2001 NISSAN ALMERA coolant temperature
[x] Cancel search: coolant temperaturePage 1227 of 2898

DescriptionNJEC1752SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONNJEC1752S01
Sensor Input Signal to ECMECM func-
tionActuator
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) Engine speed
EVAP can-
ister purge
controlEVAP canister purge volume
control solenoid valve Camshaft position sensor (PHASE) Engine speed and cylinder number
Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Battery Battery voltage
Ignition switch Start signal
Closed throttle position switch (If so
equipped)Closed throttle position
Throttle position sensor Throttle position
Heated oxygen sensor 1 (front)Density of oxygen in exhaust gas
(Mixture ratio feedback signal)
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
This system controls flow rate of fuel vapor from the EVAP canis-
ter. The opening of the vapor by-pass passage in the EVAP canis-
ter purge volume control solenoid valve changes to control the flow
rate. The EVAP canister purge volume control solenoid valve
repeats ON/OFF operation according to the signal sent from the
ECM. The opening of the valve varies for optimum engine control.
The optimum value stored in the ECM is determined by consider-
ing various engine conditions. When the engine is operating, the
flow rate of fuel vapor from the EVAP canister is regulated as the
air flow changes.
SEF337U
COMPONENT DESCRIPTIONNJEC1752S02The EVAP canister purge volume control solenoid valve uses a
ON/OFF duty to control the flow rate of fuel vapor from the EVAP
canister. The EVAP canister purge volume control solenoid valve
is moved by ON/OFF pulses from the ECM. The longer the ON
pulse, the greater the amount of fuel vapor that will flow through the
valve.
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode
NJEC1753
MONITOR ITEM CONDITION SPECIFICATION
PURG VOL C/V+Engine: After warming up
+No-loadIdle 0%
Revving engine Ð
EVAP CANISTER PURGE VOLUME CONTROL SOLENOID VALVEQG
Description
EC-503
Page 1235 of 2898

DescriptionNJEC1758SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONNJEC1758S01
Sensor Input Signal to ECMECM func-
tionActuator
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) Engine speed
Idle air
controlIACV-AAC valve Camshaft position sensor (PHASE) Engine speed and cylinder number
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Ignition switch Start signal
Throttle position sensor Throttle position
PNP switch Park/Neutral position
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner operation
Power steering oil pressure switch Power steering load signal
Battery Battery voltage
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Cooling fan Cooling fan operation
Electrical load Electrical load signal
This system automatically controls engine idle speed to a specified
level. Idle speed is controlled through fine adjustment of the
amount of air which by-passes the throttle valve via IACV-AAC
valve. The IACV-AAC valve changes the opening of the air by-pass
passage to control the amount of auxiliary air. This valve is actu-
ated by a step motor built into the valve, which moves the valve in
the axial direction in steps corresponding to the ECM output sig-
nals. One step of IACV-AAC valve movement causes the respec-
tive opening of the air by-pass passage. (i.e. when the step
advances, the opening is enlarged.) The opening of the valve is
varied to allow for optimum control of the engine idling speed. The
crankshaft position sensor (POS) detects the actual engine speed
and sends a signal to the ECM. The ECM then controls the step
position of the IACV-AAC valve so that engine speed coincides with
the target value memorized in ECM. The target engine speed is the
lowest speed at which the engine can operate steadily. The opti-
mum value stored in the ECM is determined by taking into consid-
eration various engine conditions, such as during warm up,
deceleration, and engine load (air conditioner, power steering, cool-
ing fan operation and electrical load).
SEF937W
COMPONENT DESCRIPTIONNJEC1758S02IACV-AAC ValveNJEC1758S0201The IACV-AAC valve is operated by a step motor for centralized
control of auxiliary air supply. This motor has four winding phases
and is actuated by the output signals of ECM which turns ON and
OFF two windings each in sequence. Each time the IACV-AAC
valve opens or closes to change the auxiliary air quantity, the ECM
sends a pulse signal to the step motor. When no change in the
auxiliary air quantity is needed, the ECM does not issue the pulse
signal. A certain voltage signal is issued so that the valve remains
at that particular opening.
IDLE AIR CONTROL VALVE (IACV) Ð AUXILIARY AIR CONTROL
(AAC) VALVE
QG
Description
EC-511
Page 1250 of 2898
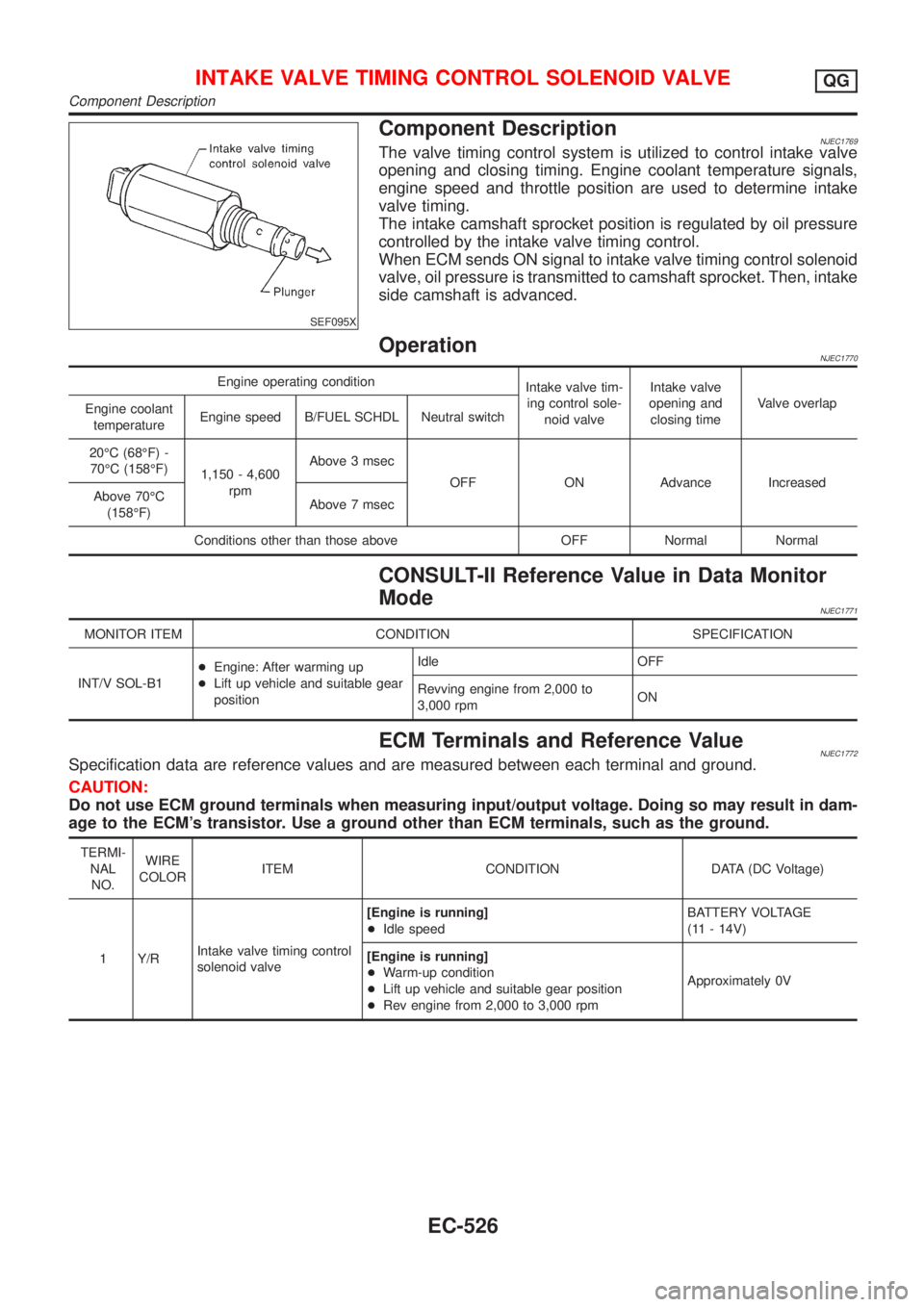
SEF095X
Component DescriptionNJEC1769The valve timing control system is utilized to control intake valve
opening and closing timing. Engine coolant temperature signals,
engine speed and throttle position are used to determine intake
valve timing.
The intake camshaft sprocket position is regulated by oil pressure
controlled by the intake valve timing control.
When ECM sends ON signal to intake valve timing control solenoid
valve, oil pressure is transmitted to camshaft sprocket. Then, intake
side camshaft is advanced.
OperationNJEC1770
Engine operating condition
Intake valve tim-
ing control sole-
noid valveIntake valve
opening and
closing timeValve overlap
Engine coolant
temperatureEngine speed B/FUEL SCHDL Neutral switch
20ÉC (68ÉF) -
70ÉC (158ÉF)
1,150 - 4,600
rpmAbove 3 msec
OFF ON Advance Increased
Above 70ÉC
(158ÉF)Above 7 msec
Conditions other than those above OFF Normal Normal
CONSULT-II Reference Value in Data Monitor
Mode
NJEC1771
MONITOR ITEM CONDITION SPECIFICATION
INT/V SOL-B1+Engine: After warming up
+Lift up vehicle and suitable gear
positionIdle OFF
Revving engine from 2,000 to
3,000 rpmON
ECM Terminals and Reference ValueNJEC1772Specification data are reference values and are measured between each terminal and ground.
CAUTION:
Do not use ECM ground terminals when measuring input/output voltage. Doing so may result in dam-
age to the ECM's transistor. Use a ground other than ECM terminals, such as the ground.
TERMI-
NAL
NO.WIRE
COLORITEM CONDITION DATA (DC Voltage)
1 Y/RIntake valve timing control
solenoid valve[Engine is running]
+Idle speedBATTERY VOLTAGE
(11 - 14V)
[Engine is running]
+Warm-up condition
+Lift up vehicle and suitable gear position
+Rev engine from 2,000 to 3,000 rpmApproximately 0V
INTAKE VALVE TIMING CONTROL SOLENOID VALVEQG
Component Description
EC-526
Page 1317 of 2898

Fuel Pressure RegulatorNJEC0467
Fuel pressure at idling
kPa (bar, kg/cm2, psi)Vacuum hose is connected Approximately 235 (2.35, 2.4, 34)
Vacuum hose is disconnected Approximately 294 (2.94, 3.0, 43)
Idle Speed and Ignition TimingNJEC0468
Target idle speed* rpmM/T: 700±50
A/T: 800±50
Air conditioner: ON rpm825 or more
Ignition timingM/T: 8±5É BTDC
A/T: 10±5É BTDC
Throttle position sensor idle position V 0.15 - 0.85
*: Under the following conditions:
+Air conditioner switch: OFF
+Electrical load: OFF (Lights, heater fan & rear window defogger)
+Steering wheel: Kept in straight-ahead position
Mass Air Flow SensorNJEC0470
Supply voltage (Heater) VBattery voltage (11 - 14)
Supply voltage (Sensor) VApproximately 5
Output voltage V1.0 - 1.7*
Mass air flow
(Using CONSULT-II or GST) g´m/sec1.0 - 4.0 at idle*
5.0 - 10.0 at 2,500 rpm*
*: Engine is warmed up to normal operating temperature and idling under no-load.
Intake Air Temperature SensorNJEC0480
Temperature ÉC (ÉF) Resistance kW
20 (68) 2.1 - 2.9
80 (176) 0.27 - 0.38
Engine Coolant Temperature SensorNJEC0471
Temperature ÉC (ÉF) Resistance kW
20 (68) 2.1 - 2.9
50 (122) 0.68 - 1.00
90 (194) 0.236 - 0.260
Throttle Position SensorNJEC0477
Throttle valve conditions Voltage (V)
Completely closed0.15 - 0.85
Completely open3.5 - 4.7
Heated Oxygen Sensor 1 Heater (Front)NJEC0478
Resistance [at 25ÉC (77ÉF)]W2.3 - 4.3
Heated Oxygen Sensor 2 Heater (Rear)NJEC0483
Resistance [at 25ÉC (77ÉF)]W2.3 - 4.3
SERVICE DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS (SDS)QG
Fuel Pressure Regulator
EC-593
Page 1333 of 2898
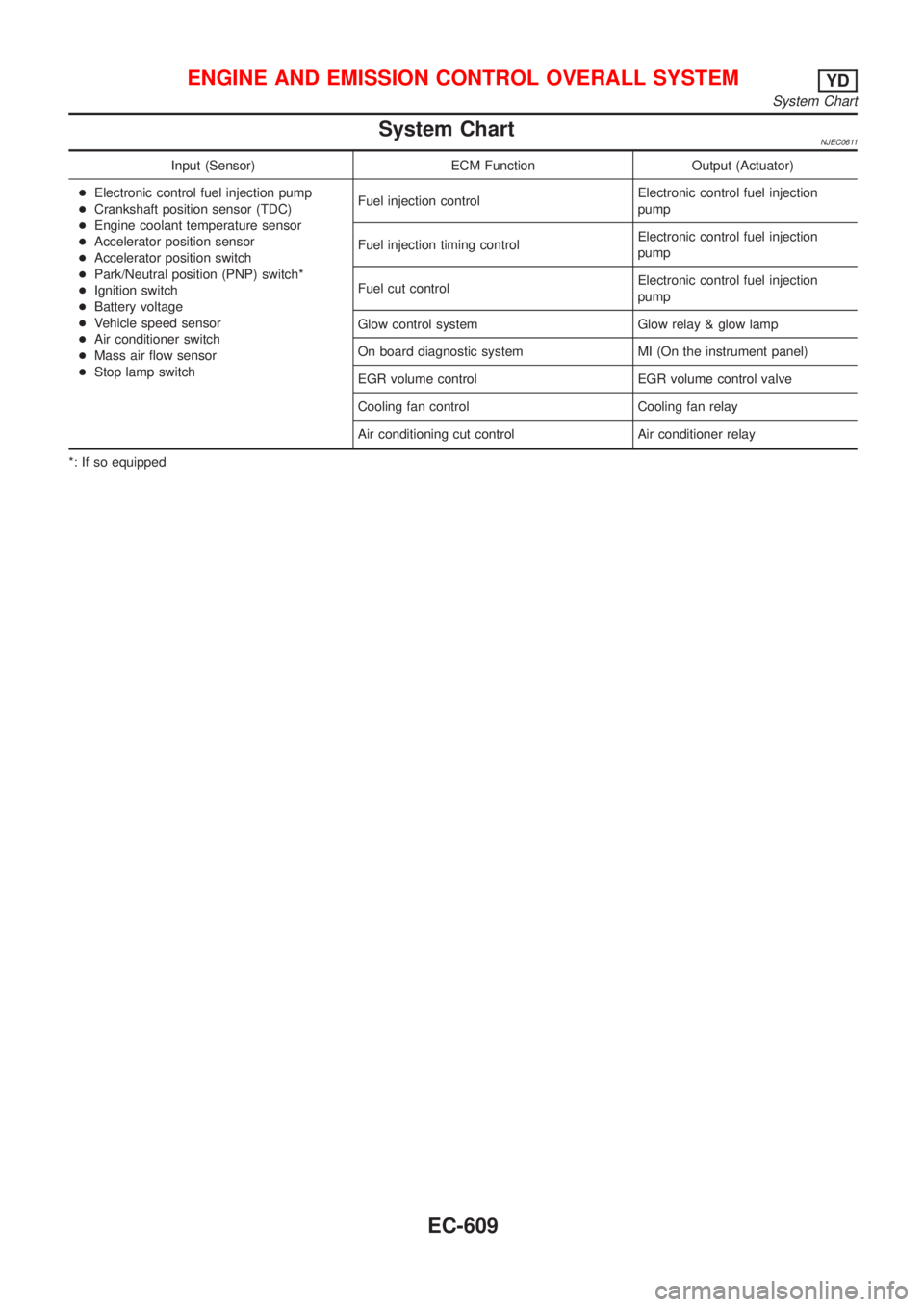
System ChartNJEC0611
Input (Sensor) ECM Function Output (Actuator)
+Electronic control fuel injection pump
+Crankshaft position sensor (TDC)
+Engine coolant temperature sensor
+Accelerator position sensor
+Accelerator position switch
+Park/Neutral position (PNP) switch*
+Ignition switch
+Battery voltage
+Vehicle speed sensor
+Air conditioner switch
+Mass air flow sensor
+Stop lamp switchFuel injection controlElectronic control fuel injection
pump
Fuel injection timing controlElectronic control fuel injection
pump
Fuel cut controlElectronic control fuel injection
pump
Glow control system Glow relay & glow lamp
On board diagnostic system MI (On the instrument panel)
EGR volume control EGR volume control valve
Cooling fan control Cooling fan relay
Air conditioning cut control Air conditioner relay
*: If so equipped
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL OVERALL SYSTEMYD
System Chart
EC-609
Page 1334 of 2898

Fuel Injection Control System
DESCRIPTIONNJEC0612System DescriptionNJEC0612S01Three types of fuel injection control are provided to accommodate engine operating conditions; normal control,
idle control and start control. The ECM determines the appropriate fuel injection control. Under each control,
the amount of fuel injected is compensated to improve engine performance.
Pulse signals are exchanged between ECM and electronic control fuel injection pump (control unit is built-in).
The fuel injection pump control unit performs duty control on the spill valve (built into the fuel injection pump)
according to the input signals to compensate the amount of fuel injected to the preset value.
Start ControlNJEC0612S02Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0612S0201
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Fuel injection
control (start
control)Electronic control fuel
injection pump Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
Ignition switch Start signal
SEF648S
When the ECM receives a start signal from the ignition switch, the ECM adapts the fuel injection system for
the start control. The amount of fuel injected at engine starting is a preset program value in the ECM. The
program is determined by the engine speed and engine coolant temperature.
For better startability under cool engine conditions, the lower the coolant temperature becomes, the greater
the amount of fuel injected. The ECM ends the start control when the engine speed reaches the specific value,
and shifts the control to the normal or idle control.
Idle ControlNJEC0612S03Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0612S0301
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Fuel injection
control (Idle con-
trol)Electronic control fuel
injection pump Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
Battery Battery voltage
Accelerator position switch Idle position
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner signal
When the ECM determines that the engine speed is at idle, the fuel injection system is adapted for the idle
control. The ECM regulates the amount of fuel injected corresponding to changes in load applied to the engine
to keep engine speed constant. The ECM also provides the system with a fast idle control in response to the
engine coolant temperature signal.
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONYD
Fuel Injection Control System
EC-610
Page 1335 of 2898
Normal ControlNJEC0612S04Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0612S0401
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speedFuel injection
control (Normal
control)Electronic control fuel
injection pump
Accelerator position sensor Accelerator position
SEF649S
The amount of fuel injected under normal driving conditions is determined according to sensor signals. The
crankshaft position sensor (TDC) detects engine speed and the accelerator position sensor detects accelera-
tor position. These sensors send signals to the ECM.
The fuel injection data, predetermined by correlation between various engine speeds and accelerator positions,
are stored in the ECM memory, forming a map. The ECM determines the optimal amount of fuel to be injected
using the sensor signals in comparison with the map.
Maximum Amount ControlNJEC0612S05Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0612S0501
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Mass air flow sensor Amount of intake air
Fuel injection
control (Maxi-
mum amount
control)Electronic control fuel
injection pump Engine coolnat temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
Accelerator position sensor Accelerator position
The maximum injection amount is controlled to an optimum by the engine speed, intake air amount, engine
coolant temperature, and accelerator opening in accordance with the driving conditions.
This prevents the oversupply of the injection amount caused by decreased air density at a high altitude or
during a system failure.
Deceleration ControlNJEC0612S06Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0612S0601
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Accelerator position switch Accelerator positionFuel injection
control (Decel-
eration control)Electronic control fuel
injection pump
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
The ECM sends a fuel cut signal to the electronic control fuel injection pump during deceleration for better
fuel efficiency. The ECM determines the time of deceleration according to signals from the accelerator posi-
tion switch and crankshaft position sensor (TDC).
Fuel Injection Timing Control System
DESCRIPTIONNJEC0613The target fuel injection timing in accordance with the engine speed and the fuel injection amount are recorded
as a map in the ECM beforehand. The ECM and the injection pump control unit exchange signals and per-
form feedback control for optimum injection timing in accordance with the map.
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONYD
Fuel Injection Control System (Cont'd)
EC-611
Page 1336 of 2898
Air Conditioning Cut Control
DESCRIPTIONNJEC0614Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0614S01
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Air conditioner switch Air conditioner ªONº signal
Air conditioner
cut controlAir conditioner relay Accelerator position sensor Accelerator valve opening angle
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Engine coolant temperature sensor Engine coolant temperature
System DescriptionNJEC0614S02This system improves acceleration when the air conditioner is used.
When the accelerator pedal is fully depressed, the air conditioner is turned off for a few seconds.
When engine coolant temperature becomes excessively high, the air conditioner is turned off. This continues
until the engine coolant temperature returns to normal.
Fuel Cut Control (at no load & high engine
speed)
DESCRIPTIONNJEC0615Input/Output Signal ChartNJEC0615S01
Sensor Input Signal to ECM ECM Function Actuator
Vehicle speed sensor Vehicle speed
Fuel cut controlElectronic control fuel
injection pump Accelerator position switch Accelerator position
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) Engine speed
If the engine speed is above 2,800 rpm with no load (for example, in neutral and engine speed over 2,800
rpm) fuel will be cut off after some time. The exact time when the fuel is cut off varies based on engine speed.
Fuel cut will operate until the engine speed reaches 1,500 rpm, then fuel cut is cancelled.
NOTE:
This function is different from deceleration control listed under ªFuel Injection Control Systemº,
EC-610.
ENGINE AND EMISSION BASIC CONTROL SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONYD
Air Conditioning Cut Control
EC-612