2001 DODGE TOWN AND COUNTRY transmission fluid
[x] Cancel search: transmission fluidPage 1622 of 2321

TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
In a standard torque converter, the impeller and
turbine are rotating at about the same speed and the
stator is freewheeling, providing no torque multipli-
cation. By applying the turbine's piston to the front
cover's friction material, a total converter engage-
ment can be obtained. The result of this engagement
is a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine
and the transmission.
The engagement and disengagement of the TCC
are automatic and controlled by the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). The engagement cannot be acti-
vated in the lower gears because it eliminates the
torque multiplication effect of the torque converter
necessary for acceleration. Inputs that determine
clutch engagement are: coolant temperature, vehicle
speed and throttle position. The torque converter
clutch is engaged by the clutch solenoid on the valve
body. The clutch will engage at approximately 56
km/h (35 mph) with light throttle, after the shift to
third gear.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 31TH - REMOVAL)
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation.(1) Lubricate converter hub and oil pump seal lip
with transmission fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 237). Surface of converter lugs
should be 1/2 in. to rear of straightedge when con-
verter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
(8) Install the transmission in the vehicle. (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 31TH - INSTALLATION)
(9) Fill the transmission with the recommended
fluid.
Fig. 237 Checking Torque Converter Seating
1 - SCALE
2 - STRAIGHTEDGE
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21 - 125
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1655 of 2321

AUTOMATIC - 41TE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
AUTOMATIC - 41TE
DESCRIPTION..........................159
OPERATION............................159
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................159
41TE TRANSAXLE GENERAL DIAGNOSIS . . . 159
ROAD TEST..........................161
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TESTS..........162
CLUTCH AIR PRESSURE TESTS..........164
TORQUE CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID
LEAKAGE............................164
REMOVAL.............................165
DISASSEMBLY..........................169
ASSEMBLY............................186
INSTALLATION..........................209
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS.............212
SPECIFICATIONS........................225
SPECIAL TOOLS........................227
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION..........................232
OPERATION............................233
AUTOSTICK SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................233
OPERATION............................233
DRIVING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION..........................234
OPERATION............................234
FINAL DRIVE
DESCRIPTION..........................234
OPERATION............................234
DISASSEMBLY..........................235
ASSEMBLY............................240
ADJUSTMENTS.........................243
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE.................246
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK.....246
FLUID AND FILTER SERVICE.............246
GEAR SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL.............................248
INSTALLATION..........................250
ADJUSTMENTS.........................251
HOLDING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION..........................251
OPERATION............................251
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY..........................252
ASSEMBLY............................259
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION..........................269
OPERATION............................269STANDARD PROCEDURE.................269
OIL PUMP VOLUME CHECK..............269
DISASSEMBLY..........................270
ASSEMBLY............................271
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
DESCRIPTION..........................271
OPERATION............................271
SEAL - OIL PUMP
REMOVAL.............................271
INSTALLATION..........................272
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION..........................272
OPERATION............................273
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................274
BRAKE/TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SOLENOID...........................274
REMOVAL.............................274
INSTALLATION..........................275
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION..........................276
OPERATION............................276
REMOVAL.............................277
INSTALLATION..........................277
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT
DESCRIPTION..........................278
OPERATION............................278
REMOVAL.............................279
INSTALLATION..........................279
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION..........................280
OPERATION............................280
REMOVAL.............................280
INSTALLATION..........................281
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION..........................281
OPERATION............................284
REMOVAL.............................286
INSTALLATION..........................286
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
DESCRIPTION..........................287
OPERATION............................287
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION..........................287
OPERATION............................287
REMOVAL.............................288
INSTALLATION..........................288
TORQUE REDUCTION LINK (TRD)
DESCRIPTION..........................289
OPERATION............................289
21 - 158 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1656 of 2321

VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION..........................289
OPERATION............................290
REMOVAL.............................290DISASSEMBLY..........................292
ASSEMBLY............................296
INSTALLATION..........................301
AUTOMATIC - 41TE
TRANSAXLE IDENTIFICATION
DESCRIPTION
The 41TE (Fig. 1) is a four-speed transaxle that is
a conventional hydraulic/mechanical assembly with
an integral differential, and is controlled with adap-
tive electronic controls and monitors. The hydraulic
system of the transaxle consists of the transaxle
fluid, fluid passages, hydraulic valves, and various
line pressure control components. An input clutch
assembly which houses the underdrive, overdrive,
and reverse clutches is used. It also utilizes separate
holding clutches: 2nd/4th gear and Low/Reverse. The
primary mechanical components of the transaxle con-
sist of the following:
²Three multiple disc input clutches
²Two multiple disc holding clutches
²Four hydraulic accumulators
²Two planetary gear sets
²Hydraulic oil pump
²Valve body
²Solenoid/Pressure switch assembly
²Integral differential assembly
Control of the transaxle is accomplished by fully
adaptive electronics. Optimum shift scheduling is
accomplished through continuous real-time sensor
feedback information provided to the Transmission
Control Module (TCM).
The TCM is the heart of the electronic control sys-
tem and relies on information from various direct
and indirect inputs (sensors, switches, etc.) to deter-
mine driver demand and vehicle operating condi-
tions. With this information, the TCM can calculate
and perform timely and quality shifts through vari-
ous output or control devices (solenoid pack, trans-
mission control relay, etc.).
The TCM also performs certain self-diagnostic
functions and provides comprehensive information
(sensor data, DTC's, etc.) which is helpful in proper
diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed
with the DRB scan tool.
The 41TE transaxle identification code is a series
of digits printed on a bar-code label that is fixed to
the transaxle case as shown in (Fig. 2).For example, the identification code K 821 1125
1316 can be broken down as follows:
²K = Kokomo Transmission Plant
²821 = Last three digits of the transaxle part
number
²1125 = Build date
²1316 = Build sequence number
If the tag is not legible or missing, the ªPKº num-
ber, which is stamped into the transaxle case behind
the transfer gear cover, can be referred to for identi-
fication. This number differs slightly in that it con-
tains the entire transaxle part number, rather than
the last three digits.
OPERATION
Transmission output is directed to an integral dif-
ferential by a transfer gear system in the following
input-to-output ratios:
First...............................2.84 : 1
Second.............................1.57 : 1
Third..............................1.00 : 1
Overdrive...........................0.69 : 1
Reverse............................2.21 : 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - 41TE TRANSAXLE
GENERAL DIAGNOSIS
NOTE: Before attempting any repair on a 41TE four-
speed automatic transaxle, check for diagnostic
trouble codes (DTC's) using the DRB scan tool.
Refer to the Transmission Diagnostic Procedures
Manual.
Transaxle malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions:
²Poor engine performance
²Improper adjustments
²Hydraulic malfunctions
²Mechanical malfunctions
²Electronic malfunctions
Diagnosis of these problems should always begin
by checking the easily accessible variables: fluid level
and condition, gearshift cable adjustment. Then per-
form a road test to determine if the problem has been
corrected or that more diagnosis is necessary. If the
problem persists after the preliminary tests and cor-
rections are completed, hydraulic pressure checks
should be performed.
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 159
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1661 of 2321

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH AIR
PRESSURE TESTS
Inoperative clutches can be located using a series
of tests by substituting air pressure for fluid pressure
(Fig. 4) (Fig. 5). The clutches may be tested by apply-
ing air pressure to their respective passages. The
valve body must be removed and Tool 6056 installed.
To make air pressure tests, proceed as follows:
NOTE: The compressed air supply must be free of
all dirt and moisture. Use a pressure of 30 psi.
Remove oil pan and valve body. See Valve body
removal.
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the overdrive clutch apply
passage and watch for the push/pull piston to move
forward. The piston should return to its starting
position when the air pressure is removed.
REVERSE CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the reverse clutch apply pas-
sage and watch for the push/pull piston to move rear-
ward. The piston should return to its starting
position when the air pressure is removed.
2/4 CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the feed hole located on the
2/4 clutch retainer. Look in the area where the 2/4
piston contacts the first separator plate and watch
carefully for the 2/4 piston to move rearward. The
piston should return to its original position after the
air pressure is removed.
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the low/reverse clutch feed
hole (rear of case, between 2 bolt holes). Then, look
in the area where the low/reverse piston contacts the
first separator plate. Watch carefully for the piston to
move forward. The piston should return to its origi-
nal position after the air pressure is removed.
UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
Because this clutch piston cannot be seen, its oper-
ation is checked by function. Air pressure is applied
to the low/reverse and the 2/4 clutches. This locks the
output shaft. Use a piece of rubber hose wrapped
around the input shaft and a pair of clamp-on pliers
to turn the input shaft. Next apply air pressure to
the underdrive clutch. The input shaft should not
rotate with hand torque. Release the air pressure
and confirm that the input shaft will rotate.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE
When diagnosing converter housing fluid leaks,
three actions must be taken before repair:
(1) Verify proper transmission fluid level.
(2) Verify that the leak originates from the con-
verter housing area and is transmission fluid.
(3) Determine the true source of the leak.
Fluid leakage at or around the torque converter
area may originate from an engine oil leak (Fig. 6).
The area should be examined closely. Factory fill
fluid is red and, therefore, can be distinguished from
engine oil.
Some suspected converter housing fluid leaks may
not be leaks at all. They may only be the result of
residual fluid in the converter housing, or excess
fluid spilled during factory fill, or fill after repair.
Fig. 4 Air Pressure Test Plate
1 - TOOL 6056
2 - ACCUMULATORS
Fig. 5 Testing Reverse Clutch
1 - TOOL 6056
2 - AIR NOZZLE
21 - 164 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
AUTOMATIC - 41TE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1663 of 2321
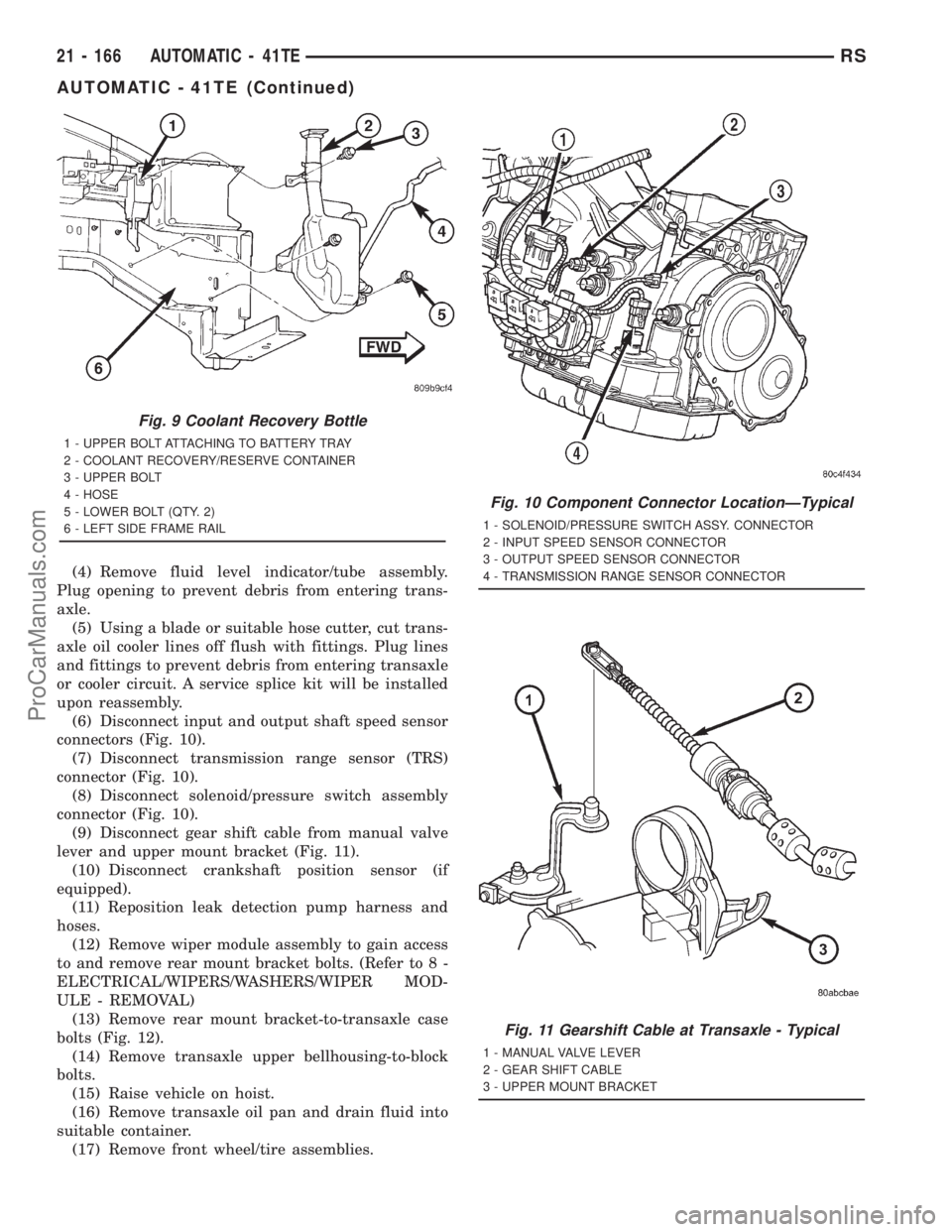
(4) Remove fluid level indicator/tube assembly.
Plug opening to prevent debris from entering trans-
axle.
(5) Using a blade or suitable hose cutter, cut trans-
axle oil cooler lines off flush with fittings. Plug lines
and fittings to prevent debris from entering transaxle
or cooler circuit. A service splice kit will be installed
upon reassembly.
(6) Disconnect input and output shaft speed sensor
connectors (Fig. 10).
(7) Disconnect transmission range sensor (TRS)
connector (Fig. 10).
(8) Disconnect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
connector (Fig. 10).
(9) Disconnect gear shift cable from manual valve
lever and upper mount bracket (Fig. 11).
(10) Disconnect crankshaft position sensor (if
equipped).
(11) Reposition leak detection pump harness and
hoses.
(12) Remove wiper module assembly to gain access
to and remove rear mount bracket bolts. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MOD-
ULE - REMOVAL)
(13) Remove rear mount bracket-to-transaxle case
bolts (Fig. 12).
(14) Remove transaxle upper bellhousing-to-block
bolts.
(15) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(16) Remove transaxle oil pan and drain fluid into
suitable container.
(17) Remove front wheel/tire assemblies.
Fig. 9 Coolant Recovery Bottle
1 - UPPER BOLT ATTACHING TO BATTERY TRAY
2 - COOLANT RECOVERY/RESERVE CONTAINER
3 - UPPER BOLT
4 - HOSE
5 - LOWER BOLT (QTY. 2)
6 - LEFT SIDE FRAME RAIL
Fig. 10 Component Connector LocationÐTypical
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY. CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 11 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle - Typical
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
21 - 166 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
AUTOMATIC - 41TE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1706 of 2321

INSTALLATION
NOTE: If transaxle assembly has been replaced or
overhauled (clutch and/or seal replacement), it is
necessary to perfrom the TCM Quick Learn proce-
dure. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CON-
TROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
NOTE: If torque converter assembly has been
replaced, it is necessary to reset the TCC Break-In
Strategy. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC
CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Using a transmission jack and a helper, posi-
tion transaxle assembly to engine. Install and torque
bolts to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install upper mount assembly to transaxle and
torque bolts to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 164).
(3) Raise engine/transaxle assembly into position.
Install and torque upper mount-to-bracket thru-bolt
to 75 N´m (55 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 164).
(4) Remove transmission jack and screw jack.
(5) Secure left wheelhouse splash shield.
(6) Install torque converter-to-drive plate bolts and
torque to 88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.)
(7) Install inspection cover.(8) Install lateral bending brace.
(9) Install starter motor.
(10) Install front mount/bracket assembly.
(11) Install rear mount and bracket assembly into
position (Fig. 165).
(12) Install and torque rear mount bolts to 54 N´m
(40 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 166).
(13) Lower vehicle.
(14) Install and torque rear mount bracket-to-tran-
saxle vertical bolts (Fig. 165) to 102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.).
(15) Raise vehicle.
(16) Install rear mount bracket-to-transaxle hori-
zontal bolt (Fig. 165) and torque to 102 N´m (75 ft.
lbs.).
(17) Install rear mount thru-bolt and torque to 54
N´m (40 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 166).
(18) Install rear mount heat shield (Fig. 167).
(19) AWD models: Install power transfer unit.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
POWER TRANSFER UNIT - INSTALLATION)
(20) Install cradle plate.
(21) Install exhaust pipe to manifold (Fig. 168).
(22) Install left and right halfshaft assemblies.
(Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF
SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(23) Install front wheel/tire assemblies.
(24) Lower vehicle.
(25) Install transaxle upper bellhousing-to-block
bolts and torque to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(26) Install wiper module assembly. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MOD-
ULE - INSTALLATION)
(27) Connect crank position sensor (if equipped).
(28) Connect gearshift cable to upper mount
bracket and transaxle manual valve lever (Fig. 169).
(29) Connect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
(Fig. 170).
(30) Connect transmission range sensor connector
(Fig. 170).
(31) Connect input and output speed sensor con-
nectors (Fig. 170).
(32) Remove plugs and install transaxle oil cooler
line service splice kit. Refer to instructions included
with kit.
(33) Remove plug and Install fluid level indicator/
tube assembly.
(34) Install coolant recovery bottle (Fig. 171).
(35) Install battery shield.
(36) Connect battery cables.
(37) Fill transaxle with suitable amount of ATF+4
(Automatic Transmission FluidÐType 9602). (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Fig. 164 Left Mount to Bracket and Transaxle
1 - BOLT - BRACKET TO FRAME RAIL 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.)
2 - BOLT - MOUNT TO RAIL THRU 75 N´m (55 ft. lbs.)
3 - BOLT - LEFT MOUNT TO TRANSAXLE 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
4 - TRANSAXLE
5 - MOUNT - LEFT
6 - BRACKET - LEFT MOUNT
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 209
AUTOMATIC - 41TE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1743 of 2321

FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL AND
CONDITION CHECK
NOTE: Only transmission fluid of the type labeled
Mopar ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid±Type
9602) should be used in this transaxle.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
The transmission sump has a fluid level indicator
(dipstick) to check oil similar to most automatic
transmissions. It is located on the left side of the
engine. Be sure to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle
before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P Park and N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in P Park
to be sure that the fluid level check is accurate.The
engine should be running at idle speed for at
least one minute, with the vehicle on level
ground.At normal operating temperature (approxi-
mately 82 C. or 180 F.), the fluid level is correct if it
is in the HOT region (cross-hatched area) on the oil
level indicator (Fig. 214). The fluid level should be
within the WARM range of the dipstick at 70É F fluid
temperature.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK USING DRB
NOTE: Engine and Transaxle should be at normal
operating temperature before performing this proce-
dure.
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Hook up DRB scan tool and select transmis-
sion.(3) Select sensors.
(4) Read the transmission temperature value.
(5) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
fluid temperature chart (Fig. 215).
(6) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
indicator according to the chart.
(7) Check transmission for leaks.
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the
gears churn up foam and cause the same conditions
which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transaxle vent where it may be mistaken
for a leak.
FLUID CONDITION
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle recondition is proba-
bly required. Be sure to examine the fluid on the dip-
stick closely. If there is any doubt about its condition,
drain out a sample for a double check.
Moparž ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid-
Type 9602) when new is red in color. The ATF is dyed
red so it can be identified from other fluids used in
the vehicle such as engine oil or antifreeze. The red
color is not permanent and is not an indicator of fluid
condition. As the vehicle is driven, the ATF will begin
to look darker in color and may eventually become
brown. This is normal. A dark brown/black fluid
accompanied with a burnt odor and/or deterioration
in shift quality may indicate fluid deterioration or
transmission component failure.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
SERVICE
NOTE: Refer to the maintenance schedules in
LUBRICATION and MAINTENANCE, or the vehicle
owner's manual, for the recommended maintenance
(fluid/filter change) intervals for this transaxle.
Fig. 214 Transaxle Fluid Level Indicator
1 - TRANSAXLE DIPSTICK
21 - 246 AUTOMATIC - 41TERS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1744 of 2321

NOTE: Only fluids of the type labeled Moparž
ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid) Type 9602
should be used. A filter change should be made at
the time of the transmission oil change. The magnet
(on the inside of the oil pan) should also be cleaned
with a clean, dry cloth.
NOTE: If the transaxle is disassembled for any rea-
son, the fluid and filter should be changed.
FLUID/FILTER SERVICE (RECOMMENDED)
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist. Refer to LUBRICA-
TION and MAINTENANCE for proper procedures.
Place a drain container with a large opening, under
transaxle oil pan.
(2) Loosen pan bolts and tap the pan at one corner
to break it loose allowing fluid to drain, then remove
the oil pan.
(3) Install a new filter and o-ring on bottom of the
valve body (Fig. 216).
(4) Clean the oil pan and magnet. Reinstall pan
using new Mopar Silicone Adhesive sealant. Tighten
oil pan bolts to 19 N´m (165 in. lbs.).
Fig. 215 Transmission Fluid Temperature Chart
Fig. 216 Filter and O-Ring
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - O-RING
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 247
FLUID (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com