2001 INFINITI QX4 wiring
[x] Cancel search: wiringPage 1771 of 2395

Engine Compartment
There are several reasons a vehicle or engine vibration could
cause an electrical complaint. Some of the things to check for are:
IConnectors not fully seated.
IWiring harness not long enough and is being stressed due to
engine vibrations or rocking.
IWires laying across brackets or moving components.
ILoose, dirty or corroded ground wires.
IWires routed too close to hot components.
To inspect components under the hood, start by verifying the integ-
rity of ground connections. (Refer to GROUND INSPECTION
described later.) First check that the system is properly grounded.
Then check for loose connection bygently shakingthe wiring or
components as previously explained. Using the wiring diagrams
inspect the wiring for continuity.
Behind The Instrument Panel
An improperly routed or improperly clamped harness can become
pinched during accessory installation. Vehicle vibration can aggra-
vate a harness which is routed along a bracket or near a screw.
Under Seating Areas
An unclamped or loose harness can cause wiring to be pinched by
seat components (such as slide guides) during vehicle vibration. If
the wiring runs under seating areas, inspect wire routing for pos-
sible damage or pinching.
SGI842
HEAT SENSITIVENBGI0004S0203The owner's problem may occur during hot weather or after car has
sat for a short time. In such cases you will want to check for a heat
sensitive condition.
To determine if an electrical component is heat sensitive, heat the
component with a heat gun or equivalent.
Do not heat components above 60ÉC (140ÉF).If incident occurs
while heating the unit, either replace or properly insulate the com-
ponent.
SGI843
FREEZINGNBGI0004S0204The customer may indicate the incident goes away after the car
warms up (winter time). The cause could be related to water freez-
ing somewhere in the wiring/electrical system.
There are two methods to check for this. The first is to arrange for
the owner to leave his car overnight. Make sure it will get cold
enough to demonstrate his complaint. Leave the car parked out-
side overnight. In the morning, do a quick and thorough diagnosis
of those electrical components which could be affected.
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Incident Simulation Tests (Cont'd)
GI-26
Page 1772 of 2395

The second method is to put the suspect component into a freezer
long enough for any water to freeze. Reinstall the part into the car
and check for the reoccurrence of the incident. If it occurs, repair
or replace the component.
SGI844
WATER INTRUSIONNBGI0004S0205The incident may occur only during high humidity or in rainy/snowy
weather. In such cases the incident could be caused by water
intrusion on an electrical part. This can be simulated by soaking the
car or running it through a car wash.
Do not spray water directly on any electrical components.
SGI845
ELECTRICAL LOADNBGI0004S0206The incident may be electrical load sensitive. Perform diagnosis
with all accessories (including A/C, rear window defogger, radio,
fog lamps) turned on.
COLD OR HOT START UPNBGI0004S0207On some occasions an electrical incident may occur only when the
car is started cold. Or it may occur when the car is restarted hot
shortly after being turned off. In these cases you may have to keep
the car overnight to make a proper diagnosis.
Circuit InspectionNBGI0004S03INTRODUCTIONNBGI0004S0302In general, testing electrical circuits is an easy task if it is
approached in a logical and organized method. Before beginning
it is important to have all available information on the system to be
tested. Also, get a thorough understanding of system operation.
Then you will be able to use the appropriate equipment and follow
the correct test procedure.
You may have to simulate vehicle vibrations while testing electrical
components.Gently shakethe wiring harness or electrical com-
ponent to do this.
OPEN A circuit is open when there is no continuity through a section of
the circuit.
SHORT There are two types of shorts.
ISHORT CIRCUIT When a circuit contacts another circuit
and causes the normal resistance to
change.
ISHORT TO GROUND When a circuit contacts a ground
source and grounds the circuit.
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
AT
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Incident Simulation Tests (Cont'd)
GI-27
Page 1776 of 2395
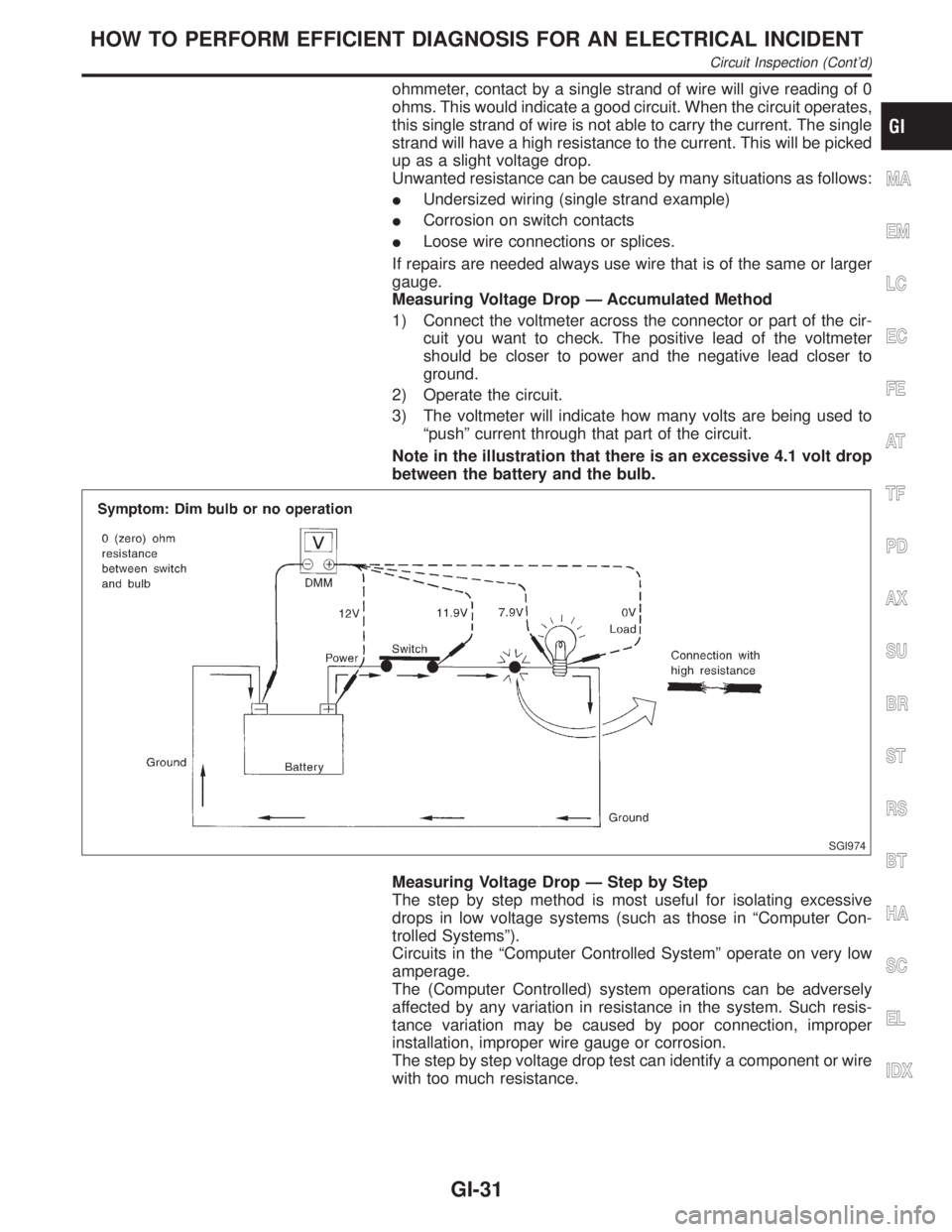
ohmmeter, contact by a single strand of wire will give reading of 0
ohms. This would indicate a good circuit. When the circuit operates,
this single strand of wire is not able to carry the current. The single
strand will have a high resistance to the current. This will be picked
up as a slight voltage drop.
Unwanted resistance can be caused by many situations as follows:
IUndersized wiring (single strand example)
ICorrosion on switch contacts
ILoose wire connections or splices.
If repairs are needed always use wire that is of the same or larger
gauge.
Measuring Voltage Drop Ð Accumulated Method
1) Connect the voltmeter across the connector or part of the cir-
cuit you want to check. The positive lead of the voltmeter
should be closer to power and the negative lead closer to
ground.
2) Operate the circuit.
3) The voltmeter will indicate how many volts are being used to
ªpushº current through that part of the circuit.
Note in the illustration that there is an excessive 4.1 volt drop
between the battery and the bulb.
SGI974
Measuring Voltage Drop Ð Step by Step
The step by step method is most useful for isolating excessive
drops in low voltage systems (such as those in ªComputer Con-
trolled Systemsº).
Circuits in the ªComputer Controlled Systemº operate on very low
amperage.
The (Computer Controlled) system operations can be adversely
affected by any variation in resistance in the system. Such resis-
tance variation may be caused by poor connection, improper
installation, improper wire gauge or corrosion.
The step by step voltage drop test can identify a component or wire
with too much resistance.
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
AT
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
HA
SC
EL
IDX
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont'd)
GI-31
Page 1779 of 2395

NBGI0005
NOTICE:
Trouble diagnoses indicates work procedures required to diagnose
problems effectively. Observe the following instructions before
diagnosing.
1)Before performing trouble diagnoses, read the ªPrelimi-
nary Checkº, the ªSymptom Chartº or the ªWork Flowº.
2)After repairs, re-check that the problem has been com-
pletely eliminated.
3)Refer to Component Parts and Harness Connector Loca-
tion for the Systems described in each section for
identification/location of components and harness con-
nectors.
4)Refer to the Circuit Diagram for quick pinpoint check.
If you need to check circuit continuity between harness
connectors in more detail, such as when a sub-harness is
used, refer to Wiring Diagram in each individual section
and Harness Layout in EL section for identification of har-
ness connectors.
5)When checking circuit continuity, ignition switch should
be OFF.
6)Before checking voltage at connectors, check battery volt-
age.
7)After accomplishing the Diagnostic Procedures and Elec-
trical Components Inspection, make sure that all harness
connectors are reconnected as they were.
HOW TO FOLLOW TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
GI-34
Page 1785 of 2395
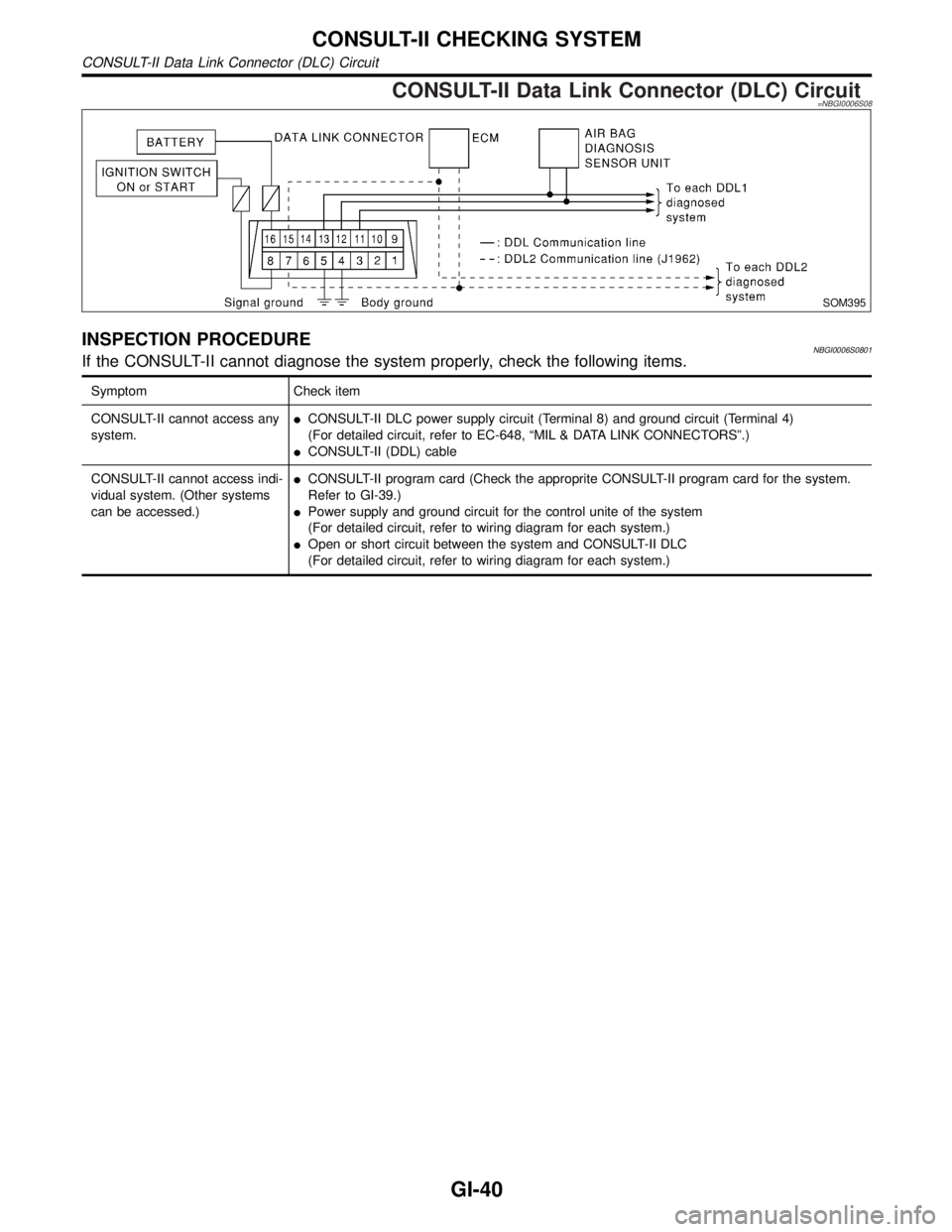
CONSULT-II Data Link Connector (DLC) Circuit=NBGI0006S08
SOM395
INSPECTION PROCEDURENBGI0006S0801If the CONSULT-II cannot diagnose the system properly, check the following items.
Symptom Check item
CONSULT-II cannot access any
system.ICONSULT-II DLC power supply circuit (Terminal 8) and ground circuit (Terminal 4)
(For detailed circuit, refer to EC-648, ªMIL & DATA LINK CONNECTORSº.)
ICONSULT-II (DDL) cable
CONSULT-II cannot access indi-
vidual system. (Other systems
can be accessed.)ICONSULT-II program card (Check the approprite CONSULT-II program card for the system.
Refer to GI-39.)
IPower supply and ground circuit for the control unite of the system
(For detailed circuit, refer to wiring diagram for each system.)
IOpen or short circuit between the system and CONSULT-II DLC
(For detailed circuit, refer to wiring diagram for each system.)
CONSULT-II CHECKING SYSTEM
CONSULT-II Data Link Connector (DLC) Circuit
GI-40
Page 1800 of 2395

HEATER &
AIR CONDITIONER
SECTION
HA
CONTENTS
PRECAUTIONS...............................................................2
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS)²AIR
BAG²and²SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER²...............2
Precautions for Working with HFC-134a (R-134a) .....2
General Refrigerant Precautions .................................3
Precautions for Leak Detection Dye............................3
Identification .................................................................4
Precautions for Refrigerant Connection ......................4
Precautions for Servicing Compressor ........................6
Precautions for Service Equipment .............................7
Wiring Diagrams and Trouble Diagnoses....................9
PREPARATION.............................................................10
Special Service Tools ................................................10
HFC-134a (R-134a) Service Tools and
Equipment .................................................................. 11
DESCRIPTION...............................................................14
Refrigeration System .................................................14
V-6 Variable Displacement Compressor....................15
Component Layout ....................................................19
Introduction ................................................................20
Features .....................................................................20
Overview of Control System ......................................23
Control Operation ......................................................23
Discharge Air Flow.....................................................25
System Description ....................................................26
TROUBLE DIAGNOSES................................................27
Component Location..................................................27
Circuit Diagram (Without Navigation System) ...........30
Wiring Diagram - A/C, A - (Without Navigation
System) ......................................................................31
Circuit Diagram (With Navigation System) ................35
Wiring Diagram - A/C, A - (With Navigation
System) ......................................................................36
Auto Amp. Terminals and Reference Value...............40
Self-diagnosis ............................................................44
How to Perform Trouble Diagnoses for Quick
and Accurate Repair ..................................................65Operational Check .....................................................66
A/C System ................................................................71
Mode Door Motor.......................................................75
Air Mix Door Motor ....................................................82
Intake Door Motor ......................................................87
Blower Motor..............................................................95
Magnet Clutch..........................................................104
Insufficient Cooling .................................................. 112
Insufficient Heating ..................................................121
Noise ........................................................................123
Self-diagnosis ..........................................................124
Memory Function .....................................................126
ECON (ECONOMY) Mode ......................................128
Ambient Sensor Circuit ............................................129
In-vehicle Sensor Circuit..........................................132
Sunload Sensor Circuit ............................................135
Intake Sensor Circuit ...............................................139
Air Mix Door Motor PBR Circuit ..............................141
Multiplex Communication Circuit .............................142
SERVICE PROCEDURE..............................................144
HFC-134a (R-134a) Service Procedure ..................144
Maintenance of Lubricant Quantity in
Compressor .............................................................146
Compressor .............................................................149
Compressor Clutch ..................................................150
Refrigerant Lines .....................................................154
Belt ...........................................................................159
Ventilation Air Filter ..................................................159
SERVICE DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS (SDS).......160
Compressor .............................................................160
Lubricant ..................................................................160
Refrigerant ...............................................................160
Engine Idling Speed (When A/C is ON) ..................160
Belt Tension .............................................................160
GI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
AT
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
SC
EL
IDX
Page 1801 of 2395

Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) ªAIR
BAGº and ªSEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONERº
NBHA0001The Supplemental Restraint System such as ªAIR BAGº and ªSEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONERº used along with
a seat belt, helps to reduce the risk or severity of injury to the driver and front passenger for certain types of
collision. The SRS system composition which is available to INFINITI QX4 is as follows:
IFor a frontal collision
The Supplemental Restraint System consists of driver air bag module (located in the center of the steer-
ing wheel), front passenger air bag module (located on the instrument panel on passenger side), seat belt
pre-tensioners, a diagnosis sensor unit, warning lamp, wiring harness and spiral cable.
IFor a side collision
The Supplemental Restraint System consists of front side air bag module (located in the outer side of front
seat), satellite sensor, diagnosis sensor unit (one of components of air bags for a frontal collision), wiring
harness, warning lamp (one of components of air bags for a frontal collision).
Information necessary to service the system safely is included in theRS sectionof this Service Manual.
WARNING:
ITo avoid rendering the SRS inoperative, which could increase the risk of personal injury or death
in the event of a collision which would result in air bag inflation, all maintenance must be performed
by an authorized INFINITI dealer.
IImproper maintenance, including incorrect removal and installation of the SRS, can lead to per-
sonal injury caused by unintentional activation of the system. For removal of Spiral Cable and Air
Bag Module, see the RS section.
IDo not use electrical test equipment on any circuit related to the SRS unless instructed to in this
Service Manual. Spiral cable and wiring harnesses covered with yellow insulation tape either just
before the harness connectors or for the complete harness are related to the SRS.
Precautions for Working with HFC-134a
(R-134a)
NBHA0002WARNING:
ICFC-12 (R-12) refrigerant and HFC-134a (R-134a) refrigerant are not compatible. If the refrigerants
are mixed and compressor failure is likely to occur, refer to ªCONTAMINATED REFRIGERANTº
below. To determine the purity of HFC-134a (R-134a) in the vehicle and recovery tank, use Refrig-
erant Recovery/Recycling Recharging equipment (ACR4) (J-39500-INF) and Refrigerant Identifier.
IUse only specified lubricant for the HFC-134a (R-134a) A/C system and HFC-134a (R-134a) compo-
nents. If lubricant other than that specified is used, compressor failure is likely to occur.
IThe specified HFC-134a (R-134a) lubricant rapidly absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. The fol-
lowing handling precautions must be observed:
a) When removing refrigerant components from a vehicle, immediately cap (seal) the component to
minimize the entry of moisture from the atmosphere.
b) When installing refrigerant components to a vehicle, do not remove the caps (unseal) until just
before connecting the components. Connect all refrigerant loop components as quickly as pos-
sible to minimize the entry of moisture into system.
c) Only use the specified lubricant from a sealed container. Immediately reseal containers of lubri-
cant. Without proper sealing, lubricant will become moisture saturated and should not be used.
d) Avoid breathing A/C refrigerant and lubricant vapor or mist. Exposure may irritate eyes, nose and
throat. Remove R-134a from the A/C system, using certified service equipment meeting require-
ments of SAE J2210 (R-134a recycling equipment), or J2209 (R-134a recovery equipment). If acci-
dental system discharge occurs, ventilate work area before resuming service. Additional health and
safety information may be obtained from refrigerant and lubricant manufacturers.
e) Do not allow lubricant (Nissan A/C System Oil Type S) to come in contact with styrofoam parts.
Damage may result.
CONTAMINATED REFRIGERANTNBHA0002S01If a refrigerant other than pure R-134a is identified in a vehicle, your options are:
IExplain to the customer that environmental regulations prohibit the release of contaminated refrigerant into
the atmosphere.
IExplain that recovery of the contaminated refrigerant could damage your service equipment and refriger-
ant supply.
PRECAUTIONS
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) ªAIR BAGº and ªSEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONERº
HA-2
Page 1808 of 2395

Wiring Diagrams and Trouble DiagnosesNBHA0007When you read wiring diagrams, refer to the following:
IGI-11, ªHOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMSº
IEL-10, ªWiring Diagram Ð POWER к for power distribution
circuit
When you perform trouble diagnoses, refer to the following:
IGI-34, ªHOW TO FOLLOW TROUBLE DIAGNOSESº
IGI-24, ªHOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR
AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENTºGI
MA
EM
LC
EC
FE
AT
TF
PD
AX
SU
BR
ST
RS
BT
SC
EL
IDX
PRECAUTIONS
Wiring Diagrams and Trouble Diagnoses
HA-9