2002 DODGE RAM ac compressor
[x] Cancel search: ac compressorPage 1281 of 2255

(4) Connect the DRBIIItto the pressure trans-
ducer following the instructions supplied with the
DRB IIIt.
(5) Enter DRBIIItinto pressure reading mode and
test drive vehicle.
(6) The turbocharger boost pressure must be
between 110 - 138 kpa (16 - 20 psi.). If pressure read-
ings are lower than 110 kpa (16 psi.) inspect for the
following:
²Restricted air inlet system
²Leak in the charge air cooler system (Refer to 11
- EXHAUST SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM/
CHARGE AIR COOLER AND PLUMBING - DIAG-
NOSIS AND TESTING)
²Turbocharger wastegate broken or misadjusted
²Turbocharger damaged (Refer to 11 - EXHAUST
SYSTEM/TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM/TURBO-
CHARGER - INSPECTION)
TURBOCHARGER
DESCRIPTION
The turbocharger is an exhaust-driven super-
charger which increases the pressure and density of
the air entering the engine. With the increase of air
entering the engine, more fuel can be injected into
the cylinders, which creates more power during com-
bustion.
The turbocharger assembly consists of four (4)
major component systems (Fig. 19) (Fig. 20) :
²Turbine section
²Compressor section
²Bearing housing
²Wastegate
OPERATION
Exhaust gas pressure and energy drive the tur-
bine, which in turn drives a centrifugal compressor
that compresses the inlet air, and forces the air into
the engine through the charge air cooler and plumb-
ing. Since heat is a by-product of this compression,
the air must pass through a charge air cooler to cool
the incoming air and maintain power and efficiency.
Increasing air flow to the engine provides:
²Improved engine performance
²Lower exhaust smoke density
²Improved operating economy
²Altitude compensation
²Noise reduction.
The turbocharger also uses a wastegate (Fig. 21) ,
which regulates intake manifold air pressure and
prevents over boosting at high engine speeds. When
the wastegate valve is closed, all of the exhaust gases
flow through the turbine wheel. As the intake mani-
fold pressure increases, the wastegate actuator opensthe valve, diverting some of the exhaust gases away
from the turbine wheel. This limits turbine shaft
speed and air output from the impeller.
Fig. 19 Turbocharger Operation
1 - TURBINE SECTION
2 - EXHAUST GAS
3 - BEARING HOUSING
4 - COMPRESSOR SECTION
5 - INLET AIR
6 - COMPRESSED AIR TO ENGINE
7 - EXHAUST GAS
8 - EXHAUST GAS TO EXHAUST PIPE
Fig. 20 Turbocharger Wastegate Actuator
1 - TURBOCHARGER
2 - DIAPHRAGM
3 - WASTE GATE ACTUATOR
11 - 14 EXHAUST SYSTEMBR/BE
TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 1283 of 2255

CAUTION: The turbocharger is only serviced as an
assembly. Do not attempt to repair the turbocharger
as turbocharger and/or engine damage can result.
CLEANING
Clean the turbocharger and exhaust manifold
mounting surfaces with a suitable scraper.
INSPECTION
Visually inspect the turbocharger and exhaust
manifold gasket surfaces. Replace stripped or eroded
mounting studs.
(1) Visually inspect the turbocharger for cracks.
The following cracks are NOT acceptable:
²Cracks in the turbine and compressor housing
that go completely through.
²Cracks in the mounting flange that are longer
than 15 mm (0.6 in.).
²Cracks in the mounting flange that intersect
bolt through-holes.
²Two (2) Cracks in the mounting flange that are
closer than 6.4 mm (0.25 in.) together.
(2) Visually inspect the impeller and compressor
wheel fins for nicks, cracks, or chips. Note: Some
impellers may have a factory placed paint mark
which, after normal operation, appears to be a crack.
Remove this mark with a suitable solvent to verify
that it is not a crack.
(3) Visually inspect the turbocharger compressor
housing for an impeller rubbing condition (Fig. 26).
Replace the turbocharger if the condition exists.
(4) Measure the turbocharger axial end play:
(a) Install a dial indicator as shown in (Fig. 27).
Zero the indicator at one end of travel.
Fig. 23 Exhaust Pipe Removal/Installation
1 - EXHAUST PIPE
2 - TURBOCHARGER EXHAUST PIPE
Fig. 24 Turbocharger Air Inlet Hose
1 - AIR FILTER HOUSING COVER
2 - TURBOCHARGER
3 - AIR INLET TUBE
4 - HOSE CLAMP
5 - HINGE TABS
6 - FILTER MINDER
7 - CLIPS (4)
8 - TUBE ALIGNMENT NOTCHES
Fig. 25 Oil Supply Line and Charge Air Cooler Inlet
Duct
1 - EXHAUST PIPE
2 - TURBOCHARGER
3 - AIR INLET TUBE
4 - COOLER INLET DUCT
11 - 16 EXHAUST SYSTEMBR/BE
TURBOCHARGER (Continued)
Page 1284 of 2255

(b) Move the impeller shaft fore and aft and
record the measurement. Allowable end play is
0.038 mm (0.0015 in.) MIN. and 0.089 mm (0.0035
in.) MAX. If the recorded measurement falls out-
side these parameters, replace the turbocharger
assembly.
(5) Measure the turbocharger bearing radial clear-
ance:
(a) Insert a narrow blade or wire style feeler
gauge between the compressor wheel and the hous-
ing (Fig. 28).
(b) Gently push the compresser wheel toward
the housing and record the clearance.
(c) With the feeler gauge in the same location,
gently push the compressor wheel away from the
housing and again record the clearance.
(d) Subtract the smaller clearance from the
larger clearance. This is the radial bearing clear-
ance.
(e) Allowable radial bearing clearance is 0.326
mm (0.0128 in.) MIN. and 0.496 mm (0.0195 in.)
MAX. If the recorded measurement falls outside
these specifications, replace the turbocharger assy.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the turbocharger. Apply anti-seize to the
studs and then tighten the turbocharger mounting
nuts to 32 N´m (24 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install the oil drain tube and oil supply line to
the turbocharger (Fig. 25). Tighten the drain tube
bolts to 24 N´m (18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3)Pre-lube the turbocharger.Pour 50 to 60 cc
(2 to 3 oz.) clean engine oil in the oil supply line fit-
ting. Carefully rotate the turbocharger impeller by
hand to distribute the oil thoroughly.
(4) Install and tighten the oil supply line fitting
nut to 20 N´m (133 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Position the charge air cooler inlet pipe to the
turbocharger. With the clamp in position, tighten the
clamp nut to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Position the air inlet hose to the turbocharger
(Fig. 24). Tighten the clamp to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.)
torque.
(7) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(8) Connect the exhaust pipe to the turbocharger
(Fig. 23) and tighten the bolts to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(9) Lower the vehicle.
(10) Connect the battery negative cables.
(11) Start the engine to check for leaks.
Fig. 26 Inspect Compressor Housing for Impeller
Rubbing Condition
Fig. 27 Measure Turbocharger Axial End Play
Fig. 28 Measure Turbocharger Bearing Radial
Clearance
1 - FEELER GAUGE
BR/BEEXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 17
TURBOCHARGER (Continued)
Page 1285 of 2255

CHARGE AIR COOLER AND
PLUMBING
DESCRIPTION
The charge air system (Fig. 29) consists of the
charge air cooler piping, charge air cooler and intake
air grid heater.
The charge air cooler is a heat exchanger that uses
air flow from vehicle motion to dissipate heat from
the intake air. As the turbocharger increases air
pressure, the air temperature increases. Lowering
the intake air temperature increases engine effi-
ciency and power.
OPERATION
Intake air is drawn through the air cleaner and
into the turbocharger compressor housing. Pressur-
ized air from the turbocharger then flows forward
through the charge air cooler located in front of the
radiator. From the charge air cooler the air flows
back into the intake manifold.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHARGE AIR
COOLER SYSTEM - LEAKS
Low turbocharger boost pressure and low engine
preformance can be caused by leaks in the charge air
cooler or it's plumbing. The following procedure out-
lines how to check for leaks in the charge air cooler
system.(1) Loosen clamp and remove turbocharger to air
inlet duct rubber sleeve from turbocharger (Fig. 30).
(2) Insert Special Tool 8442 Adapter into the rub-
ber sleeve. Tighten existing clamp to 8 N´m (72
in.lbs.).
CAUTION: Do not apply more than 138 kpa (20 psi)
air pressure to the charge air cooler system, sever
damage to the charge air cooler system may occur.
(3) Connect regulated air supply to air fitting on
Special Tool 8442 Adapter. Set air pressure to a Max-
imum of 138 kpa (20 psi).
(4) Using soapy water check the air inlet ducts,
rubber sleeves, charge air cooler and intake manifold
for leaks.
REMOVAL
WARNING: IF THE ENGINE WAS JUST TURNED
OFF, THE AIR INTAKE SYSTEM TUBES MAY BE
HOT.
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cables.
(2) Remove the front bumper (Refer to 13 -
FRAMES & BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT
BUMPER - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the front support bracket.
Fig. 29 Intake Air Circulation
1 - CHARGE AIR COOLER
2 - AIRFILTER
3 - TURBOCHARGER
Fig. 30 AIR INLET DUCT RUBBER SLEEVE
1 - CLAMP
2 - TURBOCHARGER
3 - AIR DUCT RUBBER SLEEVE
4 - AIR INLET DUCT
11 - 18 EXHAUST SYSTEMBR/BE
Page 1314 of 2255

The fuel rail is not repairable.
CAUTION: The left and right sections of the fuel rail
are connected with a flexible connecting hose. Do
not attempt to separate the rail halves at this con-
necting hose. Due to the design of this connecting
hose, it does not use any clamps. Never attempt to
install a clamping device of any kind to the hose.
When removing the fuel rail assembly for any rea-
son, be careful not to bend or kink the connecting
hose.
OPERATION - 8.0L
High pressure from the fuel pump is routed to the
fuel rail. The fuel rail then supplies the necessary
fuel to each individual fuel injector.
A fuel pressure test port is located on the fuel rail.
A quick-connect fitting with a safety latch clip is
used to attach the fuel line to the fuel rail.
The fuel rail is not repairable.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 5.9L
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH ENGINE TURNED
OFF). BEFORE SERVICING FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY,
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
To release fuel pressure, refer to Fuel System Pres-
sure Release Procedure found in this group.
CAUTION: The left and right fuel rails are replaced
as an assembly. Do not attempt to separate the rail
halves at the connecting hose (Fig. 24). Due to the
design of this connecting hose, it does use any
clamps. Never attempt to install a clamping device
of any kind to the hose. When removing the fuel rail
assembly for any reason, be careful not to bend or
kink the connecting hose.
(1) Remove negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Remove air cleaner.
(3) Perform fuel pressure release procedure.
(4) Remove throttle body from intake manifold.
Refer to Throttle Body removal in this group.
(5) If equipped with air conditioning, remove the
A-shaped A/C compressor-to-intake manifold support
bracket (three bolts) (Fig. 25).
(6) Disconnect electrical connectors at all fuel
injectors. To remove connector refer to (Fig. 26). Push
red colored slider away from injector (1). While push-
ing slider, depress tab (2) and remove connector (3)
from injector. The factory fuel injection wiring har-ness is numerically tagged (INJ 1, INJ 2, etc.) for
injector position identification. If harness is not
tagged, note wiring location before removal.
(7) Disconnect fuel tube (line) at side of fuel rail.
Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings for procedures,
(8) Remove the remaining fuel rail mounting bolts.
(9) Gently rock and pull theleftfuel rail until the
fuel injectors just start to clear the intake manifold.
Gently rock and pull therightfuel rail until the fuel
injectors just start to clear the intake manifold.
Repeat this procedure (left/right) until all fuel injec-
tors have cleared the intake manifold.
Fig. 24 Fuel Rail AssemblyÐTypical
1 - FUEL RAIL CONNECTING HOSE
2 - FUEL RAIL
3 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
Fig. 25 A/C Compressor Support BracketÐTypical
1 - AIR CONDITIONING COMPRESSOR SUPPORT BRACKET
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS
BR/BEFUEL DELIVERY - GASOLINE 14 - 15
FUEL RAIL (Continued)
Page 1328 of 2255

FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
VISUAL INSPECTIONÐ5.9L ENGINES
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected or incor-
rectly routed wires and hoses should be made. This
should be done before attempting to diagnose or ser-
vice the fuel injection system. A visual check will
help spot these faults and save unnecessary test and
diagnostic time. A thorough visual inspection will
include the following checks:
(1) Verify that the three 32±way electrical connec-
tors are fully inserted into the connector of the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) (Fig. 1).
(2) Inspect the battery cable connections. Be sure
that they are clean and tight.
(3) Inspect fuel pump relay and air conditioning
compressor clutch relay (if equipped). Inspect the
ASD relay connections. Inspect starter motor relay
connections. Inspect relays for signs of physical dam-
age and corrosion. The relays are located in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC) (Fig. 2). Refer to
label on PDC cover for relay location.
(4) Inspect ignition coil connections. Verify that
coil secondary cable is firmly connected to coil (Fig.
3).
(5) Verify that distributor cap is correctly attached
to distributor. Be sure that spark plug cables are
firmly connected to the distributor cap and the spark
plugs are in their correct firing order. Be sure that
coil cable is firmly connected to distributor cap and
coil. Be sure that camshaft position sensor wire con-nector (at the distributor) is firmly connected to har-
ness connector. Inspect spark plug condition. Refer to
8, Ignition. Connect vehicle to an oscilloscope and
inspect spark events for fouled or damaged spark
plugs or cables.
(6) Verify that generator output wire, generator
connector and ground wire are firmly connected to
the generator.
(7) Inspect the system body grounds for loose or
dirty connections. Refer to 8, Wiring for ground loca-
tions.
(8) Verify positive crankcase ventilation (PCV)
valve operation. Refer to 25, Emission Control Sys-
tem for additional information. Verify PCV valve
hose is firmly connected to PCV valve and manifold
(Fig. 4).
Fig. 1 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
1 - PCM MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
2 - POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
3 - (3) 32±WAY CONNECTORS
Fig. 2 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
1 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
Fig. 3 Ignition CoilÐ5.9L EnginesÐTypical
1 - ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT TENSIONER
2 - COIL CONNECTOR
3 - IGNITION COIL
4 - COIL MOUNTING BOLTS
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 29
Page 1330 of 2255
(22) Inspect for pinched or leaking fuel tubes.
Inspect for pinched, cracked or leaking fuel hoses.
(23) Inspect for exhaust system restrictions such
as pinched exhaust pipes, collapsed muffler or
plugged catalytic convertor.
(24) If equipped with automatic transmission, ver-
ify that electrical harness is firmly connected to park/
neutral switch. Refer to 21, Automatic Transmission.(25) Verify electrical harness is firmly connected to
rear wheel speed sensor. Verify rear wheel speed sen-
sor is firmly attached to rear axle with proper air
gap. Refer to 5, Brakes for information.
(26) If equipped with 4±wheel antilock brake sys-
tem, verify electrical harness is firmly connected to
each front wheel speed sensor. Verify both front
wheel speed sensors are firmly attached. Refer to 5,
Brakes for information.
(27) Verify that fuel pump/gauge sender unit wire
connector is firmly connected to harness connector.
(28) Inspect fuel hoses at fuel pump/gauge sender
unit for cracks or leaks.
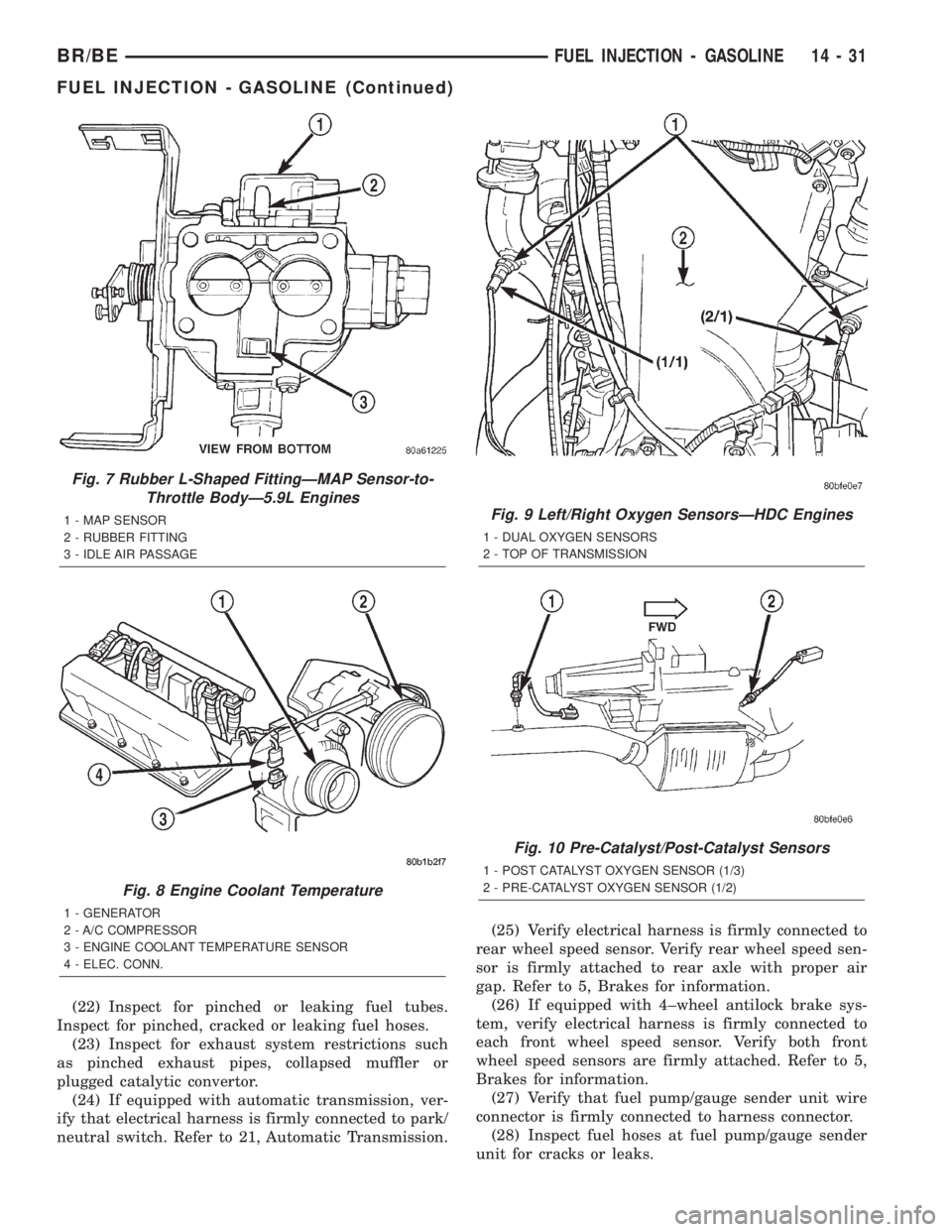
Fig. 7 Rubber L-Shaped FittingÐMAP Sensor-to-
Throttle BodyÐ5.9L Engines
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - RUBBER FITTING
3 - IDLE AIR PASSAGE
Fig. 8 Engine Coolant Temperature
1 - GENERATOR
2 - A/C COMPRESSOR
3 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
4 - ELEC. CONN.
Fig. 9 Left/Right Oxygen SensorsÐHDC Engines
1 - DUAL OXYGEN SENSORS
2 - TOP OF TRANSMISSION
Fig. 10 Pre-Catalyst/Post-Catalyst Sensors
1 - POST CATALYST OXYGEN SENSOR (1/3)
2 - PRE-CATALYST OXYGEN SENSOR (1/2)
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 31
FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE (Continued)
Page 1331 of 2255

(29) Inspect transmission torque convertor housing
(automatic transmission) or clutch housing (manual
transmission) for damage to timing ring on drive
plate/flywheel.
(30) Verify that battery cable and solenoid feed
wire connections to the starter solenoid are tight and
clean. Inspect for chaffed wires or wires rubbing up
against other components.
VISUAL INSPECTIONÐ8.0L ENGINE
A visual inspection for loose, disconnected or incor-
rectly routed wires and hoses should be made. This
should be done before attempting to diagnose or ser-
vice the fuel injection system. A visual check will
help spot these faults and save unnecessary test and
diagnostic time. A thorough visual inspection will
include the following checks:
(1) Verify that the three 32±way electrical connec-
tors are fully inserted into the connector of the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) (Fig. 12).
(2) Inspect the battery cable connections. Be sure
that they are clean and tight.
(3) Inspect fuel pump relay and air conditioning
compressor clutch relay (if equipped). Inspect the
ASD relay connections. Inspect starter motor relay
connections. Inspect relays for signs of physical dam-
age and corrosion. The relays are located in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC) (Fig. 13). Refer to
label on PDC cover for relay location.
(4) Inspect ignition coil pack primary connections.
Verify that secondary cables are firmly connected to
coils (Fig. 14).
(5) Be sure that spark plug cables are firmly con-
nected and the spark plugs are in their correct firing
order. Be sure that camshaft position sensor wire
connector is firmly connected to harness connector.
Inspect spark plug condition. Refer to 8, Ignition.Connect vehicle to an oscilloscope and inspect spark
events for fouled or damaged spark plugs or cables.
(6) Verify that generator output wire, generator
connector and ground wire are firmly connected to
the generator.
(7) Inspect the system body grounds for loose or
dirty connections. Refer to 8, Wiring for ground loca-
tions.
(8) Verify crankcase ventilation (CCV) operation.
Refer to 25, Emission Control System for additional
information.
(9) Inspect fuel tube quick-connect fitting-to-fuel
rail connections.
(10) Verify that hose connections to all ports of
vacuum fittings on intake manifold are tight and not
leaking.
Fig. 11 Oxygen SensorsFig. 12 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
1 - PCM MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
2 - POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
3 - (3) 32±WAY CONNECTORS
Fig. 13 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
1 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
14 - 32 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE (Continued)