2002 CHRYSLER CARAVAN ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 1481 of 2399

²Manifold pressure
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance programs
²Shift-point strategies (F4AC1 transmissions
only, via the PCI bus)
²Idle speed
²Decel fuel shutoff
The PCM recognizes a decrease in manifold pres-
sure by monitoring a decrease in voltage from the
reading stored in the barometric pressure memory
cell. The MAP sensor is a linear sensor; as pressure
changes, voltage changes proportionately. The range
of voltage output from the sensor is usually between
4.6 volts at sea level to as low as 0.3 volts at 26 in. of
Hg. Barometric pressure is the pressure exerted by
the atmosphere upon an object. At sea level on a
standard day, no storm, barometric pressure is 29.92
in Hg. For every 100 feet of altitude barometric pres-
sure drops .10 in. Hg. If a storm goes through it can
either add, high pressure, or decrease, low pressure,
from what should be present for that altitude. You
should make a habit of knowing what the average
pressure and corresponding barometric pressure is
for your area.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Disconnect electrical connector and vacuum
hose from MAP sensor (Fig. 18).
(3) Remove two screws holding sensor to the
intake manifold.
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Remove vacuum hose and mounting screws
from manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor (Fig.
19).
(3) Disconnect electrical connector from sensor.
Remove sensor.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Install sensor.
(2) Install two screws and tighten.
(3) Connect the electrical connector and vacuum
hose to the MAP sensor (Fig. 18).
(4) Connect the negative battery cable.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Install sensor (Fig. 19).(2) Install screws and tighten toPLASTIC MAN-
IFOLD 1.7 N´m (15 in. lbs.) ALUMINUM MANI-
FOLD 3.3 N´m (30 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect the electrical connector to the sensor.
Install vacuum hose.
(4) Connect the negative battery cable.
O2 SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The upstream oxygen sensor threads into the out-
let flange of the exhaust manifold (Fig. 20) or (Fig.
21).
Fig. 20 O2 SENSOR UPSTREAM 1/1 - 2.4L
Fig. 21 O2 SENSOR UPSTREAM 1/1 - 3.3/3.8L
14 - 30 FUEL INJECTIONRS
MAP SENSOR (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1489 of 2399

Test all fuel supply lines for restrictions or block-
age. Flush or replace as necessary. Bleed fuel system
of air once a fuel supply line has been replaced. Refer
to Air Bleed Procedure for procedures.
To test for fuel line restrictions, a vacuum restric-
tion test may be performed.
HIGH-PRESSURE LINES
Restricted (kinked or bent) high-pressure lines can
cause starting problems, poor engine performance,
engine mis-fire and white smoke from exhaust.
Examine all high-pressure lines for any damage.
Each radius on each high-pressure line must be
smooth and free of any bends or kinks.
Replace damaged, restricted or leaking high-pres-
sure fuel lines with correct replacement line.
CAUTION: High pressure lines cannot contact each
other or other components. Do not attempt to weld
high-pressure fuel lines or to repair lines that are
damaged. If line is kinked or bent, it must be
replaced. Use only recommended lines when
replacement of high-pressure fuel line is necessary.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURES - DRAINING WATER
FROM FUEL FILTER
Refer to Fuel Filter/Water Separator removal/in-
stallation for procedures.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM AIR
PURGE
(1) Remove engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
COVER - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove cap from air purge fitting on the fuel
supply line. This fitting is located just behind the
alternator (Fig. 1).
(3) Attach a hose of about 1 or 2 meters to this fit-
ting using an appropriate connector.
(4) Direct the end of the hose into an appropriate
fuel container.
(5) Turn the ignition to the ªONº position,Do not
crank the engine.Keep key on until about 1 liter of
fuel has been pumped into the container.
(6) While keeping end of hose below fuel level in
conatiner, turn the ignition ªOFFº.
(7) Remove hose from air purge fitting on the fuel
supply line and replace cap.
(8) Install engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
COVER - INSTALLATION).
STANDARD PROCEDURES - CLEANING FUEL
SYSTEM COMPONENTS
CAUTION: Cleanliness cannot be overemphasized
when handling or replacing diesel fuel system com-
ponents. This especially includes the fuel injectors,
high-pressure fuel lines, fuel rail, and fuel injection
pump. Very tight tolerances are used with these
parts. Dirt contamination could cause rapid part
wear and possible plugging of fuel injector nozzle
tip holes. This in turn could lead to possible engine
misfire. Always wash/clean any fuel system compo-
nent thoroughly before disassembly and then air
dry. Cap or cover any open part after disassembly.
Before assembly, examine each part for dirt, grease
or other contaminants and clean if necessary. When
installing new parts, lubricate them with clean
engine oil or clean diesel fuel only.
Fig. 1 AIR PURGE VALVE
1 - AIR PURGE VALVE CAP
2 - AIR PURGE VALVE
3 - ALTERNATOR
4 - ENGINE FRONT COVER
14a - 2 FUEL SYSTEMRG
FUEL SYSTEM 2.5L TURBO DIESEL (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1503 of 2399

MASS AIR FLOW (MAF)
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor is mounted
inline in the air intake between the air filter and the
turbocharger (Fig. 8).
OPERATION
The ECM uses the mass air flow (MAF) sensor to
measure air density. The MAF sensor contains a
ceramic element. A signal voltage is provided to the
element. As engine speed increases, airflow across
the ceramic element increases. Changes in air flow
and air density cause the temperature of the ceramic
element to fluxuate. The ceramic element changes
resistance respectively to changes in temperature.
The change in resistance varies the signal voltage
output to the ECM. The diesel power relay supplies
battery power the to MAF sensor. Ground is providedby the ECM. The MAF sensor signal is provided by
the ECM.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Disconnect MAF sensor electrical connector
(Fig. 9).
(3) Loosen MAF sensor retaining clamps (Fig. 9).
(4) Remove MAF sensor from airduct (Fig. 9).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install MAF sensor in airduct (Fig. 9).
(2) Tighten retaining clamps (Fig. 9).
(3) Connect MAF sensor electrical connector (Fig.
9).
(4) Connect negative battery cable.
Fig. 8 MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) SENSOR
Fig. 9 MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) SENSOR LOCATION
1 - MAF SENSOR ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - RETAINING CLAMPS
3 - MASS AIR FLOW (MAF) SENSOR
4 - AIR CLEANER HOUSING
14a - 16 FUEL INJECTIONRG
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1504 of 2399

STEERING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STEERING
DESCRIPTION - POWER STEERING SYSTEM . . 1
OPERATION - POWER STEERING SYSTEM . . . 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER
STEERING SYSTEM FLOW AND
PRESSURE TEST......................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STEERING
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHARTS............3SPECIFICATIONS
POWER STEERING FASTENER TORQUE . . . 9
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER STEERING....................9
COLUMN..............................10
GEAR.................................26
PUMP.................................36
STEERING
DESCRIPTION - POWER STEERING SYSTEM
This vehicle comes with power steering as stan-
dard equipment. The power steering system consists
of these major components:
²POWER STEERING PUMP
²POWER STEERING GEAR
²POWER STEERING FLUID
²POWER STEERING FLUID COOLER
²POWER STEERING FLUID RESERVOIR
²POWER STEERING FLUID SUPPLY HOSE
²POWER STEERING FLUID PRESSURE HOSE
²POWER STEERING FLUID RETURN HOSE
For information on the first two components, refer
to their respective sections within this service man-
ual group. Information on all other components can
be found in POWER STEERING PUMP.
OPERATION - POWER STEERING SYSTEM
Turning of the steering wheel is converted into lin-
ear (side-to-side) travel through the meshing of the
helical pinion teeth with the rack teeth within the
steering gear. The lateral travel pushes and pulls the
tie rods to change the direction of the vehicle's front
wheels.
Power assist steering is provided by a belt driven
rotary type pump. It directs fluid through power
steering fluid hoses to the power steering gear where
it is used to assist the driver's turning effort.
Manual steering control of the vehicle can be main-
tained if power steering assist is lost. However,
under this condition, steering effort is significantly
increased.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER STEERING
SYSTEM FLOW AND PRESSURE TEST
ALL ENGINES
The following procedure is to be used to test the
operation of the power steering system on this vehi-
cle. This test will provide the flow rate of the power
steering pump along with the maximum relief pres-
sure. This test is to be performed to determine if the
power steering pump or power steering gear is not
functioning properly. The following flow and pressure
test is performed using the Power Steering Analyzer
Kit, Special Tool 6815 (Fig. 1), hoses, Special Tools
6905 and 6959, and fittings from adapter kit, Special
Tool 6893.
Fig. 1 Power Steering Analyzer With Hoses Installed
1 - OUTLET
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 6815
3 - INLET
RSSTEERING19-1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1591 of 2399

(4) Read pressures on both gauges as throttle lever
on transaxle is moved from full clockwise position to
full counterclockwise position.
(5) Line pressure should read 52 to 58 psi with
throttle lever clockwise. Pressure should gradually
increase to 80 to 88 psi. as lever is moved counter-
clockwise.
(6) Lubrication pressure should be 10 to 25 psi
with lever clockwise and 10 to 35 psi with lever at
full counterclockwise.
(7) This tests pump output, pressure regulation,
and condition of rear clutch and lubrication hydraulic
circuits.
TEST THREE (SELECTOR IN D)
(1) Attach gauges to line and kickdown release
ports.
(2) Operate engine at 1600 rpm for test.
(3) Move selector lever on transaxle two detents
forward from full rearward position. This is selector
D position.
(4) Read pressures on both gauges as throttle lever
on transaxle is moved from full clockwise to the full
counterclockwise position.
(5) Line pressure should read 52 to 58 psi with
throttle lever clockwise. Pressure should gradually
increase to 80 to 88 psi. as lever is moved counter-
clockwise.
(6) Kickdown release is pressurized only in direct
drive and should be same as line pressure within 3
psi, up to kickdown point.
(7) This tests pump output, pressure regulation,
and condition of rear clutch, front clutch, and
hydraulic circuits.
TEST FOUR (SELECTOR IN REVERSE)
(1) Attach 300 psi gauge (C-3292SP) to low-reverse
port.
(2) Operate engine at 1600 rpm for test.
(3) Move selector lever on transaxle four detents
forward from full rearward position. This is selector
R position.
(4) Low/reverse pressure should read 180 to 220
psi with throttle lever clockwise. Pressure should
gradually increase to 260 to 300 psi. as lever is
moved counterclockwise.(5) This tests pump output, pressure regulation,
and condition of front clutch and rear servo hydraulic
circuits.
(6) Move selector lever on transaxle to D position
to check that low/reverse pressure drops to zero.
(7) This tests for leakage into rear servo, due to
case porosity, which can cause reverse band burn out.
TEST RESULT INDICATIONS
(1) If proper line pressure, minimum to maximum,
is found in any one test, the pump and pressure reg-
ulator are working properly.
(2) Low pressure in D, 1, and 2 but correct pres-
sure in R, indicates rear clutch circuit leakage.
(3) Low pressure in D and R, but correct pressure
in 1 indicates front clutch circuit leakage.
(4) Low pressure in R and 1, but correct pressure
in 2 indicates rear servo circuit leakage.
(5) Low line pressure in all positions indicates a
defective pump, a clogged filter, or a stuck pressure
regulator valve.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE
Test only if transaxle shifts at wrong vehicle
speeds when throttle cable is correctly adjusted.
(1) Connect a 100 psi gauge to governor pressure
port. It is located at lower right side of case, below
differential cover (Fig. 2).
(2) Operate transaxle in third gear to read pres-
sures. The governor pressure should respond
smoothly to changes in mph and should return to 0
to 3 psi when vehicle is stopped. High pressure
(above 3 psi) at standstill will prevent the transaxle
from downshifting.
THROTTLE PRESSURE
No gauge port is provided for throttle pressure.
Incorrect throttle pressure should be suspected if
part throttle upshift speeds are either delayed or
occur too early in relation to vehicle speed. Engine
runaway on shifts can also be an indicator of low
throttle pressure setting, or misadjusted throttle
cable.
In no case should throttle pressure be adjusted
until the transaxle throttle cable adjustment has
been verified to be correct.
21 - 34 31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1592 of 2399

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE
When diagnosing converter housing fluid leaks,
three actions must be taken before repair:
(1) Verify proper transmission fluid level.
(2) Verify that the leak originates from the con-
verter housing area and is transmission fluid.
(3) Determine the true source of the leak.
Fluid leakage at or around the torque converter
area may originate from an engine oil leak (Fig. 3).
The area should be examined closely. Factory fill
fluid is red and, therefore, can be distinguished from
engine oil.
Some suspected converter housing fluid leaks may
not be leaks at all. They may only be the result of
residual fluid in the converter housing, or excess
fluid spilled during factory fill, or fill after repair.
Converter housing leaks have several potential
sources. Through careful observation, a leak source
can be identified before removing the transmission
for repair.
Pump seal leaks tend to move along the drive hub
and onto the rear of the converter (Fig. 3). Pump
o-ring or pump body leaks follow the same path as a
seal leak. Pump attaching bolt leaks are generally
deposited on the inside of the converter housing and
not on the converter itself. Pump seal or gasket leaks
usually travel down the inside of the converter hous-
ing (Fig. 3).
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAKAGE
Possible sources of torque converter leakage are:
²Torque converter weld leaks at the outside diam-
eter weld (Fig. 4).
²Torque converter hub weld (Fig. 4).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH AND
SERVO AIR PRESSURE TESTS
A no drive condition might exist even with correct
fluid pressure, because of inoperative clutches or
bands. The inoperative units, clutches, bands, and
servos can be located through a series of tests. This
is done by substituting air pressure for fluid pressure
(Fig. 5).
The front and rear clutches, kickdown servo, and
low-reverse servo may be tested by applying air pres-
sure to their respective passages. To make air pres-
sure tests, proceed as follows:
NOTE: Compressed air supply must be free of all
dirt or moisture. Use a pressure of 30 psi.
Remove oil pan and valve body. Refer to Valve
Body for removal procedure.
FRONT CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to front clutch apply passage
and listen for a dull thud which indicates that front
clutch is operating. Hold air pressure on for a few
seconds and inspect system for excessive oil leaks.
Fig. 3 Converter Housing Leak Paths
1 - PUMP SEAL
2 - PUMP VENT
3 - PUMP BOLT
4 - PUMP GASKET
5 - CONVERTER HOUSING
6 - CONVERTER
7 - REAR MAIN SEAL LEAK
Fig. 4 Converter Leak PointsÐTypical
1 - OUTSIDE DIAMETER WELD
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER HUB WELD
3 - STARTER RING GEAR
4 - LUG
RS31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21-35
31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1673 of 2399

When the ignition key is in either the OFF,
ON/RUN, or START positions, the BTSI solenoid is
energized, and the solenoid plunger hook pulls the
shift lever pawl into position, prohibiting the shift
lever from moving out of PARK (P) (Fig. 212). When
the brake pedal is depressed, the ground circuit
opens, de-energizing the solenoid. This moves the
gearshift lever pawl out of the way (Fig. 213), allow-
ing the shift lever to be moved into any gear position.A conventional mechanical interlock system is also
used. This system manually prohibits shifter move-
ment when the ignition switch is in the LOCK or
ACC positions. Solenoid operation is not required in
these key positions.
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park with brake
pedal applied.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system adjustment or repair.
Fig. 211 Ignition Key/Switch Positions
1 - ACC
2 - LOCK
3 - OFF
4 - ON/RUN
5-START
Fig. 212 Pawl Engaged to Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
Fig. 213 Pawl Disengaged From Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
21 - 116 31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1674 of 2399
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park with brake
pedal applied.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system repair. Refer to the
appropriate Diagnostic Information.
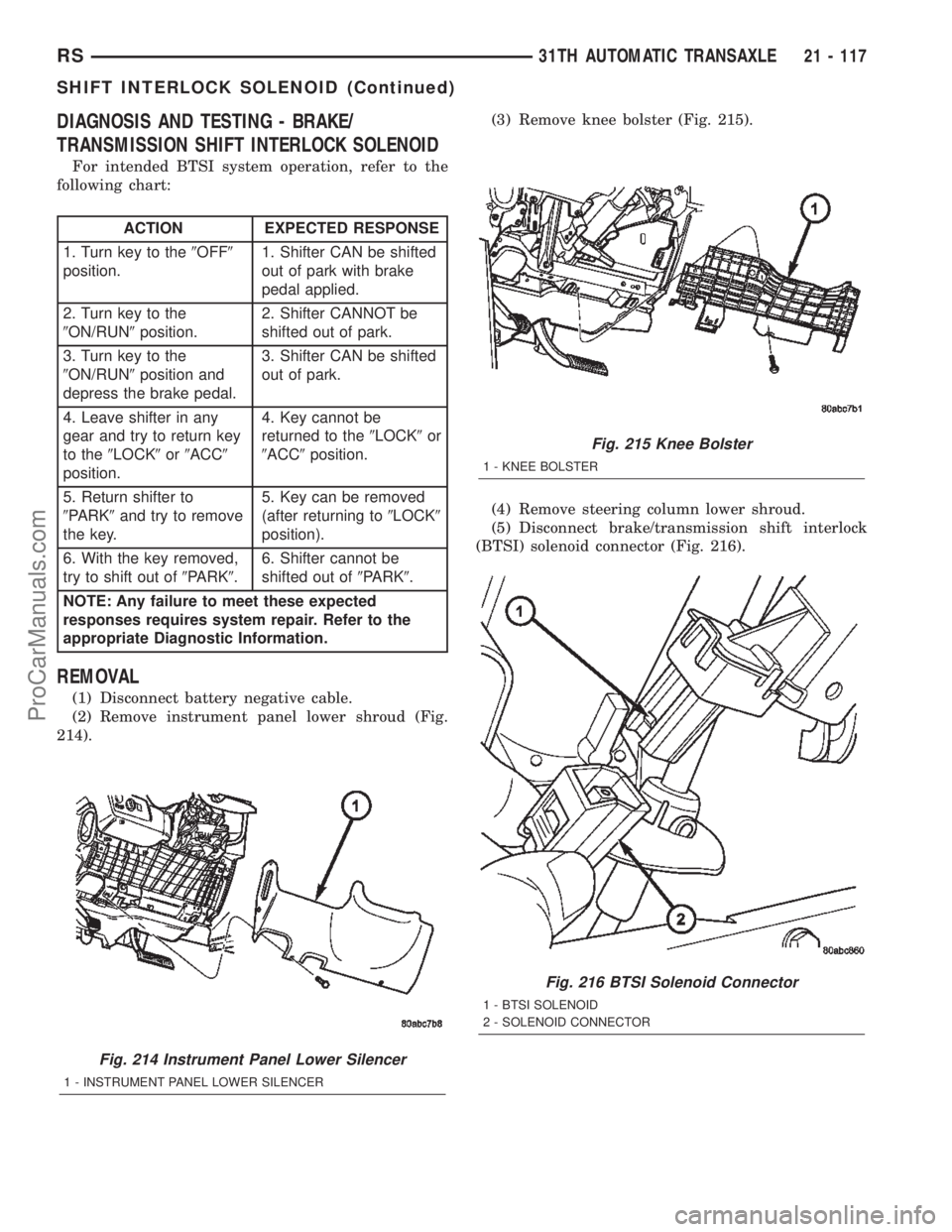
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove instrument panel lower shroud (Fig.
214).(3) Remove knee bolster (Fig. 215).
(4) Remove steering column lower shroud.
(5) Disconnect brake/transmission shift interlock
(BTSI) solenoid connector (Fig. 216).
Fig. 214 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
Fig. 215 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
Fig. 216 BTSI Solenoid Connector
1 - BTSI SOLENOID
2 - SOLENOID CONNECTOR
RS31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 117
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com