEDURE),
This will help to achieve a greater tread life.
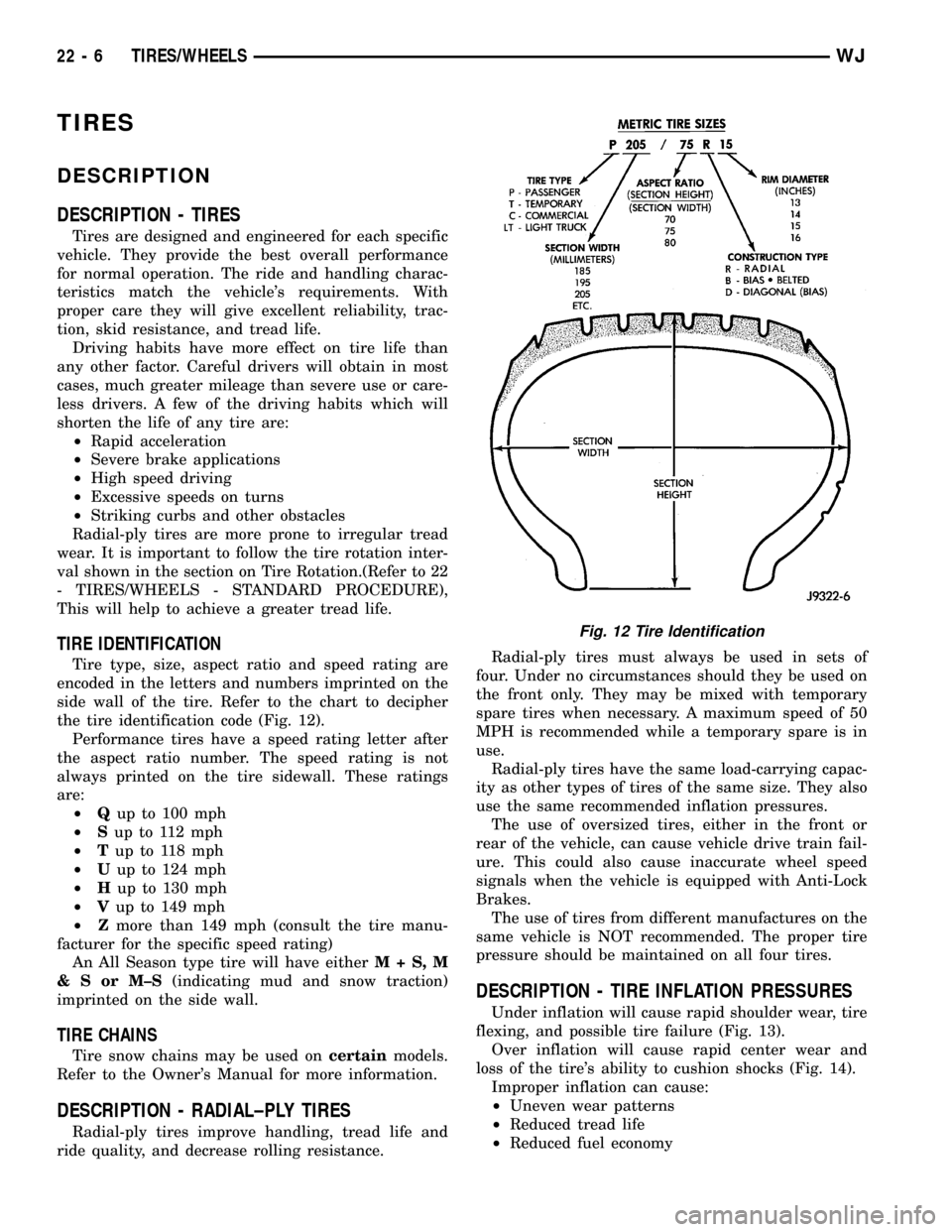
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
Tire type, size, aspect ratio and speed rating are
encoded in the letters and numbers imprinted on the
side wall of the tire. Refer to the chart to decipher
the tire identification code (Fig. 12).
Performance tires have a speed rating letter after
the aspect ratio number. The speed rating is not
always printed on the tire sidewall. These ratings
are:
²Qup to 100 mph
²Sup to 112 mph
²Tup to 118 mph
²Uup to 124 mph
²Hup to 130 mph
²Vup to 149 mph
²Zmore than 149 mph (consult the tire manu-
facturer for the specific speed rating)
An All Season type tire will have eitherM+S,M
&SorM±S(indicating mud and snow traction)
imprinted on the side wall.
TIRE CHAINS
Tire snow chains may be used oncertainmodels.
Refer to the Owner's Manual for more information.
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL±PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life and
ride quality, and decrease rolling resistance.Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of
four. Under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. They may be mixed with temporary
spare tires when necessary. A maximum speed of 50
MPH is recommended while a temporary spare is in
use.
Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
The use of oversized tires, either in the front or
rear of the vehicle, can cause vehicle drive train fail-
ure. This could also cause inaccurate wheel speed
signals when the vehicle is equipped with Anti-Lock
Brakes.
The use of tires from different manufactures on the
same vehicle is NOT recommended. The proper tire
pressure should be maintained on all four tires.
DESCRIPTION - TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES
Under inflation will cause rapid shoulder wear, tire
flexing, and possible tire failure (Fig. 13).
Over inflation will cause rapid center wear and
loss of the tire's ability to cushion shocks (Fig. 14).
Improper inflation can cause:
²Uneven wear patterns
²Reduced tread life
²Reduced fuel economy
Fig. 12 Tire Identification
22 - 6 TIRES/WHEELSWJ
Page 1867 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRESSURE
GAUGES
A quality air pressure gauge is recommended to
check tire pressure. After checking the air pressure,
replace valve cap finger tight.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TREAD WEAR
INDICATORS
Tread wear indicators are molded into the bottom
of the tread grooves. When tread depth is 1.6 mm
(1/16 in.), the tread wear indicators will appear as a
13 mm (1/2 in.) band (Fig. 15).
Tire replacement is necessary when indicators
appear in two or more grooves or if localized balding
occurs.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE WEAR
PATTERNS
Under inflation will cause wear on the shoulders of
tire. Over inflation will cause wear at the center of
tire.
Excessive camber causes the tire to run at an
angle to the road. One side of tread is then worn
more than the other (Fig. 16).
Excessive toe-in or toe-out causes wear on the
tread edges and a feathered effect across the tread
(Fig. 16).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE NOISE OR
VIBRATION
Radial-ply tires are sensitive to force impulses
caused by improper mounting, vibration, wheel
defects, or possibly tire imbalance.
To find out if tires are causing the noise or vibra-
tion, drive the vehicle over a smooth road at varying
speeds. Note the noise level during acceleration and
deceleration. The engine, differential and exhaust
noises will change as speed varies, while the tire
noise will usually remain constant.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIRING LEAKS
For proper repairing, a radial tire must be removed
from the wheel. Repairs should only be made if the
defect, or puncture, is in the tread area (Fig. 17). The
tire should be replaced if the puncture is located in
the sidewall.
Deflate tire completely before removing the tire
from the wheel. Use lubrication such as a mild soap
solution when dismounting or mounting tire. Use
tools free of burrs or sharp edges which could dam-
age the tire or wheel rim.
Before mounting tire on wheel, make sure all rust
is removed from the rim bead and repaint if neces-
sary.
Install wheel on vehicle, and tighten to proper
torque specification (Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/
WHEELS - SPECIFICATIONS).
Fig. 15 Tread Wear Indicators
1 - TREAD ACCEPTABLE
2 - TREAD UNACCEPTABLE
3 - WEAR INDICATOR
22 - 8 TIRES/WHEELSWJ
Page 1869 of 2199

SPARE TIRE
DESCRIPTION - SPARE / TEMPORARY TIRE
The temporary spare tire is designed for emer-
gency use only. The original tire should be repaired
or replaced at the first opportunity, then reinstalled.
Do not exceed speeds of 50 M.P.H. when using the
temporary spare tire. Refer to Owner's Manual for
complete details.
WHEELS
DESCRIPTION
The rim size is on the vehicle safety certification
label located on the drivers door shut face. The size
of the rim is determined by the drivetrain package.
Original equipment wheels/rims are designed for
operation up to the specified maximum vehicle capac-
ity.
All models use stamped steel, cast aluminum or
forged aluminum wheels. Every wheel has raised sec-
tions between the rim flanges and rim drop well
called safety humps (Fig. 18) .
Initial inflation of the tire forces the bead over
these raised sections. In case of rapid loss of air pres-
sure, the raised sections help hold the tire on the
wheel.
The wheel studs and nuts are designed for specific
applications. All aluminum and some steel wheels
have wheel stud nuts with an enlarged nose. This
enlarged nose is necessary to ensure proper retentionof the wheels. Do not use replacement studs or nuts
with a different design or lesser quality.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WHEEL
INSPECTION
Inspect wheels for:
²Excessive run out
²Dents or cracks
²Damaged wheel lug nut holes
²Air Leaks from any area or surface of the rim
NOTE: Do not attempt to repair a wheel by hammer-
ing, heating or welding.
If a wheel is damaged an original equipment
replacement wheel should be used. When obtaining
replacement wheels, they should be equivalent in
load carrying capacity. The diameter, width, offset,
pilot hole and bolt circle of the wheel should be the
same as the original wheel.
WARNING: FAILURE TO USE EQUIVALENT
REPLACEMENT WHEELS MAY ADVERSELY
AFFECT THE SAFETY AND HANDLING OF THE
VEHICLE. USED WHEELS ARE NOT RECOM-
MENDED. THE SERVICE HISTORY OF THE WHEEL
MAY HAVE INCLUDED SEVERE TREATMENT OR
VERY HIGH MILEAGE. THE RIM COULD FAIL WITH-
OUT WARNING.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WHEEL
REPLACEMENT
The wheel studs and nuts are designed for specific
applications. They must be replaced with equivalent
parts. Do not use replacement parts of lesser quality
or a substitute design. All aluminum and some steel
wheels have wheel stud nuts which feature an
enlarged nose. This enlarged nose is necessary to
ensure proper retention of the aluminum wheels.
NOTE: Do not use chrome plated lug nuts with
chrome plated wheels.
Before installing the wheel, be sure to remove any
build up of corrosion on the wheel mounting surfaces.
Ensure wheels are installed with good metal-to-metal
contact. Improper installation could cause loosening
of wheel nuts. This could affect the safety and han-
dling of your vehicle.
To install the wheel, first position it properly on
the mounting surface. All wheel nuts should then be
tightened just snug. Gradually tighten them in
sequence to the proper torque specification.Never
use oil or grease on studs or nuts.
Wheels must be replaced if they have:
²Excessive runout
Fig. 18 Safety Rim
1 - FLANGE
2 - RIDGE
3 - WELL
22 - 10 TIRES/WHEELSWJ
Page 1871 of 2199

TIRE PRESSURE MONITORING
DESCRIPTION
The EVIC will monitor the tire pressure signals
from the five tire sensors and determine if any tire
has gone below the low pressure threshold or raised
above the high pressure threshold. Refer to the table
below.
LOW TIRE PRESSURE THRESHOLDS
SYSTEM STATUS
INDICATORTIRE PRESSURE
ON 179 kPa (26 PSI)
OFF 214 kPa (31 PSI)
HIGH TIRE PRESSURE THRESHOLDS
SYSTEM STATUS
INDICATORTIRE PRESSURE
ON 310 kPa (45 PSI)
OFF 276 kPa (40 PSI)
The Remote Tire Pressure Monitors (RTPM) are
not internally serviceable. For a Sensor Failure or
Low Battery fault, the RTPM must be replaced.
OPERATION
If equipped with the Tire Pressure Monitoring Sys-
tem, each of the vehicle's five wheels will have a
valve stem with a pressure sensor and radio trans-
mitter built in. Signals from the tire pressure sensors
are received and interpreted by the Electronic Vehi-
cle Information Center (EVIC). A sensor in a
mounted wheel will broadcast its detected pressure
once per minute when the vehicle is moving faster
than 40 km/h (25 mph). The spare tire sensor will
broadcast once every hour. Each sensor's broadcast is
uniquely coded so that the EVIC can determine loca-
tion. The individual tire pressures can be displayed
graphically on the EVIC
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE PRESSURE
MONITORING SYSTEM
All Tire Pressure Monitoring System Faults are
specific to one location. If a9BATTERY LOW9or
9SENSOR FAILURE9fault is detected, the location
will be displayed. The appropriate sensor/transmitter
can then be replaced. If a single sensor/transmitter
cannot be detected by the EVIC, replace that sensor
transmitter. If none of the sensors/transmitters can
be detected, refer to symptoms in the EVIC section.
For additional system description and diagnosis,
refer to Tire Pressure Monitoring in the Body Diag-
nostic manual.
SENSOR
REMOVAL - TIRE PRESSURE SENSOR/
TRANSMITTER
(1) Remove the tire/wheel from the vehicle.
CAUTION: When removing the stick on balancing
weights from the wheel, do not use an abrasive
cleaner or a cleaner which will damage the protec-
tive finish on the wheel.
(2) Remove the balancing weights from the wheel.
NOTE: The cap used on this valve stem contains an
O-ring seal to prevent contamination and moisture
from entering the valve stem. Retain this valve stem
cap for re-use. Do not substitute a regular valve
stem cap in its place.
(3) Remove the cap from the valve stem.
NOTE: The valve stem used on this vehicle is made
of aluminum and the core is nickel plated brass.
The original valve stem core must be reinstalled
and not substituted for a valve stem core made of a
different material. This is required to prevent corro-
sion in the valve stem caused by the different met-
als.
(4) Using the appropriate tool, remove the core
from the valve stem (Fig. 20).
(5) Let the tire fully deflate.
Fig. 20 REMOVING VALVE STEM CORE - TYPICAL
1 - WHEEL
2 - VALVE STEM
3 - TIRE
4 - VALVE STEM CORE TOOL
22 - 12 TIRES/WHEELSWJ
Page 1874 of 2199

BODY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BODY
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WATER LEAKS........................1
WIND NOISE..........................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BODY
LUBRICATION.........................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRILLING AND
WELDING............................3
SPECIFICATIONS
BODY LUBRICANTS....................3
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE.............4
SPECIAL TOOLS
BODY...............................4DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE........5
DOOR - FRONT.........................11
DOORS - REAR.........................19
EXTERIOR.............................25
HOOD.................................33
INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEM.............36
INTERIOR..............................69
PAINT.................................81
SEATS................................83
STATIONARY GLASS.....................93
SUNROOF.............................96
WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS..................105
BODY STRUCTURE.....................112
BODY
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WATER LEAKS
Water leaks can be caused by poor sealing,
improper body component alignment, body seam
porosity, missing plugs, or blocked drain holes. Cen-
trifugal and gravitational force can cause water to
drip from a location away from the actual leak point,
making leak detection difficult. All body sealing
points should be water tight in normal wet-driving
conditions. Water flowing downward from the front of
the vehicle should not enter the passenger or luggage
compartment. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal water tight under all conditions. At
times, side glass or door seals will allow water to
enter the passenger compartment during high pres-
sure washing or hard driving rain (severe) condi-
tions. Overcompensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop a water leak that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After completing
a repair, water test vehicle to verify leak has stopped
before returning vehicle to use.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE WATER LEAK TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place, body
drains are clear, and body components are properly
aligned and sealed. If component alignment or seal-
ing is necessary, refer to the appropriate section of
this group for proper procedures.
WATER LEAK TESTS
WARNING: DO NOT USE ELECTRIC SHOP LIGHTS
OR TOOLS IN WATER TEST AREA. PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT.
When the conditions causing a water leak have
been determined, simulate the conditions as closely
as possible.
²If a leak occurs with the vehicle parked in a
steady light rain, flood the leak area with an open-
ended garden hose.
²If a leak occurs while driving at highway speeds
in a steady rain, test the leak area with a reasonable
velocity stream or fan spray of water. Direct the
spray in a direction comparable to actual conditions.
²If a leak occurs when the vehicle is parked on an
incline, hoist the end or side of the vehicle to simu-
late this condition. This method can be used when
the leak occurs when the vehicle accelerates, stops or
turns. If the leak occurs on acceleration, hoist the
front of the vehicle. If the leak occurs when braking,
hoist the back of the vehicle. If the leak occurs on left
turns, hoist the left side of the vehicle. If the leak
occurs on right turns, hoist the right side of the vehi-
cle. For hoisting recommendations refer to Group 0,
Lubrication and Maintenance, General Information
section.
WATER LEAK DETECTION
To detect a water leak point-of-entry, do a water
test and watch for water tracks or droplets forming
on the inside of the vehicle. If necessary, remove inte-
rior trim covers or panels to gain visual access to the
WJBODY 23 - 1