2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE set 1 2
[x] Cancel search: set 1 2Page 1600 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - OIL PUMP VOLUME
CHECK
Measuring the oil pump output volume will deter-
mine if sufficient oil flow to the transmission oil
cooler exists, and whether or not an internal trans-
mission failure is present.
Verify that the transmission fluid is at the proper
level. Refer to the Fluid Level Check procedure in
this section. If necessary, fill the transmission to the
proper level with MopartATF +4, type 9602, Auto-
matic Transmission Fluid.
(1) Disconnect theTo coolerline at the cooler
inlet and place a collecting container under the dis-
connected line.
CAUTION: With the fluid set at the proper level,
fluid collection should not exceed (1) quart or inter-
nal damage to the transmission may occur.
(2) Run the engineat curb idle speed, with the
shift selector in neutral.(3) If one quart of transmission fluid is collected in
the container in 20 seconds or less, oil pump flow vol-
ume is within acceptable limits. If fluid flow is inter-
mittent, or it takes more than 20 seconds to collect
one quart of fluid, refer to the Hydraulic Pressure
tests in this section for further diagnosis.
(4) Re-connect theTo coolerline to the transmis-
sion cooler inlet.
(5) Refill the transmission to proper level.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove seal ring from housing and reaction
shaft support (Fig. 110).
(2) Mark pump housing and support assembly for
alignment reference.
(3) Remove bolts attaching pump body to support
(Fig. 111).
(4) Separate support from pump housing (Fig.
112).
(5) Remove inner and outer gears from reaction
shaft support (Fig. 113).
Fig. 108 Oil Pump and Reaction Shaft Support
1 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
2 - PUMP
Fig. 109 Pump Gear Removal
1 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
2 - INNER GEAR
3 - OUTER GEAR
Fig. 110 Removing Pump Seal Ring
1 - PUMP HOUSING SEAL RING
Fig. 111 Pump Support Bolts
1 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
2 - PUMP
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 81
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1601 of 2199

(6) If pump seal was not removed during transmis-
sion disassembly, remove seal with punch and ham-
mer.
(7) Remove front clutch thrust washer from sup-
port hub (Fig. 114).
OIL PUMP BUSHING REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove pump bushing with Tool Handle
C-4171 and Bushing Remover SP-3551 from Tool Set
C-3887-J (Fig. 115).
(2) Install new pump bushing with Tool Handle
C-4171 and Bushing Installer SP-5117 (Fig. 115).
Bushing should be flush with pump housing bore.
(3) Stake new pump bushing in two places with
blunt punch (Fig. 116). Remove burrs from stake
points with knife blade afterward.
REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT BUSHING REMOVAL
(1) Assemble Bushing Remover Tools SP-1191,
3633 and 5324 (Fig. 117). Do not clamp any part of
reaction shaft or support in vise.
(2) Hold Cup Tool SP-3633 firmly against reaction
shaft and thread remover SP-5324 into bushing as
far as possible by hand. Then thread remover tool 3-4
additional turns into bushing with a wrench.(3) Turn remover tool hex nut down against
remover cup to pull bushing from shaft. Clean all
chips from shaft after bushing removal.
Fig. 112 Separating Pump Housing From Reaction
Shaft Support
1 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
2 - PUMP HOUSING
Fig. 113 Pump Gear Removal
1 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
2 - INNER GEAR
3 - OUTER GEAR
Fig. 114 Support Hub Thrust Washer
1 - BUSHING
2 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
3 - THRUST WASHER
4 - HUB
Fig. 115 Removing Oil Pump Bushing
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4171
2 - SPECIAL TOOL SP-3551
3 - BUSHING
4 - SPECIAL TOOL SP-5117
5 - BUSHING
6 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4171
7 - PUMP HOUSING
21 - 82 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1603 of 2199

CAUTION: The pump inner gear is a one way fit.
The bore on one side of the gear inside diameter
(I.D.) is chamfered. Be sure the chamfered side
faces forward (to front of pump).
(6) Install new thrust washer on hub of reaction
shaft support. Lubricate washer with transmission
fluid or petroleum jelly.
(7) If reaction shaft seal rings are being replaced,
install new seal rings on support hub (Fig. 120).
Lubricate seal rings with transmission fluid or petro-
leum jelly after installation. Squeeze each ring until
ring ends are securely hooked together.
CAUTION: The reaction shaft support seal rings will
break if overspread, or twisted. If new rings are
being installed, spread them only enough for instal-
lation. Also be very sure the ring ends are securely
hooked together after installation. Otherwise, therings will either prevent pump installation, or break
during installation.
(8) Install reaction shaft support on pump housing
(Fig. 121).
(9) Align reaction support on pump housing. Use
alignment marks made at disassembly. Or, rotate
support until bolt holes in support and pump housing
are all aligned (holes are offset for one-way fit).
(10) Install all bolts that attach support to pump
housing. Then tighten bolts finger tight.
(11) Tighten support-to-pump bolts to required
torque as follows:
(a) Reverse pump assembly and install it in
transmission case. Position pump so bolts are fac-
ing out and are accessible.
(b) Secure pump assembly in case with 2 or 3
bolts, or with pilot studs.
(c) Tighten support-to-pump bolts to 20 N´m (15
ft. lbs.).
(d) Remove pump assembly from transmission
case.
Fig. 118 Supporting Pump And Installing Outer Gear
1 - OUTER GEAR
2 - PUMP HOUSING
3 - WOOD BLOCKS
Fig. 119 Pump Inner Gear Installation
1 - OUTER GEAR
2 - INNER GEAR
Fig. 120 Hub Seal Ring Position
1 - SEAL RINGS
2 - SUPPORT HUB
Fig. 121 Assembling Reaction Shaft Support And
Pump Housing
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
21 - 84 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1605 of 2199
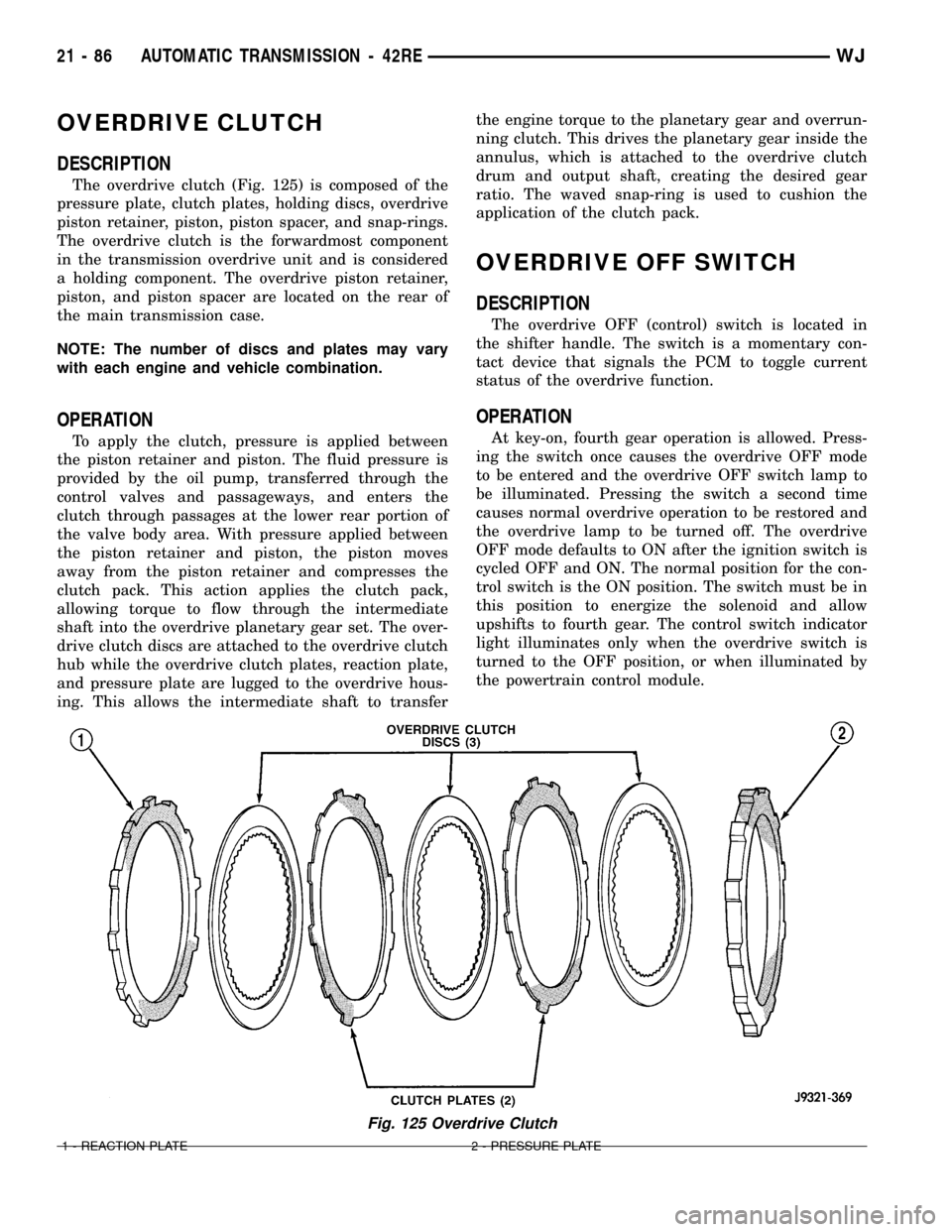
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The overdrive clutch (Fig. 125) is composed of the
pressure plate, clutch plates, holding discs, overdrive
piston retainer, piston, piston spacer, and snap-rings.
The overdrive clutch is the forwardmost component
in the transmission overdrive unit and is considered
a holding component. The overdrive piston retainer,
piston, and piston spacer are located on the rear of
the main transmission case.
NOTE: The number of discs and plates may vary
with each engine and vehicle combination.
OPERATION
To apply the clutch, pressure is applied between
the piston retainer and piston. The fluid pressure is
provided by the oil pump, transferred through the
control valves and passageways, and enters the
clutch through passages at the lower rear portion of
the valve body area. With pressure applied between
the piston retainer and piston, the piston moves
away from the piston retainer and compresses the
clutch pack. This action applies the clutch pack,
allowing torque to flow through the intermediate
shaft into the overdrive planetary gear set. The over-
drive clutch discs are attached to the overdrive clutch
hub while the overdrive clutch plates, reaction plate,
and pressure plate are lugged to the overdrive hous-
ing. This allows the intermediate shaft to transferthe engine torque to the planetary gear and overrun-
ning clutch. This drives the planetary gear inside the
annulus, which is attached to the overdrive clutch
drum and output shaft, creating the desired gear
ratio. The waved snap-ring is used to cushion the
application of the clutch pack.
OVERDRIVE OFF SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The overdrive OFF (control) switch is located in
the shifter handle. The switch is a momentary con-
tact device that signals the PCM to toggle current
status of the overdrive function.
OPERATION
At key-on, fourth gear operation is allowed. Press-
ing the switch once causes the overdrive OFF mode
to be entered and the overdrive OFF switch lamp to
be illuminated. Pressing the switch a second time
causes normal overdrive operation to be restored and
the overdrive lamp to be turned off. The overdrive
OFF mode defaults to ON after the ignition switch is
cycled OFF and ON. The normal position for the con-
trol switch is the ON position. The switch must be in
this position to energize the solenoid and allow
upshifts to fourth gear. The control switch indicator
light illuminates only when the overdrive switch is
turned to the OFF position, or when illuminated by
the powertrain control module.
Fig. 125 Overdrive Clutch
1 - REACTION PLATE 2 - PRESSURE PLATE
21 - 86 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
Page 1620 of 2199

(5) Install new seal in gear case. On 4x4 gear case,
use Tool Handle C-4171 and Installer C-3860-A to
seat seal in case. On4x2gear case, use same Han-
dle C-4171 and Installer C-3995-A to seat seal in
case.
(6) Verify that tab ends of rear bearing locating
ring extend into access hole in gear case (Fig. 175).
(7) Support geartrain on Tool 6227-1 (Fig. 176). Be
sure tool is securely seated in clutch hub.
(8) Install overdrive gear case on geartrain (Fig.
176).
(9) Expand front bearing locating ring with snap-
ring pliers (Fig. 177). Then slide case downward until
locating ring locks in bearing groove and release
snap-ring.
(10) Install locating ring access cover and gasket
in overdrive unit case (Fig. 178).
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
(1) Install overdrive clutch reaction ring first.
Reaction ring is flat with notched ends (Fig. 179).
(2) Install wave spring on top of reaction ring (Fig.
180). Reaction ring and wave ring both fit in same
ring groove. Use screwdriver to seat each ring
securely in groove. Also ensure that the ends of the
two rings are offset from each other.
NOTE: The 42RE transmission has 3 overdrive
clutch discs and 2 plates.
(3) Assemble overdrive clutch pack (Fig. 181).
(4) Install overdrive clutch reaction plate first.
Fig. 173 Reaction Plug Locating Pin And Snap-Ring
1 - REACTION PLUG SNAP-RING (DO NOT OVERCOMPRESS
TO INSTALL)
2 - LOCATING PIN
3 - PARK LOCK REACTION PLUG
Fig. 174 Reaction Plug And Snap-Ring Installation
1 - REACTION PLUG SNAP-RING
2 - SNAP-RING PLIERS
Fig. 175 Correct Rear Bearing Locating Ring
Position
1 - CASE ACCESS HOLE
2 - TAB ENDS OF LOCATING RING
Fig. 176 Overdrive Gear Case Installation
1 - GEARTRAIN ASSEMBLY
2 - GEAR CASE
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 101
OVERDRIVE UNIT (Continued)
Page 1631 of 2199

PLANETARY GEARTRAIN/
OUTPUT SHAFT
DESCRIPTION
The planetary gearsets (Fig. 203) are designated as
the front, rear, and overdrive planetary gear assem-
blies and located in such order. A simple planetary
gearset consists of three main members:
²The sun gear which is at the center of the sys-
tem.
²The planet carrier with planet pinion gears
which are free to rotate on their own shafts and are
in mesh with the sun gear.
²The annulus gear, which rotates around and is
in mesh with the planet pinion gears.
NOTE: The number of pinion gears does not affect
the gear ratio, only the duty rating.
OPERATION
With any given planetary gearset, several condi-
tions must be met for power to be able to flow:
²One member must be held.
²Another member must be driven or used as an
input.
²The third member may be used as an output for
power flow.
²For direct drive to occur, two gear members in
the front planetary gearset must be driven.
NOTE: Gear ratios are dependent on the number of
teeth on the annulus and sun gears.
DISASSEMBLY
(1) Remove planetary snap-ring (Fig. 204).
(2) Remove front annulus and planetary assembly
from driving shell (Fig. 204).
(3) Remove snap-ring that retains front planetary
gear in annulus gear (Fig. 205).
(4) Remove tabbed thrust washer and tabbed
thrust plate from hub of front annulus (Fig. 206).
(5) Separate front annulus and planetary gears
(Fig. 206).
(6) Remove front planetary gear front thrust
washer from annulus gear hub.
(7) Separate and remove driving shell, rear plane-
tary and rear annulus from output shaft (Fig. 207).
(8) Remove front planetary rear thrust washer
from driving shell.
(9) Remove tabbed thrust washers from rear plan-
etary gear.
(10) Remove lock ring that retains sun gear in
driving shell. Then remove sun gear, spacer and
thrust plates.
Fig. 203 Planetary Gearset
1 - ANNULUS GEAR
2 - SUN GEAR
3 - PLANET CARRIER
4 - PLANET PINIONS (4)
Fig. 204 Front Annulus And Planetary Assembly
Removal
1 - DRIVING SHELL
2 - FRONT ANNULUS AND PLANETARY ASSEMBLY
3 - PLANETARY SNAP-RING
Fig. 205 Front Planetary Snap-Ring Removal
1 - FRONT ANNULUS GEAR
2 - PLANETARY SNAP-RING
21 - 112 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
Page 1632 of 2199

INSPECTION
Check sun gear and driving shell condition.
Replace the gear if damaged or if the bushings are
scored or worn. The bushings are not serviceable.
Replace the driving shell if worn, cracked or dam-
aged.Replace planetary gear sets if gears, pinion pins, or
carrier are damaged in any way. Replace the annulus
gears and supports if either component is worn or
damaged.
Inspect the geartrain spacers, thrust plates, snap-
rings, and thrust washers. Replace any of these parts
that are worn, distorted or damaged. Do not attempt
to reuse these parts.
The planetary gear thrust washers are different
sizes. The large diameter washers go on the front
planetary and the smaller washers go on the rear
planetary. All the washers have four locating tabs on
them. These tabs fit in the holes or slots provided in
each planetary gear.
Inspect the output shaft carefully. Pay particular
attention to the machined bushing/bearing surfaces
on the shaft and the governor valve shaft bore at the
shaft rear.
Replace the output shaft if the machined surfaces
are scored, pitted, or damaged in any way. Also
replace the shaft if the splines are damaged, or
exhibits cracks at any location (especially at the gov-
ernor valve shaft bore).
The annulus gears can be removed from their sup-
ports if necessary. Just remove the snap-rings and
separate the two parts when replacement is neces-
sary. In addition, the annulus gear bushings can be
replaced if severely worn, or scored. However it is not
necessary to replace the bushings if they only exhibit
normal wear. Check bushing fit on the output shaft
to be sure.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Lubricate output shaft and planetary compo-
nents with transmission fluid. Use petroleum jelly to
lubricate and hold thrust washers and plates in posi-
tion.
(2) Assemble rear annulus gear and support if dis-
assembled. Be sure support snap-ring is seated and
that shoulder-side of support faces rearward (Fig.
208).
(3) Install rear thrust washer on rear planetary
gear. Use enough petroleum jelly to hold washer in
place. Also be sure all four washer tabs are properly
engaged in gear slots.
(4) Install rear annulus over and onto rear plane-
tary gear (Fig. 208).
(5) Install assembled rear planetary and annulus
gear on output shaft (Fig. 209). Verify that assembly
is fully seated on shaft.
Fig. 206 Front Planetary And Annulus Gear
Disassembly
1 - FRONT ANNULUS
2 - THRUST WASHER
3 - THRUST PLATE
4 - FRONT THRUST WASHER
5 - FRONT PLANETARY
Fig. 207 Removing Driving Shell, Rear Planetary
And Rear Annulus
1 - REAR ANNULUS
2 - REAR PLANETARY
3 - DRIVING SHELL
4 - OUTPUT SHAFT
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 113
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN/OUTPUT SHAFT (Continued)
Page 1645 of 2199

A solenoid can also be described by the method by
which it is controlled. Some of the possibilities
include variable force, pulse-width modulated, con-
stant ON, or duty cycle. The variable force and pulse-
width modulated versions utilize similar methods to
control the current flow through the solenoid to posi-
tion the solenoid plunger at a desired position some-
where between full ON and full OFF. The constant
ON and duty cycled versions control the voltage
across the solenoid to allow either full flow or no flow
through the solenoid's valve.
OPERATION
When an electrical current is applied to the sole-
noid coil, a magnetic field is created which produces
an attraction to the plunger, causing the plunger to
move and work against the spring pressure and the
load applied by the fluid the valve is controlling. The
plunger is normally directly attached to the valve
which it is to operate. When the current is removed
from the coil, the attraction is removed and the
plunger will return to its original position due to
spring pressure.
The plunger is made of a conductive material and
accomplishes this movement by providing a path for
the magnetic field to flow. By keeping the air gap
between the plunger and the coil to the minimum
necessary to allow free movement of the plunger, the
magnetic field is maximized.
SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The speed sensor (Fig. 240) is located in the over-
drive gear case. The sensor is positioned over the
park gear and monitors transmission output shaft
rotating speed.
OPERATION
Speed sensor signals are triggered by the park
gear lugs as they rotate past the sensor pickup face.
Input signals from the sensor are sent to the trans-
mission control module for processing. Signals from
this sensor are shared with the powertrain control
module.
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
DESCRIPTION
Transmission throttle valve cable adjustment is
extremely important to proper operation. This adjust-
ment positions the throttle valve, which controls shift
speed, quality, and part-throttle downshift sensitivity.
If cable setting is too loose, early shifts and slip-
page between shifts may occur. If the setting is too
tight, shifts may be delayed and part throttle down-
shifts may be very sensitive.
The transmission throttle valve is operated by a
cam on the throttle lever. The throttle lever is oper-
ated by an adjustable cable (Fig. 241). The cable is
attached to an arm mounted on the throttle lever
shaft. A retaining clip at the engine-end of the cable
is removed to provide for cable adjustment. The
retaining clip is then installed back onto the throttle
valve cable to lock in the adjustment.
ADJUSTMENTS - TRANSMISSION THROTTLE
VALVE CABLE
A correctly adjusted throttle valve cable (Fig. 242)
will cause the throttle lever on the transmission to
move simultaneously with the throttle body lever
from the idle position. Proper adjustment will allow
Fig. 240 Transmission Output Speed Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION OUTPUT SHAFT SPEED SENSOR
2 - SEAL
Fig. 241 Throttle Valve Cable
1 - THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
2 - THROTTLE VALVE LEVER
3 - THROTTLE BODY
21 - 126 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
SOLENOID (Continued)