2002 DODGE RAM power
[x] Cancel search: powerPage 1337 of 2255
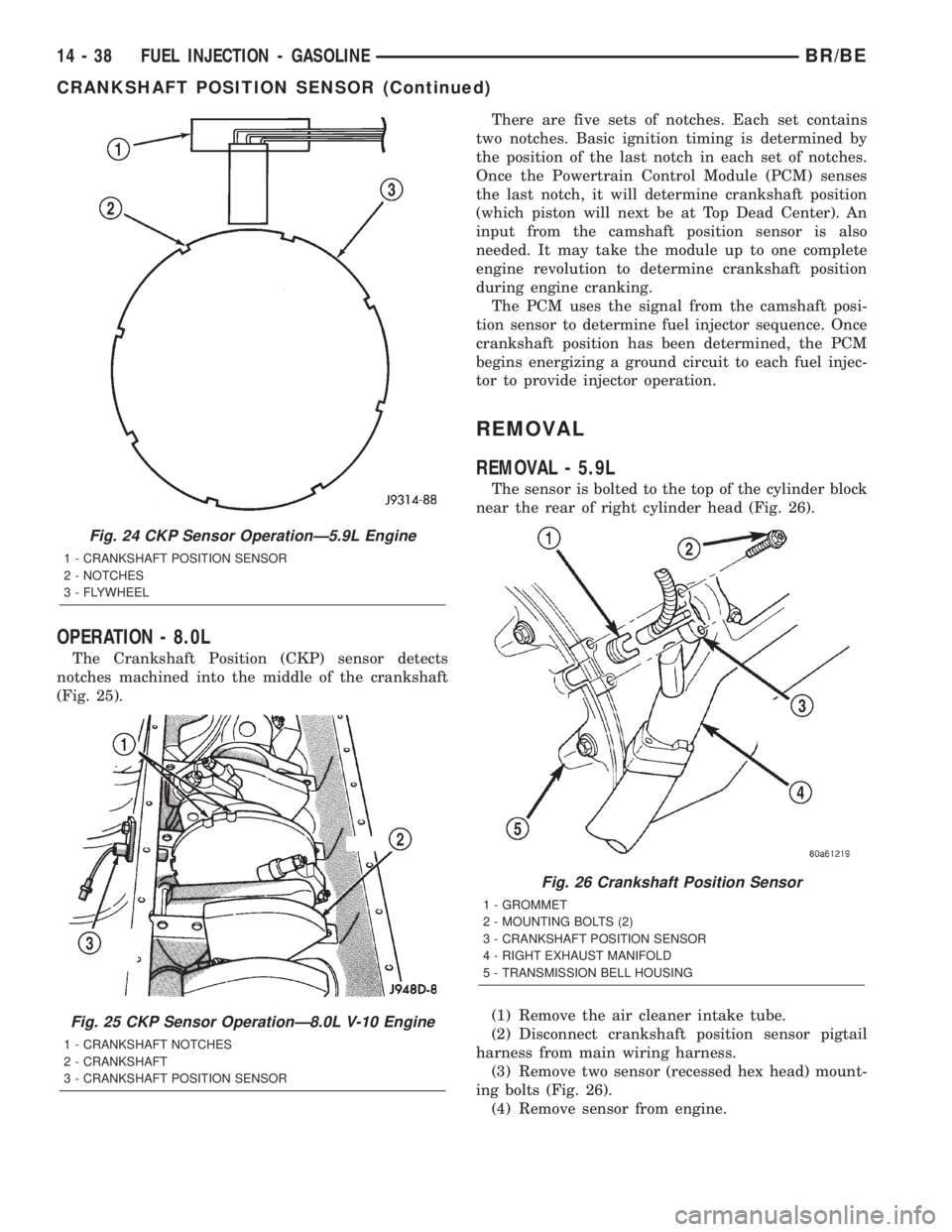
OPERATION - 8.0L
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor detects
notches machined into the middle of the crankshaft
(Fig. 25).There are five sets of notches. Each set contains
two notches. Basic ignition timing is determined by
the position of the last notch in each set of notches.
Once the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) senses
the last notch, it will determine crankshaft position
(which piston will next be at Top Dead Center). An
input from the camshaft position sensor is also
needed. It may take the module up to one complete
engine revolution to determine crankshaft position
during engine cranking.
The PCM uses the signal from the camshaft posi-
tion sensor to determine fuel injector sequence. Once
crankshaft position has been determined, the PCM
begins energizing a ground circuit to each fuel injec-
tor to provide injector operation.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 5.9L
The sensor is bolted to the top of the cylinder block
near the rear of right cylinder head (Fig. 26).
(1) Remove the air cleaner intake tube.
(2) Disconnect crankshaft position sensor pigtail
harness from main wiring harness.
(3) Remove two sensor (recessed hex head) mount-
ing bolts (Fig. 26).
(4) Remove sensor from engine.
Fig. 24 CKP Sensor OperationÐ5.9L Engine
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 - NOTCHES
3 - FLYWHEEL
Fig. 25 CKP Sensor OperationÐ8.0L V-10 Engine
1 - CRANKSHAFT NOTCHES
2 - CRANKSHAFT
3 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
Fig. 26 Crankshaft Position Sensor
1 - GROMMET
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS (2)
3 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
4 - RIGHT EXHAUST MANIFOLD
5 - TRANSMISSION BELL HOUSING
14 - 38 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1339 of 2255

CAUTION: Before tightening sensor mounting bolt,
be sure sensor is completely flush to cylinder block
(Fig. 28). If sensor is not flush, damage to sensor
mounting tang may result.
(3) Install mounting bolt and tighten to 8 N´m (70
in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect sensor pigtail harness to main engine
wiring harness
(5) Install new plastic tie strap (Fig. 27) to secure
sensor pigtail harness to side of engine block. Thread
tie strap through casting hole on cylinder block.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The 5±pin, 12±volt, fuel pump relay is located in
the Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to the
label on the PDC cover for relay location.
OPERATION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) energizes
the electric fuel pump through the fuel pump relay.
The fuel pump relay is energized by first applying
battery voltage to it when the ignition key is turned
ON, and then applying a ground signal to the relay
from the PCM.
Whenever the ignition key is turned ON, the elec-
tric fuel pump will operate. But, the PCM will shut-
down the ground circuit to the fuel pump relay in
approximately 1±3 seconds unless the engine is oper-
ating or the starter motor is engaged.
REMOVAL
The fuel pump relay is located in the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC) (Fig. 30). Refer to label on PDC
cover for relay location.
(1) Remove PDC cover.
(2) Remove relay from PDC.
(3) Check condition of relay terminals and PDC
connector terminals for damage or corrosion. Repair
if necessary before installing relay.
(4) Check for pin height (pin height should be the
same for all terminals within the PDC connector).
Repair if necessary before installing relay.
INSTALLATION
The fuel pump relay is located in the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC) (Fig. 30) . Refer to label on PDC
cover for relay location.
(1) Install relay to PDC.
(2) Install cover to PDC.
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The IAC stepper motor is mounted to the throttle
body, and regulates the amount of air bypassing the
control of the throttle plate. As engine loads and
ambient temperatures change, engine rpm changes.
A pintle on the IAC stepper motor protrudes into a
passage in the throttle body, controlling air flow
through the passage. The IAC is controlled by the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to maintain the
target engine idle speed.
OPERATION
At idle, engine speed can be increased by retract-
ing the IAC motor pintle and allowing more air to
pass through the port, or it can be decreased by
restricting the passage with the pintle and diminish-
ing the amount of air bypassing the throttle plate.
The IAC is called a stepper motor because it is
moved (rotated) in steps, or increments. Opening the
IAC opens an air passage around the throttle blade
which increases RPM.
The PCM uses the IAC motor to control idle speed
(along with timing) and to reach a desired MAP dur-
ing decel (keep engine from stalling).
The IAC motor has 4 wires with 4 circuits. Two of
the wires are for 12 volts and ground to supply elec-
trical current to the motor windings to operate the
stepper motor in one direction. The other 2 wires are
also for 12 volts and ground to supply electrical cur-
rent to operate the stepper motor in the opposite
direction.
Fig. 30 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
1 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
14 - 40 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1340 of 2255

To make the IAC go in the opposite direction, the
PCM just reverses polarity on both windings. If only
1 wire is open, the IAC can only be moved 1 step
(increment) in either direction. To keep the IAC
motor in position when no movement is needed, the
PCM will energize both windings at the same time.
This locks the IAC motor in place.
In the IAC motor system, the PCM will count
every step that the motor is moved. This allows the
PCM to determine the motor pintle position. If the
memory is cleared, the PCM no longer knows the
position of the pintle. So at the first key ON, the
PCM drives the IAC motor closed, regardless of
where it was before. This zeros the counter. From
this point the PCM will back out the IAC motor and
keep track of its position again.
When engine rpm is above idle speed, the IAC is
used for the following:
²Off-idle dashpot (throttle blade will close quickly
but idle speed will not stop quickly)
²Deceleration air flow control
²A/C compressor load control (also opens the pas-
sage slightly before the compressor is engaged so
that the engine rpm does not dip down when the
compressor engages)
²Power steering load control
The PCM can control polarity of the circuit to con-
trol direction of the stepper motor.
IAC Stepper Motor Program:The PCM is also
equipped with a memory program that records the
number of steps the IAC stepper motor most recently
advanced to during a certain set of parameters. For
example: The PCM was attempting to maintain a
1000 rpm target during a cold start-up cycle. The last
recorded number of steps for that may have been
125. That value would be recorded in the memory
cell so that the next time the PCM recognizes the
identical conditions, the PCM recalls that 125 steps
were required to maintain the target. This program
allows for greater customer satisfaction due to
greater control of engine idle.
Another function of the memory program, which
occurs when the power steering switch (if equipped),
or the A/C request circuit, requires that the IAC step-
per motor control engine rpm, is the recording of the
last targeted steps into the memory cell. The PCM
can anticipate A/C compressor loads. This is accom-
plished by delaying compressor operation for approx-
imately 0.5 seconds until the PCM moves the IAC
stepper motor to the recorded steps that were loaded
into the memory cell. Using this program helps elim-
inate idle-quality changes as loads change. Finally,
the PCM incorporates a9No-Load9engine speed lim-
iter of approximately 1800 - 2000 rpm, when it rec-
ognizes that the TPS is indicating an idle signal and
IAC motor cannot maintain engine idle.A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the IAC motor through the PCM.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 5.9L
The IAC motor is located on the back of the throt-
tle body (Fig. 31).
(1) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from IAC motor.
(3) Remove two mounting bolts (screws) (Fig. 31).
(4) Remove IAC motor from throttle body.
REMOVAL - 8.0L
The IAC motor is located on the back of the throt-
tle body (Fig. 32).
(1) Remove the air cleaner cover.
(2) Remove the 4 air cleaner housing mounting
nuts and remove housing from throttle body.
(3) Disconnect electrical connector from IAC motor.
(4) Remove two mounting bolts (screw).
(5) Remove IAC motor from throttle body.
Fig. 31 Mounting Bolts (Screws)ÐIAC MotorÐ5.9L
Engines
1 - MOUNTING SCREWS
2 - IDLE SPEED MOTOR
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 41
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (Continued)
Page 1341 of 2255

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 5.9L
The IAC motor is located on the back of the throt-
tle body (Fig. 31).
(1) Install IAC motor to throttle body.
(2) Install and tighten two mounting bolts (screws)
to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install electrical connector.
(4) Install air cleaner assembly.
INSTALLATION - 8.0L
The IAC motor is located on the back of the throt-
tle body (Fig. 32).
(1) Install IAC motor to throttle body.
(2) Install and tighten two mounting bolts (screws)
to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install electrical connector.
(4) Install air cleaner housing to throttle body.
(5) Install 4 air cleaner housing mounting nuts.
Tighten nuts to 11 N´m (96 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Install air cleaner housing cover.
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION - 5.9L/8.0L
The 2±wire Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT)
sensor is installed in the intake manifold with the
sensor element extending into the air stream.
The IAT sensor is a two-wire Negative Thermal
Coefficient (NTC) sensor. Meaning, as intake mani-
fold temperature increases, resistance (voltage) in thesensor decreases. As temperature decreases, resis-
tance (voltage) in the sensor increases.
OPERATION - 5.9L/8.0L
The IAT sensor provides an input voltage to the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) indicating the
density of the air entering the intake manifold based
upon intake manifold temperature. At key-on, a
5±volt power circuit is supplied to the sensor from
the PCM. The sensor is grounded at the PCM
through a low-noise, sensor-return circuit.
The PCM uses this input to calculate the following:
²Injector pulse-width
²Adjustment of spark timing (to help prevent
spark knock with high intake manifold air-charge
temperatures)
The resistance values of the IAT sensor is the same
as for the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 5.9L
The intake manifold air temperature sensor is
located in the front/side of the intake manifold (Fig.
33).
(1) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector at sensor (Fig.
33).
(3) Remove sensor from intake manifold.
Fig. 32 IAC MotorÐ8.0L Engine
1 - IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
2 - INTAKE MANIFOLD (UPPER HALF)
3 - THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
4 - THROTTLE BODY
Fig. 33 Air Temperature SensorÐ5.9L
1 - INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
14 - 42 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (Continued)
Page 1342 of 2255

REMOVAL - 8.0L
The intake manifold air temperature sensor is
located in the side of the intake manifold near the
front of throttle body (Fig. 34).
(1) Disconnect electrical connector at sensor.
(2) Remove sensor from intake manifold.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 5.9L
The intake manifold air temperature sensor is
located in the front/side of the intake manifold (Fig.
33).
(1) Install sensor to intake manifold. Tighten to
12±15 N´m (110±130 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install electrical connector.
(3) Install air cleaner.
INSTALLATION - 8.0L
The intake manifold air temperature sensor is
located in the side of the intake manifold near the
front of throttle body (Fig. 34).
(1) Install sensor to intake manifold. Tighten to
12±15 N´m (110±130 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install electrical connector.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION - 5.9L/8.0L
On 5.9L engines, the MAP sensor is mounted on
the side of the engine throttle body. The sensor is
connected to the throttle body with a rubber
L-shaped fitting.On the 8.0L 10±cylinder engine, the MAP sensor is
mounted into the right side of the intake manifold.
OPERATION - 5.9L/8.0L
The MAP sensor is used as an input to the Power-
train Control Module (PCM). It contains a silicon
based sensing unit to provide data on the manifold
vacuum that draws the air/fuel mixture into the com-
bustion chamber. The PCM requires this information
to determine injector pulse width and spark advance.
When manifold absolute pressure (MAP) equals
Barometric pressure, the pulse width will be at max-
imum.
A 5 volt reference is supplied from the PCM and
returns a voltage signal to the PCM that reflects
manifold pressure. The zero pressure reading is 0.5V
and full scale is 4.5V. For a pressure swing of 0±15
psi, the voltage changes 4.0V. To operate the sensor,
it is supplied a regulated 4.8 to 5.1 volts. Ground is
provided through the low-noise, sensor return circuit
at the PCM.
The MAP sensor input is the number one contrib-
utor to fuel injector pulse width. The most important
function of the MAP sensor is to determine baromet-
ric pressure. The PCM needs to know if the vehicle is
at sea level or at a higher altitude, because the air
density changes with altitude. It will also help to cor-
rect for varying barometric pressure. Barometric
pressure and altitude have a direct inverse correla-
tion; as altitude goes up, barometric goes down. At
key-on, the PCM powers up and looks at MAP volt-
age, and based upon the voltage it sees, it knows the
current barometric pressure (relative to altitude).
Once the engine starts, the PCM looks at the voltage
again, continuously every 12 milliseconds, and com-
pares the current voltage to what it was at key-on.
The difference between current voltage and what it
was at key-on, is manifold vacuum.
During key-on (engine not running) the sensor
reads (updates) barometric pressure. A normal range
can be obtained by monitoring a known good sensor.
As the altitude increases, the air becomes thinner
(less oxygen). If a vehicle is started and driven to a
very different altitude than where it was at key-on,
the barometric pressure needs to be updated. Any
time the PCM sees Wide Open Throttle (WOT), based
upon Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) angle and RPM,
it will update barometric pressure in the MAP mem-
ory cell. With periodic updates, the PCM can make
its calculations more effectively.
The PCM uses the MAP sensor input to aid in cal-
culating the following:
²Manifold pressure
²Barometric pressure
²Engine load
²Injector pulse-width
Fig. 34 Air Temperature SensorÐ8.0L Engine
1 - INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR TEMP. SENSOR
2 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 43
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1345 of 2255

around 70ÉF, the resistance of the heating element is
approximately 4.5 ohms. As the sensor's temperature
increases, resistance in the heater element increases.
This allows the heater to maintain the optimum
operating temperature of approximately 930É-1100ÉF
(500É-600É C). Although the sensors operate the
same, there are physical differences, due to the envi-
ronment that they operate in, that keep them from
being interchangeable.
Maintaining correct sensor temperature at all
times allows the system to enter into closed loop
operation sooner. Also, it allows the system to remain
in closed loop operation during periods of extended
idle.
In Closed Loop operation, the PCM monitors cer-
tain O2 sensor input(s) along with other inputs, and
adjusts the injector pulse width accordingly. During
Open Loop operation, the PCM ignores the O2 sensor
input. The PCM adjusts injector pulse width based
on preprogrammed (fixed) values and inputs from
other sensors.
Upstream Sensors:Two upstream sensors are
used (1/1 and 2/1). The 1/1 sensor is the first sensor
to receive exhaust gases from the #1 cylinder. They
provide an input voltage to the PCM. The input tells
the PCM the oxygen content of the exhaust gas. The
PCM uses this information to fine tune fuel delivery
to maintain the correct oxygen content at the down-
stream oxygen sensors. The PCM will change the air/
fuel ratio until the upstream sensors input a voltage
that the PCM has determined will make the down-
stream sensors output (oxygen content) correct.
The upstream oxygen sensors also provide an input
to determine mini-catalyst efficiency. Main catalytic
convertor efficiency is not calculated with this pack-
age.
Downstream Sensors:Two downstream sensors
are used (1/2 and 2/2). The downstream sensors are
used to determine the correct air-fuel ratio. As the
oxygen content changes at the downstream sensor,
the PCM calculates how much air-fuel ratio change is
required. The PCM then looks at the upstream oxy-
gen sensor voltage, and changes fuel delivery until
the upstream sensor voltage changes enough to cor-
rect the downstream sensor voltage (oxygen content).
The downstream oxygen sensors also provide an
input to determine mini-catalyst efficiency. Main cat-
alytic convertor efficiency is not calculated with this
package.
Medium and Heavy Duty 8.0L V-10 Engine:
Four oxygen sensors are used (2 upstream, 1 pre-cat-
alyst and 1 post-catalyst). The upstream sensors (1/1
and 2/1) will fine-tune the air-fuel ratio through the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The pre-catalyst
(1/2) and post-catalyst (1/3) sensors will determine
catalytic convertor efficiency (efficiency of the maincatalytic convertor). This is also done through the
PCM.
Heavy Duty 5.9L Engine:Downstream sensors
are not used with this emissions package, meaning
catalytic convertor efficiency is not calculated with
this package. Two upstream sensors are used. The
left upstream sensor (1/1) will monitor cylinders 1, 3,
5 and 7. The right upstream sensor (2/1) will monitor
cylinders 2, 4, 6 and 8. The PCM monitors the oxy-
gen content of the sensors, and will fine-tune the air-
fuel ratio.
Engines equipped with either a downstream sen-
sor(s), or a post-catalytic sensor, will monitor cata-
lytic convertor efficiency. If efficiency is below
emission standards, the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) will be illuminated and a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) will be set. Refer to Monitored Systems
in Emission Control Systems for additional informa-
tion.
REMOVAL
Never apply any type of grease to the oxygen
sensor electrical connector, or attempt any sol-
dering of the sensor wiring harness.
The O2S (oxygen sensors) are numbered 1/1, 1/2,
1/3, 2/1 and 2/2.
On HDC engines, the pre-catalyst/post catalyst
O2S sensors are located at the inlet and outlet ends
of the catalytic converter (Fig. 38).
The 1/1 and 2/1 sensors are located before the
mini-cats (Fig. 39). The 1/2 and 2/2 sensors are
located after the mini-cats (Fig. 39).
WARNING: THE EXHAUST MANIFOLD, EXHAUST
PIPES AND CATALYTIC CONVERTER BECOME
VERY HOT DURING ENGINE OPERATION. ALLOW
ENGINE TO COOL BEFORE REMOVING OXYGEN
SENSOR.
Fig. 38 Pre-catalyst/Post catalyst Oxygen SensorsÐ
HDC Engines
1 - POST CATALYST OXYGEN SENSOR (1/3)
2 - PRE-CATALYST OXYGEN SENSOR (1/2)
14 - 46 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
O2 SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1346 of 2255

(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Disconnect the wire connector from the O2S
sensor.
CAUTION: When disconnecting the sensor electrical
connector, do not pull directly on wire going into
sensor.
(3) Remove the O2S sensor with an oxygen sensor
removal and installation tool.
INSTALLATION
Threads of new oxygen sensors are factory coated
with anti-seize compound to aid in removal.DO
NOT add any additional anti-seize compound to
the threads of a new oxygen sensor.
(1) Install the O2S sensor. Tighten to 30 N´m (22
ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect the O2S sensor wire connector.
(3) Lower the vehicle.
PTO SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
This Powertrain Control Module (PCM) input is
used only on models equipped with aftermarket
Power Take Off (PTO) units.
OPERATION
The input is used only to tell the PCM that the
PTO has been engaged. The PCM will disable (tem-
porarily shut down) certain OBD II diagnostic trou-
ble codes when the PTO is engaged.
When the aftermarket PTO switch has been
engaged, a 12V + signal is sent through circuit G113
to PCM pin A13. The PCM will then sense and deter-
mine that the PTO has been activated.
THROTTLE BODY
DESCRIPTION
The throttle body is located on the intake manifold.
Fuel does not enter the intake manifold through the
throttle body. Fuel is sprayed into the manifold by
the fuel injectors.
OPERATION
Filtered air from the air cleaner enters the intake
manifold through the throttle body. The throttle body
contains an air control passage controlled by an Idle
Air Control (IAC) motor. The air control passage is
used to supply air for idle conditions. A throttle valve
(plate) is used to supply air for above idle conditions.
Certain sensors are attached to the throttle body.
The accelerator pedal cable, speed control cable and
transmission control cable (when equipped) are con-
nected to the throttle body linkage arm.
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the PCM.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 5.9L
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM).
(1) Remove the air cleaner.
(2) Disconnect throttle body electrical connectors
at MAP sensor, IAC motor and TPS (Fig. 40).
(3) Remove vacuum line at throttle body.
(4) Remove all control cables from throttle body
(lever) arm. Refer to the Accelerator Pedal and Throt-
tle Cable section of this group for additional informa-
tion.
(5) Remove four throttle body mounting bolts (Fig.
41).
(6) Remove throttle body from intake manifold.
(7) Discard old throttle body-to-intake manifold
gasket.
REMOVAL - 8.0L
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM).
(1) Remove the air cleaner cover.
Fig. 39 Oxygen SensorsÐ5.9L California Engines
BR/BEFUEL INJECTION - GASOLINE 14 - 47
O2 SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1347 of 2255

(2) Remove the 4 air cleaner housing mounting
nuts and remove housing from throttle body.
(3) Disconnect throttle body electrical connectors
at the IAC motor and TPS.
(4) Remove all control cables from throttle body
(lever) arm. Refer to the Accelerator Pedal and Throt-tle Cable section of this group for additional informa-
tion.
(5) Remove four throttle body mounting nuts (Fig.
42).
(6) Remove throttle body from intake manifold.
(7) Discard old throttle body-to-intake manifold
gasket.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 5.9L
A (factory adjusted) set screw is used to mechani-
cally limit the position of the throttle body throttle
plate.Never attempt to adjust the engine idle
speed using this screw.All idle speed functions are
controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM).
(1) Clean the mating surfaces of the throttle body
and the intake manifold.
(2) Install new throttle body-to-intake manifold
gasket.
(3) Install throttle body to intake manifold.
(4) Install four mounting bolts. Tighten bolts to 23
N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Install control cables.
(6) Install vacuum line to throttle body.
(7) Install electrical connectors.
(8) Install air cleaner.
Fig. 40 Sensor Electrical ConnectorsÐ5.9L
EnginesÐTypical
1 - MAP SENSOR
2 - IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
3 - THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
Fig. 41 Throttle Body
1 - THROTTLE BODY MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
2 - THROTTLE BODY
Fig. 42 Throttle Body Mounting NutsÐ8.0L Engine
1 - INTAKE MANIFOLD UPPER HALF
2 - GASKET
3 - THROTTLE BODY
4 - MOUNTING NUTS (4)
14 - 48 FUEL INJECTION - GASOLINEBR/BE
THROTTLE BODY (Continued)