2002 CHRYSLER TOWN AND COUNTRY timing
[x] Cancel search: timingPage 483 of 2399

INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Install coil over studs on bracket.
(2) Install 2 bolts to ignition coil.
(3) Install 2 nuts to the ignition coil studs. Tighten
nuts and bolts.
(4) Connect the electrical connector to the ignition
coil.
(5) Install the ignition cables to the ignition coil.
(6) Reposition the Power steering reservoir. Slide
bracket over the mounting stud (Fig. 11).
(7) Install 2 bolts to the Power steering reservoir
to intake manifold.
(8) Tighten the lower nut to stud on ignition coil
bracket.
(9) Install the throttle and speed control cables to
clip.
(10) Connect the negative battery cable.
KNOCK SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The knock sensor threads into the cylinder block.
The knock sensor is designed to detect engine vibra-
tion that is caused by detonation.
OPERATION
When the knock sensor detects a knock in one of
the cylinders, it sends an input signal to the PCM. In
response, the PCM retards ignition timing for all cyl-
inders by a scheduled amount.
Knock sensors contain a piezoelectric material
which constantly vibrates and sends an input voltage
(signal) to the PCM while the engine operates. As the
intensity of the crystal's vibration increases, the
knock sensor output voltage also increases.
The voltage signal produced by the knock sensor
increases with the amplitude of vibration. The PCM
receives as an input the knock sensor voltage signal.
If the signal rises above a predetermined level, the
PCM will store that value in memory and retard
ignition timing to reduce engine knock. If the knock
sensor voltage exceeds a preset value, the PCM
retards ignition timing for all cylinders. It is not a
selective cylinder retard.
The PCM ignores knock sensor input during engine
idle conditions. Once the engine speed exceeds a
specified value, knock retard is allowed.
Knock retard uses its own short term and long
term memory program.
Long term memory stores previous detonation
information in its battery-backed RAM. The maxi-
mum authority that long term memory has over tim-
ing retard can be calibrated.
Short term memory is allowed to retard timing up
to a preset amount under all operating conditions (aslong as rpm is above the minimum rpm) except WOT.
The PCM, using short term memory, can respond
quickly to retard timing when engine knock is
detected. Short term memory is lost any time the
ignition key is turned off.
NOTE: Over or under tightening affects knock sen-
sor performance, possibly causing improper spark
control.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L
The knock sensor threads into the side of the cyl-
inder block in front of the starter (Fig. 12).
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from knock sen-
sor.
(2) Use a crow foot socket to remove the knock
sensors.
REMOVAL - 3.8L
The knock sensor threads into the side of the cyl-
inder block in the rear.
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Raise vehicle and support.
(3) On All Wheel Drive vehicles remove the PTU
(Power Transfer Unit), refer to the Transmission sec-
tion for more information.
(4) Disconnect electrical connector from knock sen-
sor.
(5) Use a crow foot socket to remove the knock
sensor.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
The knock sensor threads into the side of the cyl-
inder block in front of the starter (Fig. 12).
(1) Install knock sensor. Tighten knock sensor to
10 N´m (7 ft. lbs.) torque.Over or under tighten-
ing effects knock sensor performance, possibly
causing improper spark control.
(2) Attach electrical connector to knock sensor.
INSTALLATION - 3.8L
The knock sensor threads into the side of the cyl-
inder block in the rear.
(1) Install knock sensor. Tighten knock sensor to
10 N´m (7 ft. lbs.) torque.Over or under tighten-
ing effects knock sensor performance, possibly
causing improper spark control.
(2) Attach electrical connector to knock sensor.
8I - 8 IGNITION CONTROLRS
IGNITION COIL (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1204 of 2399

EXHAUST MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION.........................62
OPERATION...........................62
REMOVAL.............................62
CLEANING............................62
INSPECTION..........................62
INSTALLATION.........................62
TIMING BELT COVER(S)
REMOVAL.............................63
INSTALLATION.........................63
TIMING BELT AND SPROCKET(S)
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - TIMING BELT...............64REMOVAL - CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET....66
CLEANING............................66
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET . 66
INSTALLATION - TIMING BELT...........67
TIMING BELT TENSIONER & PULLEY
REMOVAL.............................68
INSTALLATION.........................69
BALANCE SHAFTS AND CARRIER ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION.........................69
OPERATION...........................70
REMOVAL.............................70
INSTALLATION.........................71
ENGINE 2.4L
DESCRIPTION
The 2.4 Liter (148 cu. in.) in-line four cylinder
engine is a double over head camshaft with hydraulic
lash adjusters and four valve per cylinder design.
The engine is free-wheeling; meaning it has provi-
sions for piston-to-valve clearance. However valve-to-
valve interference can occur, if camshafts are rotated
independently.
The cylinders are numbered from front of the
engine to the rear. The firing order is 1±3±4±2.
The engine identification number is located on the
rear of the cylinder block (Fig. 1).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.
These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).
Refer to the Engine Mechanical and the Engine
Performance diagnostic charts, for possible causes
and corrections of malfunctions (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MECHANICAL)
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
- PERFORMANCE).
For fuel system diagnosis, (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
²Hydraulic Lash Adjuster Noise Diagnosis
²Engine Oil Leak Inspection
Fig. 1 Engine Identification
1 - ENGINE IDENTIFICATION LOCATION
RSENGINE 2.4L9-3
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1205 of 2399
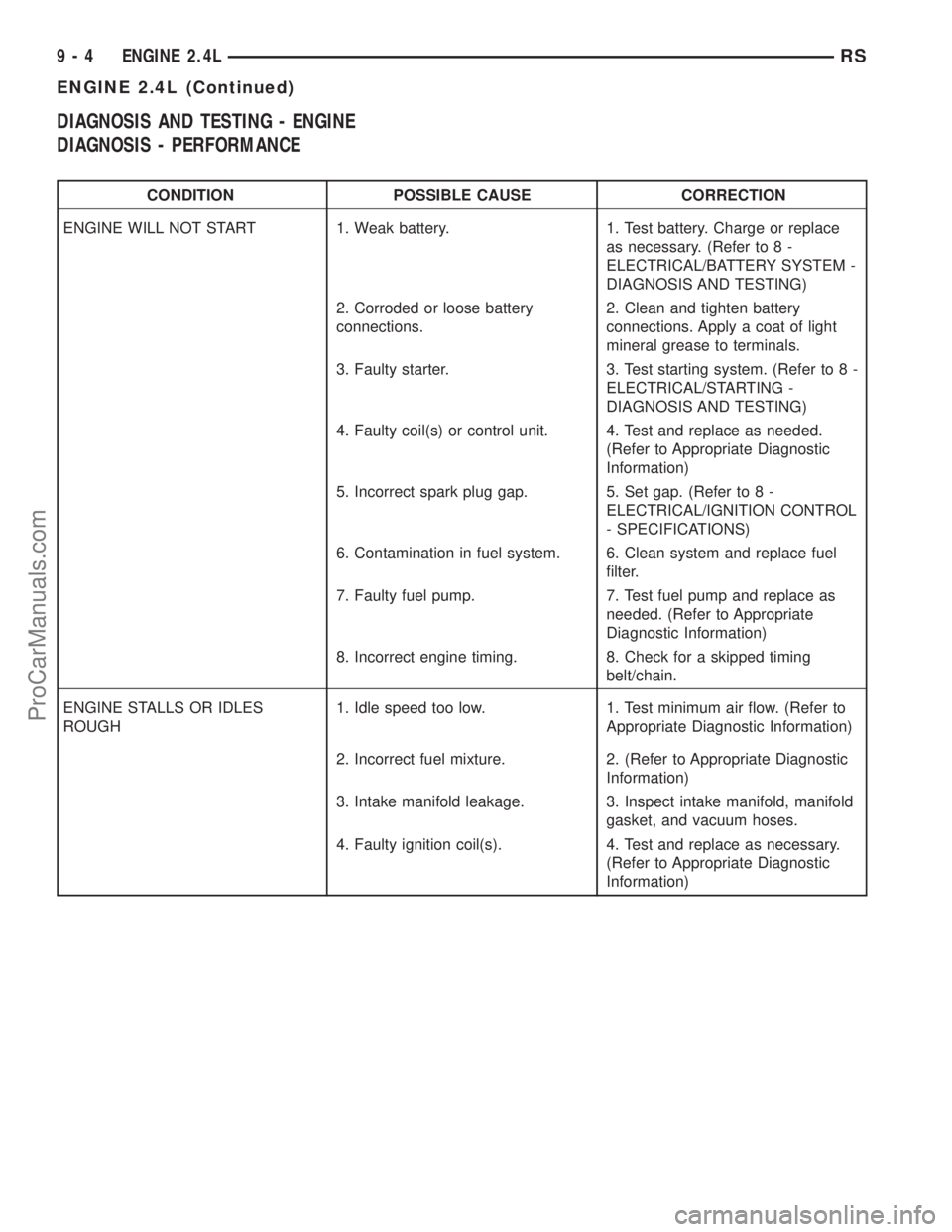
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery. 1. Test battery. Charge or replace
as necessary. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. Test starting system. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/STARTING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
4. Faulty coil(s) or control unit. 4. Test and replace as needed.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. Set gap. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL
- SPECIFICATIONS)
6. Contamination in fuel system. 6. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
7. Faulty fuel pump. 7. Test fuel pump and replace as
needed. (Refer to Appropriate
Diagnostic Information)
8. Incorrect engine timing. 8. Check for a skipped timing
belt/chain.
ENGINE STALLS OR IDLES
ROUGH1. Idle speed too low. 1. Test minimum air flow. (Refer to
Appropriate Diagnostic Information)
2. Incorrect fuel mixture. 2. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
3. Intake manifold leakage. 3. Inspect intake manifold, manifold
gasket, and vacuum hoses.
4. Faulty ignition coil(s). 4. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
9 - 4 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1206 of 2399

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE LOSS OF POWER 1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped plugs. 1. Clean plugs and set gap.
2. Contamination in fuel system. 2. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
3. Faulty fuel pump. 3. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
4. Incorrect valve timing. 4. Correct valve timing.
5. Leaking cylinder head gasket. 5. Replace cylinder head gasket.
6. Low compression. 6. Test compression of each
cylinder.
7. Burned, warped, or pitted valves. 7. Replace valves.
8. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system.8. Perform exhaust restriction test.
(Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) Install
new parts, as necessary.
9. Faulty ignition coil(s). 9. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs.1. Clean spark plugs and set gap.
2. Contamination in Fuel System. 2. Clean fuel system and replace
fuel filter.
3. Burned, warped, or pitted valves. 3. Replace valves.
4. Faulty ignition coil(s). 4. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
ENGINE MISSES AT HIGH SPEED 1. Dirty or incorrect spark plug gap. 1. Clean spark plugs and set gap.
2. Faulty ignition coil(s). 2. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
3. Dirty fuel injector(s). 3. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
4. Contamination in fuel system. 4. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
RSENGINE 2.4L9-5
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1219 of 2399

DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Wear Limit 0.075 mm
(0.003 in.)
Bore DiameterÐPiston
Pin20.96±20.98 mm
(0.8252±0.8260 in.)
Bore DiameterÐ
Crankshaft End53.007±52.993 mm
(2.0868±2.0863 in.)
Side Clearance 0.13±0.38 mm
(0.005±0.015 in.)
Wear Limit 0.40 mm
(0.016 in.)
WeightÐTotal (Less
Bearing)565.8 grams
(19.96 oz.)
Crankshaft
Connecting Rod Journal
Diameter49.984±50.000 mm
(1.968±1.9685 in.)
Main Bearing Journal
Diameter59.992±60.008 mm
(2.362±2.3625 in.)
Journal Out-of-Round
(Max.)0.0035 mm
(0.0003 in.)
Journal Taper (Max.) 0.007 mm
(0.0001 in.)
End Play 0.09±0.24 mm
(0.0035±0.0094 in.)
Wear Limit 0.38 mm
(0.015 in.)
Main Bearing Diametrical
Clearance0.018±0.062 mm
(0.0007±0.0024 in.)
Hydraulic Lash Adjuster
Body Diameter 15.901±15.913 mm
(0.626±0.6264 in.)
Plunger Travel Minimum
(Dry)3.0 mm
(0.118 in.)
Cylinder Head Camshaft Bearing Bore Diameter
Journals No.1±6 26.020±26.041 mm
(1.024±1.025 in.)
Camshaft
Journal Diameter No. 1±6 25.951±25.970 mm
(1.021±1.022 in.)
Bearing ClearanceÐ
Diametrical0.069±0.071 mm
(0.0027±0.003 in.)
End Play 0.05±0.17 mm
(0.0019±0.0066 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Lift (Zero Lash)
Intake 8.25 mm
(0.324 in.)
Exhaust 6.60 mm
(0.259 in.)
Intake Valve Timing*
Closes (ABDC) 51É
Opens (BTDC) 1É
Duration 232É
Exhaust Valve Timing*
Closes (ATDC) 7É
Opens (BBDC) 47É
Duration 234É
Valve Overlap 8É
*All readings in crankshaft degrees. Timing points @
4É from top of Ramps.
Cylinder Head
Material Cast Aluminum
Gasket Thickness
(Compressed)0.71 mm
(0.028 in.)
Valve Seat
Angle 44.5±45É
Seat DiameterÐIntake 34.37±34.63 mm
(1.353±1.363 in.)
Seat DiameterÐExhaust 27.06±27.32 mm
(1.065±1.075 in.)
Runout (Max.) 0.05 mm
(0.002 in.)
Valve Seat WidthÐIntake
and Exhaust0.9±1.3 mm
(0.035±0.051 in.)
Service LimitÐIntake 2.0 mm
(0.079 in.)
Service LimitÐExhaust 2.5 mm
(0.098 in.)
Valve Guide
Diameter I.D. 5.975±6.000 mm
(0.235±0.236 in.)
Guide Bore Diameter 11.0±11.02 mm
(0.4330±0.4338 in.)
Guide Height (spring seat
to guide tip)13.25±13.75 mm
(0.521±0.541 in.)
9 - 18 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1221 of 2399

SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Balance Shaft Carrier to
BlockÐBolts54 40 Ð
Balance Shaft Gear
CoverÐDouble Ended
Fastener12 Ð 105
Balance Shaft SprocketÐ
Bolt28 Ð 250
Balance Shaft Chain
TensionerÐBolts12 Ð 105
Balance Shaft Carrier
CoverÐBolts12 Ð 105
Camshaft SprocketÐBolt 101 75 Ð
Connecting Rod
CapÐBolts27 +
1¤4
turn20
+1¤4
turnÐ
Crankshaft Main Bearing
Cap/Bedplate
ÐM8 Bolts 28 250
ÐM11 Bolts 41 +
1¤4
Turn30
+1¤4
TurnÐ
Crankshaft Damper 136 100 Ð
Cylinder HeadÐBolts (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD -
INSTALLATION)
Cylinder Head CoverÐ
Bolts12 Ð 105
Flex Plate to Crankshaft 95 70 Ð
Engine Mount Bracket
RightÐBolts61 45 Ð
Engine MountingÐBolts (Refer to 9 ENGINE/
ENGINE MOUNTING)
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Exhaust Manifold to
Cylinder HeadÐBolts19 Ð 170
Exhaust Manifold Heat
ShieldÐBolts12 Ð 105
Intake Manifold - Lower
ÐBolts28 Ð 250
Intake Manifold -
UpperÐBolts28 Ð 250
Oil Filter 12 Ð 105
Oil PanÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Oil Pan DrainÐPlug 27 20 Ð
Oil Pressure Switch 21 Ð 190
Oil Pump to BlockÐBolts 28 Ð 250
Oil Pump Cover
PlateÐBolts12 Ð 105
Oil Pump Pick-up
TubeÐBolt28 20 Ð
Oil Pump Relief
ValveÐCap41 30 Ð
Spark Plugs 18 13 Ð
Structural Collar (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/
STRUCTURAL COVER -
INSTALLATION)
Timing Belt Covers
- Front Covers to Rear
CoverÐBolts7Ð60
- Rear CoverÐM6 Bolts 12 Ð 105
ÐM8 Bolts 28 Ð 250
Timing Belt Tensioner
AssemblyÐBolts61 45 Ð
9 - 20 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1227 of 2399

(13) Remove timing belt and camshaft sprockets.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - REMOVAL)
(14) Remove timing belt idler pulley and rear tim-
ing belt cover. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIM-
ING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) -
REMOVAL)
(15) Remove cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(16) Remove camshafts (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/CAMSHAFT(S) - REMOVAL).
NOTE: Identify rocker arm position to ensure cor-
rect re-installation in original position, if reused.
(17) Remove rocker arms. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS - REMOVAL)
(18) Remove cylinder head bolts in REVERSE
sequence of tightening (Fig. 19).
(19) Remove cylinder head from engine block.
(20) Inspect and clean cylinder head. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSPECTION) (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - CLEANING)
CLEANING
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components and multi-layer
steel cylinder head gaskets.
NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets require
a scratch free sealing surface.
Remove all gasket material from cylinder head and
block (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE). Be careful not to gouge or scratch the alumi-
num head sealing surface.
Clean all engine oil passages.
INSPECTION
(1) Cylinder head must be flat within 0.1 mm
(0.004 in.) (Fig. 14).
(2) Inspect camshaft bearing journals for scoring.
(3) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from
inside of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
(4) Using a small hole gauge and a micrometer,
measure valve guides in 3 places top, middle and bot-
tom (Fig. 15). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICA-
TIONS) Replace guides if they are not within
specification.
(5) Check valve guide height (Fig. 16).
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD
NOTE: The Cylinder head bolts should be examined
BEFORE reuse. If the threads are necked down, the
bolts must be replaced (Fig. 17).
Necking can be checked by holding a scale or
straight edge against the threads. If all the threads
do not contact the scale, the bolt should be replaced.
(1) Before installing the bolts, the threads should
be coated with engine oil.
(2) Position cylinder head gasket on engine block
(Fig. 18).
(3) Install cylinder head on engine block.
(4) Tighten the cylinder head bolts in the sequence
shown in (Fig. 19). Using the 4 step torque turn
method, tighten according to the following values:
²First All to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.)
Fig. 14 Checking Cylinder Head Flatness
1 - FEELER GAUGE
2 - STRAIGHT EDGE
Fig. 15 Checking Wear on Valve GuideÐTypical
1-TOP
2 - MIDDLE
3 - BOTTOM
4 - CUT AWAY VIEW OF VALVE GUIDE MEASUREMENT
LOCATIONS
9 - 26 ENGINE 2.4LRS
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1228 of 2399
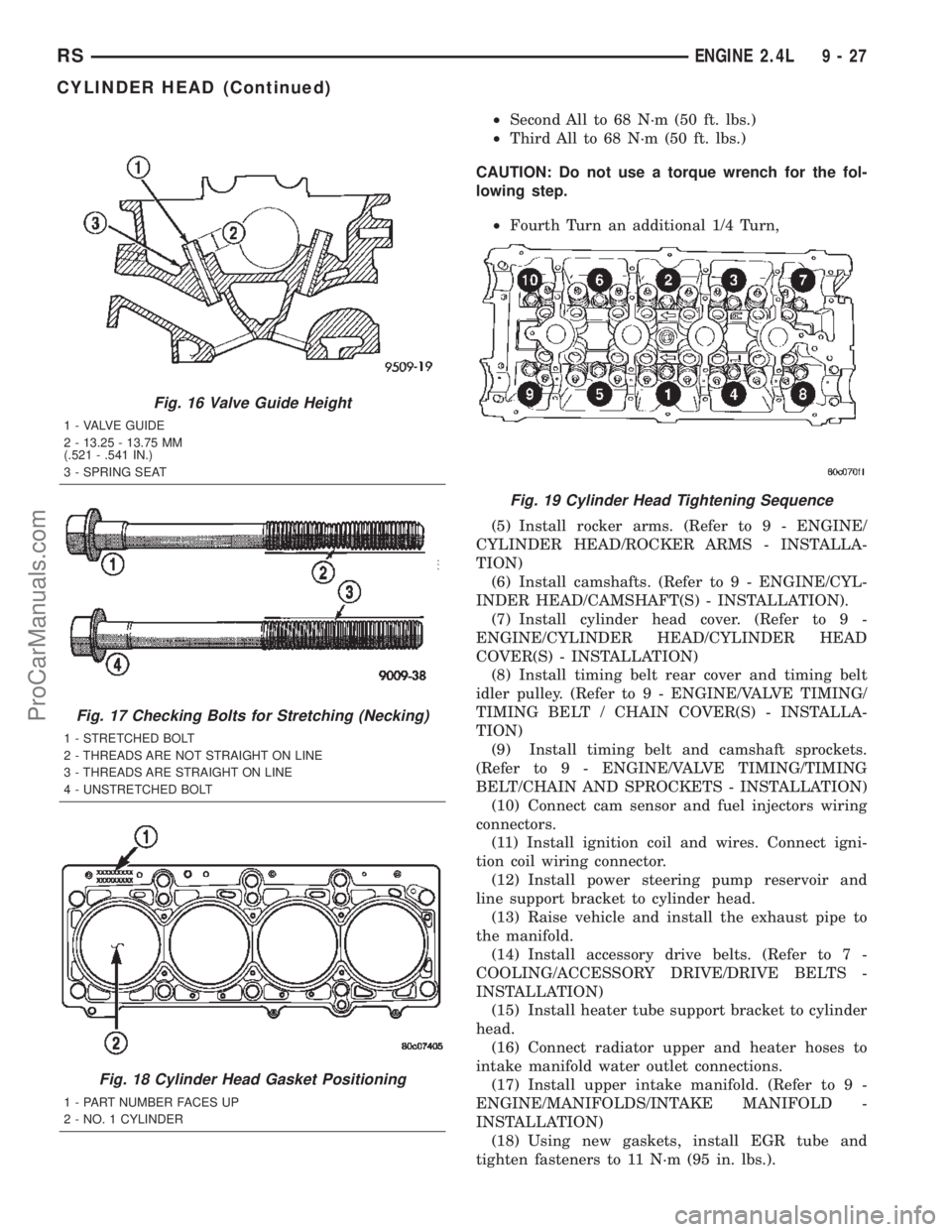
²Second All to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.)
²Third All to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.)
CAUTION: Do not use a torque wrench for the fol-
lowing step.
²Fourth Turn an additional 1/4 Turn,
(5) Install rocker arms. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS - INSTALLA-
TION)
(6) Install camshafts. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYL-
INDER HEAD/CAMSHAFT(S) - INSTALLATION).
(7) Install cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
(8) Install timing belt rear cover and timing belt
idler pulley. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/
TIMING BELT / CHAIN COVER(S) - INSTALLA-
TION)
(9) Install timing belt and camshaft sprockets.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT/CHAIN AND SPROCKETS - INSTALLATION)
(10) Connect cam sensor and fuel injectors wiring
connectors.
(11) Install ignition coil and wires. Connect igni-
tion coil wiring connector.
(12) Install power steering pump reservoir and
line support bracket to cylinder head.
(13) Raise vehicle and install the exhaust pipe to
the manifold.
(14) Install accessory drive belts. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION)
(15) Install heater tube support bracket to cylinder
head.
(16) Connect radiator upper and heater hoses to
intake manifold water outlet connections.
(17) Install upper intake manifold. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION)
(18) Using new gaskets, install EGR tube and
tighten fasteners to 11 N´m (95 in. lbs.).
Fig. 16 Valve Guide Height
1 - VALVE GUIDE
2 - 13.25 - 13.75 MM
(.521 - .541 IN.)
3 - SPRING SEAT
Fig. 17 Checking Bolts for Stretching (Necking)
1 - STRETCHED BOLT
2 - THREADS ARE NOT STRAIGHT ON LINE
3 - THREADS ARE STRAIGHT ON LINE
4 - UNSTRETCHED BOLT
Fig. 18 Cylinder Head Gasket Positioning
1 - PART NUMBER FACES UP
2 - NO. 1 CYLINDER
Fig. 19 Cylinder Head Tightening Sequence
RSENGINE 2.4L9-27
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com