2002 FORD EXPLORER rear
[x] Cancel search: rearPage 183 of 312

Understanding gearshift positions
Hold the brake pedal down while you move the gearshift lever
from P (Park) to another position. If you do not hold the brake
pedal down, your vehicle may move unexpectedly and injure someone.
P (Park)
To put your vehicle in gear, start the engine, depress the brake pedal,
then move gearshift lever out of P (Park).
Always come to a complete stop
before shifting into P (Park). Make
sure the gearshift lever is securely
latched in P (Park). This position locks the transmission and prevents
the rear wheels from turning.
Always set the parking brake fully and make sure the gearshift is
latched in P (Park). Turn off the ignition whenever you leave
your vehicle.
R (Reverse)
With the gearshift lever in R
(Reverse), the vehicle will move
backward. Always come to a
complete stop before shifting into and out of R (Reverse).
N (Neutral)
With the gearshift lever in N
(Neutral), the vehicle can be started
and is free to roll. Hold the brake
pedal down while in this position.
D (Overdrive)
(Overdrive) can be deactivated by
pressing the transmission control
switch on the end of the gearshift
lever.
O/D OFF
Driving
183
Page 188 of 312

4x4 High and 4x4 Low operation is not recommended on dry
pavement. Doing so could result in difficult disengagement of the
transfer case, increased tire wear and decreased fuel economy.
Control-Trac automatic four-wheel drive system (if equipped)
The 4WD system uses all four wheels to power the vehicle. This
increases traction, enabling you to drive your 4x4 over terrain and road
conditions not normally traveled by two-wheel drive vehicles.
Power is supplied to all four wheels through a transfer case that allows
you to select a four-wheel drive mode best suited for your current
driving conditions.
Positions of the Control-Trac system
The Control-Trac system functions in three modes:
²The 4x4 Auto mode provides
four-wheel drive with full power
delivered to the rear axle, and to
the front axle as required for
increased traction. This is
appropriate for normal on-road
operating conditions, such as dry
road surfaces, wet pavement,
snow and gravel.
4X4
Low4X4
High4X4
Auto
Driving
188
Page 193 of 312

Water intrusion into the transmission may damage the transmission.
If the rear axle is submerged in water, the rear axle lubricant should be
checked and changed, if necessary. The rear axle is filled with a
synthetic lubricant and does not normally require a lubricant change for
the life of the vehicle. Rear axle lubricant quantities should not need to
be checked unless a leak is suspected.
Driving on hilly or sloping terrain
When driving on a hill, avoid driving crosswise or turning on steep
slopes. You could lose traction and slip sideways. Drive straight up,
straight down or avoid the hill completely. Know the conditions on the
other side of a hill before driving over the crest.
When climbing a steep hill, start in a lower gear rather than downshifting
to a lower gear from a higher gear once the ascent has started. This
reduces the strain on the engine.
When descending a steep hill, avoid sudden braking. Shift to a lower gear
when added engine braking is desired.
When speed control is on and you are driving uphill, your vehicle speed
may drop considerably, especially if you are carrying a heavy load.
If vehicle speed drops more than 16 km/h (10 mph), the speed control
will cancel automatically. Resume speed with accelerator pedal.
If speed control cancels after climbing the hill, reset speed by pressing and
holding the SET ACCEL button (to resume speeds over 50 km/h (30 mph).
Automatic transmissions may shift frequently while driving up steep
grades. Eliminate frequent shifting by shifting out ofD(Overdrive) into
D (Drive).
Driving on snow and ice
A 4WD vehicle has advantages over 2WD vehicles in snow and ice but
can skid like any other vehicle.
Avoid sudden applications of power and quick changes of direction on
snow and ice. Apply the accelerator slowly and steadily when starting
from a full stop.
When braking, apply the brakes as you normally would. In order to allow
the anti-lock brake system (ABS) to operate properly, keep steady
pressure on the brake pedal.
Allow more stopping distance and drive slower than usual. Consider
using one of the lower gears.
Driving
193
Page 194 of 312

TRACTION-LOK AXLE (IF EQUIPPED)
This axle provides added traction on slippery surfaces, particularly when
one wheel is on a poor traction surface. Under normal conditions, the
Traction-Lok axle functions like a standard rear axle.
Extended use of other than the manufacturer's specified size tires on a
Traction-Lok rear axle could result in a permanent reduction in
effectiveness. This loss of effectiveness does not affect normal driving
and should not be noticeable to the driver.
To avoid injury, never run the engine with one wheel off the
ground, such as when changing a tire.
VEHICLE LOADING
Before loading a vehicle, familiarize yourself with the following terms:
²Base Curb Weight:Weight of the vehicle including any standard
equipment, fluids, lubricants, etc. It does not include passengers or
aftermarket equipment.
²Payload:Combined maximum allowable weight of cargo, passengers
and optional equipment. The payload equals the gross vehicle weight
rating minus base curb weight.
²GVW (Gross Vehicle Weight):Base curb weight plus payload
weight. The GVW is not a limit or a specification.
²GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating):Maximum total weight of
the base vehicle, passengers, optional equipment and cargo. The
GVWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the Safety
Certification Label on the driver's door pillar.
²GAWR (Gross Axle Weight Rating):Carrying capacity for each axle
system. The GAWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the
Safety Certification Label on the driver's door pillar.
²GCW (Gross Combined Weight):The combined weight of the
towing vehicle (including passengers and cargo) and the trailer.
²GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating):Maximum combined
weight of towing vehicle (including passengers and cargo) and the
trailer. The GCWR indicates the maximum loaded weight that the
vehicle is designed to tow.
Driving
194
Page 195 of 312

²Maximum Trailer Weight Rating:Maximum weight of a trailer the
vehicle is permitted to tow. The maximum trailer weight rating is
determined by subtracting the vehicle curb weight for each
engine/transmission combination, any required option weight for trailer
towing and the weight of the driver from the GCWR for the towing
vehicle.
²Maximum Trailer Weight:Maximum weight of a trailer the loaded
vehicle (including passengers and cargo) is permitted to tow. It is
determined by subtracting the weight of the loaded trailer towing
vehicle from the GCWR for the towing vehicle.
²Trailer Weight Range:Specified weight range that the trailer must
fall within that ranges from zero to the maximum trailer weight rating.
Remember to figure in the tongue load of your loaded trailer when
figuring the total weight.
Do not exceed the GVWR or the GAWR specified on the
certification label.
Do not use replacement tires with lower load carrying capacities than the
originals because they may lower the vehicle's GVWR and GAWR
limitations. Replacement tires with a higher limit than the originals do
not increase the GVWR and GAWR limitations.
The Safety Certification Label, found on the driver's door pillar, lists
several important vehicle weight rating limitations. Before adding any
additional equipment, refer to these limitations. If you are adding weight
to the front of your vehicle, (potentially including weight added to the
cab), the weight added should not exceed the front gross axle weight
rating (FGAWR). Additional frontal weight may be added to the front
axle reserve capacity provided you limit your payload in other ways (i.e.
restrict the number of passengers or amount of cargo carried).
Always ensure that the weight of passengers, cargo and equipment being
carried is within the weight limitations that have been established for
your vehicle including both gross vehicle weight and Front and rear
gross axle weight rating limits. Under no circumstance should these
limitations be exceeded. Exceeding any vehicle weight rating limitation
could result in serious damage to the vehicle and/or personal injury.
Driving
195
Page 196 of 312

Special loading instructions for owners of pickup trucks and
utility-type vehicles
For important information regarding safe operation of this type
of vehicle, see thePreparing to drive your vehiclesection in
theDrivingchapter of this owner guide.
Loaded vehicles, with a higher center of gravity, may handle
differently than unloaded vehicles. Extra precautions, such as
slower speeds and increased stopping distance, should be taken when
driving a heavily loaded vehicle.
Your vehicle has the capability to haul more cargo and people than most
passenger cars. Depending upon the type and placement of the load,
hauling cargo and people may raise the center of gravity of the vehicle.
Calculating the load your vehicle can carry/tow
1. Use the appropriate maximum gross combined weight rating (GCWR)
chart to find the maximum GCWR for your type engine and rear axle
ratio.
2. Weigh your vehicle as you customarily operate the vehicle without
cargo. To obtain correct weights, try taking your vehicle to a shipping
company or an inspection station for trucks.
3. Subtract your loaded vehicle weight from the maximum GCWR on the
following charts. This is the maximum trailer weight your vehicle can tow
and must fall below the maximum shown under maximum trailer weight
on the chart.
DRIVING THROUGH WATER
Do not drive quickly through standing water, especially if the depth is
unknown. Traction or brake capability may be limited and if the ignition
system gets wet, your engine may stall. Water may also enter your
engine's air intake and severely damage your engine.
If driving through deep or standing water is unavoidable, proceed very
slowly. Never drive through water that is higher than the bottom of the
hubs (for trucks) or the bottom of the wheel rims (for cars).
Once through the water, always try the brakes. Wet brakes do not stop the
vehicle as effectively as dry brakes. Drying can be improved by moving
your vehicle slowly while applying light pressure on the brake pedal.
Driving
196
Page 198 of 312
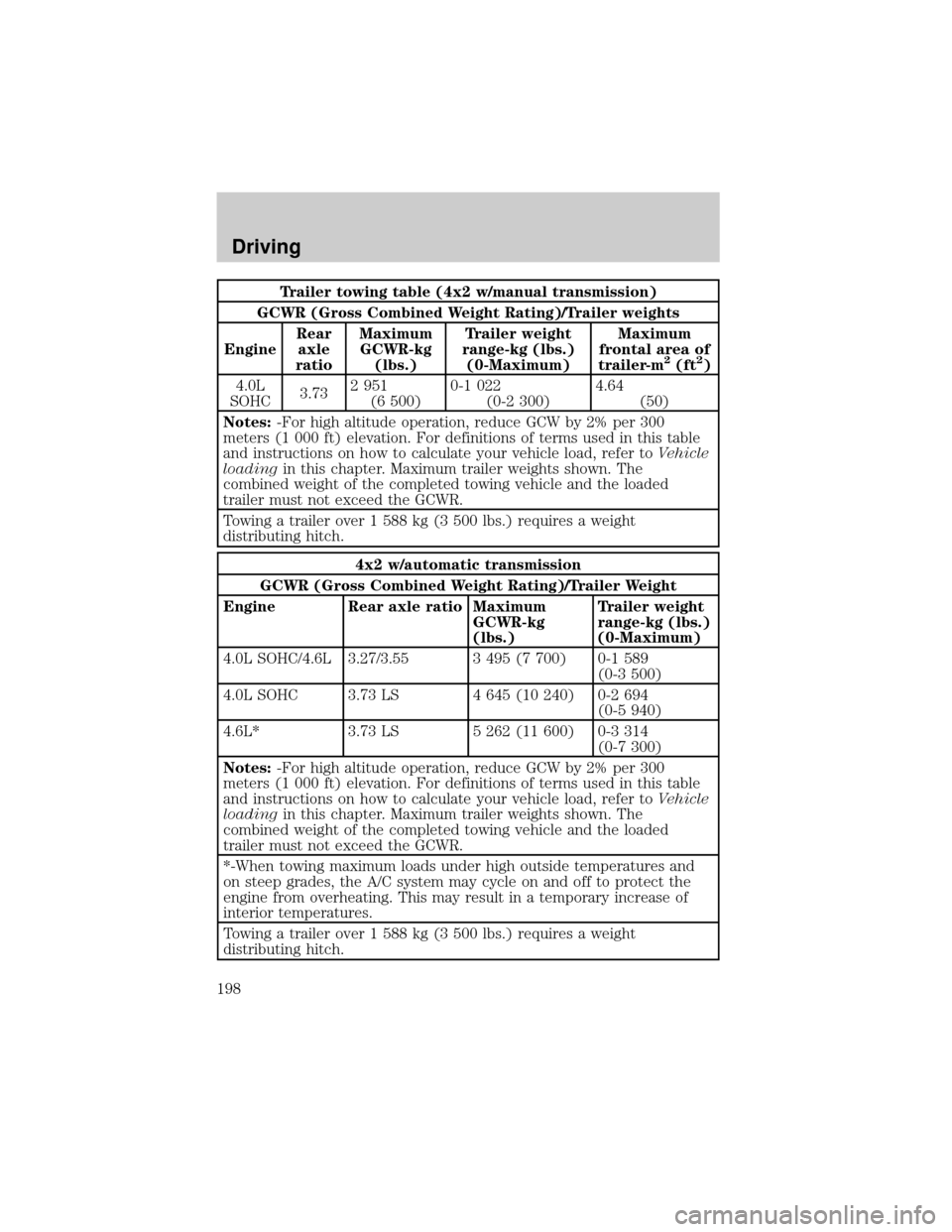
Trailer towing table (4x2 w/manual transmission)
GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating)/Trailer weights
EngineRear
axle
ratioMaximum
GCWR-kg
(lbs.)Trailer weight
range-kg (lbs.)
(0-Maximum)Maximum
frontal area of
trailer-m
2(ft2)
4.0L
SOHC3.732 951
(6 500)0-1 022
(0-2 300)4.64
(50)
Notes:-For high altitude operation, reduce GCW by 2% per 300
meters (1 000 ft) elevation. For definitions of terms used in this table
and instructions on how to calculate your vehicle load, refer toVehicle
loadingin this chapter. Maximum trailer weights shown. The
combined weight of the completed towing vehicle and the loaded
trailer must not exceed the GCWR.
Towing a trailer over 1 588 kg (3 500 lbs.) requires a weight
distributing hitch.
4x2 w/automatic transmission
GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating)/Trailer Weight
Engine Rear axle ratio Maximum
GCWR-kg
(lbs.)Trailer weight
range-kg (lbs.)
(0-Maximum)
4.0L SOHC/4.6L 3.27/3.55 3 495 (7 700) 0-1 589
(0-3 500)
4.0L SOHC 3.73 LS 4 645 (10 240) 0-2 694
(0-5 940)
4.6L* 3.73 LS 5 262 (11 600) 0-3 314
(0-7 300)
Notes:-For high altitude operation, reduce GCW by 2% per 300
meters (1 000 ft) elevation. For definitions of terms used in this table
and instructions on how to calculate your vehicle load, refer toVehicle
loadingin this chapter. Maximum trailer weights shown. The
combined weight of the completed towing vehicle and the loaded
trailer must not exceed the GCWR.
*-When towing maximum loads under high outside temperatures and
on steep grades, the A/C system may cycle on and off to protect the
engine from overheating. This may result in a temporary increase of
interior temperatures.
Towing a trailer over 1 588 kg (3 500 lbs.) requires a weight
distributing hitch.
Driving
198
Page 199 of 312
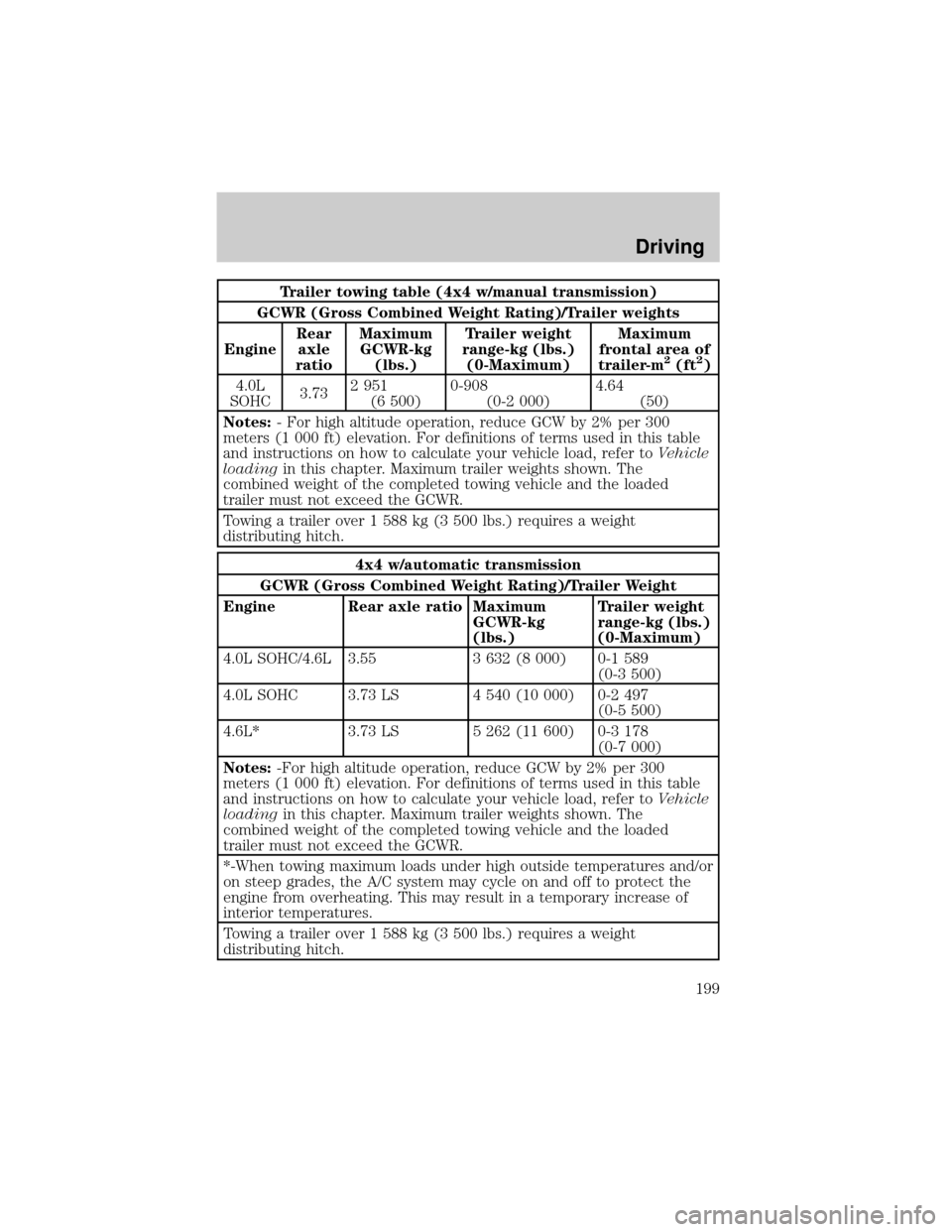
Trailer towing table (4x4 w/manual transmission)
GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating)/Trailer weights
EngineRear
axle
ratioMaximum
GCWR-kg
(lbs.)Trailer weight
range-kg (lbs.)
(0-Maximum)Maximum
frontal area of
trailer-m
2(ft2)
4.0L
SOHC3.732 951
(6 500)0-908
(0-2 000)4.64
(50)
Notes:- For high altitude operation, reduce GCW by 2% per 300
meters (1 000 ft) elevation. For definitions of terms used in this table
and instructions on how to calculate your vehicle load, refer toVehicle
loadingin this chapter. Maximum trailer weights shown. The
combined weight of the completed towing vehicle and the loaded
trailer must not exceed the GCWR.
Towing a trailer over 1 588 kg (3 500 lbs.) requires a weight
distributing hitch.
4x4 w/automatic transmission
GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating)/Trailer Weight
Engine Rear axle ratio Maximum
GCWR-kg
(lbs.)Trailer weight
range-kg (lbs.)
(0-Maximum)
4.0L SOHC/4.6L 3.55 3 632 (8 000) 0-1 589
(0-3 500)
4.0L SOHC 3.73 LS 4 540 (10 000) 0-2 497
(0-5 500)
4.6L* 3.73 LS 5 262 (11 600) 0-3 178
(0-7 000)
Notes:-For high altitude operation, reduce GCW by 2% per 300
meters (1 000 ft) elevation. For definitions of terms used in this table
and instructions on how to calculate your vehicle load, refer toVehicle
loadingin this chapter. Maximum trailer weights shown. The
combined weight of the completed towing vehicle and the loaded
trailer must not exceed the GCWR.
*-When towing maximum loads under high outside temperatures and/or
on steep grades, the A/C system may cycle on and off to protect the
engine from overheating. This may result in a temporary increase of
interior temperatures.
Towing a trailer over 1 588 kg (3 500 lbs.) requires a weight
distributing hitch.
Driving
199