2002 FORD EXPLORER SPORT TRAC weight
[x] Cancel search: weightPage 91 of 200

The importance of shoulder belts
Using a booster without a shoulder belt increases the risk of a child’s
head hitting a hard surface in a collision. For this reason, you should
never use a booster seat with a lap belt only. It is best to use a booster
seat with lap/shoulder belts in the back seat- the safest place for children
to ride.
Follow all instructions provided by the manufacturer of the
booster seat.
Never put the shoulder belt under a child’s arm or behind the
back because it eliminates the protection for the upper part of
the body and may increase the risk of injury or death in a collision.
Never use pillows, books, or towels to boost a child. They can
slide around and increase the likelihood of injury or death in a
collision.
SAFETY SEATS FOR CHILDREN
Child and infant or child safety seats
Use a safety seat that is recommended for the size and weight of the
child. Carefully follow all of the manufacturer’s instructions with the
safety seat you put in your vehicle. If you do not install and use the
safety seat properly, the child may be injured in a sudden stop or
collision.
Seating and Safety Restraints
91
Page 116 of 200

Brakessection of this chapter for additional information on the
operation of the anti-lock brake system. If your vehicle is not equipped
with ABS, use a“squeeze”braking technique. Push on the brake pedal
with a steadily increasing force which allows the wheels to brake yet
continue to roll so that you may steer in the direction you want to travel.
If you lock the wheels, release the brake pedal and repeat the squeeze
technique.
Never drive with chains on the front tires of 4WD vehicles without also
putting them on the rear tires. This could cause the rear to slide and
swing around during braking.
Maintenance and Modifications
Ford strongly recommends that you do not add or removing steering or
suspension parts (such as lift kits or stabilizer bars) or by using
replacement parts not equivalent to the original factory equipment. Do
not use aftermarket“lift kits”or other suspension modifications. These
could adversely affect the vehicle’s handling characteristics, which could
lead to loss of vehicle control or roll over and serious injury. Frequent
inspection of vehicle chassis components is recommended if the vehicle
is subjected to heavy off-road usage.
DRIVING THROUGH WATER
If driving through deep or standing water is unavoidable, proceed very
slowly especially if the depth is not known. Never drive through water
that is higher than the bottom of the hubs (for trucks) or the bottom of
the wheel rims (for cars). Traction or brake capability may be limited
and your vehicle may stall. Water may also enter your engine’s air intake
and severely damage your engine.
Once through the water, always dry the brakes by moving your vehicle
slowly while applying light pressure on the brake pedal. Wet brakes do
not stop the vehicle as quickly as dry brakes.Driving through deep
water where the transmission vent tube is submerged may allow
water into the transmission and cause internal transmission
damage.
VEHICLE LOADING
Before loading a vehicle, familiarize yourself with the following terms:
•Base Curb Weight:Weight of the vehicle including any standard
equipment, fluids, lubricants, etc. It does not include occupants or
aftermarket equipment.
•Payload:Combined maximum allowable weight of cargo, occupants
and optional equipment. The payload equals the gross vehicle weight
rating minus base curb weight.
Driving
116
Page 117 of 200

•GVW (Gross Vehicle Weight):Base curb weight plus payload
weight.
•GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating):Maximum allowable total
weight of the base vehicle, occupants, optional equipment and cargo.
The GVWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the Safety
Certification Label on the driver’s door pillar.
•GAWR (Gross Axle Weight Rating):Carrying capacity for each axle
system. The GAWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the
Safety Certification Label on the driver’s door pillar.
•GCW (Gross Combined Weight):The combined weight of the
towing vehicle (including occupants and cargo) and the loaded trailer.
•GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating):Maximum allowable
combined weight of towing vehicle (including occupants and cargo)
and the loaded trailer
•Maximum Trailer Weight Rating:Maximum weight of a trailer the
vehicle is permitted to tow. The maximum trailer weight rating is
determined by subtracting the vehicle curb weight for each
engine/transmission combination, any required option weight for trailer
towing and the weight of the driver from the GCWR for the towing
vehicle.
•Maximum Trailer Weight:Maximum weight of a trailer the loaded
vehicle, including occupants and cargo, is permitted to tow. It is
determined by subtracting the weight of the loaded trailer towing
vehicle from the GCWR for the towing vehicle.
•Trailer Weight Range:Specified range of trailer weight from zero to
the maximum trailer weight rating.
Remember to figure in the tongue load of your loaded trailer when
figuring the total weight.
The Safety Certification Label, located on the driver’s door pillar, lists
vehicle weight rating limitations. Before adding any additional equipment,
refer to these limitations.
Always ensure that the weight of occupants, cargo and equipment is
within the weight limitations, including both gross vehicle weight and
front and rear gross axle weight rating limits.
Note:Do not exceed the GVWR or the GAWR specified on the
certification label.
Driving
117
Page 118 of 200

Exceeding any vehicle weight rating limitation could result in
serious damage to the vehicle loss of vehicle control, vehicle
rollover, and/or personal injury.
Do not use replacement tires with lower load carrying capacities than the
originals because they may lower the vehicle’s GVWR and GAWR
limitations. Replacement tires with a higher limit than the originals do
not increase the GVWR and GAWR limitations.
Special loading instructions for owners of pickup trucks and
utility-type vehicles
For important information regarding safe operation of this type
of vehicle, see thePreparing to drive your vehiclesection in
this chapter.
Loaded vehicles may handle differently than unloaded vehicles.
Extra precautions, such as slower speeds and increased stopping
distance, should be taken when driving a heavily loaded vehicle.
Your vehicle can haul more cargo and people than most passenger cars.
Depending upon the type and placement of the load, hauling cargo and
people may raise the center of gravity of the vehicle.
Calculating the load your vehicle can carry/tow
1. Use the appropriate maximum GCWR chart (in theTrailer Towing
section in this chapter) for your type of engine and rear axle ratio.
2. Weigh your vehicle without cargo. To obtain correct weights, take your
vehicle to a shipping company or an inspection station for trucks.
3. Subtract your loaded weight from the maximum GCWR in the chart.
This is the maximum trailer weight your vehicle can tow. It must be
below the maximum trailer weight shown in the chart.
TRAILER TOWING
Trailer towing with your vehicle may require the use of a trailer tow
option package.
Trailer towing puts additional loads on your vehicle’s engine,
transmission, axle, brakes, tires, and suspension. For your safety and to
maximize vehicle performance, be sure to use the proper equipment
while towing.
Driving
118
Page 119 of 200
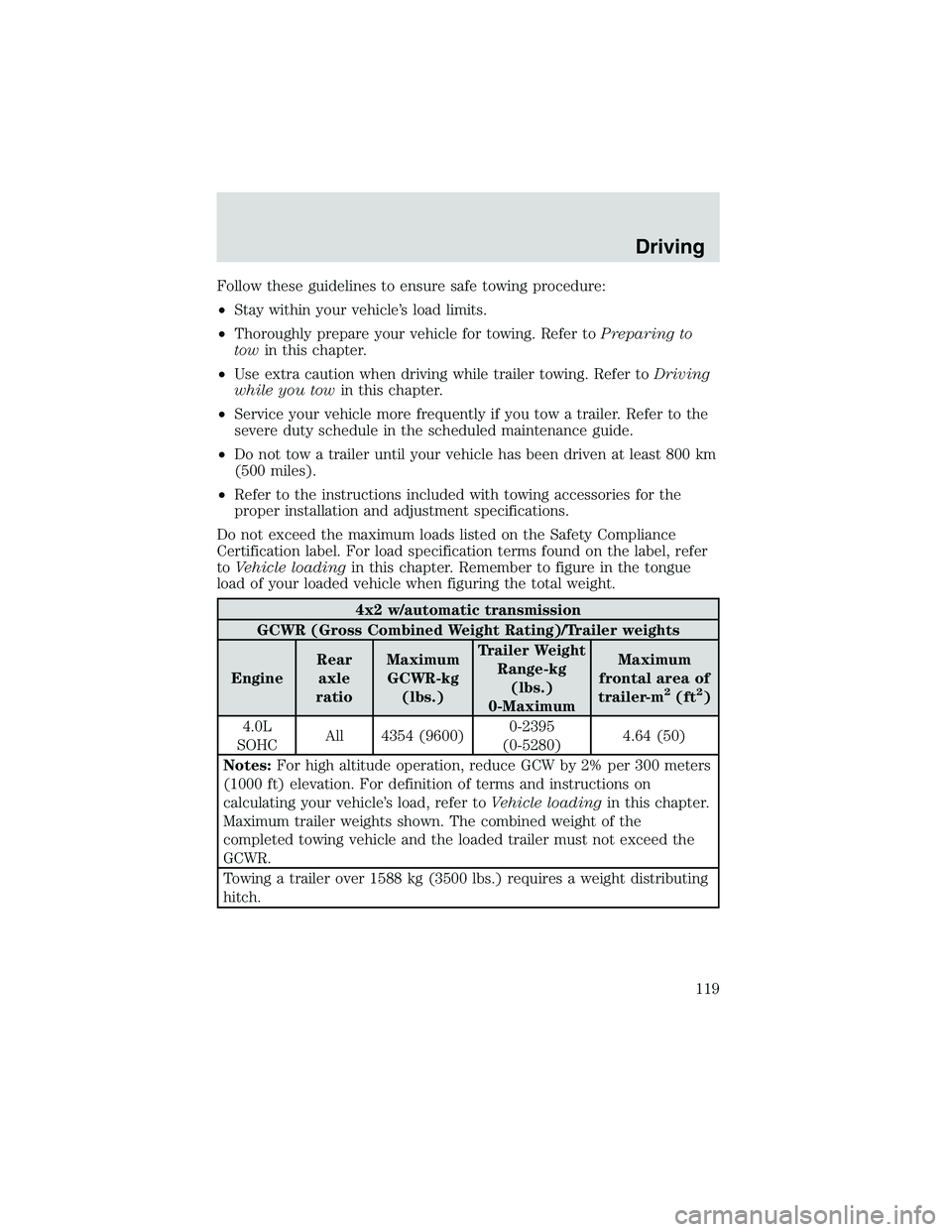
Follow these guidelines to ensure safe towing procedure:
•Stay within your vehicle’s load limits.
•Thoroughly prepare your vehicle for towing. Refer toPreparing to
towin this chapter.
•Use extra caution when driving while trailer towing. Refer toDriving
while you towin this chapter.
•Service your vehicle more frequently if you tow a trailer. Refer to the
severe duty schedule in the scheduled maintenance guide.
•Do not tow a trailer until your vehicle has been driven at least 800 km
(500 miles).
•Refer to the instructions included with towing accessories for the
proper installation and adjustment specifications.
Do not exceed the maximum loads listed on the Safety Compliance
Certification label. For load specification terms found on the label, refer
toVehicle loadingin this chapter. Remember to figure in the tongue
load of your loaded vehicle when figuring the total weight.
4x2 w/automatic transmission
GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating)/Trailer weights
EngineRear
axle
ratioMaximum
GCWR-kg
(lbs.)Trailer Weight
Range-kg
(lbs.)
0-MaximumMaximum
frontal area of
trailer-m
2(ft2)
4.0L
SOHCAll 4354 (9600)0-2395
(0-5280)4.64 (50)
Notes:For high altitude operation, reduce GCW by 2% per 300 meters
(1000 ft) elevation. For definition of terms and instructions on
calculating your vehicle’s load, refer toVehicle loadingin this chapter.
Maximum trailer weights shown. The combined weight of the
completed towing vehicle and the loaded trailer must not exceed the
GCWR.
Towing a trailer over 1588 kg (3500 lbs.) requires a weight distributing
hitch.
Driving
119
Page 120 of 200
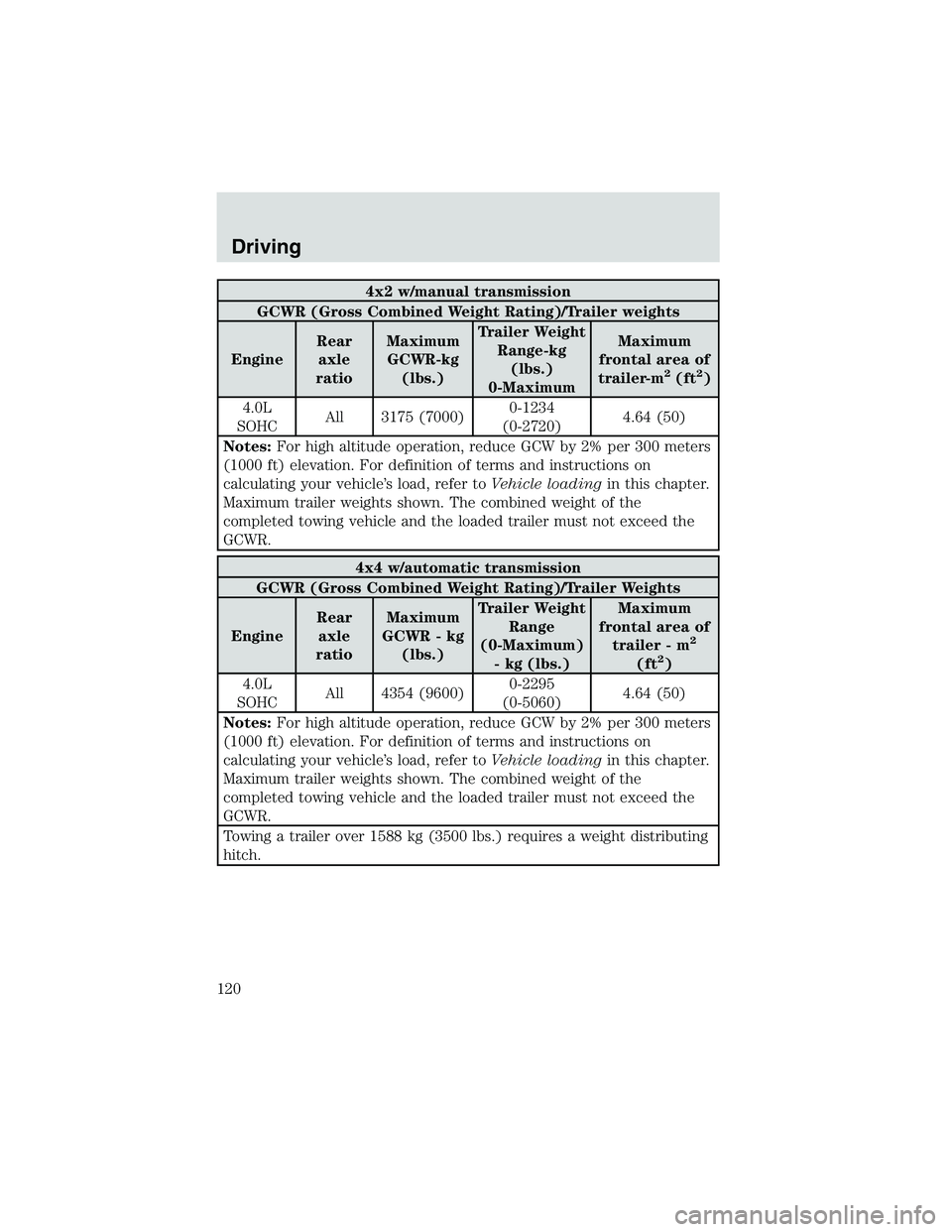
4x2 w/manual transmission
GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating)/Trailer weights
EngineRear
axle
ratioMaximum
GCWR-kg
(lbs.)Trailer Weight
Range-kg
(lbs.)
0-MaximumMaximum
frontal area of
trailer-m
2(ft2)
4.0L
SOHCAll 3175 (7000)0-1234
(0-2720)4.64 (50)
Notes:For high altitude operation, reduce GCW by 2% per 300 meters
(1000 ft) elevation. For definition of terms and instructions on
calculating your vehicle’s load, refer toVehicle loadingin this chapter.
Maximum trailer weights shown. The combined weight of the
completed towing vehicle and the loaded trailer must not exceed the
GCWR.
4x4 w/automatic transmission
GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating)/Trailer Weights
EngineRear
axle
ratioMaximum
GCWR - kg
(lbs.)Trailer Weight
Range
(0-Maximum)
- kg (lbs.)Maximum
frontal area of
trailer - m
2
(ft2)
4.0L
SOHCAll 4354 (9600)0-2295
(0-5060)4.64 (50)
Notes:For high altitude operation, reduce GCW by 2% per 300 meters
(1000 ft) elevation. For definition of terms and instructions on
calculating your vehicle’s load, refer toVehicle loadingin this chapter.
Maximum trailer weights shown. The combined weight of the
completed towing vehicle and the loaded trailer must not exceed the
GCWR.
Towing a trailer over 1588 kg (3500 lbs.) requires a weight distributing
hitch.
Driving
120
Page 121 of 200
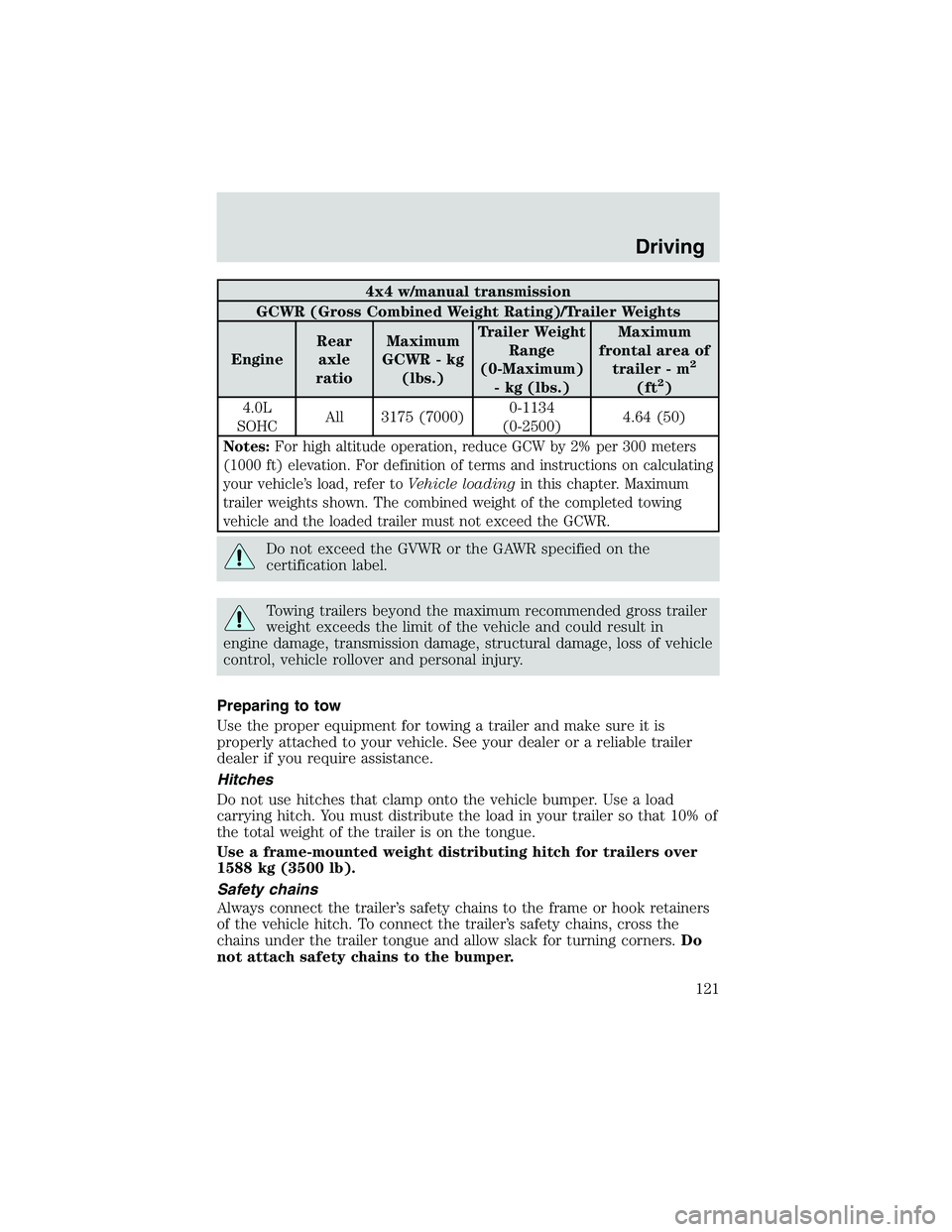
4x4 w/manual transmission
GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating)/Trailer Weights
EngineRear
axle
ratioMaximum
GCWR - kg
(lbs.)Trailer Weight
Range
(0-Maximum)
- kg (lbs.)Maximum
frontal area of
trailer - m
2
(ft2)
4.0L
SOHCAll 3175 (7000)0-1134
(0-2500)4.64 (50)
Notes:For high altitude operation, reduce GCW by 2% per 300 meters
(1000 ft) elevation. For definition of terms and instructions on calculating
your vehicle’s load, refer toVehicle loadingin this chapter. Maximum
trailer weights shown. The combined weight of the completed towing
vehicle and the loaded trailer must not exceed the GCWR.
Do not exceed the GVWR or the GAWR specified on the
certification label.
Towing trailers beyond the maximum recommended gross trailer
weight exceeds the limit of the vehicle and could result in
engine damage, transmission damage, structural damage, loss of vehicle
control, vehicle rollover and personal injury.
Preparing to tow
Use the proper equipment for towing a trailer and make sure it is
properly attached to your vehicle. See your dealer or a reliable trailer
dealer if you require assistance.
Hitches
Do not use hitches that clamp onto the vehicle bumper. Use a load
carrying hitch. You must distribute the load in your trailer so that 10% of
the total weight of the trailer is on the tongue.
Use a frame-mounted weight distributing hitch for trailers over
1588 kg (3500 lb).
Safety chains
Always connect the trailer’s safety chains to the frame or hook retainers
of the vehicle hitch. To connect the trailer’s safety chains, cross the
chains under the trailer tongue and allow slack for turning corners.Do
not attach safety chains to the bumper.
Driving
121
Page 122 of 200

Trailer brakes
Electric brakes and manual, automatic or surge-type trailer brakes are
safe if installed properly and adjusted to the manufacturer’s
specifications.
Do not connect a trailer’s hydraulic brake system directly to your
vehicle’s brake system. Your vehicle may not have enough
braking power and your chances of having a collision greatly increase.
The braking system of the towing vehicle is rated for operation at the
GVWR not GCWR.
Trailer lamps
Make sure your trailer lamps conform to local and Federal regulations.
See your dealer or trailer rental agency for proper instructions and
equipment for hooking up trailer lamps.
Never connect any trailer lighting to the vehicle’s taillamp
circuits, because it may damage the electrical system resulting in
fire. Contact your local Ford dealership for assistance in proper trailer
tow wiring installation. Additional electrical equipment may be
required.
Using a step bumper
The rear bumper is equipped with an integral hitch and requires only a
ball with a 19 mm (3/4 inch) shank diameter. The bumper has a 1,590 kg
(3,500 lb.) trailer weight and 159 kg (350 lb.) tongue weight capability.
Use a frame-mounted weight distributing hitch for trailers over 1,590 kg
(3,500 lb).
Driving while you tow
When towing a trailer:
•Turn off your speed control. The speed control may shut off
automatically when you are towing on long, steep grades.
•Consult your local motor vehicle speed regulations for towing a trailer.
•Use a lower gear when towing up or down steep hills.
•Anticipate stops and brake gradually.
Servicing after towing
If you tow a trailer for long distances, your vehicle will require more
frequent service intervals. Refer to your scheduled maintenance guide for
more information.
Driving
122