Page 138 of 256
4. Move the 4WD control to the
2WD position.
5. Wait for the 4WD low indicator
light to turn off.
Shifting between 4X4 HIGH (4WD high) and 4X4 LOW (4WD low)
1. Bring the vehicle to a stop.
2. Depress the brake.
3. Place the gearshift in N (Neutral).
4. Move the 4WD control to the 4X4
HIGH or 4X4 LOW position.
5. Wait for the selected 4WD mode
indicator light to illuminate.
Driving off-road with 4WD
Your vehicle is specially equipped for driving on sand, snow, mud and
rough terrain and has operating characteristics that are somewhat
different from conventional vehicles, both on and off the road.
Maintain steering wheel control at all times, especially in rough terrain.
Since sudden changes in terrain can result in abrupt steering wheel
motion, make sure you grip the steering wheel from the outside. Do not
grip the spokes.
Drive cautiously to avoid vehicle damage from concealed objects such as
rocks and stumps.
4X4
HIGH
2WD4X4
LOW
2WD4X4
LOW4X4
HIGH
Driving
138
Page 139 of 256

You should either know the terrain or examine maps of the area before
driving. Map out your route before driving in the area. For more
information on driving off-road, read the ªFour Wheelingº supplement in
your owner's portfolio.
If your vehicle gets stuck
If the vehicle is stuck it may be rocked out by shifting from forward and
reverse gears, stopping between shifts, in a steady pattern. Press lightly
on the accelerator in each gear.
Do not rock the vehicle if the engine is not at normal operating
temperature or damage to the transmission may occur.
Do not rock the vehicle for more than a few minutes or damage
to the transmission and tires may occur or the engine may
overheat.
Do not spin the wheels at over 56 km/h (35 mph). The tires may
fail and injure a passenger or bystander.
Sand
When driving over sand, try to keep all four wheels on the most solid
area of the trail. Do not reduce the tire pressures but shift to a lower
gear and drive steadily through the terrain. Apply the accelerator slowly
and avoid spinning the wheels.
Mud and water
If you must drive through high water, drive slowly. Traction or brake
capability may be limited.
When driving through water, determine the depth; avoid water higher
than the bottom of the hubs (if possible) and proceed slowly. If the
ignition system gets wet, the vehicle may stall.
Once through water, always try the brakes. Wet brakes do not stop the
vehicle as effectively as dry brakes. Drying can be improved by moving
your vehicle slowly while applying light pressure on the brake pedal.
After driving through mud, clean off residue stuck to the driveshafts and
tires. Excess mud stuck on tires and rotating driveshafts causes an
imbalance that could damage drive components.
If the transmission, transfer case or front axle are submerged in water,
their fluids should be checked and changed, if necessary.
Driving
139
Page 149 of 256

²do not allow waves to break higher than 15 cm (6 inches) above the
bottom edge of the rear bumper.
Exceeding these limits may allow water to enter critical vehicle
components, adversely affecting driveability, emissions, reliability and
causing internal transmission damage.
Replace the rear axle lubricant any time the axle has been submerged in
water. Rear axle lubricant quantities are not to be checked or changed
unless a leak is suspected or repair required.
Disconnect the wiring to the trailer before backing the trailer into the
water. Reconnect the wiring to the trailer after the trailer is removed
from the water.
Recreational towing
All Rear Wheel Drive (RWD) vehicles with automatic transmissions
This applies to all cars and 4x2 trucks/sport utilities with rear wheel
drive capability.
An example of recreational towing is towing your vehicle behind a
motorhome. The following recreational towing guidelines are designed to
ensure that your transmission is not damaged.
²Place the transmission in N (Neutral).
²Maximum speed is 56 km/h (35 mph).
²Maximum distance is 80 km (50 miles).
If a distance of 80 km (50 miles) or a speed of 56 km/h (35 mph)
must be exceeded, you must disconnect the driveshaft. Ford
recommends the driveshaft be removed/installed only by a
qualified technician. See your local dealer for driveshaft
removal/installation.
Improper removal/installation of the driveshaft can cause
transmission fluid loss, damage to the driveshaft and internal
transmission components.
In case of a roadside emergency with a disabled vehicle (without access
to wheel dollies, a car hauling trailer or a flatbed transport vehicle), your
vehicle can be flat towed (all wheels on the ground) under the following
conditions:
²Release the parking brake.
²Turn the ignition to the OFF position.
Driving
149
Page 163 of 256
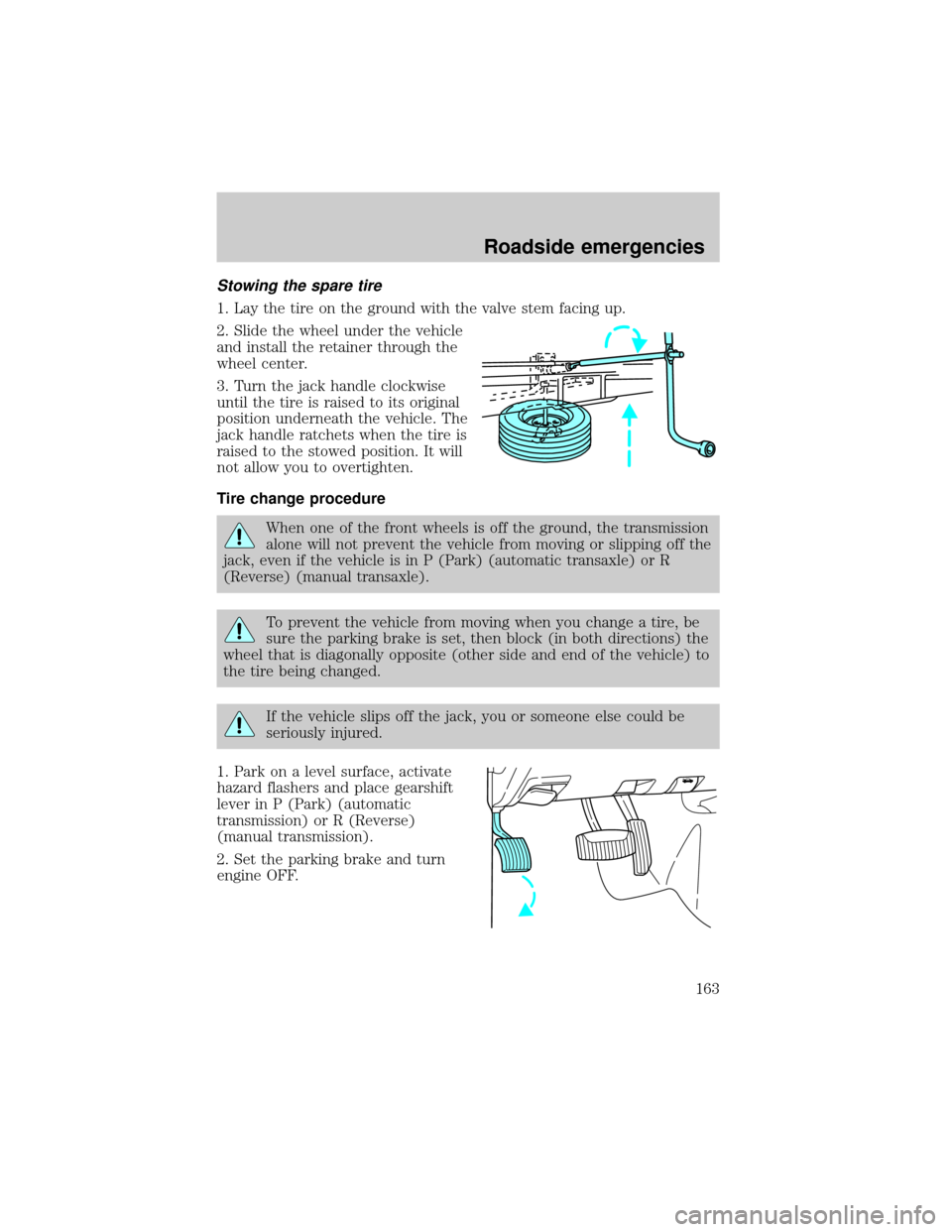
Stowing the spare tire
1. Lay the tire on the ground with the valve stem facing up.
2. Slide the wheel under the vehicle
and install the retainer through the
wheel center.
3. Turn the jack handle clockwise
until the tire is raised to its original
position underneath the vehicle. The
jack handle ratchets when the tire is
raised to the stowed position. It will
not allow you to overtighten.
Tire change procedure
When one of the front wheels is off the ground, the transmission
alone will not prevent the vehicle from moving or slipping off the
jack, even if the vehicle is in P (Park) (automatic transaxle) or R
(Reverse) (manual transaxle).
To prevent the vehicle from moving when you change a tire, be
sure the parking brake is set, then block (in both directions) the
wheel that is diagonally opposite (other side and end of the vehicle) to
the tire being changed.
If the vehicle slips off the jack, you or someone else could be
seriously injured.
1. Park on a level surface, activate
hazard flashers and place gearshift
lever in P (Park) (automatic
transmission) or R (Reverse)
(manual transmission).
2. Set the parking brake and turn
engine OFF.
Roadside emergencies
163
Page 188 of 256

CHECKING AND ADDING POWER STEERING FLUID
Check the power steering fluid.
Refer to the scheduled maintenance
guide for the service interval
schedules. If adding fluid is
necessary, use only MERCONtAT F.
1. Start the engine and let it run until it reaches normal operating
temperature (the engine coolant temperature gauge indicator will be
near the center of the normal area between H and C).
2. While the engine idles, turn the steering wheel left and right several
times.
3. Turn the engine off.
4. Check the fluid level in the reservoir. It should be between the MIN
and MAX lines. Do not add fluid if the level is within this range.
5. If the fluid is low, add fluid in small amounts, continuously checking
the level until it reaches the correct operating range. Be sure to put the
cap back on the reservoir.
TRANSMISSION FLUID
Checking automatic transmission fluid (if equipped)
Refer to your scheduled maintenance guide for scheduled intervals for
fluid checks and changes. Your transmission does not consume fluid.
However, the fluid level should be checked if the transmission is not
working properly, i.e., if the transmission slips or shifts slowly or if you
notice some sign of fluid leakage.
Automatic transmission fluid expands when warmed. To obtain an
accurate fluid check, drive the vehicle until it is at normal operating
temperature (approximately 30 km [20 miles]). If your vehicle has been
DONOTOVERFILLPOWERSTEERINGFLUID
Maintenance and care
188