2002 DODGE RAM overheating
[x] Cancel search: overheatingPage 305 of 2255

(1) Drill a 3.18-mm (1/8-in) diameter hole in the
top center of the fan shroud.
(2) Obtain a dial thermometer with an 8 inch stem
(or equivalent). It should have a range of -18É-to-
105ÉC (0É-to-220É F). Insert thermometer through the
hole in the shroud. Be sure that there is adequate
clearance from the fan blades.
(3) Connect a tachometer and an engine ignition
timing light. The timing light is to be used as a
strobe light. This step cannot be used on the diesel
engine.
(4) Block the air flow through the radiator. Secure
a sheet of plastic in front of the radiator (or air con-
ditioner condenser). Use tape at the top to secure the
plastic and be sure that the air flow is blocked.
(5) Be sure that the air conditioner (if equipped) is
turned off.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR FAN. DO
NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(6) Start the engine and operate at 2400 rpm.
Within ten minutes the air temperature (indicated on
the dial thermometer) should be up to 88É C (190É F).
Fan driveengagementshould start to occur at/be-
tween:
²5.9L gas engines Ð 79É C (175É F)
²8.0L engine Ð 88É to 96É C (190É to 205É F)
²5.9L diesel engine Ð 71É to 82É C (160É to 179É
F) Engagement is distinguishable by a definite
increasein fan flow noise (roaring). The timing light
also will indicate an increase in the speed of the fan
(non-diesel only).
(7) When viscous drive engagement is verified,
remove the plastic sheet. Fan drivedisengagement
should start to occur at between 57É to 79É C (135É to
175É F). A definitedecreaseof fan flow noise (roar-
ing) should be noticed. If not, replace the defective
viscous fan drive unit.
CAUTION: Some engines equipped with serpentine
drive belts have reverse rotating fans and viscous
fan drives. They are marked with the word
REVERSE to designate their usage. Installation of
the wrong fan or viscous fan drive can result in
engine overheating.
CAUTION: If the viscous fan drive is replaced
because of mechanical damage, the cooling fan
blades should also be inspected. Inspect for fatigue
cracks, loose blades, or loose rivets that could
have resulted from excessive vibration. Replace fan
blade assembly if any of these conditions arefound. Also inspect water pump bearing and shaft
assembly for any related damage due to a viscous
fan drive malfunction.
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH
- 5.9L DIESEL
DESCRIPTION
The thermal viscous fan drive (Fig. 30) is a sili-
cone-fluid- filled coupling used to connect the fan
blades to the water pump shaft. The coupling allows
the fan to be driven in a normal manner. This is
done at low engine speeds while limiting the top
speed of the fan to a predetermined maximum level
at higher engine speeds.
OPERATION
A thermostatic bimetallic spring coil is located on
the front face of the viscous fan drive unit (a typical
viscous unit is shown in (Fig. 31). This spring coil
reacts to the temperature of the radiator discharge
air. It engages the viscous fan drive for higher fan
speed if the air temperature from the radiator rises
above a certain point. Until additional engine cooling
is necessary, the fan will remain at a reduced rpm
regardless of engine speed.
Only when sufficient heat is present, will the vis-
cous fan drive engage. This is when the air flowing
through the radiator core causes a reaction to the
Fig. 30 Viscous Fan
1 - THREADED SHAFT
2 - BOLT (4)
3 - FAN BLADE
4 - THREADED NUT
5 - VISCOUS FAN DRIVE
7 - 56 ENGINEBR/BE
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH - 5.9L/8.0L (Continued)
Page 307 of 2255

CAUTION: Some engines equipped with serpentine
drive belts have reverse rotating fans and viscous
fan drives. They are marked with the word
REVERSE to designate their usage. Installation of
the wrong fan or viscous fan drive can result in
engine overheating.
CAUTION: If the viscous fan drive is replaced
because of mechanical damage, the cooling fan
blades should also be inspected. Inspect for fatigue
cracks, loose blades, or loose rivets that could
have resulted from excessive vibration. Replace fan
blade assembly if any of these conditions are
found. Also inspect water pump bearing and shaft
assembly for any related damage due to a viscous
fan drive malfunction.
RADIATOR - 5.9L
DESCRIPTION
The radiator is a aluminum cross-flow design with
horizontal tubes through the radiator core and verti-
cal plastic side tanks (Fig. 32).
This radiator contains an internal transmission oil
cooler only on the V-10 gas engine and the 5.9L die-
sel engine combinations.
OPERATION
The radiator supplies sufficient heat transfer using
the cooling fins interlaced between the horizontal
tubes in the radiator core to cool the engine.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐRADIATOR
COOLANT FLOW
Use the following procedure to determine if coolant
is flowing through the cooling system.
(1) Idle engine until operating temperature is
reached. If the upper radiator hose is warm to the
touch, the thermostat is opening and coolant is flow-
ing to the radiator.
WARNING: HOT, PRESSURIZED COOLANT CAN
CAUSE INJURY BY SCALDING. USING A RAG TO
COVER THE RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP, OPEN
RADIATOR CAP SLOWLY TO THE FIRST STOP. THIS
WILL ALLOW ANY BUILT-UP PRESSURE TO VENT
TO THE RESERVE/OVERFLOW TANK. AFTER PRES-
SURE BUILD-UP HAS BEEN RELEASED, REMOVE
CAP FROM FILLER NECK.
(2) Drain a small amount of coolant from the radi-
ator until the ends of the radiator tubes are visible
through the filler neck. Idle the engine at normal
operating temperature. If coolant is flowing past the
exposed tubes, the coolant is circulating.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cables.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
(2) Drain the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
6094). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER HPC-20)
MAY BE USED FOR LARGER CLAMPS. ALWAYS
WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVICING CON-
STANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only an original equipment clamp
with a matching number or letter.
Fig. 32 Cross Flow RadiatorÐTypical
1 - COOLING TUBES
2 - TANKS
7 - 58 ENGINEBR/BE
FAN DRIVE VISCOUS CLUTCH - 5.9L DIESEL (Continued)
Page 476 of 2255

SPARK PLUG OVERHEATING
Overheating is indicated by a white or gray center
electrode insulator that also appears blistered (Fig.
34). The increase in electrode gap will be consider-
ably in excess of 0.001 inch per 2000 miles of opera-
tion. This suggests that a plug with a cooler heat
range rating should be used. Over advanced ignition
timing, detonation and cooling system malfunctions
can also cause spark plug overheating.
REMOVAL
On 5.9L engines, spark plug cable heat shields are
pressed into the cylinder head to surround each cable
boot and spark plug (Fig. 35).
(1) Always remove spark plug or ignition coil
cables by grasping at the cable boot (Fig. 37). Turn
the cable boot 1/2 turn and pull straight back in a
steady motion. Never pull directly on the cable.
Internal damage to cable will result.
Fig. 32 Chipped Electrode Insulator
1 - GROUND ELECTRODE
2 - CENTER ELECTRODE
3 - CHIPPED INSULATOR
Fig. 33 Preignition Damage
1 - GROUND ELECTRODE STARTING TO DISSOLVE
2 - CENTER ELECTRODE DISSOLVED
Fig. 34 Spark Plug Overheating
1 - BLISTERED WHITE OR GRAY COLORED INSULATOR
Fig. 35 Heat ShieldsÐ5.9L Engines
1 - AIR GAP
2 - SPARK PLUG BOOT HEAT SHIELD
BR/BEIGNITION CONTROL 8I - 19
SPARK PLUG (Continued)
Page 1096 of 2255

OPERATION
OPERATIONÐCYLINDER HEAD
The cylinder head closes the combustion chamber
allowing the pistons to compress the air fuel mixture
to the correct ratio for ignition. The valves located in
the cylinder head open and close to either allow clean
air into the combustion chamber or to allow the
exhaust gases out, depending on the stroke of the
engine.
OPERATION - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
GASKET
The steel-backed silicone gasket is designed to seal
the cylinder head cover for long periods of time
through extensive heat and cold, without failure. The
gasket is designed to be reusable.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET FAILURE
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
²Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
²Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test in this
section. An engine cylinder head gasket leaking
between adjacent cylinders will result in approxi-
mately a 50±70% reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove the air cleaner resonator and duct
work.
(4) Remove the intake manifold-to-generator
bracket support rod. Remove the generator.
(5) Remove closed crankcase ventilation system.
(6) Disconnect the evaporation control system.
(7) Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release pro-
cedure (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIV-
ERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE). Disconnect the
fuel supply line (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FITTING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(8) Disconnect accelerator linkage and if so
equipped, the speed control and transmission kick-
down cables.
(9) Remove distributor cap and wires.
(10) Disconnect the coil wires.
(11) Disconnect heat indicator sending unit wire.
(12) Disconnect heater hoses and bypass hose.
(13) Remove cylinder head covers and gaskets
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLIN-
DER HEAD COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(14) Remove intake manifold (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL) and throttle body as an assembly. Dis-
card the flange side gaskets and the front and rear
cross-over gaskets.
BR/BEENGINE 5.9L 9 - 21
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1151 of 2255

CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The alloy cast iron cylinder heads (Fig. 7) are held
in place by 12 bolts. The spark plugs are located in
the peak of the wedge between the valves.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET FAILURE
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
²Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
²Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test in this
section. An engine cylinder head gasket leaking
between adjacent cylinders will result in approxi-
mately a 50±70% reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative cable from the battery.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Remove the heat shields (Fig. 8).
(4) Remove the intake manifold-to-generator
bracket support rod. Remove the generator (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/CHARGING/GENERATOR -
REMOVAL).
(5) Remove closed crankcase ventilation system.
(6) Disconnect the evaporation control system.
(7) Remove the air cleaner.
(8) Perform the Fuel System Pressure release pro-
cedure (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIV-
Fig. 7 Cylinder Head Assembly
1 - SPARK PLUG
2 - INTAKE VALVES
3 - SPARK PLUG
4 - INTAKE VALVES
5 - SPARK PLUG
6 - SPARK PLUG
7 - INTAKE VALVE
8 - SPARK PLUG
9 - EXHAUST VALVE
10 - EXHAUST VALVES
11 - EXHAUST VALVES
9 - 76 ENGINE 8.0LBR/BE
Page 1273 of 2255

INSPECTION
Look at the stainless steel body of the converter,
inspect for bulging or other distortion that could be a
result of overheating. If the converter has a heat
shield attached make sure it is not bent or loose.
If you suspect internal damage to the catalyst, tap-
ping the bottom of the catalyst with a rubber mallet
may indicate a damaged core.
INSTALLATION
(1) Assemble converter and clamps loosely in
place.
(2) Install the exhaust pipe onto exhaust mani-
folds, tighten 31 N´m (23 ft. lbs.).
(3) Tighten all clamp nuts to 48 N´m (35 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(4) Lower the vehicle.
(5) Start the engine and inspect for exhaust leaks
and exhaust system contact with the body panels. A
minimum of 25.4 mm (1.0 in.) is required between
exhaust system components and body/frame parts.
Adjust the alignment, if needed.
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - 5.9L
HD/8.0L
DESCRIPTION
The stainless steel catalytic converter is located
under the vehicle, attached to the exhaust pipe(s).
OPERATION
The catalytic converter captures and burns any
unburned fuel mixture exiting the combustion cham-
bers during the exhaust stroke of the engine. This
process aids in reducing emissions output.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Saturate the bolts and nuts with heat valve
lubricant. Allow 5 minutes for penetration.
(3) Remove clamps and nuts (Fig. 5) (Fig. 6).
(4) Remove the catalytic converter.
INSPECTION
Look at the stainless steel body of the converter,
inspect for bulging or other distortion that could be a
result of overheating. If the converter has a heat
shield attached make sure it is not bent or loose.
If you suspect internal damage to the catalyst, tap-
ping the bottom of the catalyst with a rubber mallet
may indicate a damaged core.
Fig. 4 Catalytic Converter and Exhaust Pipe 3.9L,
5.2L and 5.9L Light Duty ( California )
1 - BOLT
2 - RETAINER
3 - EXHAUST MANIFOLD
4 - NUT
5 - MINI CATALYTIC CONVERTER
6 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER WITH PIPES
Fig. 5 Catalytic Converter 5.9L Heavy Duty
1 - DOWN PIPE RIGHT
2 - CLAMP
3 - CLAMP
4 - HANGER ASSY. DUAL CLAMP
5 - MUFFLER
6 - EXTENSION PIPE
7 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
8 - DOWN PIPE LEFT
11 - 6 EXHAUST SYSTEMBR/BE
CATALYTIC CONVERTER - 3.9L/5.2L/5.9L (Continued)
Page 1399 of 2255
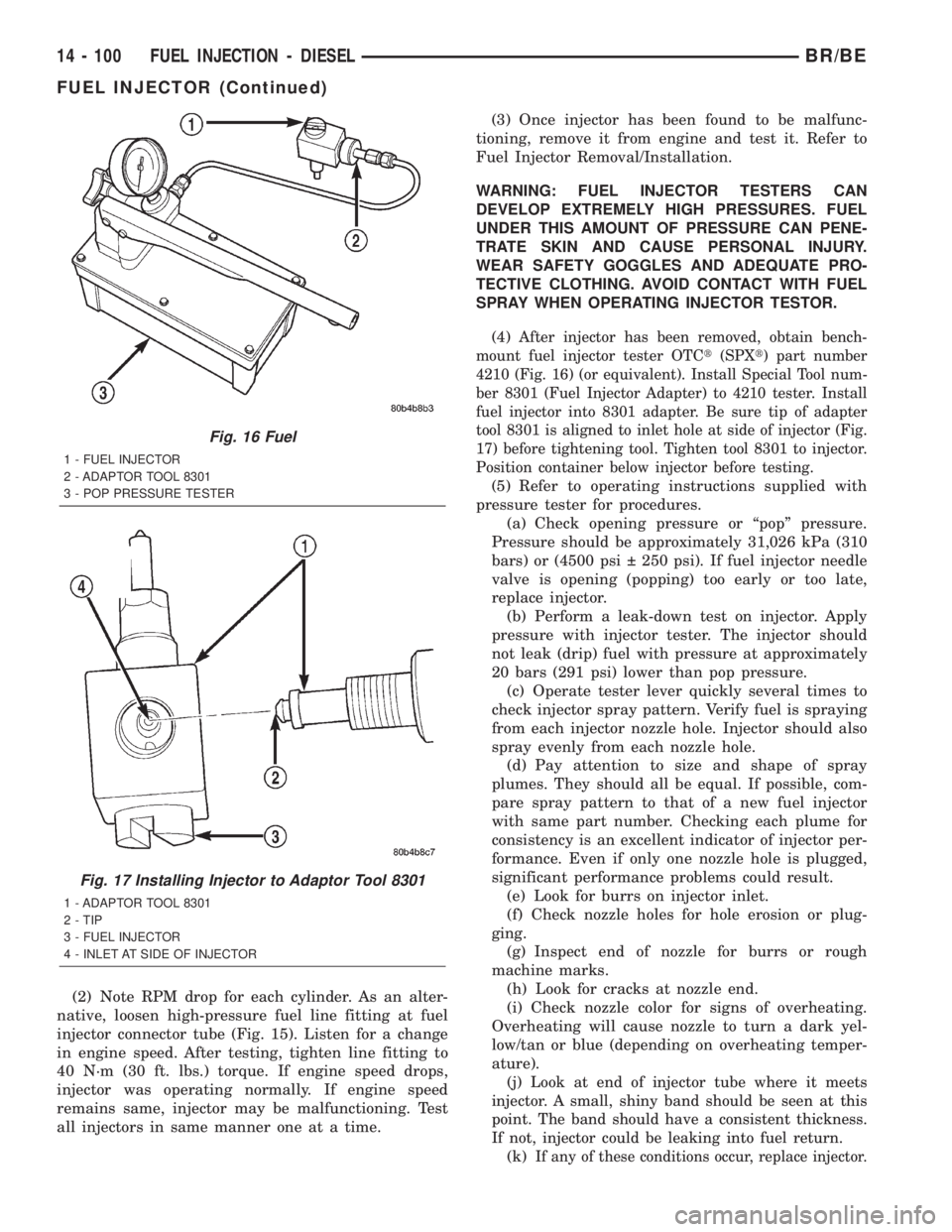
(2) Note RPM drop for each cylinder. As an alter-
native, loosen high-pressure fuel line fitting at fuel
injector connector tube (Fig. 15). Listen for a change
in engine speed. After testing, tighten line fitting to
40 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque. If engine speed drops,
injector was operating normally. If engine speed
remains same, injector may be malfunctioning. Test
all injectors in same manner one at a time.(3) Once injector has been found to be malfunc-
tioning, remove it from engine and test it. Refer to
Fuel Injector Removal/Installation.
WARNING: FUEL INJECTOR TESTERS CAN
DEVELOP EXTREMELY HIGH PRESSURES. FUEL
UNDER THIS AMOUNT OF PRESSURE CAN PENE-
TRATE SKIN AND CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY.
WEAR SAFETY GOGGLES AND ADEQUATE PRO-
TECTIVE CLOTHING. AVOID CONTACT WITH FUEL
SPRAY WHEN OPERATING INJECTOR TESTOR.
(4)
After injector has been removed, obtain bench-
mount fuel injector tester OTCt(SPXt) part number
4210 (Fig. 16) (or equivalent). Install Special Tool num-
ber 8301 (Fuel Injector Adapter) to 4210 tester. Install
fuel injector into 8301 adapter. Be sure tip of adapter
tool 8301 is aligned to inlet hole at side of injector (Fig.
17) before tightening tool. Tighten tool 8301 to injector.
Position container below injector before testing.
(5) Refer to operating instructions supplied with
pressure tester for procedures.
(a) Check opening pressure or ªpopº pressure.
Pressure should be approximately 31,026 kPa (310
bars) or (4500 psi 250 psi). If fuel injector needle
valve is opening (popping) too early or too late,
replace injector.
(b) Perform a leak-down test on injector. Apply
pressure with injector tester. The injector should
not leak (drip) fuel with pressure at approximately
20 bars (291 psi) lower than pop pressure.
(c) Operate tester lever quickly several times to
check injector spray pattern. Verify fuel is spraying
from each injector nozzle hole. Injector should also
spray evenly from each nozzle hole.
(d) Pay attention to size and shape of spray
plumes. They should all be equal. If possible, com-
pare spray pattern to that of a new fuel injector
with same part number. Checking each plume for
consistency is an excellent indicator of injector per-
formance. Even if only one nozzle hole is plugged,
significant performance problems could result.
(e) Look for burrs on injector inlet.
(f) Check nozzle holes for hole erosion or plug-
ging.
(g) Inspect end of nozzle for burrs or rough
machine marks.
(h) Look for cracks at nozzle end.
(i) Check nozzle color for signs of overheating.
Overheating will cause nozzle to turn a dark yel-
low/tan or blue (depending on overheating temper-
ature).
(j)
Look at end of injector tube where it meets
injector. A small, shiny band should be seen at this
point. The band should have a consistent thickness.
If not, injector could be leaking into fuel return.
(k)If any of these conditions occur, replace injector.
Fig. 16 Fuel
1 - FUEL INJECTOR
2 - ADAPTOR TOOL 8301
3 - POP PRESSURE TESTER
Fig. 17 Installing Injector to Adaptor Tool 8301
1 - ADAPTOR TOOL 8301
2 - TIP
3 - FUEL INJECTOR
4 - INLET AT SIDE OF INJECTOR
14 - 100 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)
Page 1401 of 2255
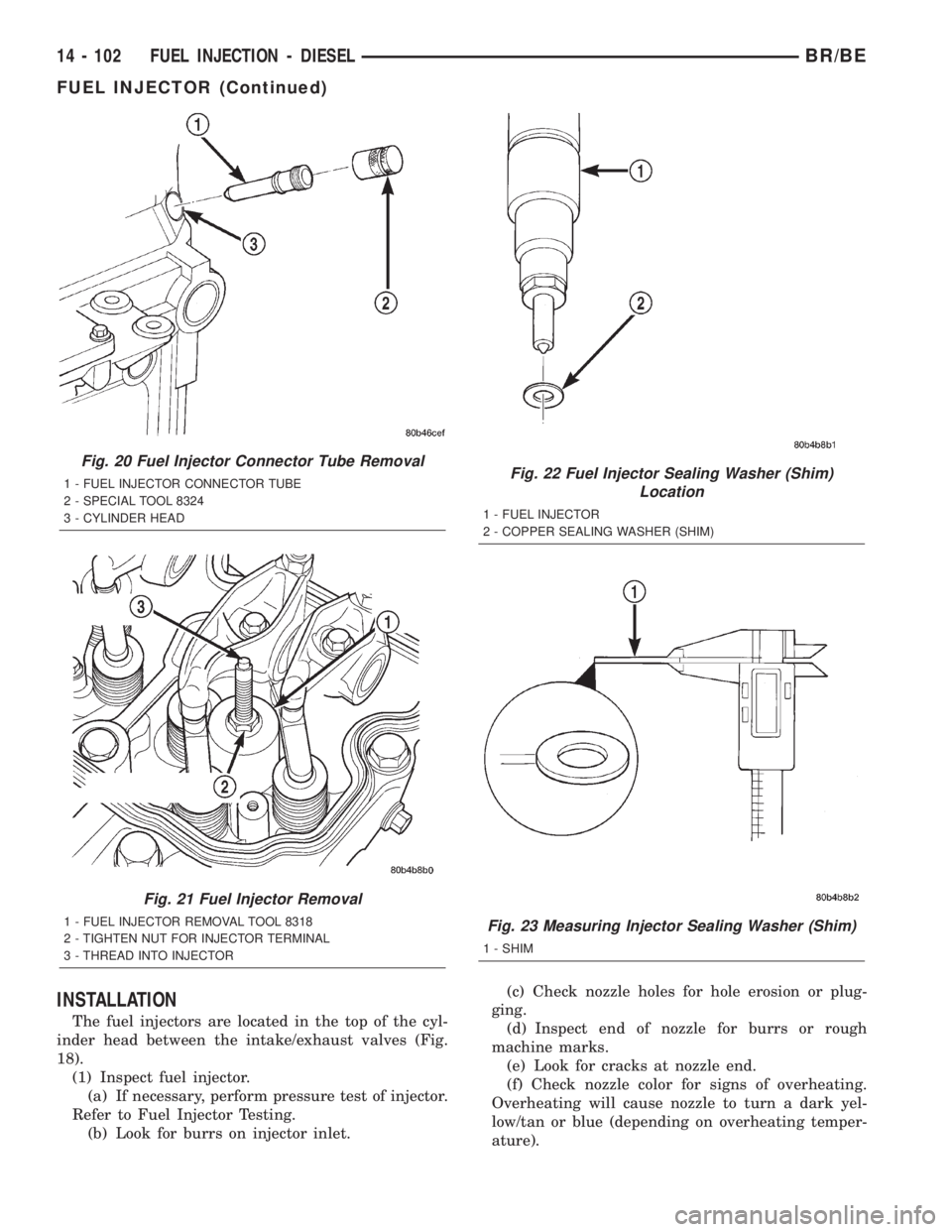
INSTALLATION
The fuel injectors are located in the top of the cyl-
inder head between the intake/exhaust valves (Fig.
18).
(1) Inspect fuel injector.
(a) If necessary, perform pressure test of injector.
Refer to Fuel Injector Testing.
(b) Look for burrs on injector inlet.(c) Check nozzle holes for hole erosion or plug-
ging.
(d) Inspect end of nozzle for burrs or rough
machine marks.
(e) Look for cracks at nozzle end.
(f) Check nozzle color for signs of overheating.
Overheating will cause nozzle to turn a dark yel-
low/tan or blue (depending on overheating temper-
ature).
Fig. 20 Fuel Injector Connector Tube Removal
1 - FUEL INJECTOR CONNECTOR TUBE
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 8324
3 - CYLINDER HEAD
Fig. 21 Fuel Injector Removal
1 - FUEL INJECTOR REMOVAL TOOL 8318
2 - TIGHTEN NUT FOR INJECTOR TERMINAL
3 - THREAD INTO INJECTOR
Fig. 22 Fuel Injector Sealing Washer (Shim)
Location
1 - FUEL INJECTOR
2 - COPPER SEALING WASHER (SHIM)
Fig. 23 Measuring Injector Sealing Washer (Shim)
1 - SHIM
14 - 102 FUEL INJECTION - DIESELBR/BE
FUEL INJECTOR (Continued)