2002 CHRYSLER VOYAGER oil pressure sensor
[x] Cancel search: oil pressure sensorPage 2316 of 2399

(14) Remove the two screws that secure the expan-
sion valve to the evaporator tube tapping plate.
(15) Disconnect the HVAC wire harness connector
for the evaporator temperature sensor from the sen-
sor on the top of the expansion valve.
(16) Remove the expansion valve from the evapo-
rator inlet and outlet tube fittings.
(17) Remove the seals from the evaporator inlet
and outlet tube fittings and discard.
(18) Install plugs in, or tape over the opened evap-
orator inlet and outlet tube fittings and both expan-
sion valve ports.
INSTALLATION
(1) Remove the tape or plugs from the evaporator
inlet and outlet tube fittings and both ports on the
back of the expansion valve.
(2) Lubricate new rubber O-ring seals with clean
refrigerant oil and install them on the evaporator
inlet and outlet tube fittings.
(3) Position the expansion valve onto the evapora-
tor inlet and outlet tube fittings.
(4) Install and tighten the two screws that secure
the expansion valve to the evaporator tube tapping
plate plate. Tighten the screws to 11 N´m (97 in.
lbs.).
(5) Reconnect the HVAC wire harness connector
for the evaporator temperature sensor to the sensor
connector receptacle on the top of the expansion
valve.
(6) Remove the tape or plugs from the front liquid
line rear section and suction line fittings for the
expansion valve and both ports on the front of the
expansion valve.
(7) Lubricate new rubber O-ring seals with clean
refrigerant oil and install them on the front liquid
line rear section and suction line fittings for the
expansion valve.
(8) Reconnect the liquid line and suction line fit-
tings to the expansion valve.
(9) Install and tighten the nut that secures the
suction line and liquid line fittings to the stud on the
expansion valve. Tighten the nut to 23 N´m (17 ft.
lbs.).
(10) Remove the tape or plugs from the liquid line
rear section fitting for the filter-drier and the filter-
drier outlet port.
(11) Lubricate a new rubber O-ring seal with clean
refrigerant oil and install it on the liquid line fitting.
(12) Reconnect the liquid line fitting to the filter-
drier outlet port on the top of the filter-drier.
(13) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
liquid line fitting to the filter-drier. Tighten the screw
to 2 N´m (18 in. lbs.).(14) Reconnect the headlamp and dash wire har-
ness connector for the A/C pressure transducer to the
transducer on the front liquid line rear section.
(15) Reconnect the drain tube to the wiper module
drain on the right side of the engine compartment.
(16) Reinstall the air cleaner housing into the
right side of the engine compartment.
(17) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(18) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM EVACUATE).
(19) Charge the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM CHARGE).
HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION
The heater core is located in the distribution hous-
ing of the heater-A/C unit, under the instrument
panel. It is a heat exchanger made of rows of tubes
and fins. One end of the core is fitted with a molded
plastic tank that includes integral heater core inlet
and outlet ports. The removable heater core tubes
are held in place these ports by a sealing plate
secured with a screw to the heater core tank. This
removable heater core tube arrangement allows the
heater core to be serviced without removing the heat-
er-A/C unit housing from the vehicle. The heater core
cannot be repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must
be replaced.
OPERATION
Engine coolant is circulated through heater hoses
to the heater core at all times. As the coolant flows
through the heater core, heat removed from the
engine is transferred to the heater core fins and
tubes. Air directed through the heater core picks up
the heat from the heater core fins. The blend air door
allows control of the heater output air temperature
by controlling how much of the air flowing through
the heater-A/C unit housing is directed through the
heater core.
RSPLUMBING - FRONT24-73
EXPANSION VALVE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2343 of 2399

OPERATION
A mechanical sensor in the expansion valve control
head monitors the temperature and pressure of the
refrigerant leaving the evaporator coil through the
suction line, and adjusts the orifice size at the liquid
line to let the proper amount of refrigerant into the
evaporator coil to meet the vehicle cooling require-
ments. Controlling the refrigerant flow through the
evaporator ensures that none of the refrigerant leav-
ing the evaporator is still in a liquid state, which
could damage the compressor.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EXPANSION VALVE
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - FRONT - WARNING - A/C PLUMBING)
and (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - FRONT - CAUTION - A/C PLUMBING).
NOTE: The expansion valve should only be tested
following testing of the compressor.
NOTE: Liquid CO is required to test the expansion
valve. This material is available from most welding
supply facilities. Liquid CO is also available from
companies which service and sell fire extinguish-
ers.
When testing the expansion valve, the work area
and the vehicle temperature must be 21É to 27É C
(70É to 85É F). To test the expansion valve:
(1) Connect a charging station or manifold gauge
set to the refrigerant system service ports. Verify the
refrigerant charge level.
(2) Close all doors, windows and vents to the pas-
senger compartment.
(3) Set the heater-air conditioner controls so that
the compressor is operating, the temperature control
is in the highest temperature position, the mode door
is directing the output to the floor outlets, and the
blower is operating at the highest speed setting.
(4) Start the engine and allow it to idle at 1000
rpm. After the engine has reached normal operating
temperature, allow the passenger compartment to
heat up. This will create the need for maximum
refrigerant flow into the evaporator.
(5) If the refrigerant charge is sufficient, the dis-
charge (high pressure) gauge should read 965 to 1655
kPa (140 to 240 psi). The suction (low pressure)
gauge should read 140 kPa to 207 kPa (20 psi to 30
psi). If OK, go to Step 6. If not OK, replace the faulty
expansion valve.WARNING: PROTECT THE SKIN AND EYES FROM
EXPOSURE TO LIQUID CO. PERSONAL INJURY
CAN RESULT.
(6) If the suction (low pressure) gauge reads
within the specified range, freeze the expansion valve
control head for 30 seconds using liquid CO or
another suitable super-cold material.Do not spray
R-134a or R-12 refrigerant on the expansion
valve control head for this test.The suction (low
pressure) gauge reading should drop by 10 psi. If OK,
go to Step 7 If not OK, replace the faulty expansion
valve.
(7) Allow the expansion valve control head to thaw.
The suction (low pressure) gauge reading should sta-
bilize at 140 kPa to 240 kPa (20 psi to 30 psi). If not
OK, replace the faulty expansion valve.
(8) When expansion valve testing is complete, test
the overall air conditioner performance. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING - A/C PERFORMANCE TEST).
Remove all test equipment before returning the vehi-
cle to service.
REMOVAL
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION.
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - FRONT - WARNING - A/C PLUMBING),
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - FRONT - CAUTION - A/C PLUMBING),
and (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - FRONT - WARNING - HEATER PLUMB-
ING).
(1) Remove the rear heater-A/C unit housing from
the vehicle. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/DISTRIBUTION - REAR/REAR HEATER-
A/C HOUSING - REMOVAL).
(2) Carefully remove the foam insulator wrap from
the rear expansion valve.
(3) Remove the rear evaporator line extension from
the expansion valve. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - REAR/EVAPORA-
TOR - REMOVAL - EVAPORATOR LINE EXTEN-
SION).
(4) Remove the two screws that secure the expan-
sion valve to the evaporator tube sealing plate.
(5) Remove the expansion valve from the evapora-
tor tubes.
(6) Remove the seals from the evaporator tube fit-
tings and discard.
(7) Install plugs in, or tape over the opened evap-
orator tube fittings and both expansion valve ports.
24 - 100 PLUMBING - REARRS
EXPANSION VALVE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2361 of 2399

The following is a list of the monitored compo-
nents:
²Comprehensive Components
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Catalyst Monitor
COMPREHENSIVE COMPONENTS
Along with the major monitors, OBD II requires
that the diagnostic system monitor any component
that could affect emissions levels. In many cases,
these components were being tested under OBD I.
The OBD I requirements focused mainly on testing
emissions-related components for electrical opens and
shorts.
However, OBD II also requires that inputs from
powertrain components to the PCM be tested for
rationality, and that outputs to powertrain compo-
nents from the PCM be tested forfunctionality.
Methods for monitoring the various Comprehensive
Component monitoring include:
(1) Circuit Continuity
²Open
²Shorted high
²Shorted to ground
(2) Rationality or Proper Functioning
²Inputs tested for rationality
²Outputs tested for functionality
NOTE: Comprehensive component monitors are
continuous. Therefore, enabling conditions do not
apply.
Input RationalityÐWhile input signals to the
PCM are constantly being monitored for electrical
opens and shorts, they are also tested for rationality.
This means that the input signal is compared against
other inputs and information to see if it makes sense
under the current conditions.
PCM sensor inputs that are checked for rationality
include:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Oxygen Sensor (O2S)
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
²Intake/inlet Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Ambient/Battery Temperature Sensors
²Power Steering Switch
²Oxygen Sensor Heater
²Engine Controller
²Brake Switch
²Leak Detection Pump Switch (if equipped)
²P/N Switch
²Trans ControlsOutput FunctionalityÐPCM outputs are tested
for functionality in addition to testing for opens and
shorts. When the PCM provides a voltage to an out-
put component, it can verify that the command was
carried out by monitoring specific input signals for
expected changes. For example, when the PCM com-
mands the Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor to a specific
position under certain operating conditions, it expects
to see a specific (target) idle speed (RPM). If it does
not, it stores a DTC.
PCM outputs monitored for functionality include:
²Fuel Injectors
²Ignition Coils
²Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
²Idle Air Control
²Purge Solenoid
²EGR Solenoid (if equipped)
²LDP Solenoid (if equipped)
²Radiator Fan Control
²Trans Controls
OXYGEN SENSOR (O2S) MONITOR
DESCRIPTIONÐEffective control of exhaust
emissions is achieved by an oxygen feedback system.
The most important element of the feedback system
is the O2S. The O2S is located in the exhaust path.
Once it reaches operating temperature 300É to 350ÉC
(572É to 662ÉF), the sensor generates a voltage that
is inversely proportional to the amount of oxygen in
the exhaust. When there is a large amount of oxygen
in the exhaust caused by a lean condition, the sensor
produces a low voltage, below 450 mV. When the oxy-
gen content is lower, caused by a rich condition, the
sensor produces a higher voltage, above 450mV.
The information obtained by the sensor is used to
calculate the fuel injector pulse width. The PCM is
programmed to maintain the optimum air/fuel ratio.
At this mixture ratio, the catalyst works best to
remove hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO)
and nitrous oxide (NOx) from the exhaust.
The O2S is also the main sensing element for the
EGR (if equipped), Catalyst and Fuel Monitors.
The O2S may fail in any or all of the following
manners:
²Slow response rate (Big Slope)
²Reduced output voltage (Half Cycle)
²Heater Performance
Slow Response Rate (Big Slope)ÐResponse rate
is the time required for the sensor to switch from
lean to rich signal output once it is exposed to a
richer than optimum A/F mixture or vice versa. As
the PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio, the sensor must
be able to rapidly detect the change. As the sensor
ages, it could take longer to detect the changes in the
oxygen content of the exhaust gas. The rate of
change that an oxygen sensor experiences is called
25 - 2 EMISSIONS CONTROLRS
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2362 of 2399

ªBig Slopeº. The PCM checks the oxygen sensor volt-
age in increments of a few milliseconds.
Reduced Output Voltage (Half Cycle)ÐThe
output voltage of the O2S ranges from 0 to 1 volt. A
good sensor can easily generate any output voltage in
this range as it is exposed to different concentrations
of oxygen. To detect a shift in the A/F mixture (lean
or rich), the output voltage has to change beyond a
threshold value. A malfunctioning sensor could have
difficulty changing beyond the threshold value. Each
time the voltage signal surpasses the threshold, a
counter is incremented by one. This is called the Half
Cycle Counter.
Heater PerformanceÐThe heater is tested by a
separate monitor. Refer to the Oxygen Sensor Heater
Monitor.
OPERATIONÐAs the Oxygen Sensor signal
switches, the PCM monitors the half cycle and big
slope signals from the oxygen sensor. If during the
test neither counter reaches a predetermined value, a
malfunction is entered and Freeze Frame data is
stored. Only one counter reaching its predetermined
value is needed for the monitor to pass.
The Oxygen Sensor Monitor is a two trip monitor
that is tested only once per trip. When the Oxygen
Sensor fails the test in two consecutive trips, the
MIL is illuminated and a DTC is set. The MIL is
extinguished when the Oxygen Sensor monitor
passes in three consecutive trips. The DTC is erased
from memory after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles
without test failure.
Enabling ConditionsÐThe following conditions
must typically be met for the PCM to run the oxygen
sensor monitor:
²Battery voltage
²Engine temperature
²Engine run time
²Engine run time at a predetermined speed
²Engine run time at a predetermined speed and
throttle opening
²Transmission in gear and brake depressed (auto-
matic only)
²Fuel system in Closed Loop
²Long Term Adaptive (within parameters)
²Power Steering Switch in low PSI (no load)
²Engine at idle
²Fuel level above 15%
²Ambient air temperature
²Barometric pressure
²Engine RPM within acceptable range of desired
idle
Pending ConditionsÐThe Task Manager typi-
cally does not run the Oxygen Sensor Monitor if over-
lapping monitors are running or the MIL is
illuminated for any of the following:
²Misfire Monitor²Front Oxygen Sensor and Heater Monitor
²MAP Sensor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
²Throttle Position Sensor
²Engine Controller Self Test Faults
²Cam or Crank Sensor
²Injector and Coil
²Idle Air Control Motor
²EVAP Electrical
²EGR Solenoid Electrical (if equipped)
²Intake/inlet Air Temperature
²5 Volt Feed
ConflictÐThe Task Manager does not run the
Oxygen Sensor Monitor if any of the following condi-
tions are present:
²A/C ON (A/C clutch cycling temporarily sus-
pends monitor)
²Purge flow in progress
²Ethanel content learn is takeng place and the
ethenal used once flag is set (if equipped)
SuspendÐThe Task Manager suspends maturing
a fault for the Oxygen Sensor Monitor if any of the
following are present:
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor, Priority 1
²Misfire Monitor, Priority 2
OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER MONITOR
DESCRIPTIONÐIf there is an oxygen sensor
(O2S) DTC as well as a O2S heater DTC, the O2S
fault MUST be repaired first. After the O2S fault is
repaired, verify that the heater circuit is operating
correctly.
The voltage readings taken from the O2S are very
temperature sensitive. The readings are not accurate
below 300ÉC. Heating of the O2S is done to allow the
engine controller to shift to closed loop control as
soon as possible. The heating element used to heat
the O2S must be tested to ensure that it is heating
the sensor properly.
The heater element itself is not tested. The sensor
output is used to test the heater by isolating the
effect of the heater element on the O2S output volt-
age from the other effects. The resistance is normally
between 100 ohms and 4.5 megaohms. When oxygen
sensor temperature increases, the resistance in the
internal circuit decreases. The PCM sends a 5 volts
biased signal through the oxygen sensors to ground
this monitoring circuit. As the temperature increases,
resistance decreases and the PCM detects a lower
voltage at the reference signal. Inversely, as the tem-
perature decreases, the resistance increases and the
PCM detects a higher voltage at the reference signal.
The O2S circuit is monitored for a drop in voltage.
OPERATIONÐThe Oxygen Sensor Heater Moni-
tor begins after the ignition has been turned OFF.
RSEMISSIONS CONTROL25-3
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2364 of 2399

is enabled to run another test during that trip. When
the test fails 6 times, the counter increments to 3, a
malfunction is entered, and a Freeze Frame is stored,
the code is matured and the MIL is illuminated. If
the first test passes, no further testing is conducted
during that trip.
The MIL is extinguished after three consecutive
good trips. The good trip criteria for the catalyst
monitor is more stringent than the failure criteria. In
order to pass the test and increment one good trip,
the downstream sensor switch rate must be less than
45% of the upstream rate. The failure percentages
are 59% respectively.
Enabling ConditionsÐThe following conditions
must typically be met before the PCM runs the cat-
alyst monitor. Specific times for each parameter may
be different from engine to engine.
²Accumulated drive time
²Enable time
²Ambient air temperature
²Barometric pressure
²Catalyst warm-up counter
²Engine coolant temperature
²Vehicle speed
²MAP
²RPM
²Engine in closed loop
²Fuel level
Pending ConditionsÐ
²Misfire DTC
²Front Oxygen Sensor Response
²Front Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Front Oxygen Sensor Electrical
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Rationality (middle check)
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Rear Oxygen Sensor Electrical
²Fuel System Monitor
²All TPS faults
²All MAP faults
²All ECT sensor faults
²Purge flow solenoid functionality
²Purge flow solenoid electrical
²All PCM self test faults
²All CMP and CKP sensor faults
²All injector and ignition electrical faults
²Idle Air Control (IAC) motor functionality
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Brake switch (auto trans only)
²Intake air temperature
ConflictÐThe catalyst monitor does not run if any
of the following are conditions are present:
²EGR Monitor in progress (if equipped)
²Fuel system rich intrusive test in progress
²EVAP Monitor in progress
²Time since start is less than 60 seconds
²Low fuel level-less than 15 %²Low ambient air temperature
²Ethanel content learn is takeng place and the
ethenal used once flag is set
SuspendÐThe Task Manager does not mature a
catalyst fault if any of the following are present:
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor, Priority 1
²Oxygen Sensor Heater, Priority 1
²EGR Monitor, Priority 1 (if equipped)
²EVAP Monitor, Priority 1
²Fuel System Monitor, Priority 2
²Misfire Monitor, Priority 2
OPERATION - NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor all circuits, systems
and conditions that could have malfunctions causing
driveability problems. However, problems with these
systems may cause the PCM to store diagnostic trou-
ble codes for other systems or components. For exam-
ple, a fuel pressure problem will not register a fault
directly, but could cause a rich/lean condition or mis-
fire. This could cause the PCM to store an oxygen
sensor or misfire diagnostic trouble code.
The major non-monitored circuits are listed below
along with examples of failures modes that do not
directly cause the PCM to set a DTC, but for a sys-
tem that is monitored.
FUEL PRESSURE
The fuel pressure regulator controls fuel system
pressure. The PCM cannot detect a clogged fuel
pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel filter, or a
pinched fuel supply or return line. However, these
could result in a rich or lean condition causing the
PCM to store an oxygen sensor, fuel system, or mis-
fire diagnostic trouble code.
SECONDARY IGNITION CIRCUIT
The PCM cannot detect an inoperative ignition coil,
fouled or worn spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or
open spark plug cables. The misfire will however,
increase the oxygen content in the exhaust, deceiving
the PCM in to thinking the fuel system is too lean.
Also misfire detection.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION
The PCM cannot detect uneven, low, or high engine
cylinder compression. Low compression lowers O2
content in the exhaust. Leading to fuel system, oxy-
gen sensor, or misfire detection fault.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
The PCM cannot detect a plugged, restricted or
leaking exhaust system. It may set a EGR (if
equipped) or Fuel system or O2S fault.
RSEMISSIONS CONTROL25-5
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2394 of 2399
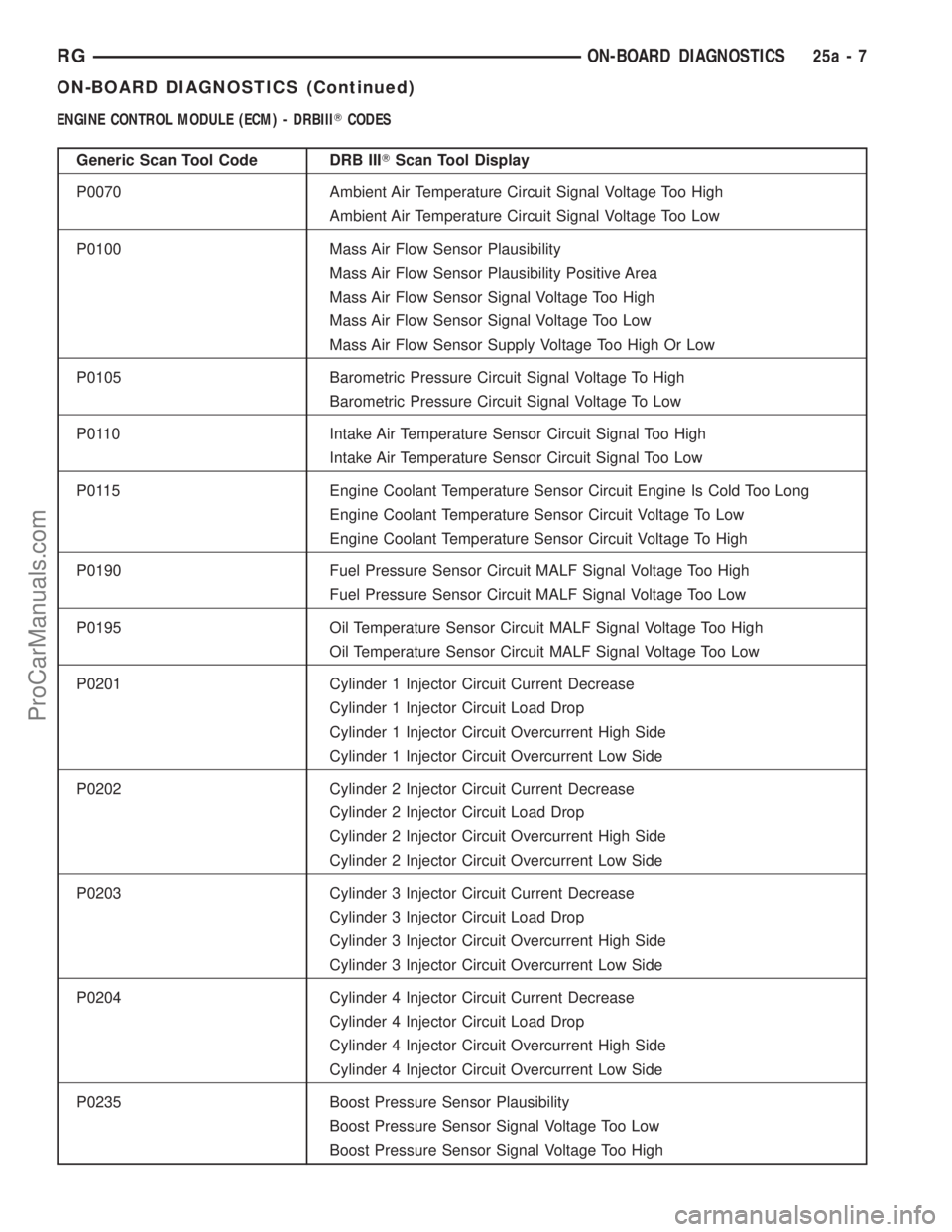
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE (ECM) - DRBIIITCODES
Generic Scan Tool Code DRB IIITScan Tool Display
P0070 Ambient Air Temperature Circuit Signal Voltage Too High
Ambient Air Temperature Circuit Signal Voltage Too Low
P0100 Mass Air Flow Sensor Plausibility
Mass Air Flow Sensor Plausibility Positive Area
Mass Air Flow Sensor Signal Voltage Too High
Mass Air Flow Sensor Signal Voltage Too Low
Mass Air Flow Sensor Supply Voltage Too High Or Low
P0105 Barometric Pressure Circuit Signal Voltage To High
Barometric Pressure Circuit Signal Voltage To Low
P0110 Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit Signal Too High
Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit Signal Too Low
P0115 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Engine Is Cold Too Long
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Voltage To Low
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit Voltage To High
P0190 Fuel Pressure Sensor Circuit MALF Signal Voltage Too High
Fuel Pressure Sensor Circuit MALF Signal Voltage Too Low
P0195 Oil Temperature Sensor Circuit MALF Signal Voltage Too High
Oil Temperature Sensor Circuit MALF Signal Voltage Too Low
P0201 Cylinder 1 Injector Circuit Current Decrease
Cylinder 1 Injector Circuit Load Drop
Cylinder 1 Injector Circuit Overcurrent High Side
Cylinder 1 Injector Circuit Overcurrent Low Side
P0202 Cylinder 2 Injector Circuit Current Decrease
Cylinder 2 Injector Circuit Load Drop
Cylinder 2 Injector Circuit Overcurrent High Side
Cylinder 2 Injector Circuit Overcurrent Low Side
P0203 Cylinder 3 Injector Circuit Current Decrease
Cylinder 3 Injector Circuit Load Drop
Cylinder 3 Injector Circuit Overcurrent High Side
Cylinder 3 Injector Circuit Overcurrent Low Side
P0204 Cylinder 4 Injector Circuit Current Decrease
Cylinder 4 Injector Circuit Load Drop
Cylinder 4 Injector Circuit Overcurrent High Side
Cylinder 4 Injector Circuit Overcurrent Low Side
P0235 Boost Pressure Sensor Plausibility
Boost Pressure Sensor Signal Voltage Too Low
Boost Pressure Sensor Signal Voltage Too High
RGON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS25a-7
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2395 of 2399
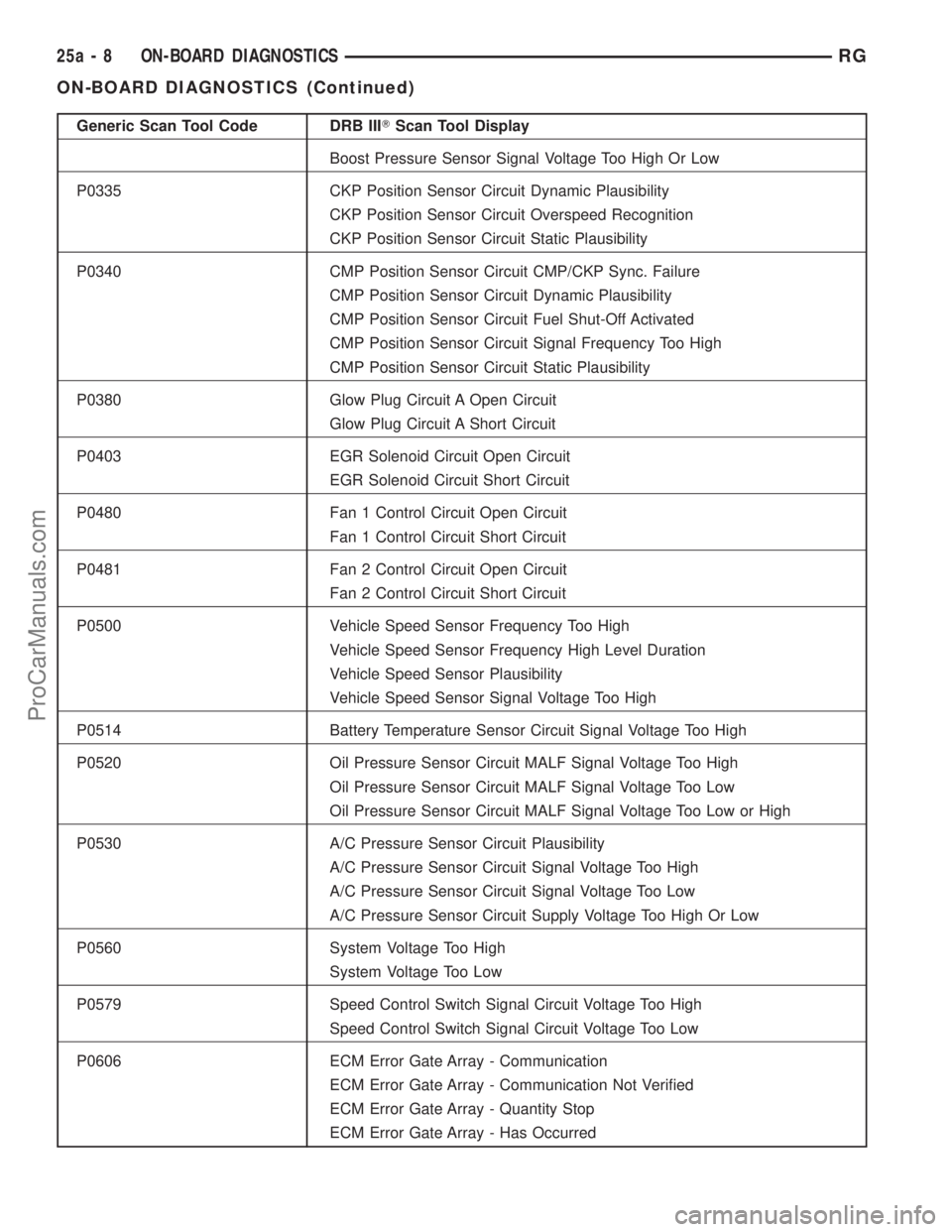
Generic Scan Tool Code DRB IIITScan Tool Display
Boost Pressure Sensor Signal Voltage Too High Or Low
P0335 CKP Position Sensor Circuit Dynamic Plausibility
CKP Position Sensor Circuit Overspeed Recognition
CKP Position Sensor Circuit Static Plausibility
P0340 CMP Position Sensor Circuit CMP/CKP Sync. Failure
CMP Position Sensor Circuit Dynamic Plausibility
CMP Position Sensor Circuit Fuel Shut-Off Activated
CMP Position Sensor Circuit Signal Frequency Too High
CMP Position Sensor Circuit Static Plausibility
P0380 Glow Plug Circuit A Open Circuit
Glow Plug Circuit A Short Circuit
P0403 EGR Solenoid Circuit Open Circuit
EGR Solenoid Circuit Short Circuit
P0480 Fan 1 Control Circuit Open Circuit
Fan 1 Control Circuit Short Circuit
P0481 Fan 2 Control Circuit Open Circuit
Fan 2 Control Circuit Short Circuit
P0500 Vehicle Speed Sensor Frequency Too High
Vehicle Speed Sensor Frequency High Level Duration
Vehicle Speed Sensor Plausibility
Vehicle Speed Sensor Signal Voltage Too High
P0514 Battery Temperature Sensor Circuit Signal Voltage Too High
P0520 Oil Pressure Sensor Circuit MALF Signal Voltage Too High
Oil Pressure Sensor Circuit MALF Signal Voltage Too Low
Oil Pressure Sensor Circuit MALF Signal Voltage Too Low or High
P0530 A/C Pressure Sensor Circuit Plausibility
A/C Pressure Sensor Circuit Signal Voltage Too High
A/C Pressure Sensor Circuit Signal Voltage Too Low
A/C Pressure Sensor Circuit Supply Voltage Too High Or Low
P0560 System Voltage Too High
System Voltage Too Low
P0579 Speed Control Switch Signal Circuit Voltage Too High
Speed Control Switch Signal Circuit Voltage Too Low
P0606 ECM Error Gate Array - Communication
ECM Error Gate Array - Communication Not Verified
ECM Error Gate Array - Quantity Stop
ECM Error Gate Array - Has Occurred
25a - 8 ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICSRG
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com