2002 DODGE RAM power
[x] Cancel search: powerPage 1397 of 2255
OPERATION
High-pressure fuel is supplied from the injection
pump, through a high-pressure fuel line, through a
steel connector and into the fuel injector. When fuel
pressure rises to approximately 31,026 kPa (4,500
psi), the needle valve spring tension is overcome. The
needle valve rises and fuel flows through the spray
holes in the nozzle tip into the combustion chamber.
The pressure required to lift the needle valve is the
nozzle opening pressure. This is sometimes referred
to as the ªpopº pressure setting.
Each fuel injector is connected to each high-pres-
sure fuel line with a steel connector (Fig. 11). This
steel connector is positioned into the cylinder head
and sealed with an o-ring. The connectors are sealed
to the high-pressure fuel lines with fittings (Fig. 11).
The ferrule (Fig. 11) on the end of the high-pressure
fuel line pushes against the steel connector when the
fuel line fitting is torqued into the cylinder head.
This torquing force provides a sealing pressure
between both the fuel line-to-connector and the fuel
connector-to-fuel injector.The fitting torque is
very critical.If the fitting is under torqued, the
mating surfaces will not seal and a high-pressure
fuel leak will result. If the fitting is over torqued, the
connector and injector will deform and also cause a
high-pressure fuel leak. This leak will be inside the
cylinder head and will not be visible. The result will
be a possible fuel injector miss-fire and low power.
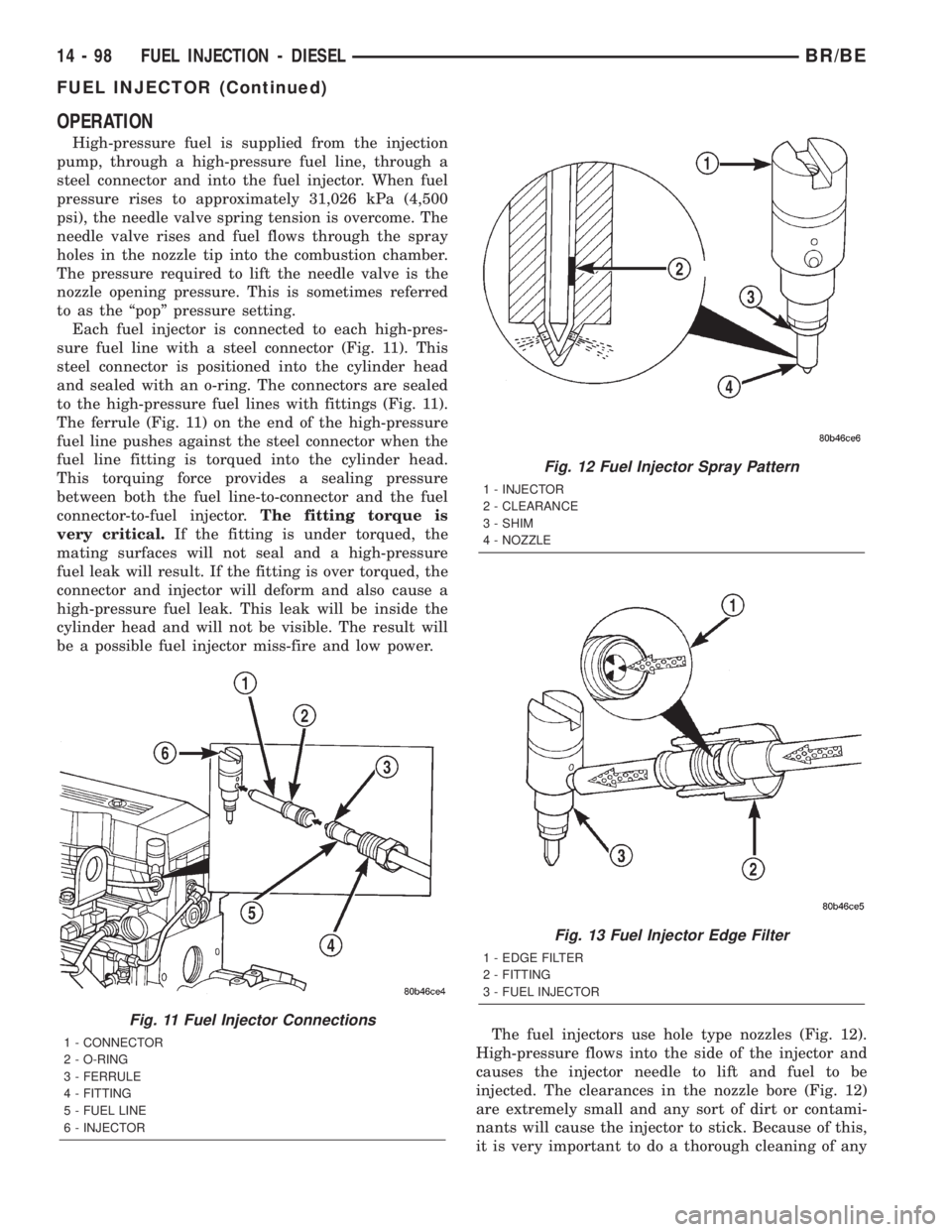
The fuel injectors use hole type nozzles (Fig. 12).
High-pressure flows into the side of the injector and
causes the injector needle to lift and fuel to be
injected. The clearances in the nozzle bore (Fig. 12)
are extremely small and any sort of dirt or contami-
nants will cause the injector to stick. Because of this,
it is very important to do a thorough cleaning of any
Fig. 11 Fuel Injector Connections
1 - CONNECTOR
2 - O-RING
3 - FERRULE
4 - FITTING
5 - FUEL LINE
6 - INJECTOR
Fig. 12 Fuel Injector Spray Pattern
1 - INJECTOR
2 - CLEARANCE
3 - SHIM
4 - NOZZLE
Fig. 13 Fuel Injector Edge Filter
1 - EDGE FILTER
2 - FITTING
3 - FUEL INJECTOR
14 - 98 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 1398 of 2255

lines before opening up any fuel system component.
Always cover or cap any open fuel connections before
a fuel system repair is performed.
Each fuel injector connector tube contains an edge
filter (Fig. 13) that breaks up small contaminants
that enter the injector. The edge filter uses the injec-
tors pulsating high-pressure to break up most parti-
cles so they are small enough to pass through the
injector.The edge filters are not a substitute for
proper cleaning and covering of all fuel system
components during repair.
The bottom of each fuel injector is sealed to the
cylinder head with a1.5mmthick copper shim (gas-
ket) (Fig. 12). The correct thickness shim must
always be re-installed after removing an injector.
Fuel pressure in the injector circuit decreases after
injection. The injector needle valve is immediately
closed by the needle valve spring and fuel flow into
the combustion chamber is stopped. Exhaust gases
are prevented from entering the injector nozzle by
the needle valve.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐFUEL INJECTOR
TEST
The fuel injectors are located in the top of the cyl-
inder head between the intake/exhaust valves (Fig.
14).A leaking fuel injector can cause fuel knock, poor
performance, black smoke, poor fuel economy and
rough engine idle. If fuel injector needle valve does
not operate properly, engine may misfire and produce
low power.
A leak in injection pump-to-injector high-pressure
fuel line can cause many of same symptoms as mal-
functioning injector. Inspect for leaks in high-pres-
sure lines before checking for malfunctioning fuel
injector.
WARNING: THE INJECTION PUMP SUPPLIES HIGH-
PRESSURE FUEL OF UP TO APPROXIMATELY
120,000 kPa (17,400 psi) TO EACH INDIVIDUAL
INJECTOR THROUGH HIGH-PRESSURE LINES.
FUEL UNDER THIS AMOUNT OF PRESSURE CAN
PENETRATE SKIN AND CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY.
WEAR SAFETY GOGGLES AND ADEQUATE PRO-
TECTIVE CLOTHING. AVOID CONTACT WITH FUEL
SPRAY WHEN BLEEDING HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL
LINES.
WARNING: DO NOT BLEED AIR FROM FUEL SYS-
TEM OF A HOT ENGINE. DO NOT ALLOW FUEL TO
SPRAY ONTO EXHAUST MANIFOLD WHEN BLEED-
ING AIR FROM FUEL SYSTEM.
(1) To determine which fuel injector is malfunc-
tioning, run engine and isolate each cylinder using
DRB scan tool.The DRB scan tool lists the injec-
tor firing order in both cylinder numerical
order (1±2±3±4±5±6), and actual firing order
(1±5±3±6±2±4).
Fig. 14 Fuel Injector Connections
1 - CONNECTOR
2 - O-RING
3 - FERRULE
4 - FITTING
5 - FUEL LINE
6 - INJECTOR
Fig. 15 Inspecting Injector Operation
1 - HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINE
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 99
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 1402 of 2255

(g) If any of these conditions occur, replace injec-
tor.
(2) Thoroughly clean fuel injector cylinder head
bore with special Cummins wire brush tool or equiv-
alent (Fig. 24). Blow out bore hole with compressed
air.
(3) The bottom of fuel injector is sealed to cylinder
head bore with a copper sealing washer (shim) of a
certain thickness. A new shim with correct thickness
must always be re-installed after removing injector.
Measure thickness of injector shim (Fig. 23).Shim
Thickness: 1.5 mm (.060º)
(4) Install new shim (washer) to bottom of injector
(Fig. 22). Apply light coating of clean engine oil to
washer. This will keep washer in place during instal-
lation.
(5) Install new o-ring to fuel injector. Apply small
amount of clean engine oil to o-ring.
(6) Note fuel inlet hole on side of fuel injector. This
hole must be positioned towards injector connector
tube. Position injector into cylinder head bore being
extremely careful not to allow injector tip to touch
sides of bore. Press fuel injector into cylinder head
with finger pressure only.Do not use any tools to
press fuel injector into position. Damage to
machined surfaces may result.
(7) Position fuel injector hold down clamp into
shouldered bolt while aligning slot in top of injector
into groove in bottom of clamp. Tighten opposite
clamp bolt (Fig. 18) to 10 N´m (89 in. lbs.) torque.
(8) Install new o-ring to fuel injector connector
tube. Apply small amount of clean engine oil to
o-ring.(9) Press injector connector tube into cylinder head
with finger pressure only.Do not use any tools to
press tube into position. Damage to machined
surfaces may result.
(10) Connect high-pressure fuel lines. Refer to
High-Pressure Fuel Lines Removal/Installation.The
fuel line fitting torque is very critical.If fitting
is under torqued, the mating surfaces will not seal
and a high-pressure fuel leak will result. If fitting is
over torqued, the connector and injector will deform
and also cause a high-pressure fuel leak. This leak
will be inside cylinder head and will not be visible
resulting in a possible fuel injector miss and low
power.
(11) Install valve cover. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S) -
INSTALLATION).
(12) (If necessary) install intake manifold air
heater assembly. Refer to Intake Manifold Air Heater
Removal/Installation.
(13) (If necessary) install engine lifting bracket.
Tighten 2 bolts to 77 N´m (57 ft. lbs.) torque.
(14) Connect negative battery cables to both bat-
teries.
(15) Bleed air from high-pressure lines (Refer to 14
- FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
FUEL INJECTION PUMP
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The fuel injection pump relay is located in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to label
under PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION
The Engine Control Module (ECM) energizes the
electric fuel injection pump through the fuel injection
pump relay. Battery voltage is applied to the fuel
injection pump relay at all times. When the key is
turned ON, the relay is energized when a 12±volt sig-
nal is provided by the ECM. When energized,
12±volts is supplied to the Fuel Pump Control Mod-
ule. The Fuel Pump Control Module is located on the
top of the fuel injection pump and is non-servicable.
Fig. 24 Cleaning Cylinder Head Injector BoreÐ
TYPICAL BORE
1 - INJECTOR BORE
2 - WIRE BRUSH
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 103
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 1403 of 2255

FUEL TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Two different fuel temperature sensors are used.
One of the sensors is located inside of the Bosch
VP44 fuel injection pump and is a non-serviceable
part. The other fuel temperature sensor is located in
the top of the fuel filter housing and is serviceable
(serviceable if replacing the fuel heater).
OPERATION
The sensor located in the Bosch VP44 fuel injection
pump is used to check fuel temperature within the
injection pump and to set a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) if a specific high fuel temperature has been
reached. If high temperature has been reached,
engine power will be de-rated by the Engine Control
Module (ECM).
The sensor located in the top of the fuel filter hous-
ing is used to control the fuel heater element. Refer
to Fuel Heater Description and Operation for addi-
tional information.
INTAKE AIR HEATER
DESCRIPTION
The intake manifold air heater element assembly
is located in the top of the intake manifold (Fig. 25).
OPERATION
The air heater elements are used to heat incoming
air to the intake manifold. This is done to help
engine starting and improve driveability with cool or
cold outside temperatures.
Electrical supply for the 2 air heater elements is
controlled by the Engine Control Module (ECM)
through the 2 air heater relays. Refer to Intake Man-
ifold Air Heater Relays for more information.
Two heavy-duty cables connect the 2 air heater ele-
ments to the 2 air heater relays. Each of these cables
will supply approximately 95 amps at 12 volts to an
individual heating element within the heater block
assembly.
Refer to the Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
manual for an electrical operation and complete
description of the intake heaters, including pre-heat
and post-heat cycles.
REMOVAL
The 2 intake manifold air heater elements are
attached to a metal block located at the top of the
intake manifold (Fig. 26). If servicing either of the
heater elements, the entire block/element assembly
must be replaced.
(1) Disconnect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
(2) Disconnect clamp from rubber hose at air
intake housing.
(3) Disconnect rubber hose at air intake housing.
Fig. 25 Air Heater Elements Location
1 - AIR HEATER ELEMENTS
2 - LOWER GASKET
3 - BLOCK
4 - UPPER GASKET
Fig. 26 Intake Manifold Air Heater Element Location
1 - AIR HEATER ELEMENTS
2 - LOWER GASKET
3 - BLOCK
4 - UPPER GASKET
14 - 104 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELBR/BE
Page 1404 of 2255

(4) Remove engine oil dipstick tube mounting bolt
(Fig. 28). Position dipstick tube to the side.(5) Disconnect heater electrical cables at cable
mounting studs (Fig. 28).
(6) Disconnect ground cable bolt and ground cable
from housing (Fig. 27).
(7) Remove 4 housing bolts (Fig. 28).
(8) Remove air intake housing from top of heater
elements.
(9) Remove heater element assembly from intake
manifold.
(10) Clean old gasket material from air intake
housing and intake manifold.
(11) Clean old gasket material from both ends of
heater block (Fig. 26).
INSTALLATION
The 2 intake manifold air heater elements are
attached to a metal block located at the top of the
intake manifold (Fig. 26). If servicing either of the
heater elements, the entire block/element assembly
must be replaced.
(1) Using 2 new gaskets, position element assem-
bly and air housing to intake manifold.
(2) Position ground cable (Fig. 27) to air housing.
(3) Install 4 housing bolts and tighten to 24 N´m
(18 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect heater cables at cable mounting studs
(Fig. 28).Do not allow the cable eyelets to con-
tact any other metal source other than the
cable nuts/studs.
(5) Install engine oil dipstick tube and mounting
bolt.
(6) Connect rubber hose to air intake housing.
(7) Connect clamp to rubber hose at air intake
housing.
(8) Connect both negative battery cables at both
batteries.
INTAKE AIR HEATER RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The 2 intake manifold air heater relays are located
in the engine compartment, attached to the left inner
fender below the left battery (Fig. 29).
OPERATION
The Engine Control Module (ECM) operates the 2
heating elements through the 2 intake manifold air
heater relays.
Refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures for an
electrical operation and complete description of the
intake heaters, including pre-heat and post-heat
cycles.
Fig. 27 Air Intake Housing (Front View)
1 - GROUND CABLE BOLT
2 - INTAKE AIR HOUSING
3 - CABLE BRACKET HOUSING BOLTS (3)
4 - GROUND CABLE
Fig. 28 Air Intake Housing (Rear View)
1 - TUBE MOUNTING BOLT
2 - HOUSING BOLTS (2)
3 - INTAKE HEATER CABLE MOUNTING STUDS (2)
4 - DIPSTICK TUBE
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - DIESEL 14 - 105
INTAKE AIR HEATER (Continued)
Page 1407 of 2255

MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL
The MAP sensor is installed into the rear of the
intake manifold (Fig. 31).
OPERATION - DIESEL
The MAP sensor reacts to air pressure changes in
the intake manifold. It provides an input voltage to
the Engine Control Module (ECM). As pressure
changes, MAP sensor voltage will change. The
change in MAP sensor voltage results in a different
input voltage to the ECM. The ECM uses this input,
along with inputs from other sensors to provide fuel
timing, fuel control and engine protection. Engine
protection is used to derate (drop power off) the
engine if turbocharger pressure becomes to high.
REMOVAL - DIESEL
The MAP sensor is located in the left/rear side of
the intake manifold (Fig. 34).
The MAP sensor is located in the left/rear side of
the intake manifold (Fig. 34).
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from MAP sen-
sor (Fig. 34).
(2) Remove MAP sensor from intake manifold (Fig.
35).
(3) Discard sensor o-ring (Fig. 35).
INSTALLATION
The MAP sensor is located in the left/rear side of
the intake manifold (Fig. 34).
(1) Clean sensor mounting hole (Fig. 35) of rust or
contaminants.
(2) Install new o-ring to sensor. Apply clean engine
oil to sensor o-ring and sensor threads.
(3) Install MAP sensor into intake manifold.
Tighten to 14 N´m (10 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect sensor electrical connector.
PTO SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
OPERATION
This Engine Control Module (ECM) input is used
only on models equipped with aftermarket Power
Take Off (PTO) units.
The input is used to tell the ECM that the PTO
has been engaged. When engaged, the ECM will dis-
able certain OBD II functions until the PTO has been
turned off.
Fig. 34 MAP Sensor Location
1 - MANIFOLD AIR PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR
2 - REAR OF CYLINDER HEAD
3 - IAT SENSOR
4 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
5 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
Fig. 35 MAP Sensor Removal/Installation
1 - SENSOR MOUNTING HOLES
2 - O-RING
3 - IAT SENSOR
4 - MAP SENSOR
5 - O-RING
14 - 108 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELBR/BE
Page 1410 of 2255

STEERING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STEERING
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
STEERING SYSTEM....................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
STEERING FLOW AND PRESSURE........4COLUMN...............................6
GEAR.................................16
PUMP.................................33
LINKAGE - 2WD.........................40
LINKAGE - 4WD.........................42
STEERING
DESCRIPTION
The power steering system consist of a steering col-
umn, steering gear and hydraulic pump. The gear is
mounted to the frame rail and attaches to the steer-
ing linkage. The pump is a constant flow rate and
displacement vane-type pump. The pump supplies
hydraulic fluid pressure to the power steering gear
(Fig. 1).
Vehicles equipped with trailer tow option have a
power steering pump oil cooler.
OPERATION
The gear acts as a rolling thread between the
worm shaft and rack piston. The worm shaft is sup-
ported by a thrust bearing at the lower end and a
bearing assembly at the upper end. When the worm
shaft is turned from input from the steering column
the rack piston moves. The rack piston teeth mesh
with the pitman shaft. Turning the worm shaft, turns
the pitman shaft, which turns the steering linkage.
Fig. 1 Power Steering Gear & Pump
1 - HYDRAULIC PUMP ASSEMBLY
2 - RETURN LINE HOSE ASSEMBLY
3 - FITTINGS
4 - STEERING GEAR ASSEMBLY (RECIRCULATING BALL GEAR
SHOWN)
5 - PRESSURE HOSE ASSEMBLY
BR/BESTEERING 19 - 1
Page 1411 of 2255
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER STEERING SYSTEM
STEERING NOISE
There is some noise in all power steering systems. One of the most common is a hissing sound evident at a
standstill parking. Or when the steering wheel is at the end of it's travel. Hiss is a high frequency noise similar
to that of a water tap being closed slowly. The noise is present in all valves that have a high velocity fluid passing
through an orifice. There is no relationship between this noise and steering performance.
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OBJECTIONAL HISS OR
WHISTLE1. Steering intermediate shaft to dash panel
seal.1. Check and repair seal at dash
panel.
2. Noisy valve in power steering gear. 2. Repair steering gear.
RATTLE OR CLUNK 1. Gear mounting bolts loose. 1. Tighten bolts to specification.
2. Loose or damaged suspension
components.2. Inspect and repair suspension.
3. Loose or damaged steering linkage. 3. Inspect and repair steering
linkage.
4. Internal gear noise. 4. Repair steering gear.
5. Pressure hose in contact with other
components.5. Reposition hose.
6. Loose or damaged intermediate shaft or
column.6. Inspect and repair or replace.
CHIRP OR SQUEAL 1. Loose belt. 1. Adjust or replace.
WHINE OR GROWL 1. Low fluid level. 1. Fill to proper level.
2. Pressure hose in contact with other
components.2. Reposition hose.
3. Internal pump noise. 3. Replace pump.
SUCKING AIR SOUND 1. Loose return line clamp. 1. Replace clamp.
2. O-ring missing or damaged on hose
fitting.2. Replace o-ring.
3. Low fluid level. 3. Fill to proper level.
4. Air leak between pump and reservoir. 4. Repair as necessary.
5. Reservoir cap not installed correctly. 5. Install reservoir cap correctly.
SCRUBBING OR
KNOCKING1. Wrong tire size. 1. Verify tire size.
2. Wrong gear. 2. Verify gear.
19 - 2 STEERINGBR/BE
STEERING (Continued)