2002 JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE set 1 2
[x] Cancel search: set 1 2Page 1510 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PUMP LEAKAGE
(1) Possible areas of pump leakage (Fig. 3).
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - INITIAL OPERATION
- 4.0L
WARNING: THE FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE
CHECKED WITH ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT INJURY
FROM MOVING COMPONENTS.
CAUTION: Use MOPAR Power Steering Fluid or
equivalent. Do not use automatic transmission fluid
and do not overfill.
Wipe filler cap clean, then check the fluid level.
The dipstick should indicateCOLDwhen the fluid is
at normal ambient temperature.
(1) Fill the pump fluid reservoir to the proper level
and let the fluid settle for at least two minutes.
(2) Start the engine and let run for a few seconds
then turn engine off.
(3) Add fluid if necessary. Repeat the above proce-
dure until the fluid level remains constant after run-
ning the engine.
(4) Raise the front wheels off the ground.
(5) Slowly turn the steering wheel right and left,
lightly contacting the wheel stops at least 20 times.(6) Check the fluid level add if necessary.
(7) Lower the vehicle, start the engine and turn
the steering wheel slowly from lock to lock.
(8) Stop the engine and check the fluid level and
refill as required.
(9) If the fluid is extremely foamy or milky look-
ing, allow the vehicle to stand a few minutes and
repeat the procedure.
CAUTION: Do not run a vehicle with foamy fluid for
an extended period. This may cause pump damage.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - INITIAL OPERATION
- 4.7L
WARNING: THE FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE
CHECKED WITH ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT INJURY
FROM MOVING COMPONENTS.
NOTE: Remove as much of the old fluid out of the
system as possible with a suction tool or by remov-
ing a hose, When a component has failed. Then
refill it with fresh fluid until it is clean. This may
have to be done more than once.
CAUTION: Use MOPAR Power Steering Fluid or
equivalent. Do not use automatic transmission fluid
and do not overfill.
Wipe filler cap clean, then check the fluid level.
The dipstick should indicateCOLDwhen the fluid is
at normal ambient temperature.
(1) Fill the pump fluid reservoir to the proper level
and let the fluid settle for at least two minutes.
(2) Start the engine and let run for a few seconds
then turn engine off.
(3) Add fluid if necessary. Repeat the above proce-
dure until the fluid level remains constant after run-
ning the engine.
(4) Raise the front wheels off the ground.
(5) Slowly turn the steering wheel right and left,
lightly contacting the wheel stops at least 20 times.
(6) Check the fluid level add if necessary.
(7) Lower the vehicle, start the engine, and use
the DRB III to activate the hydraulic fan on full fan
operation.
(8)
Turn the steering wheel slowly from lock to lock.
(9) Stop the engine, check the fluid level and refill
as required and repeat the process
CAUTION: Do not run a vehicle with foamy fluid for
an extended period. This may cause pump damage.
(10) If the fluid is extremely foamy or milky look-
ing, allow the vehicle to stand a few minutes and
repeat the procedure.
Fig. 3 4.0L Power Steering Pump
WJPUMP 19 - 33
PUMP (Continued)
Page 1513 of 2199

SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER STEERING PUMP
FLUID COOLER
DESCRIPTION
4.7L models of this vehicle are equipped with a
cooler for the power steering system fluid. The power
steering fluid cooler is located at the front of the
vehicle. It is mounted to the radiator support just
forward of the air-conditioning condenser and just
rearward of the front fascia (Fig. 6). The cooler is
positioned so it is in the air flow through the front
fascia of the vehicle.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Drain the power steering fluid out of the reser-
voir.
(3) Remove the front fascia grille assembly,(Refer
to 13 - FRAMES & BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT
FASCIA - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the grille opening reinforcement panel
(5) Place a drain pan under the cooler.
(6) Disconnect the lower hose at cooler (Fig. 6).
(7) Disconnect the upper hose at cooler (Fig. 6).
(8) Remove the three cooler mounting bolts (Fig.
6).
(9) Remove the cooler from the vehicle.
Analyzer Set, Power Steering Flow/Pressure 6815
Adapters, Power Steering Flow/Pressure Tester
6893
4.7L HYDRAULIC POWER STEERING TEST
ADAPTER KIT - 8630
Puller C-4333
Installer, Power Steering Pulley C-4063B
Fig. 6 POWER STEERING FLUID COOLER
1 - POWER STEERING COOLER
2 - POWER STEERING COOLER LINES CLIP
19 - 36 PUMPWJ
PUMP (Continued)
Page 1522 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - TORQUE
CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE........134
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................134
OPERATION..........................134
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION........................135
OPERATION..........................139REMOVAL............................154
DISASSEMBLY........................155
CLEANING...........................165
INSPECTION.........................166
ASSEMBLY...........................167
INSTALLATION........................175
ADJUSTMENTS - VALVE BODY...........175
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION -
42RE
DESCRIPTION
The 42RE is a four speed fully automatic transmis-
sion (Fig. 1) with an electronic governor. The 42RE is
equipped with a lock-up clutch in the torque con-
verter. First through third gear ranges are provided
by the clutches, bands, overrunning clutch, and plan-
etary gear sets in the transmission. Fourth gear
range is provided by the overdrive unit that contains
an overdrive clutch, direct clutch, planetary gear set,
and overrunning clutch.The transmission contains a front, rear, and direct
clutch which function as the input driving compo-
nents. It also contains the kickdown (front) and the
low/reverse (rear) bands which, along with the over-
running clutch and overdrive clutch, serve as the
holding components. The driving and holding compo-
nents combine to select the necessary planetary gear
components, in the front, rear, or overdrive planetary
gear set, transfer the engine power from the input
shaft through to the output shaft.
The valve body is mounted to the lower side of the
transmission and contains the valves to control pres-
sure regulation, fluid flow control, and clutch/band
application. The oil pump is mounted at the front of
the transmission and is driven by the torque con-
verter hub. The pump supplies the oil pressure nec-
essary for clutch/band actuation and transmission
lubrication.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 3
Page 1526 of 2199

REVERSE POWERFLOW
When the gear selector is moved into the
REVERSE position (Fig. 5), the front clutch and the
rear band are applied. With the application of the
front clutch, engine torque is applied to the sun gear,
turning it in a clockwise direction. The clockwise
rotation of the sun gear causes the rear planet pin-
ions to rotate against engine rotation in a counter-
clockwise direction. The rear band is holding the low
reverse drum, which is splined to the rear carrier.
Since the rear carrier is being held, the torque fromthe planet pinions is transferred to the rear annulus
gear, which is splined to the output shaft. The output
shaft in turn rotates with the annulus gear in a
counterclockwise direction giving a reverse gear out-
put. The entire transmission of torque is applied to
the rear planetary gearset only. Although there is
torque input to the front gearset through the sun
gear, no other member of the gearset is being held.
During the entire reverse stage of operation, the
front planetary gears are in an idling condition.
Fig. 5 Reverse Powerflow
1 - FRONT CLUTCH ENGAGED 5 - OUTPUT SHAFT
2 - OUTPUT SHAFT 6 - INPUT SHAFT
3 - LOW/REVERSE BAND APPLIED 7 - FRONT CLUTCH ENGAGED
4 - INPUT SHAFT 8 - LOW/REVERSE BAND APPLIED
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 7
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1528 of 2199

SECOND GEAR POWERFLOW
In DRIVE-SECOND (Fig. 7), the same elements
are applied as in MANUAL-SECOND. Therefore, the
power flow will be the same, and both gears will be
discussed as one in the same. In DRIVE-SECOND,
the transmission has proceeded from first gear to its
shift point, and is shifting from first gear to second.
The second gear shift is obtained by keeping the rear
clutch applied and applying the front (kickdown)
band. The front band holds the front clutch retainer
that is locked to the sun gear driving shell. With the
rear clutch still applied, the input is still on the front
annulus gear turning it clockwise at engine speed.Now that the front band is holding the sun gear sta-
tionary, the annulus rotation causes the front planets
to rotate in a clockwise direction. The front carrier is
then also made to rotate in a clockwise direction but
at a reduced speed. This will transmit the torque to
the output shaft, which is directly connected to the
front planet carrier. The rear planetary annulus gear
will also be turning because it is directly splined to
the output shaft. All power flow has occurred in the
front planetary gear set during the drive-second
stage of operation, and now the over-running clutch,
in the rear of the transmission, is disengaged and
freewheeling on its hub.
Fig. 7 Second Gear Powerflow
1 - KICKDOWN BAND APPLIED 6 - INPUT SHAFT
2 - OUTPUT SHAFT 7 - REAR CLUTCH APPLIED
3 - REAR CLUTCH ENGAGED 8 - KICKDOWN BAND APPLIED
4 - OUTPUT SHAFT 9 - INPUT SHAFT
5 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH FREE-WHEELING
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 9
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1529 of 2199

DIRECT DRIVE POWERFLOW
The vehicle has accelerated and reached the shift
point for the 2-3 upshift into direct drive (Fig. 8).
When the shift takes place, the front band is
released, and the front clutch is applied. The rear
clutch stays applied as it has been in all the forward
gears. With the front clutch now applied, engine
torque is now on the front clutch retainer, which is
locked to the sun gear driving shell. This means that
the sun gear is now turning in engine rotation (clock-
wise) and at engine speed. The rear clutch is still
applied so engine torque is also still on the frontannulus gear. If two members of the same planetary
set are driven, direct drive results. Therefore, when
two members are rotating at the same speed and in
the same direction, it is the same as being locked up.
The rear planetary set is also locked up, given the
sun gear is still the input, and the rear annulus gear
must turn with the output shaft. Both gears are
turning in the same direction and at the same speed.
The front and rear planet pinions do not turn at all
in direct drive. The only rotation is the input from
the engine to the connected parts, which are acting
as one common unit, to the output shaft.
Fig. 8 Direct Drive Powerflow
1 - FRONT CLUTCH APPLIED 6 - INPUT SHAFT
2 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH FREE-WHEELING 7 - OVER-RUNNING CLUTCH FREE-WHEELING
3 - OUTPUT SHAFT 8 - REAR CLUTCH APPLIED
4 - REAR CLUTCH APPLIED 9 - FRONT CLUTCH APPLIED
5 - OUTPUT SHAFT 10 - INPUT SHAFT
21 - 10 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1536 of 2199
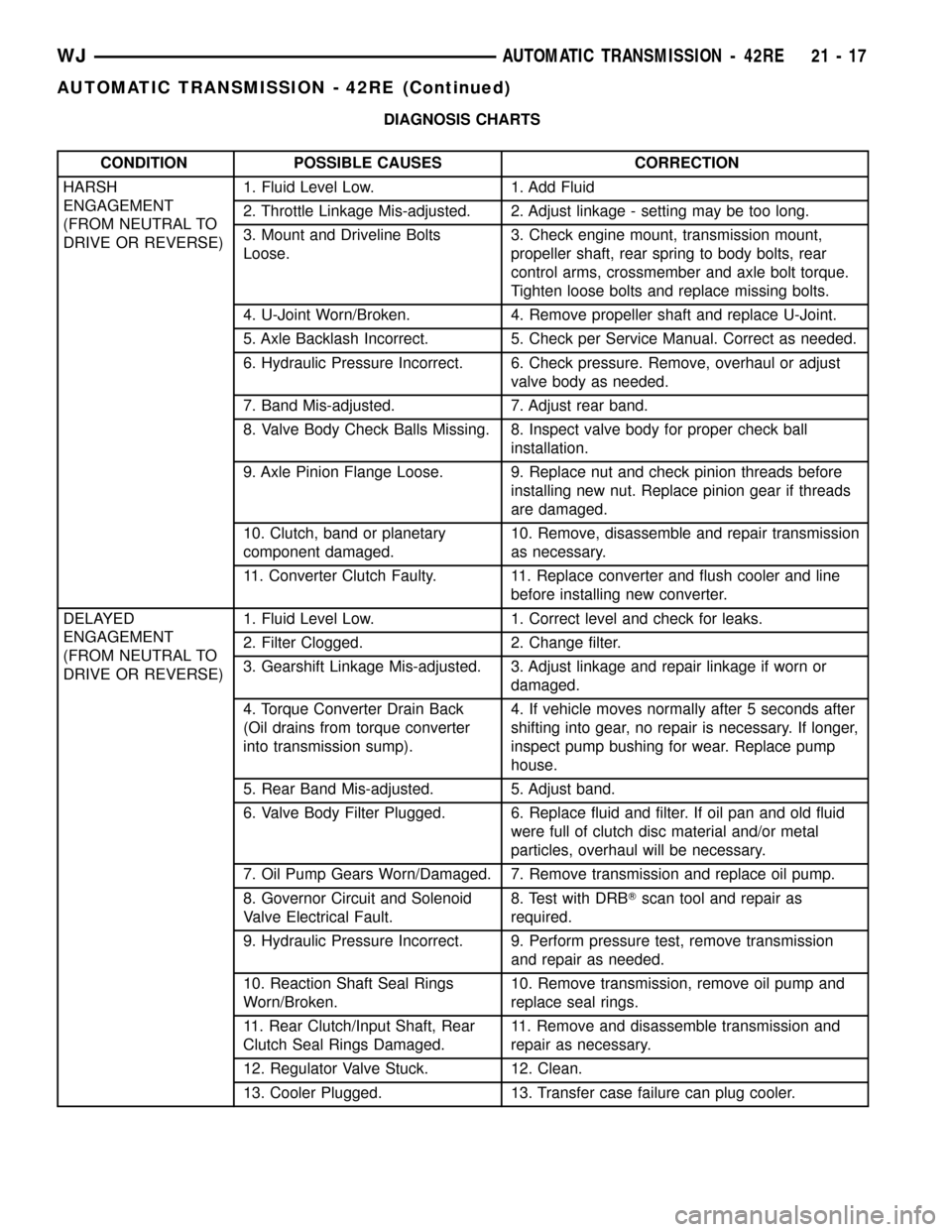
DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
HARSH
ENGAGEMENT
(FROM NEUTRAL TO
DRIVE OR REVERSE)1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add Fluid
2. Throttle Linkage Mis-adjusted. 2. Adjust linkage - setting may be too long.
3. Mount and Driveline Bolts
Loose.3. Check engine mount, transmission mount,
propeller shaft, rear spring to body bolts, rear
control arms, crossmember and axle bolt torque.
Tighten loose bolts and replace missing bolts.
4. U-Joint Worn/Broken. 4. Remove propeller shaft and replace U-Joint.
5. Axle Backlash Incorrect. 5. Check per Service Manual. Correct as needed.
6. Hydraulic Pressure Incorrect. 6. Check pressure. Remove, overhaul or adjust
valve body as needed.
7. Band Mis-adjusted. 7. Adjust rear band.
8. Valve Body Check Balls Missing. 8. Inspect valve body for proper check ball
installation.
9. Axle Pinion Flange Loose. 9. Replace nut and check pinion threads before
installing new nut. Replace pinion gear if threads
are damaged.
10. Clutch, band or planetary
component damaged.10. Remove, disassemble and repair transmission
as necessary.
11. Converter Clutch Faulty. 11. Replace converter and flush cooler and line
before installing new converter.
DELAYED
ENGAGEMENT
(FROM NEUTRAL TO
DRIVE OR REVERSE)1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Correct level and check for leaks.
2. Filter Clogged. 2. Change filter.
3. Gearshift Linkage Mis-adjusted. 3. Adjust linkage and repair linkage if worn or
damaged.
4. Torque Converter Drain Back
(Oil drains from torque converter
into transmission sump).4. If vehicle moves normally after 5 seconds after
shifting into gear, no repair is necessary. If longer,
inspect pump bushing for wear. Replace pump
house.
5. Rear Band Mis-adjusted. 5. Adjust band.
6. Valve Body Filter Plugged. 6. Replace fluid and filter. If oil pan and old fluid
were full of clutch disc material and/or metal
particles, overhaul will be necessary.
7. Oil Pump Gears Worn/Damaged. 7. Remove transmission and replace oil pump.
8. Governor Circuit and Solenoid
Valve Electrical Fault.8. Test with DRBTscan tool and repair as
required.
9. Hydraulic Pressure Incorrect. 9. Perform pressure test, remove transmission
and repair as needed.
10. Reaction Shaft Seal Rings
Worn/Broken.10. Remove transmission, remove oil pump and
replace seal rings.
11. Rear Clutch/Input Shaft, Rear
Clutch Seal Rings Damaged.11. Remove and disassemble transmission and
repair as necessary.
12. Regulator Valve Stuck. 12. Clean.
13. Cooler Plugged. 13. Transfer case failure can plug cooler.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 17
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1541 of 2199
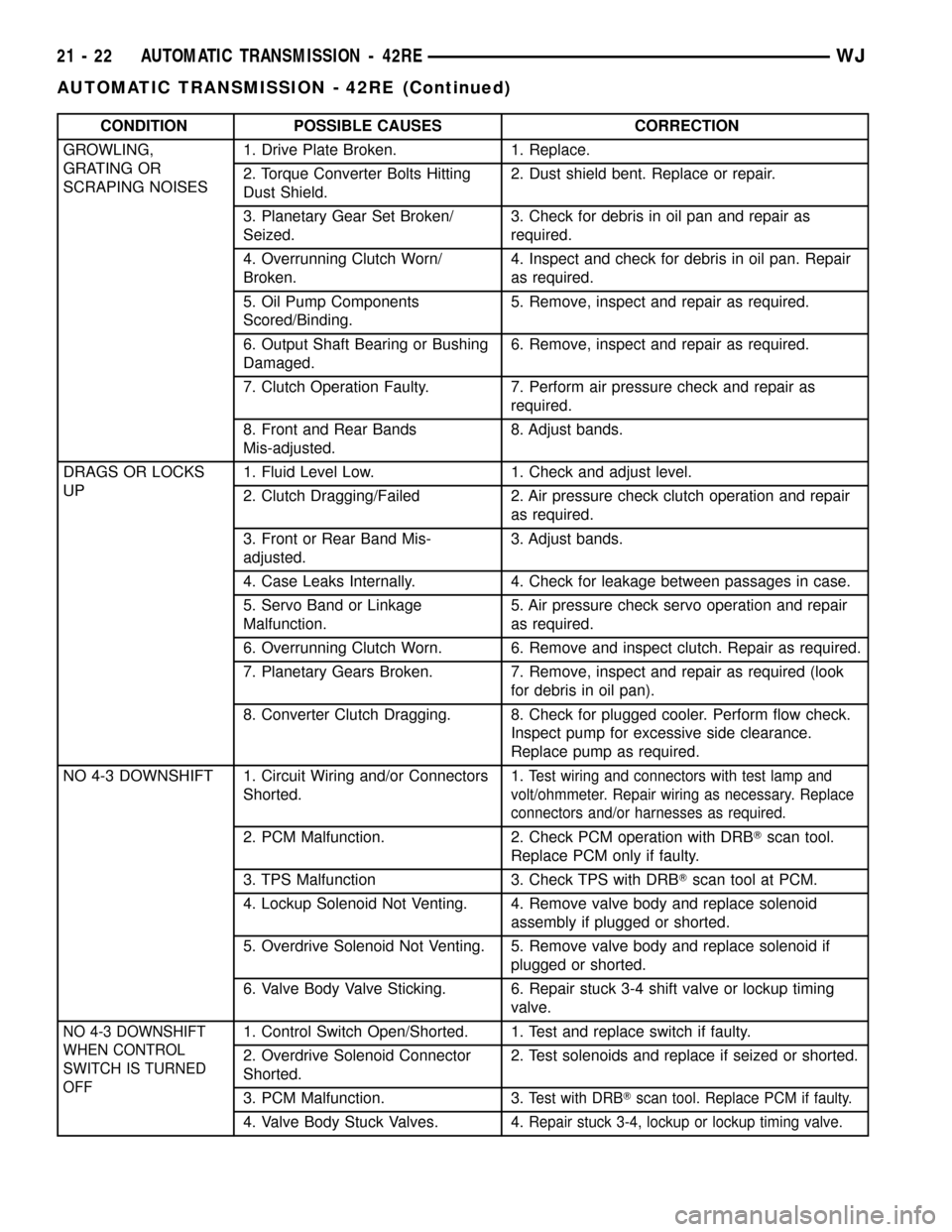
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
GROWLING,
GRATING OR
SCRAPING NOISES1. Drive Plate Broken. 1. Replace.
2. Torque Converter Bolts Hitting
Dust Shield.2. Dust shield bent. Replace or repair.
3. Planetary Gear Set Broken/
Seized.3. Check for debris in oil pan and repair as
required.
4. Overrunning Clutch Worn/
Broken.4. Inspect and check for debris in oil pan. Repair
as required.
5. Oil Pump Components
Scored/Binding.5. Remove, inspect and repair as required.
6. Output Shaft Bearing or Bushing
Damaged.6. Remove, inspect and repair as required.
7. Clutch Operation Faulty. 7. Perform air pressure check and repair as
required.
8. Front and Rear Bands
Mis-adjusted.8. Adjust bands.
DRAGS OR LOCKS
UP1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Check and adjust level.
2. Clutch Dragging/Failed 2. Air pressure check clutch operation and repair
as required.
3. Front or Rear Band Mis-
adjusted.3. Adjust bands.
4. Case Leaks Internally. 4. Check for leakage between passages in case.
5. Servo Band or Linkage
Malfunction.5. Air pressure check servo operation and repair
as required.
6. Overrunning Clutch Worn. 6. Remove and inspect clutch. Repair as required.
7. Planetary Gears Broken. 7. Remove, inspect and repair as required (look
for debris in oil pan).
8. Converter Clutch Dragging. 8. Check for plugged cooler. Perform flow check.
Inspect pump for excessive side clearance.
Replace pump as required.
NO 4-3 DOWNSHIFT 1. Circuit Wiring and/or Connectors
Shorted.1.
Test wiring and connectors with test lamp and
volt/ohmmeter. Repair wiring as necessary. Replace
connectors and/or harnesses as required.
2. PCM Malfunction. 2. Check PCM operation with DRBTscan tool.
Replace PCM only if faulty.
3. TPS Malfunction 3. Check TPS with DRBTscan tool at PCM.
4. Lockup Solenoid Not Venting. 4. Remove valve body and replace solenoid
assembly if plugged or shorted.
5. Overdrive Solenoid Not Venting. 5. Remove valve body and replace solenoid if
plugged or shorted.
6. Valve Body Valve Sticking. 6. Repair stuck 3-4 shift valve or lockup timing
valve.
NO 4-3 DOWNSHIFT
WHEN CONTROL
SWITCH IS TURNED
OFF1. Control Switch Open/Shorted. 1. Test and replace switch if faulty.
2. Overdrive Solenoid Connector
Shorted.2. Test solenoids and replace if seized or shorted.
3. PCM Malfunction. 3.
Test with DRBTscan tool. Replace PCM if faulty.
4. Valve Body Stuck Valves. 4.Repair stuck 3-4, lockup or lockup timing valve.
21 - 22 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)