Page 1846 of 2399

OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 333) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 334).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-
clockwise direction. When this happens the over±run-
ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the statorfrom rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid
that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock±up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
In a standard torque converter, the impeller and
turbine are rotating at about the same speed and the
stator is freewheeling, providing no torque multipli-
cation. By applying the turbine's piston to the front
cover's friction material, a total converter engage-
ment can be obtained. The result of this engagement
is a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine
and the transmission.
The engagement and disengagement of the TCC
are automatic and controlled by the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). The engagement cannot be acti-
vated in the lower gears because it eliminates the
torque multiplication effect of the torque converter
necessary for acceleration. Inputs that determine
clutch engagement are: coolant temperature, vehicle
speed and throttle position. The torque converter
Fig. 333 Torque Converter Fluid Operation
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 289
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1869 of 2399
1ST GEAR
Engine power is transmitted to the input shaft via
the clutch assembly and the input shaft turns. The
input shaft first gear is integral to the input shaft,
and is in constant mesh with the intermediate shaft
first speed gear. Because of this constant mesh, the
intermediate shaft first speed gear freewheels until
first gear is selected. As the gearshift lever is moved
to the first gear position, the 1-2 fork moves the 1-2
synchronizer sleeve towards first gear on the inter-
mediate shaft. The synchronizer sleeve engages the
first gear clutch teeth, fixing the gear to the interme-
diate shaft, and allowing power to transmit through
the intermediate shaft to the differential (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4 1st Gear Operation
21 - 312 T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLERS
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1870 of 2399
2ND GEAR
Engine power is transmitted to the input shaft via
the clutch assembly and the input shaft turns. The
input shaft second gear is integral to the input shaft,
and is in constant mesh with the intermediate shaft
second speed gear. Because of this constant mesh,
the intermediate shaft second speed gear freewheels
until second gear is selected. As the gearshift lever is
moved to the second gear position, the 1-2 fork moves
the 1-2 synchronizer sleeve towards second gear on
the intermediate shaft. The synchronizer sleeve
engages the second gear clutch teeth, fixing the gear
to the intermediate shaft, and allowing power to
transmit through the intermediate shaft to the differ-
ential (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5 2nd Gear Operation
RST850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE21 - 313
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1871 of 2399
3RD GEAR
Engine power is transmitted to the input shaft via
the clutch assembly and the input shaft turns. The
input shaft third speed gear is in constant mesh with
the intermediate shaft 3-4 cluster gear, which is fixed
to the intermediate shaft. Because of this constant
mesh, the input shaft third speed gear freewheels
until third gear is selected. As the gearshift lever is
moved to the third gear position, the 3-4 fork moves
the 3-4 synchronizer sleeve towards third gear on the
input shaft. The synchronizer sleeve engages the
third gear clutch teeth, fixing the gear to the input
shaft, and allowing power to transmit through the
intermediate shaft to the differential (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6 3rd Gear Operation
21 - 314 T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLERS
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1872 of 2399
4TH GEAR
Engine power is transmitted to the input shaft via
the clutch assembly and the input shaft turns. The
input shaft fourth speed gear is in constant mesh
with the intermediate shaft 3-4 cluster gear, which is
fixed to the intermediate shaft. Because of this con-
stant mesh, the input shaft fourth speed gear free-
wheels until fourth gear is selected. As the gearshift
lever is moved to the fourth gear position, the 3-4
fork moves the 3-4 synchronizer sleeve towards
fourth gear on the input shaft. The synchronizer
sleeve engages the fourth gear clutch teeth, fixing
the gear to the input shaft, and allowing power to
transmit through the intermediate shaft to the differ-
ential (Fig. 7).
Fig. 7 4th Gear Operation
RST850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE21 - 315
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1873 of 2399
5TH GEAR
Engine power is transmitted to the input shaft via
the clutch assembly and the input shaft turns. The
input shaft fifth gear is pressed on to the input shaft,
and is in constant mesh with the intermediate shaft
fifth speed gear. Because of this constant mesh, the
intermediate shaft fifth speed gear freewheels until
fifth gear is selected. As the gearshift lever is moved
to the fifth gear position, the 5-R fork moves the 5-R
synchronizer sleeve towards the intermediate shaft
fifth speed gear. The synchronizer sleeve engages the
fifth gear clutch teeth, fixing the gear to the input
shaft, and allowing power to transmit through the
intermediate shaft to the differential (Fig. 8).
Fig. 8 5th Gear Operation
21 - 316 T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLERS
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1874 of 2399
REVERSE GEAR
Engine power is transmitted to the input shaft via
the clutch assembly and the input shaft turns. The
input shaft reverse gear is integral to the input
shaft, and is in constant mesh with the reverse idler
gear. The reverse idler gear, which reverses the rota-
tion of the intermediate shaft, is in constant mesh
with the intermediate shaft reverse gear. Because of
this constant mesh, the intermediate shaft reverse
gear freewheels until reverse gear is selected. As the
gearshift lever is moved to the reverse gear position,
the 5-R fork moves the 5-R synchronizer sleeve
towards the intermediate shaft reverse gear. The
synchronizer sleeve engages the reverse gear clutch
teeth, fixing the gear to the intermediate shaft, and
allowing power to transmit through the intermediate
shaft to the differential (in reverse) (Fig. 9).
Fig. 9 Reverse Gear Operation
RST850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE21 - 317
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1876 of 2399
(9) Using Tool 6638A, disconnect clutch hydraulic
circuit quick connect (located on slave cylinder tube).
Remove clutch slave cylinder by depressing towards
case and rotating counter-clockwise 60É, while lifting
anti-rotation tab out of case slot with screwdriver
(Fig. 12).
(10) Remove engine left mount bracket.
(11) Remove starter motor (Fig. 13).
(12) Disconnect back-up lamp switch connector.
(13) Remove structural collar.
(14) Remove modular clutch assembly-to-drive
plate bolts.
(15) Position screw jack and wood block to engine
oil pan.
(16) Remove transmission upper mount through-
bolt from left frame rail.
(17) Lower engine/transaxle assembly on screw
jack.
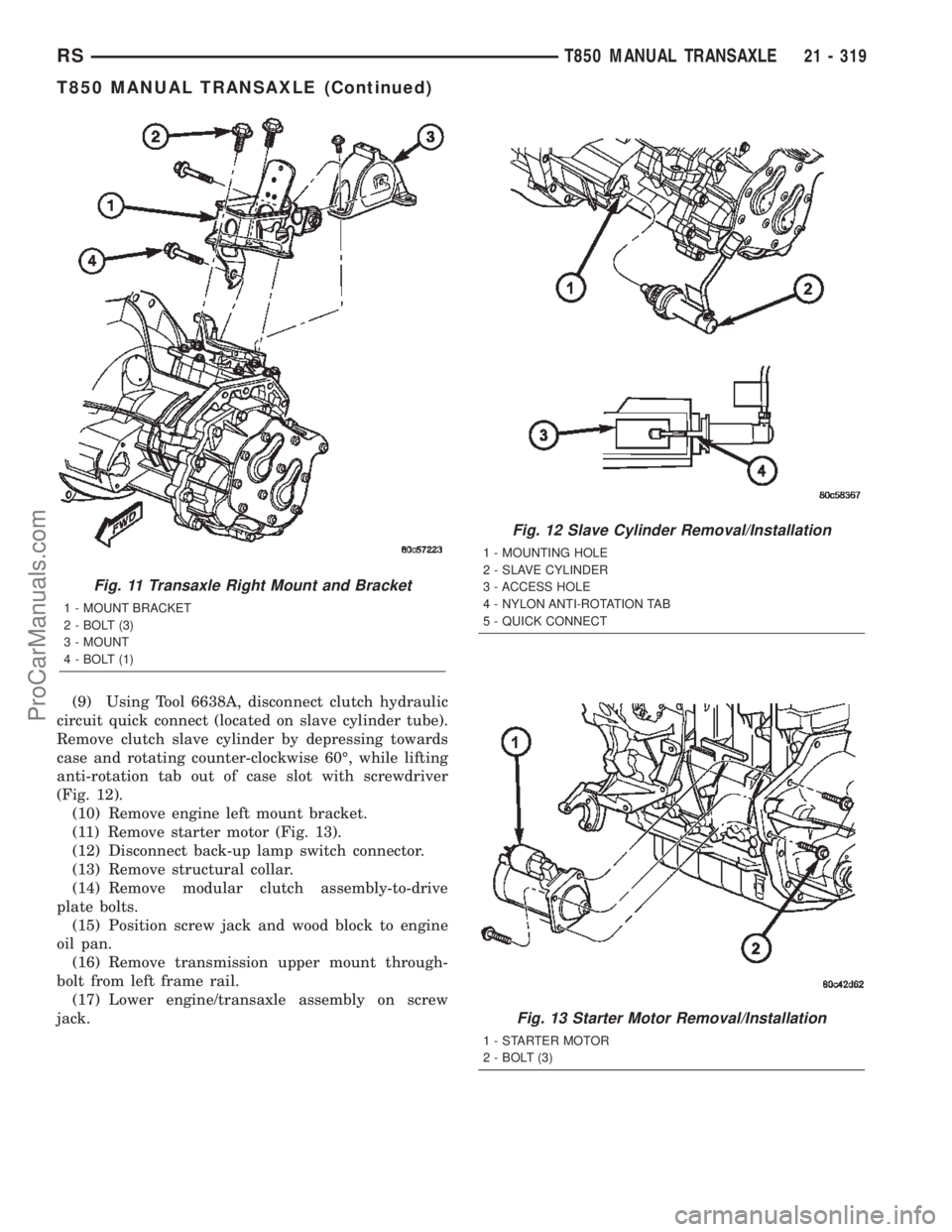
Fig. 11 Transaxle Right Mount and Bracket
1 - MOUNT BRACKET
2 - BOLT (3)
3 - MOUNT
4 - BOLT (1)
Fig. 12 Slave Cylinder Removal/Installation
1 - MOUNTING HOLE
2 - SLAVE CYLINDER
3 - ACCESS HOLE
4 - NYLON ANTI-ROTATION TAB
5 - QUICK CONNECT
Fig. 13 Starter Motor Removal/Installation
1 - STARTER MOTOR
2 - BOLT (3)
RST850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE21 - 319
T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com