2002 DODGE RAM engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 47 of 2255
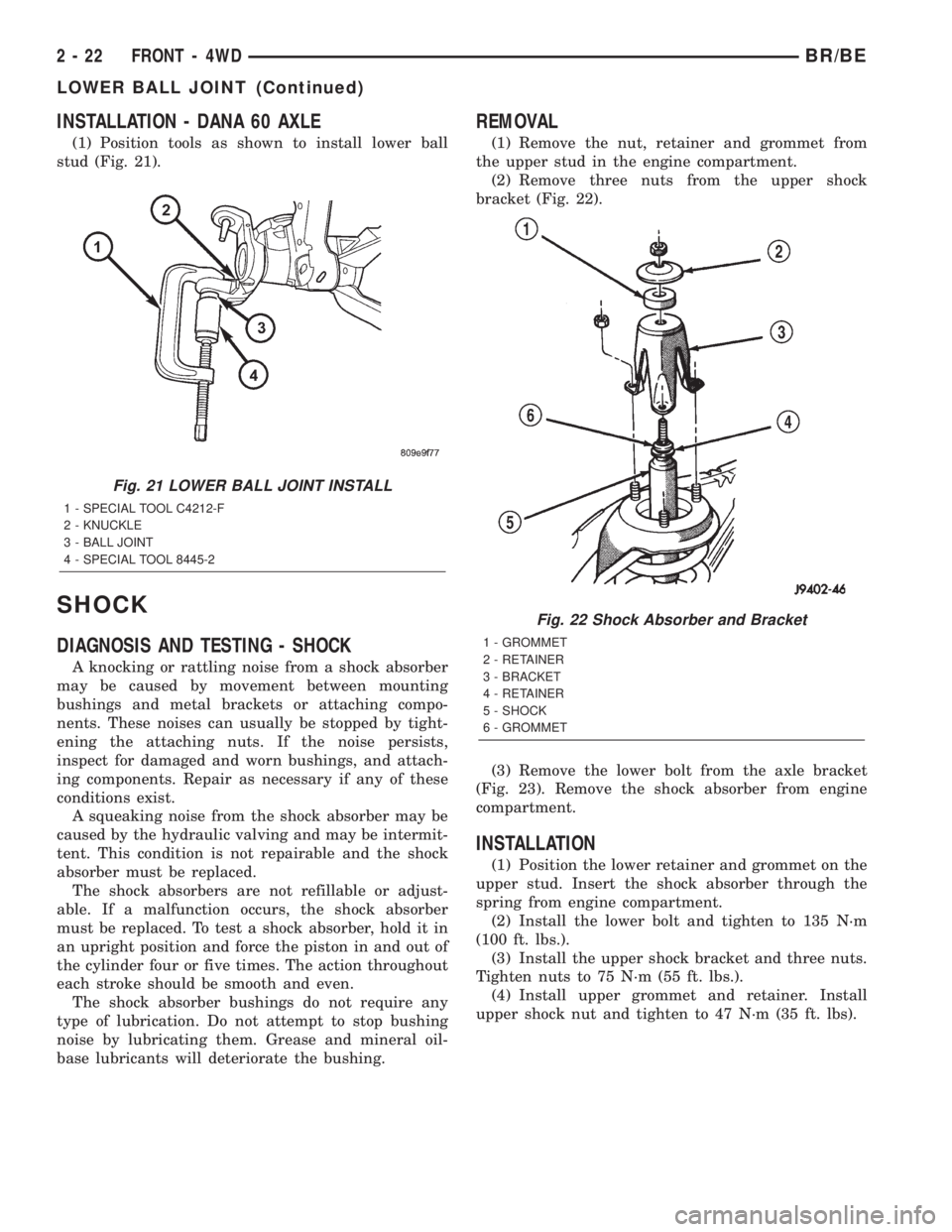
INSTALLATION - DANA 60 AXLE
(1) Position tools as shown to install lower ball
stud (Fig. 21).
SHOCK
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SHOCK
A knocking or rattling noise from a shock absorber
may be caused by movement between mounting
bushings and metal brackets or attaching compo-
nents. These noises can usually be stopped by tight-
ening the attaching nuts. If the noise persists,
inspect for damaged and worn bushings, and attach-
ing components. Repair as necessary if any of these
conditions exist.
A squeaking noise from the shock absorber may be
caused by the hydraulic valving and may be intermit-
tent. This condition is not repairable and the shock
absorber must be replaced.
The shock absorbers are not refillable or adjust-
able. If a malfunction occurs, the shock absorber
must be replaced. To test a shock absorber, hold it in
an upright position and force the piston in and out of
the cylinder four or five times. The action throughout
each stroke should be smooth and even.
The shock absorber bushings do not require any
type of lubrication. Do not attempt to stop bushing
noise by lubricating them. Grease and mineral oil-
base lubricants will deteriorate the bushing.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the nut, retainer and grommet from
the upper stud in the engine compartment.
(2) Remove three nuts from the upper shock
bracket (Fig. 22).
(3) Remove the lower bolt from the axle bracket
(Fig. 23). Remove the shock absorber from engine
compartment.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the lower retainer and grommet on the
upper stud. Insert the shock absorber through the
spring from engine compartment.
(2) Install the lower bolt and tighten to 135 N´m
(100 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install the upper shock bracket and three nuts.
Tighten nuts to 75 N´m (55 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install upper grommet and retainer. Install
upper shock nut and tighten to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs).
Fig. 21 LOWER BALL JOINT INSTALL
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C4212-F
2 - KNUCKLE
3 - BALL JOINT
4 - SPECIAL TOOL 8445-2
Fig. 22 Shock Absorber and Bracket
1 - GROMMET
2 - RETAINER
3 - BRACKET
4 - RETAINER
5 - SHOCK
6 - GROMMET
2 - 22 FRONT - 4WDBR/BE
LOWER BALL JOINT (Continued)
Page 56 of 2255

DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PROPELLER SHAFT......................1
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI....................14
REAR AXLE - 248RBI.....................46REAR AXLE - 267RBI.....................78
REAR AXLE - 286RBI....................107
PROPELLER SHAFT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PROPELLER SHAFT
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PROPELLER
SHAFT...............................1
STANDARD PROCEDURES................3
SPECIFICATIONS
PROPELLER SHAFT....................6
SPECIAL TOOLS
PROPELLER SHAFT....................6
PROPELLER SHAFT - FRONT
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................7
PROPELLER SHAFT - REAR
REMOVAL.............................7INSTALLATION..........................7
CENTER BEARING
REMOVAL.............................8
INSTALLATION..........................8
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - CENTER BEARING........8
SINGLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS
DISASSEMBLY..........................8
ASSEMBLY.............................9
DOUBLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS
DISASSEMBLY.........................10
ASSEMBLY............................11
PROPELLER SHAFT
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PROPELLER
SHAFT
VIBRATION
Tires that are out-of-round or wheels that are
unbalanced will cause a low frequency vibration.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
Brake drums that are unbalanced will cause a
harsh, low frequency vibration. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)Driveline vibration can also result from loose or
damaged engine mounts.
Propeller shaft vibration increases as the vehicle
speed is increased. A vibration that occurs within a
specific speed range is not usually caused by a pro-
peller shaft being unbalanced. Defective universal
joints or an incorrect propeller shaft angle, are usu-
ally the cause of such a vibration.
BR/BEDIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE 3 - 1
Page 57 of 2255

DRIVELINE VIBRATION
Drive Condition Possible Cause Correction
Propeller Shaft Noise 1) Undercoating or other foreign
material on shaft.1) Clean exterior of shaft and wash
with solvent.
2) Loose U-joint clamp screws. 2) Install new clamps and screws
and tighten to proper torque.
3) Loose or bent U-joint yoke or
excessive runout.3) Install new yoke.
4) Incorrect driveline angularity. 4) Measure and correct driveline
angles.
5) Rear spring center bolt not in
seat.5) Loosen spring u-bolts and seat
center bolt.
6) Worn U-joint bearings. 6) Install new U-joint.
7) Propeller shaft damaged or out
of balance.7) Installl new propeller shaft.
8) Broken rear spring. 8) Install new rear spring.
9) Excessive runout or unbalanced
condition.9) Re-index propeller shaft, test,
and evaluate.
10) Excessive drive pinion gear
shaft runout.10) Re-index propeller shaft and
evaluate.
11) Excessive axle yoke deflection. 11) Inspect and replace yoke if
necessary.
12) Excessive transfer case runout. 12) Inspect and repair as necessary.
Universal Joint Noise 1) Loose U-joint clamp screws. 1) Install new clamps and screws
and tighten to proper torque.
2) Lack of lubrication. 2) Replace as U-joints as
necessary.
BALANCE
NOTE: Removing and re-indexing the propeller
shaft 180É relative to the yoke may eliminate some
vibrations.
If propeller shaft is suspected of being unbalanced,
it can be verified with the following procedure:
(1) Raise the vehicle.
(2) Clean all the foreign material from the propel-
ler shaft and the universal joints.
(3) Inspect the propeller shaft for missing balance
weights, broken welds and bent areas.If the propel-
ler shaft is bent, it must be replaced.
(4) Inspect the universal joints to ensure that they
are not worn, properly installed and correctly aligned
with the shaft.
(5) Check the universal joint clamp screws torque.
(6) Remove the wheels and tires. Install the wheel
lug nuts to retain the brake drums or rotors.
(7) Mark and number the shaft six inches from the
yoke end at four positions 90É apart.(8) Run and accelerate the vehicle until vibration
occurs. Note the intensity and speed the vibration
occurred. Stop the engine.
(9) Install a screw clamp at position 1 (Fig. 1).
(10) Start the engine and re-check for vibration. If
there is little or no change in vibration, move the
clamp to one of the other three positions. Repeat the
vibration test.
(11) If there is no difference in vibration at the
other positions, the source of the vibration may not
be propeller shaft.
(12) If the vibration decreased, install a second
clamp (Fig. 2) and repeat the test.
(13) If the additional clamp causes an additional
vibration, separate the clamps (1/2 inch above and
below the mark). Repeat the vibration test (Fig. 3).
(14) Increase distance between the clamp screws
and repeat the test until the amount of vibration is
at the lowest level. Bend the slack end of the clamps
so the screws will not loosen.
3 - 2 PROPELLER SHAFTBR/BE
PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
Page 63 of 2255

CENTER BEARING
REMOVAL
(1) Remove rear propeller shaft.
(2) Remove slip joint boot clamp and separate the
two half-shafts.
(3) Use hammer and punch to tap slinger away
from shaft to provide room for bearing splitter.
(4) Position Bearing Splitter Tool 1130 between
slinger and shaft.
CAUTION: Do not damage shaft spline during
removal of center bearing.
(5)
Set shaft in press and press bearing off the shaft.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Two types of center bearings are used and
are not interchangeable. Install the same type as
the vehicle was built with.
(1) Install new slinger on shaft and drive into posi-
tion with appropriate installer tool.
(2) Install new center bearing on shaft with Bear-
ing Installer Tool 6052. Drive on shaft with hammer
until bearing is seated.
(3) Clean shaft splines and apply a coat of multi-
purpose grease.
(4) Align master splines and slide front and rear
half-shafts together. Reposition slip yoke boot and
install new clamp.
(5) Install propeller shaft in vehicle.
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - CENTER BEARING
Launch shudder is a vibration that occurs at first
acceleration from a stop. Shudder vibration usually
peaks at the engines highest torque output. Shudder is
a symptom associated with vehicles using a two-piece
propeller shaft. To decrease shudder, lower the center
bearing in 1/8 inch increments. Use shim stock or fab-
ricated plates. Plate stock must be used to maintain
compression of the rubber insulator around the bearing.
Do not use washers. Replace the original bolts with the
appropriate increased length bolts.
SINGLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL
JOINTS
DISASSEMBLY
Individual components of cardan universal joints
are not serviceable. If worn or leaking, they must be
replaced as an assembly.
(1) Remove the propeller shaft.
(2) With a soft drift, tap the outside of the bearing
cap assembly to loosen snap ring.
(3) Remove snap rings from both sides of yoke
(Fig. 12).
(4) Set the yoke in an arbor press or vise with a
socket whose inside diameter is large enough to
receive the bearing cap positioned beneath the yoke.
(5) Position the yoke with the grease fitting, if
equipped, pointing up.
(6) Place a socket with an outside diameter
smaller than the upper bearing cap on the upper
bearing cap and press the cap through the yoke to
release the lower bearing cap (Fig. 13).
Fig. 12 Remove Snap Ring
1 - SNAP RING
3 - 8 PROPELLER SHAFTBR/BE
Page 69 of 2255

FRONT AXLE - 248FBI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI
DESCRIPTION.........................14
OPERATION...........................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AXLE..........15
REMOVAL.............................18
INSTALLATION.........................18
ADJUSTMENTS........................19
SPECIFICATIONS
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI.................27
SPECIAL TOOLS
FRONT AXLE........................27
AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29
AXLE SHAFTS - INTERMEDIATE
REMOVAL.............................30
INSTALLATION - INTERMEDIATE AXLE......30
AXLE SHAFT SEALS
REMOVAL.............................31
INSTALLATION.........................31
AXLE VACUUM MOTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................31
OPERATION...........................31DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VACUUM MOTOR . 32
REMOVAL.............................34
DISASSEMBLY.........................34
ASSEMBLY............................34
INSTALLATION.........................34
SINGLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL JOINTS
REMOVAL.............................34
INSTALLATION.........................35
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL.............................37
DISASSEMBLY.........................38
ASSEMBLY............................38
INSTALLATION.........................39
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS
REMOVAL.............................40
INSTALLATION.........................41
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR
REMOVAL.............................41
INSTALLATION.........................43
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI
DESCRIPTION
The Front Beam-design Iron (FBI) axle consists of a
cast iron center casting differential housing with axle
shaft tubes extending from each side. The tubes are
pressed into the differential housing and welded. The
axles is equipped with semi-floating axle shafts, mean-
ing that loads are supported by the hub bearings.
The differential case is a one-piece design. Differ-
ential bearing preload and ring gear backlash is
adjusted by the use of shims located between the dif-
ferential bearing cones and case. Pinion bearing pre-load is set and maintained by the use of a collapsible
spacer. The stamped steel cover provides a means for
inspection and servicing the differential.
OPERATION
The axle receives power from the transfer case
through the front propeller shaft. The front propeller
shaft is connected to the pinion gear which rotates
the differential through the gear mesh with the ring
gear bolted to the differential case. The engine power
is transmitted to the axle shafts through the pinion
mate and side gears. The side gears are splined to
the axle shafts.
3 - 14 FRONT AXLE - 248FBIBR/BE
Page 71 of 2255

LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).
²Worn or out of balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rear end
vibration. Do not overlook engine accessories, brack-
ets and drive belts.All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged) can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
Condition Possible Causes Correction
Wheel Noise 1. Wheel loose. 1. Tighten loose nuts.
2. Faulty, brinelled wheel bearing. 2. Replace bearing.
Axle Shaft Noise 1. Misaligned axle tube. 1. Inspect axle tube alignment.
Correct as necessary.
2. Bent or sprung axle shaft. 2. Inspect and correct as necessary.
3. End-play in pinion bearings. 3. Refer to pinion pre-load
information and correct as
necessary.
4. Excessive gear backlash
between the ring gear and pinion.4. Check adjustment of the ring
gear and pinion backlash. Correct
as necessary.
5. Improper adjustment of pinion
gear bearings.5. Adjust the pinion bearings
pre-load.
6. Loose pinion yoke nut. 6. Tighten the pinion yoke nut.
7. Scuffed gear tooth contact
surfaces.7. Inspect and replace as
necessary.
3 - 16 FRONT AXLE - 248FBIBR/BE
FRONT AXLE - 248FBI (Continued)
Page 86 of 2255

AXLE SHAFT SEALS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove hub bearings and axle shafts.
(2) Remove axle shaft seal from the differential
housing with a long drift or punch.Be careful not
to damage housing.
(3) Clean the inside perimeter of the differential
housing with fine crocus cloth.
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply a light film of oil to the inside lip of the
new axle shaft seal.
(2) Install the inner axle seal (Fig. 25).
(3) Install axles and hub bearings.
AXLE VACUUM MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The disconnect axle control system consists of:
²Shift motor.
²Indicator switch.
²Vacuum switch.
²Vacuum harness (Fig. 26).
OPERATION
The shift motor receives a vacuum signal from the
switch mounted on the transfer case when the vehi-
cle operator wants to switch from two wheel drive
mode to four wheel drive mode, or vice versa. When
this signal is received, the shift motor begins to move
the shift fork and collar within the axle housing. In
the four wheel drive mode, the shift collar connects
the axle intermediate shaft to the axle shaft to sup-
ply engine power to both front wheels. In two wheel
drive mode, the shift collar is disengaged from the
intermediate shaft and the intermediate shaft is
allowed to free-spin. When the two shafts are disen-
gaged, the load on the engine is reduced, thereby pro-
viding better fuel economy and road handling.
Fig. 25 SEAL INSTALLATION
1 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
2 - POSITION FOR OPEN-END WRENCH
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 5041-2
4 - SPECIAL TOOL 8417
5 - SEAL
6 - SPECIAL TOOL 8411
Fig. 26 VACUUM CONTROL SYSTEM
1 - CHECK VALVE
2 - CONTROL SWITCH ON TRANSFER CASE
3 - AIR VENT FILTER
4 - AXLE SHIFT MOTOR
5 - INDICATOR SWITCH
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 248FBI 3 - 31
Page 92 of 2255
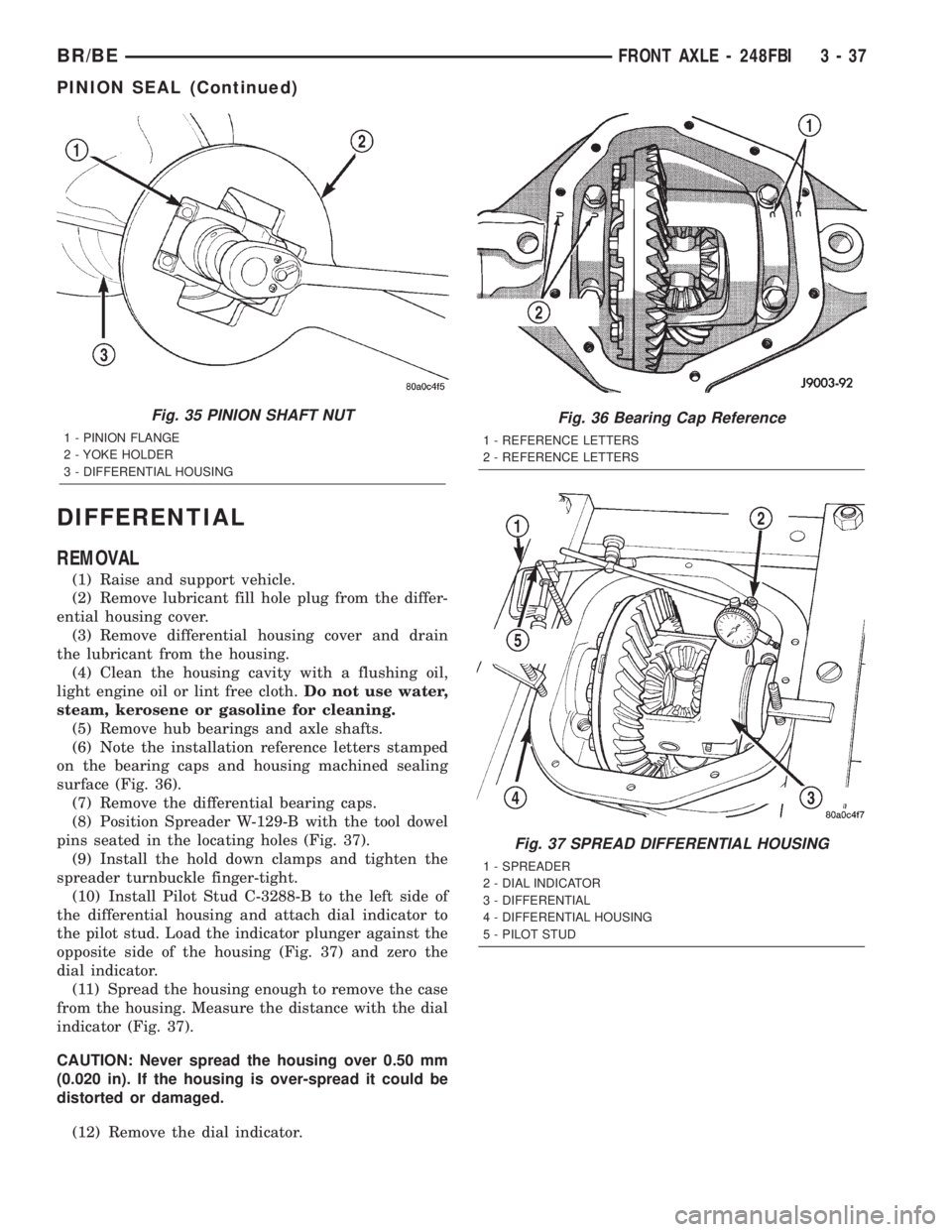
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove lubricant fill hole plug from the differ-
ential housing cover.
(3) Remove differential housing cover and drain
the lubricant from the housing.
(4) Clean the housing cavity with a flushing oil,
light engine oil or lint free cloth.Do not use water,
steam, kerosene or gasoline for cleaning.
(5) Remove hub bearings and axle shafts.
(6) Note the installation reference letters stamped
on the bearing caps and housing machined sealing
surface (Fig. 36).
(7) Remove the differential bearing caps.
(8) Position Spreader W-129-B with the tool dowel
pins seated in the locating holes (Fig. 37).
(9) Install the hold down clamps and tighten the
spreader turnbuckle finger-tight.
(10) Install Pilot Stud C-3288-B to the left side of
the differential housing and attach dial indicator to
the pilot stud. Load the indicator plunger against the
opposite side of the housing (Fig. 37) and zero the
dial indicator.
(11) Spread the housing enough to remove the case
from the housing. Measure the distance with the dial
indicator (Fig. 37).
CAUTION: Never spread the housing over 0.50 mm
(0.020 in). If the housing is over-spread it could be
distorted or damaged.
(12) Remove the dial indicator.
Fig. 35 PINION SHAFT NUT
1 - PINION FLANGE
2 - YOKE HOLDER
3 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
Fig. 36 Bearing Cap Reference
1 - REFERENCE LETTERS
2 - REFERENCE LETTERS
Fig. 37 SPREAD DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
1 - SPREADER
2 - DIAL INDICATOR
3 - DIFFERENTIAL
4 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
5 - PILOT STUD
BR/BEFRONT AXLE - 248FBI 3 - 37
PINION SEAL (Continued)